Abstract
Background
Female fertility is an important trait in cattle breeding programs. In the Nordic countries selection is based on a fertility index (FTI). The fertility index is a weighted combination of four female fertility traits estimated breeding values for number of inseminations per conception (AIS), 56-day non-return rate (NRR), number of days from first to last insemination (IFL), and number of days between calving and first insemination (ICF). The objective of this study was to identify associations between sequence variants and fertility traits in Jersey cattle based on 1,225 Jersey sires from Denmark with official breeding values for female fertility traits. The association analyses were carried out in two steps: first the cattle genome was scanned for quantitative trait loci using a sire model for FTI using imputed whole genome sequence variants; second the significant quantitative trait locus regions were re-analyzed using a linear mixed model (animal model) for both FTI and its component traits AIS, NRR, IFL and ICF. The underlying traits were analyzed separately for heifers (first parity cows) and cows (later parity cows) for AIS, NRR, and IFL.
Results
In the first step 6 QTL were detected for FTI: one QTL on each of BTA7, BTA20, BTA23, BTA25, and two QTL on BTA9 (QTL9–1 and QTL9–2). In the second step, ICF showed association with the QTL regions on BTA7, QTL9–2 QTL2 on BTA9, and BTA25, AIS for cows on BTA20 and BTA23, AIS for heifers on QTL9–2 on BTA9, IFL for cows on BTA20, BTA23 and BTA25, IFL for heifers on BTA7 and QTL9-2 on BTA9, NRR for heifers on BTA7 and BTA23, and NRR for cows on BTA23.
Conclusion
The genome wide association study presented here revealed 6 genomic regions associated with FTI. Screening these 6 QTL regions for the underlying female fertility traits revealed that different female fertility traits showed associations with different subsets of the individual FTI QTL peaks. The result of this study contributed to a better insight into the genetic control of FTI in the Danish Jersey.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12863-015-0210-3) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Female fertility, Jersey cattle, Sequence analysis, Association study
Background
Female fertility in dairy cattle is a trait of economic importance. Impaired fertility leads to extra inseminations, higher veterinary costs, and higher culling rate causing higher replacement costs. In fact, reproduction problems are cited as the most common reason for culling in dairy industry [1]. In the Nordic countries female fertility is included in the breeding goal via an index trait. The fertility index (FTI) is composed of four different female fertility traits namely: number of inseminations per conception, interval from calving to first insemination, days from first to last insemination, and 56-day non-return rate. FTI reflects how easily a cow or a heifer conceives. Therefore it is of interest to study the genetics of the fertility index in order to understand the biological mechanisms involved and to improve the general fertility level in the population by breeding.
The heritabilities of female fertility traits in the Danish Jersey population typically are in the range of 0.015-0.04 [2]. Not many quantitative trait locus (QTL) studies have been published based on the Jersey breed. Mai et al. [3] studied QTL for milk production traits in Danish Jersey using Bovine SNP50 Beadchip (Illumina Inc. US). However no genome-wide association study for female fertility traits in Danish Jersey has been published. GWA studies for female fertility traits have predominantly been carried out for Holstein cattle. The initial QTL studies for female fertility were based on microsatellite markers and linkage analysis (e.g. [4]). Since the introduction of the 50 k SNP array association studies for female fertility have been published [5]. Recently the Jersey breed has been used to validate QTL for female fertility segregating in the Nordic Holstein [6]. However, SNP array data were not successful in identifying causal mutations underlying fertility QTLs. The development of the new generation sequence technology as well as the development of imputation methods facilitates the detection of QTL. The availability of sequence information could potentially map the causative mutation or the SNP in strong linkage disequilibrium (LD) with the quantitative trait nucleotide (QTN).
The aim of this study was two-fold: 1) to conduct a genome scan for variants associated with fertility index in Danish Jersey using whole genome sequence data, and 2) to conduct an analysis of regions identified in the genome scan for effects on individual female fertility traits to identify candidate genes underlying the major QTLs.
Methods
The association analyses were carried out in two steps. In the first step, the whole genome was screened for SNPs significantly associated with FTI. The scan was based on Illumina 50 k chip data imputed to whole genome variation. A sire model without considering relationship among individuals (except sire and sons) was used in step I. In the second step, genome-wide significant regions were selected and analyzed for all component traits included in fertility index using an animal model including relationship among all individuals.
Animals and phenotype data
A total of 1,225 Jersey sires from Denmark with official breeding values for female fertility traits were used for the association study. Estimated breeding values (EBVs) were predicted for each animal using the Nordic Cattle Genetic Evaluation criteria based on first to third parity data in cows, using the BLUP and sire models. The EBVs were adjusted for the same systematic environmental effects as in the official routine evaluations. The EBVs are available from national evaluations based on data collected since 1985. Separate breeding values were predicted for cows and heifers where relevant. For more information see http://www.nordicebv.info. The reliability of the breeding value is in the range of 35 to 96 % with a mean of 54 % (Additional file 1: Figure S1).
In step I, only female fertility index was analyzed. The FTI is a compound index. The traits in the FTI included: number of inseminations per conception in cows (AISc) and heifers (AISh); the length in days of the interval from calving to first insemination in cows (IFC); days from first to last insemination in cows (IFLc) and heifers (IFLh) and 56-day non-return rate in cows (NRRc) and heifers (NRRh). FTI is meant to reflect the ease with which a cow or heifer conceive. NRR had no weight in the FTI. Single trait breeding values (STBV) from the national evaluation were available for both 1st parity animals (heifers) as well as 2nd and 3rd parity animals (cows), except of ICF for which only one breeding value is estimated per animal.
In step II, selected QTL regions for FTI from step I analyses were screened for effects on sub-traits as well as analyzed for FTI using an animal model with considering the relationship among all the individuals in the study.
Whole genome sequencing
The sequences for the reference population used for imputation of Nordic animals consisted of the whole genome sequence carried out at Aarhus University and in the 1,000 Bull genome project. The sequencing of additional Nordic bulls at Aarhus University, Foulum was done using Illumina sequencers at Beijing Genomics Institute (BGI), Shenzhen, China, at Aros A/S, Aarhus, Denmark and at Aarhus University. Whole genome sequence data for 242 bulls belonging to dairy breeds were available. Sequencing was shotgun paired-end sequencing. Reads were aligned to the UMD3.1 assembly of the cattle genome [7] using bwa [8]. They were converted to raw BAM files using samtools [9]. Sequences were realigned around insertion/deletions using the Genome Analysis Toolkit [10]. Quality scores were re-calibrated using the Genome Analysis Toolkit following the Human 1,000 Genome guidelines incorporating information from dbSNP version 133 [11]. Variants were called using the Genome Analysis Toolkit’s UnifiedGenotyper. Genomes for the 1,000 Bull Genomes project were sequenced in a number of laboratories and collected at the Department of Primary Industries, Victoria, Australia [12]. Sequences were aligned to the same reference genome as used at Aarhus University. Variant calling was done using samtools’s mpileup function. Variant Call Files [13] from Aarhus University and the 1,000 Bull Genomes project were combined using the Genome Analysis Toolkit’s CombineVariants with precedence given to calls from the Nordic dataset for animals appearing in both datasets.
Imputation HD and Sequence data
Imputation of 50 k SNP to the full sequence was done in two steps. First, in another study (N.K. Kadri, pers. comm.) the 50 k genotypes for 12,322 Nordic bulls were imputed to high-density (HD) genotypes using the software IMPUTE2 [14]. The reference population consisted of HD genotypes (BovineHD BeadChip, Illumina Inc. US) for 2,036 bulls (902 Holstein, 735 Nordic Red and 399 Danish Jersey) available at Aarhus University. In the second imputation step, the 12,322 bulls imputed to HD genotypes were further imputed to the full sequence level. The whole genome sequences from 242 dairy cattle (135 dairy animal genomes available at Aarhus University plus 107 animal genomes from the 1,000 Bull Genomes Project) were used as reference to impute the imputed HD data to the whole genome level using the software Beagle [15]. For imputation from HD to sequence data, chromosomes were divided into chunks of about 20,000 consecutive markers with an overlap of 250 markers at each end to minimize imputation error at ends of the chunks [16].
Only polymorphisms identified both at Aarhus University dataset and the 1,000 Bull Genomes dataset were imputed [16]. For positions containing both a SNP and an insertion-deletion polymorphism (INDEL), the INDEL was deleted. SNPs at positions with disagreements between alleles observed in sequence data and HD data were deleted. The reference data was pre-phased with Beagle v3.3.2 [15] and all markers with an imputation certainty (R2) value below 0.90 were removed. This left a total of 8,938,927 markers for chromosomes 1–29 [16].
Statistical method for Association analysis
Step I: Sire Model (SM) for Genome Scan for FTI
A sire model was used for the initial screening of the genome for association with FTI. A SNP-by-SNP analysis was carried out in which each SNP was tested in turn for association with FTI. The following model was used to estimate SNP effects:
Where yij was the estimated breeding value (EBV) of individual j, belonging to the half-sib in sire family i, μ was the general mean, b was the allelic substitution effect, xij was the number of copies of an allele (with an arbitrary labeling) of the SNP count in the half-sib ij (corresponding to 0, 1, or 2 copies), and si was the random effect of the i-th sire family assumed to be normally distributed si ~ N(0, σ2s) where σ2s is the sire variance, and eij was a random residual of individual ij, assumed to follow a normal distribution, eij ~ N(0, σ2e). All statistical analyses were conducted using DMU [17]. The null hypothesis H0: b = 0 was tested with a two-sided t-test. A SNP was considered significant at the genome wide level of 8.25 (−log10(0.05/8,938,927)) corresponding to a nominal type I error rate of 0.05 after Bonferroni correction for 8,938,927 tests.
Step II: Sire model for the selected regions
Step II analyses were done only for the selected genomic regions based on Step I analyses. A region was defined as 0.5 Mb on both sides of the genome-wide significant SNPs for FTI identified in the Step I analysis. The selected regions were screened for the individual female fertility traits underlying FTI i.e. AISh, AISc, ICF, IFLh, IFLc, NRRh, and NRRc. For this part of the analysis we used an animal model with considering the relationship among all the sires in the study.
The association between the SNP and the phenotype was assessed by a single-locus regression analysis for each SNP separately, using a linear mixed model [18]. The model was as follows:
where yj is the phenotype EBV for j-th bull, μ was the general mean, b was the allelic substitution effect, xj was the number of copies of an allele (with an arbitrary labeling) of the SNP count in the individual j (corresponding to 0, 1, or 2 copies), uj is the random polygenic effects with a multivariate normal distribution u ~N(0, Aσ2u) where A was the additive relationship matrix between sires and σ2u was the polygenic variance, and e was a vector of random environmental deviates with a multivariate normal distribution, e ~ N(0,Iσe2) where I was an identity matrix and σe2 was the residual error variance. The model was fitted by REML using the software DMU. The estimates and standard errors of the fixed effects estimates were obtained from DMU. Testing for the presence of an effect of a marker was done using a two-sided t-test against a null hypothesis of H0: b = 0. The Bonferroni corrected significance threshold was (−log10(p-value) = 8.25) corresponding to a nominal type I error rate of 0.05.
Annotation of the top SNP
Based on the physical location of the genome-wide significant SNP marker in selected regions corresponding gene information was extracted from ENSEMBL Bos taurus 75 [19]. When a SNP was located in an intron this SNP was assigned to the corresponding gene. Variants were annotated with terms from the Sequence Ontology project [20].
Results
Step I
The significant SNP markers for FTI based on the sire model without taking into account the sire relationship (Step I analyses) are presented in Figure 1. In total 566 genome-wide significant SNP associations (−log10(P-value) > 8.25) were detected and these SNPs were located on 5 chromosomes representing 6 QTL peaks (Additional file 2: Table S1). The genome-wide significant SNP were located on Bos taurus autosome (BTA) 7 (2 SNP), BTA9 (4 SNP for QTL peak1 (QTL9–1) and 5 SNP markers for QTL peak2 (QTL9–2)), BTA20 (115 SNP), BTA23 (372 SNP), and BTA25 (68 SNP). Table 1 represents the 6 selected regions ordered by significance of the most significant marker within a QTL region. The most significant SNP was identified on BTA20 (−log10(P-value) = 10.48) followed by BTA23, BTA7 and BTA25 with a -log10(P-value) of 9.72, 8.96, and 8.72, respectively. BTA9 had two peaks, one peak ranging from 38.5 to 39.6 Mbp with a -log10(P-value) of 8.82 (QTL9–1) and another ranging from 103.2 to 104.2 Mbp with a -log10(P-value) of 8.49 (QTL9–2). The regions presented in Table 1 entered step II analyses.
Fig. 1.
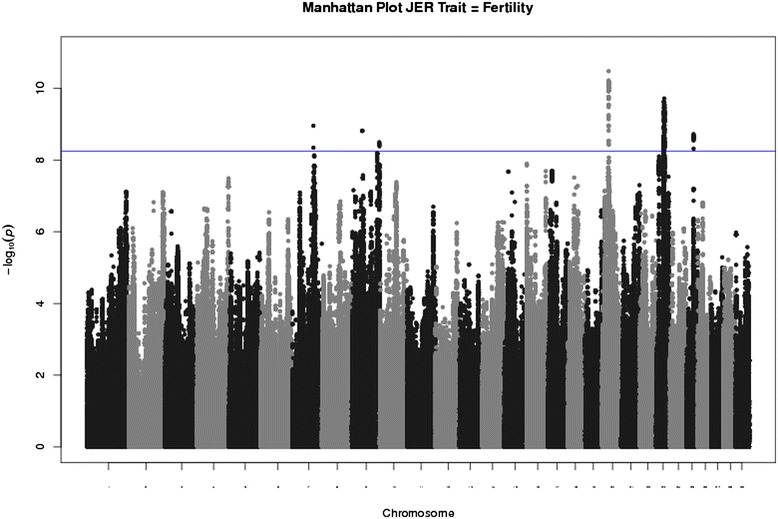
Manhattan plot of the association results of Fertility index in Danish Jersey cattle. On the x-axis the chromosomes are represented. On the y-axis the –log10(P-value) is presented. The horizontal blue line indicates Bonferroni corrected P-value at the 5 % level.
Table 1.
Overview of the genome-wide significant QTL for fertility index in Danish Jersey cattle analyzed with a sire model
| Chromosome | Start position (bp) | End position (bp) | Position of the most significantly associated SNP (bp) | MAF | -log 10 (P-value) | Allele substitution effect | Standard errors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 23,958,004 | 24,957,002 | 24,457,090 | 0.20 | 10.48 | −4.22 | 0.63 |
| 23 | 30,137,773 | 31,137,022 | 30,637,085 | 0.39 | 9.72 | −3.49 | 0.54 |
| 7 | 79,273,583 | 80,130,796 | 79,631,927 | 0.07 | 8.96 | −6.22 | 1.01 |
| 9 | 38,571,753 | 39,570,749 | 39,070,817 | 0.34 | 8.82 | −3.36 | 0.55 |
| 25 | 26,311,042 | 27,310,599 | 26,810,616 | 0.27 | 8.72 | −3.62 | 0.59 |
| 9 | 103,247,641 | 104,245,698 | 103,745,893 | 0.23 | 8.49 | −3.65 | 0.61 |
Step II
The regions presented in Table 1 were analyzed for association with female fertility component traits. The most significant SNPs for the fertility index and individual female fertility traits in each of these regions are presented in Table 2. On BTA20, the same SNP (rs381143208) located at 24,457,090 bp showed highest association with FTI, AISc, AISh, IFLc, NRRC and NRRh. This SNP was intergenic and located between COX8A (BTA20: 24,442,440-24,442,887) and SNX18 (BTA20: 24,570,227-24,596,518). The most significant SNP (rs210183318) for ICF was also intergenic and located at 24,814,046 bp between HSPB3 (BTA20: 24,659,525-24,660,204) and ARL15 (BTA20: 24,955,390-25,026,808).
Table 2.
Most significantly associated SNP for female fertility traits in the regions selected based on QTL segregating for the fertility index
| BTA20 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait name 2 | SNP | MAF | -log 10 (P-value) | Annotation 1 | Ensemble name | Gene name | Gene description |
| FTI | Chr20:24457090 | 0.20 | 11.42 | intergenic_variant | |||
| AISc | Chr20:24457090 | 0.20 | 10.56 | intergenic_variant | |||
| AISh | Chr20:24457090 | 0.20 | 5.99 | intergenic_variant | |||
| ICF | Chr20:24814046 | 0.22 | 12.21 | intergenic_variant | |||
| IFLc | Chr20:24457090 | 0.20 | 11.88 | intergenic_variant | |||
| IFLh | Chr20:24811587 | 0.24 | 8.89 | intergenic_variant | |||
| NRRc | Chr20:24457090 | 0.20 | 7.69 | intergenic_variant | |||
| NRRh | Chr20:24457090 | 0.20 | 5.68 | intergenic_variant | |||
| BTA23 | |||||||
| FTI | Chr23:30817360 | 0.42 | 9.51 | intergenic_variant | |||
| AISc | Chr23:30586684 | 0.38 | 12.43 | missense_variant | ENSBTAG00000005885 | F1N1L2 | Olfactory receptor |
| AISh | Chr23:30634587 | 0.39 | 9.63 | intergenic_variant | |||
| ICF | Chr23:30364272 | 0.02 | 5.82 | intergenic_variant | |||
| IFLc | Chr23:30831993 | 0.47 | 10.75 | downstream_gene_variant | ENSBTAG00000044946 | Novel miRNA | |
| IFLh | Chr23:30634587 | 0.39 | 8.66 | intergenic_variant | |||
| NRRc | Chr23:30090044 | 0.37 | 11.13 | missense_variant | ENSBTAG00000008943 | ZSCAN12 | Bos taurus zinc finger and SCAN domain containing 12 |
| NRRh | Chr23:30602861 | 0.43 | 10.22 | upstream_gene_variant | ENSBTAG00000040307 | F1N7S5 | Olfactory receptor |
| BTA7 | |||||||
| FTI | Chr7:79631927 | 0.07 | 8.98 | intergenic_variant | |||
| AISc | Chr7:78685481 | 0.06 | 5.73 | intergenic_variant | |||
| AISh | Chr7:78685062 | 0.06 | 13.16 | intergenic_variant | |||
| ICF | Chr7:78287019 | 0.07 | 12.3 | intergenic_variant | |||
| IFLc | Chr7:78685481 | 0.06 | 6.54 | intergenic_variant | |||
| IFLh | Chr7:78685481 | 0.06 | 14.86 | intergenic_variant | |||
| NRRc | Chr7:78380148 | 0.08 | 4.28 | intergenic_variant | |||
| NRRh | Chr7:78685062 | 0.06 | 10.50 | intergenic_variant | |||
| BTA9 QTL1 | |||||||
| FTI | Chr9:39070817 | 0.34 | 6.79 | intergenic_variant | |||
| AISc | Chr9:40178726 | 0.48 | 8.22 | intergenic_variant | |||
| AISh | Chr9:39056106 | 0.29 | 10.86 | intergenic_variant | |||
| ICF | Chr9:43897568 | 0.16 | 9.19 | intron_variant | ENSBTAG00000017527 | AIM1 | absent in melanoma 1 |
| IFLc | Chr9:43027665 | 0.30 | 7.12 | intron_variant | ENSBTAG00000019175 | SOBP | sine oculis binding protein homolog (Drosophila) |
| IFLh | Chr9:40147543 | 0.47 | 8.30 | intergenic_variant | |||
| NRRc | Chr9:40176331 | 0.48 | 7.59 | intergenic_variant | |||
| NRRh | Chr9:39056106 | 0.29 | 8.37 | intergenic_variant | |||
| BTA9 QTL2 | |||||||
| FTI | Chr9:103675274 | 0.14 | 9.01 | intergenic_variant | |||
| AISc | Chr9:102992258 | 0.37 | 7.52 | intron_variant | ENSBTAG00000021741 | RPS6KA2 | ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90 kDa, polypeptide 2 |
| AISh | Chr9:103880081 | 0.43 | 9.57 | intron_variant | ENSBTAG00000005557 | MLLT4 | myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (trithorax homolog, Drosophila); translocated to, 4 |
| ICF | Chr9:103664731 | 0.14 | 10.66 | intergenic_variant | |||
| IFLc | Chr9:104308602 | 0.44 | 9.45 | intron_variant | ENSBTAG00000013176 | SMOC2 | SPARC related modular calcium binding 2 |
| IFLh | Chr9:103861364 | 0.39 | 12.27 | intron_variant&feature_truncation | ENSBTAG00000005557 | MLLT4 | myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (trithorax homolog, Drosophila); translocated to, 4 |
| NRRc | Chr9:103788916 | 0.20 | 4.46 | intergenic_variant | |||
| NRRh | Chr9:103861364 | 0.39 | 9.21 | intron_variant&feature_truncation | ENSBTAG00000005557 | MLLT4 | myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (trithorax homolog, Drosophila); translocated to, 4 |
| BTA25 | |||||||
| FTI | Chr25:26810616 | 0.27 | 9.37 | upstream_gene_variant | ENSBTAG00000031852 | TBC1D10B | TBC1 domain family, member 10B |
| AISc | Chr25:26864302 | 0.39 | 7.40 | downstream_gene_variant | ENSBTAG00000010851 | SEPHS2 | selenophosphate synthetase 2 |
| AISh | Chr25:27783308 | 0.17 | 8.86 | downstream_gene_variant | ENSBTAG00000047734 | C16orf58 | chromosome 16 open reading frame 58 |
| ICF | Chr25:29847729 | 0.39 | 10.27 | intergenic_variant | |||
| IFLc | Chr25:26810616 | 0.27 | 10.77 | upstream_gene_variant | ENSBTAG00000031852 | TBC1D10B | TBC1 domain family, member 10B |
| NRRc | Chr25:27784063 | 0.17 | 6.45 | downstream_gene_variant | ENSBTAG00000047734 | C16orf58 | chromosome 16 open reading frame 58 |
| NRRh | Chr25:27784062 | 0.17 | 7.56 | downstream_gene_variant | ENSBTAG00000047734 | C16orf58 | chromosome 16 open reading frame 58 |
1In case the SNP marker is annotated as a downstream_gene_variant or an upstream_gene_variant the gene closest located to this SNP is listed.
2Fertility index (FTI); number of inseminations per conception in cows (AISc) and heifers (AISh); the length in days of the interval from calving to first insemination in cows (IFC); days from first to last insemination in cows (IFLc) and heifers (IFLh) and 56-day non-return rate in cows (NRRc) and heifers (NRRh).
The second most significant QTL region for FTI was located on BTA23. For 8 fertility traits analyzed, there were seven different SNPs within the QTL region on BTA23 showed highest association. Only one common SNP (Chr23:30634587) showed highest association with two traits: AISh and IFLh (Table 2). Two of these SNPs were missense variants, one downstream gene variant, one upstream gene variant and rest were intergenic variants. The missense variants were found for F1N1L2 (AISc) and ZSCAN12 (NRRc).
In the QTL region on BTA7, a SNP (rs377795316 at 78,685,481 bp) had the strongest significant association for AISc, IFLc and IFLh. The strongest associated SNPs were not located within any known genes.
There were two QTL regions on BTA9 for FTI (Table 1). At 38.5-39.6 Mbp (QTL9–1), the most significantly associated SNPs for ICF and IFLc were intron variants in the genes AIM1 and SOBP, respectively. At 103.2-104.2 Mbp on BTA9 (QTL9–2), the most significant SNP for AISh, IFLh and NRRh was an intronic variant in the gene MLLT4. The most significant SNPs for AISc and IFLc were also intronic variants in genes RPS6KA2 and SMOC2, respectively.
In the QTL region on BTA25 the strongest associated SNPs were annotated as up-stream or down-stream gene variants. The SNP showing strongest association with FTI and IFLc was an upstream gene variant of TBC1D10B. The strongest associated SNPs for AISh, NRRC and NRRh were downstream variants of C16orf58. The strongest associated SNP for AISc was a downstream gene variant of SEPHS2.
Discussion
In this study we have performed an association study for the fertility index trait and its component traits in Jersey cattle breed in a two-step approach. First the genome was screened for fertility index using a sire model to identify the QTL for fertility index using imputed genome sequence data. In the second step, 6 QTL regions with genome-wide significant association with FTI (Table 1) were targeted and analyzed for the female fertility traits underlying fertility index (Table 2) using an animal model taking the relationship among all sires into account. The advantage of this two-step approach is that the first step is computationally efficient. The second step using an animal model while computationally expensive can control rates of false associations due to family structure and population stratification in cattle [21, 22].
Thus the two-step procedure maintains computational feasibility. The cost of choosing this procedure is that certain regions outside the six regions investigated here might potentially have shown up as significant if the full model had been applied to the whole genome. However for the tests for significance of the associations between traits and polymorphisms we still used a Bonferroni correction for the full number of markers in the genome. Thus the significance thresholds used were set as though the full genome had been investigated. Therefore confidence in the results is maintained, but computational efficiency is achieved at the cost of a certain loss of power.
Fertility index and its component traits
No pronounced overlap between QTL affecting cow and heifer traits was observed except on BTA20. This is in line with results for female fertility in Holstein. There much fewer QTL were found affecting female fertility in heifers than in cows [6]. In general the genetic correlation between heifer and cow traits is low [23] indicating that different genes are involved in the fertility traits for heifers and lactating cows. Furthermore the QTL regions from Table 1 did not exhibit overlap with the QTL regions detected for fertility index in the Holstein found by Höglund et al. [6]. The closest match between QTL for female fertility was observed in Nordic Holstein on BTA9 at 101.8 Mb and Danish Jersey between 103.2 and 104.2 Mb.
BTA20
The most significant association for female fertility traits on BTA20 within the FTI QTL region (23 to 25 Mbp) were observed for AISc, ICF and IFLc in Danish Jersey. In Holstein QTL or associations have been detected for (female) fertility on BTA20. Sahana et al. [5] detected a significant SNP (rs41638409) for FTI and IFLc in the Nordic Holstein population. This SNP is located at 24,744,585 bp which is within the region defined in our present study for FTI. Furthermore Höglund et al. [4] using linkage analysis detected a QTL for heat intensity in a region of 31 cM to 49 cM on BTA20. Oikonomou et al. [24] found a QTL for conception rate at 33.6 cM. As the confidence intervals in the linkage analysis studies span large parts of the chromosome, it would be difficult to determine whether the QTL detected in Höglund et al. [4] and Oikonomou et al. [24] coincide with the region detected for FTI in the present study.
BTA23
The most significant association for the component traits in the FTI QTL region (30 – 32 Mbp) on BTA23 were for AISc, IFLc, NRRc and NRRh (Table 2). In Holstein cattle a number of QTL affecting female fertility traits have been reported on BTA23 [5, 25]. The most significant SNP marker (rs109572712) for FTI was located at 28 Mbp in Danish and Swedish Holstein [5], whereas Pimentel et al. [25] detected QTL (rs109744988) for IFL and NRR around 16 Mbp. The location of the most significant markers detected in Sahana et al. [5] and Pimentel et al. [25] indicated that these QTL do not overlap with the QTL region for FTI in Danish Jersey. In the targeted region on BTA23 four SNPs were located within genes. Two of the genes were F1N1L2 (AISc) and F1N7S5 (IFLc). They are believed to be olfactory receptors (http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/F1N7S5; http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/F1N1L2). One SNP was in a zinc finger-related gene and one was in a miRNA gene. The relation of these genes to female fertility is at this moment unknown.
BTA7
The region for FTI on BTA7 is of interest because the heifer traits (AISh, IFLh, NRRh) showed the most significant associations in this region. In addition a significant association was observed with ICF. Several studies have previously identified QTL regions or SNPs involved in female fertility in Holstein cattle on this chromosome. These include conception rate, heat intensity, AIS, IFL and NRR [4, 5, 25–27]. However, none of the markers associated to these female fertility trait were located in the region associated with FTI in the Danish Jersey in this study.
BTA9
On BTA9 two peaks of association for FTI were detected in the Danish Jersey, one between 38.5 and 39.5 Mbp (QTL9–1) and another between 103.2 and 104.2 Mbp (QTL9–2). AISh showed the most significant association for QTL9–1, while ICF showed the most significant association for QTL9–2. In Holstein cattle SNP on BTA9 were associated with FTI and fertility treatments [5]. These SNPs however are not located in the regions associated with FTI in the Danish Jersey on BTA9 in this study. For QTL9–2 the most significant SNPs for each individual female fertility traits AISh, IFLh and NRRh were all located within the same gene, MLLT4. This gene encodes a multi-domain protein involved in signaling and organization of cell junctions during embryogenesis in human [28].
BTA25
The most significantly associated SNPs for the female fertility traits on BTA25 are downstream or upstream gene variants. FTI and IFLc associate most strongly with the same SNP marker. This marker is located up-stream of TBC1D10B. Small G proteins of the RAB family function in intracellular vesicle trafficking by switching from the GTP-bound state to the GDP-bound state with the assistance of guanine nucleotide exchange factors and GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs). TBC1D10B functions as a GAP for several proteins of the Rab family [29]. However, whether and how this gene influences female fertility is unknown. Höglund et al. [4] identified a QTL for NRRc on BTA25, however the region found in their study did not coincide with the region for FTI identified in this study.
Studies on a more functional level will be required to be able to identify causative variants. Some progress may be made where obvious candidates such as deletions, SIFT deleterious missense variants or non-sense variants are observed. More information may be gleaned from allele specific expression studies as to whether up- or downstream polymorphisms affect expression levels in key tissues. However, the exact design of such studies is very much going to depend on the nature of the genes affected and the nature of the polymorphisms.
Substantial number of intergenic variants were observed as strongly associated with various female fertility traits. Several reasons for this may be hypothesized: gene annotations for dairy cattle may be incomplete – some transcribed regions such as non-translated RNA may remain undiscovered or there may be undiscovered longer transcripts of already identified genes, or the intergenic polymorphisms act through their effects on regulatory elements in the genome. The latter are at this point poorly annotated in the cattle genome.
Step I model did not include the full relationship among all sires
We did not consider the full relationship matrix in the step I model which is required to avoid false positive association due to population and family structure. This was done to reduce the computational burden. The lambda value (median chi-square values from the analysis/medium chi-square value under the null model) from step I analyses was 1.88 for FTI. This value is high and could be partly due to non-inclusion of full relationship matrix. But some inflation is also expected due to highly polygenic nature of the trait and high LD in cattle especially with sequence variants [30]. However, as the targeted region was reanalyzed with full-model and a very stringent genome-wide significant threshold was fixed, the major QTL we are reporting here are unlikely to be false positive due to family structure.
Conclusion
In total 6 QTL for the fertility index trait in Danish Jersey cattle were detected in a genome-wide scan based on whole genome sequence data. Screening the 6 QTL regions for the underlying traits for fertility index revealed which female fertility traits were affected by these QTLs for fertility index as well as identified potential candidate genes for these underlying female fertility traits. Overlap between QTL observed in Holstein and Jersey was very limited. Little overlap was observed between QTL affecting fertility traits of cows and of heifers.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Danish Cattle Federation/NAV for providing the phenotypic data used in this study. This work was supported by a grant (No. 3405-10-0137) funded jointly by the Green Development and Demonstration Program of the Danish Ministry of Food, Agriculture and Fisheries, The Milk Levy Fund, Viking Genetics, and Nordic Cattle Genetic Evaluation. Semen samples were kindly provided by the Swedish Farmers Foundation for Agricultural Research in conjunction with Viking Genetics. The 1,000 Genomes Project is kindly acknowledged for sharing data to impute the genome sequence.
Additional files
Plot of the distribution of the accuracy for the Estimated Breeding Values for Fertility Index in Danish Jersey cattle.
SNPs significantly associated with Fertility index in the Danish Jersey. A genome wide association scan was performed on the Danish Jersey cattle for the fertility index. SNPs were considered significant at Bonferroni corrected P-value < 0.05 (−log10(P-value) > 8.25).
Footnotes
Competing interests
Authors declare no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
Conceived and designed the experiment: JKH, GS, BG, MSL. Analysed the data: JKH, GS. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: MSL, BG, GS. Wrote the paper: JKH. All authors contributed to the discussion of the results, read and approved the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Johanna K. Höglund, Email: johanna.hoglund@anis.au.dk
Bernt Guldbrandtsen, Email: bernt.guldbrandtsen@mbg.au.dk.
Mogens S. Lund, Email: mogens.lund@mbg.au.dk
Goutam Sahana, Email: goutam.sahana@mbg.au.dk.
References
- 1.Ahlman T, Berglund B, Rydhmer L, Strandberg E. Culling reasons in organic and conventional dairy herds and genotype by environment interaction for longevity. J Dairy Sci. 2011;94:1568–1575. doi: 10.3168/jds.2010-3483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Knowledge Centre for Agriculture: Cattle, Denmark, 2013. Årsstatistik Avl 2012/13. http://www.danskholstein.dk/NR/rdonlyres/4682FFBE-11E1-4969-87F2-5246D30E72B2/0/aarsstat_2014.pdf.
- 3.Mai MD, Sahana G, Christiansen FB, Guldbrandtsen B. A genome-wide association study for milk production traits in Danish Jersey cattle using a 50 K single nucleotide polymorphism chip. J Anim Sci. 2010;88:3522–3528. doi: 10.2527/jas.2009-2713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Höglund JK, Guldbrandtsen B, Su G, Thomsen B, Lund MS. Genome scan detects quantitative trait loci affecting female fertility traits in Danish and Swedish Holstein cattle. J Dairy Sci. 2009;92:2136–2143. doi: 10.3168/jds.2008-1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sahana G, Guldbrandtsen B, Bendixen C, Lund MS. Genome-wide association mapping for female fertility traits in Danish and Swedish Holstein cattle. Anim Genet. 2010;41:579–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.2010.02064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Höglund JK, Sahana G, Guldbrandtsen B, Lund MS. Validation of associations for female fertility traits in Nordic Holstein, Nordic Red and Jersey dairy cattle. BMC Genet. 2014;15:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-15-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zimin AV, Delcher AL, Florea L, Kelley DR, Schatz MC, Puiu D, Hanrahan F, Pertea G, Van Tassell CP, Sonstegard TS, Marçais G, Roberts M, Subramanian P, Yorke JA, Salzberg SL. A whole-genome assembly of the domestic cow. Bos taurus Genome Biol. 2009;10:R42. doi: 10.1186/gb-2009-10-4-r42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:1754–1760. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R, 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:2078–2079. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly M, DePristo MA. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010;20:1297–1303. doi: 10.1101/gr.107524.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sherry ST, Ward MH, Kholodov M, Baker J, Phan L, Smigielski EM, Sirotkin K. dbSNP: the NCBI database of genetic variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29:308–311. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.1.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Daetwyler HD, Capitan A, Pausch H, Stothard P, van Binsbergen R, Brøndum RF, Liao X, Djari A, Rodriguez SC, Grohs C, Esquerré D, Bouchez O, Rossignol MN, Klopp C, Rocha D, Fritz S, Eggen A, Bowman PJ, Coote D, Chamberlain AJ, Anderson C, VanTassell CP, Hulsegge I, Goddard ME, Guldbrandtsen B, Lund MS, Veerkamp RF, Boichard DA, Fries R, Hayes BJ. Whole-genome sequencing of 234 bulls facilitates mapping of monogenic and complex traits in cattle. Nat Genet. 2014;46:858–865. doi: 10.1038/ng.3034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Danecek P, Auton A, Abecasis G, Albers CA, Banks E, DePristo MA, Handsaker RE, Lunter G, Marth GT, Sherry ST, McVean G, Durbin R, 1000 Genomes Project Analysis Group The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:2156–2158. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Howie BN, Donnelly P, Marchini J. A flexible and accurate genotype imputation method for the next generation of genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet. 2009;5 doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Browning BL, Browning SR. A unified approach to genotype imputation and haplotype-phase inference for large data sets of trios and unrelated individuals. Am J Hum Genet. 2009;84:210–223. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.01.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Brøndum RF, Guldbrandtsen B, Sahana G, Lund MS, Su G. Strategies for imputation to whole genome sequence using a single or multi-breed reference population in cattle. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:728. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Madsen, P. and J. Jensen. 2013. A user’s guide to DMU. A package for analyzing multivariate mixed models. http://dmu.agrsci.dk/DMU/Doc/Current/dmuv6_guide.5.2.pdf.
- 18.Yu J, Pressoir G, Briggs WH, Vroh Bi I, Yamasaki M, Doebley JF, McMullen MD, Gaut BS, Nielsen DM, Holland JB, Kresovich S, Buckler ES. A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet. 2006;38:203–208. doi: 10.1038/ng1702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Flicek P, Amode MR, Barrell D, Beal K, Billis K, Brent S, Carvalho-Silva D, Clapham P, Coates G, Fitzgerald S, Gil L, Girón CG, Gordon L, Hourlier T, Hunt S, Johnson N, Juettemann T, Kähäri AK, Keenan S, Kulesha E, Martin FJ, Maurel T, McLaren WM, Murphy DN, Nag R, Overduin B, Pignatelli M, Pritchard B, Pritchard E, Riat HS, Ruffier M, Sheppard D, Taylor K, Thormann A, Trevanion SJ, Vullo A, Wilder SP, Wilson M, Zadissa A, Aken BL, Birney E, Cunningham F, Harrow J, Herrero J, Hubbard TJ, Kinsella R, Muffato M, Parker A, Spudich G, Yates A, Zerbino DR, Searle SM. Ensembl 2014. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(Database issue):D749–D755. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Eilbeck K, Lewis SE, Mungall CJ, Yandell M, Stein L, Durbin R, Ashburner M. The Sequence Ontology: a tool for the unification of genome annotations. Genome Biol. 2005;6:R44. doi: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-5-r44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sahana G, Guldbrandtsen B, Thomsen B, Holm LE, Panitz F, Brøndum RF, Bendixen C, Lund MS: Genome-wide association study using high-density single nucleotide polymorphism arrays and whole-genome sequences for clinical mastitis traits in dairy cattle. J Dairy Sci. 2014;97:7258–75. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 22.Kadri NK, Guldbrandtsen B, Sørensen P, Sahana G. Comparison of genome-wide association methods in analyses of admixed populations with complex familial relationships. PLoS One. 2014;9 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pedersen J, Jensen J. Proceedings International workshop on workshop on genetic improvement of functional traits in cattle. January 1996. 12. Gembloux, Belgium: Interbull bulletin; 1996. Evaluation of female fertility of Danish dairy sires; pp. 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Oikonomou G, Angelopoulou K, Arsenos G, Zygoyiannis D, Banos G. The effects of polymorphisms in the DGAT1, leptin and growth hormone receptor gene loci on body energy, blood metabolic and reproductive traits of Holstein cows. Anim Genet. 2009;40:10–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.2008.01789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pimentel EC, Bauersachs S, Tietze M, Simianer H, Tetens J, Thaller G, Reinhardt F, Wolf E, König S. Exploration of relationships between production and fertility traits in dairy cattle via association studies of SNPs within candidate genes derived by expression profiling. Anim Genet. 2011;42:251–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2052.2010.02148.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Boichard D, Grohs C, Bourgeois F, Cerqueira F, Faugeras R, Neau A, Rupp R, Amigues Y, Boscher MY, Levéziel H. Detection of genes influencing economic traits in three French dairy cattle breeds. Genet Sel Evol. 2003;35:77–101. doi: 10.1186/1297-9686-35-1-77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ron M, Feldmesser E, Golik M, Tager-Cohen I, Kliger D, Reiss V, Domochovsky R, Alus O, Seroussi E, Ezra E, Weller JI. A complete genome scan of the Israeli Holstein population for quantitative trait loci by a daughter design. J Dairy Sci. 2004;87:476–490. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(04)73187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ikeda W, Nakanishi H, Miyoshi J, Mandai K, Ishizaki H, Tanaka M, Togawa A, Takahashi K, Nishioka H, Yoshida H, Mizoguchi A, Nishikawa S, Takai Y. Afadin: A key molecule essential for structural organization of cell-cell junctions of polarized epithelia during embryogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1999;146:1117–1132. doi: 10.1083/jcb.146.5.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ishibashi K, Kanno E, Itoh T, Fukuda M. Identification and characterization of a novel Tre-2/Bub2/Cdc16 (TBC) protein that possesses Rab3A-GAP activity. Genes Cells. 2009;14:41–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2008.01251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yang J, Weedon MN, Purcell S, Lettre G, Estrada K, Willer CJ, Smith AV, Ingelsson E, O'Connell JR, Mangino M, Mägi R, Madden PA, Heath AC, Nyholt DR, Martin NG, Montgomery GW, Frayling TM, Hirschhorn JN, McCarthy MI, Goddard ME, Visscher PM, GIANT Consortium Genomic inflation factors under polygenic inheritance. Eur J Hum Genet. 2011;19:807–812. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2011.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


