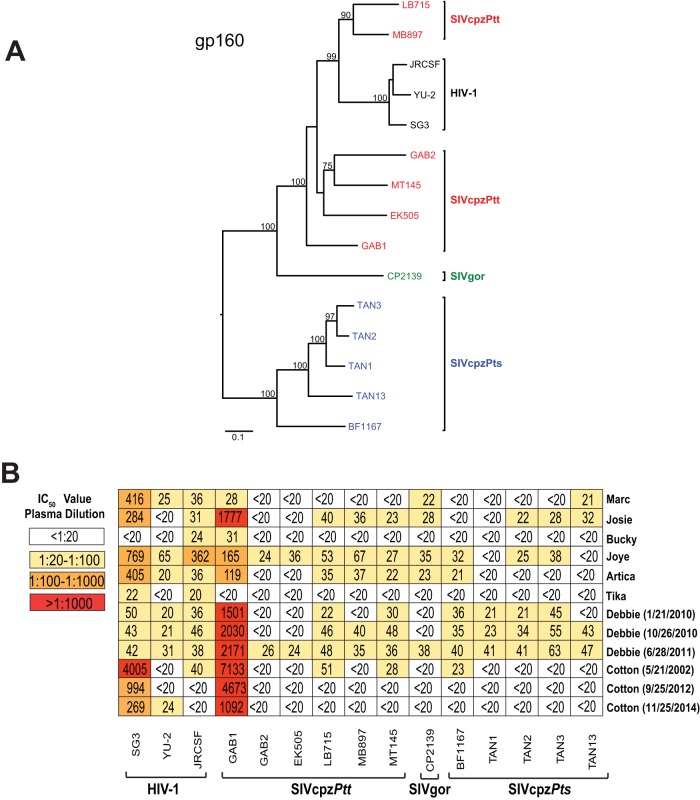
FIG 1 .
Neutralizing antibody responses in long-term HIV-1- and SIVcpz-infected chimpanzees. (A) Phylogenetic relationship of HIV-1, SIVcpz, and SIVgor infectious molecular clones (IMCs). A maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of Env (gp160) protein sequences is depicted, with sequences color coded to differentiate HIV-1 (black), SIVgor (green), SIVcpzPtt (red), and SIVcpzPts (blue) strains. Bootstrap values of ≥70% are shown; the scale bar represents 0.1 amino acid replacement per site. (B) Plasma samples from eight long-term-infected chimpanzees (listed on the right and shown in Table 1) were tested against HIV-1 (n = 3), SIVcpzPtt (n = 6), SIVgor (n = 1), and SIVcpzPts (n = 5) strains (bottom) in the TZM-bl neutralization assay. (Collection dates are indicated for samples from the same individual.) IC50s (expressed as plasma dilutions) averaged from three replicate experiments are shown, with a heat map indicating the relative neutralization potency.