Abstract
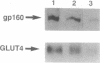
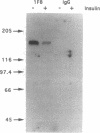
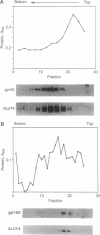
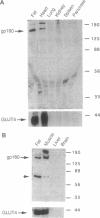
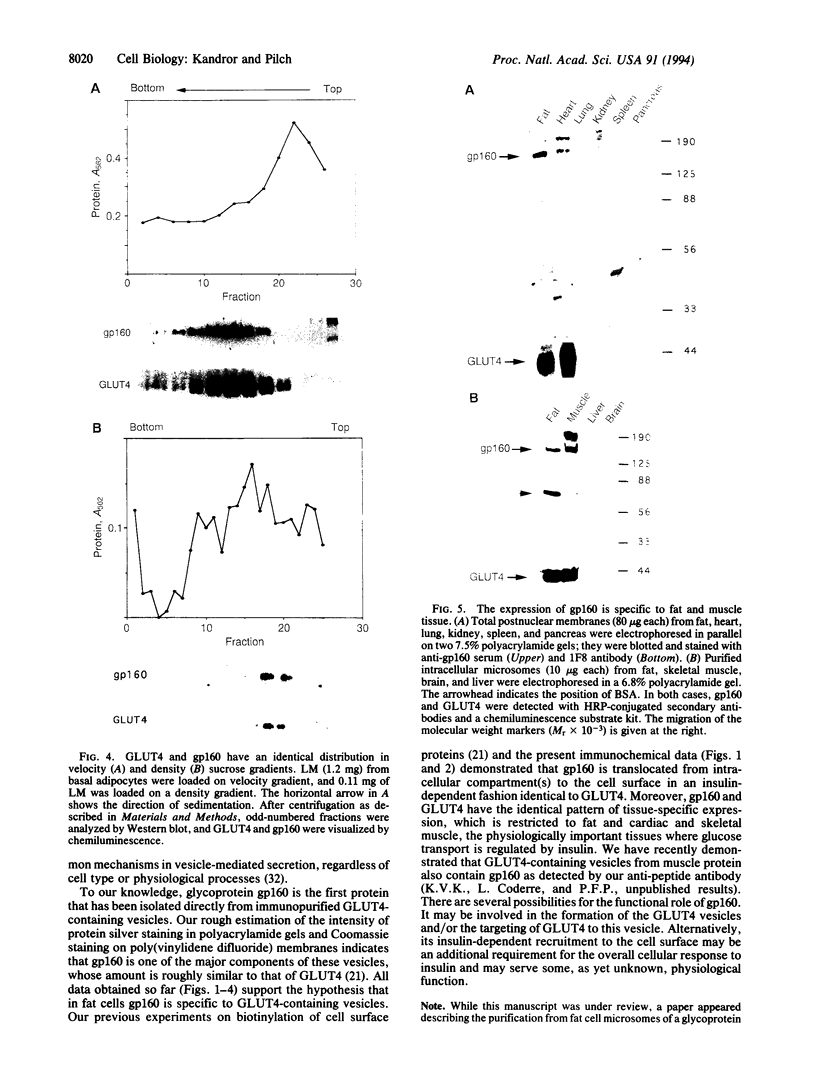
We have isolated and partially sequenced a M(r) 160,000 glycoprotein whose rate of cycling to and from the adipocyte cell surface is enhanced by insulin in a manner apparently identical to the effect of insulin on GLUT4 cycling. Based on the protein sequence, we have prepared an antipeptide antibody against this protein, gp160. The antibody recognizes a M(r) 160,000 protein whose subcellular distribution is identical to that of GLUT4. This was determined by three separate criteria: (i) Western blotting of fractionated adipocyte membranes from cells exposed to insulin or not, (ii) adsorption of vesicles with anti-GLUT4 antibodies followed by Western blotting, and (iii) separation of microsomal vesicles by sucrose velocity and density gradients. By all three criteria, GLUT4 and gp160 are completely colocalized in rat fat cells. Moreover, gp160 can be detected by Western blot only in fat and cardiac and skeletal muscles and was absent from all other tissues tested. Thus, gp160 is an additional marker for physiologically important, insulin-sensitive glucose transport. Its further study at the protein and DNA level may reveal information about the mechanistic details of insulin-activated GLUT4 translocation as well as information concerning the tissue-specific expression of GLUT4 and gp160.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano T., Takata K., Katagiri H., Tsukuda K., Lin J. L., Ishihara H., Inukai K., Hirano H., Yazaki Y., Oka Y. Domains responsible for the differential targeting of glucose transporter isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19636–19641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin S. A. Mammalian passive glucose transporters: members of an ubiquitous family of active and passive transport proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jun 8;1154(1):17–49. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(93)90015-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begum N., Leitner W., Reusch J. E., Sussman K. E., Draznin B. GLUT-4 phosphorylation and its intrinsic activity. Mechanism of Ca(2+)-induced inhibition of insulin-stimulated glucose transport. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3352–3356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Scheller R. H. The molecular machinery for secretion is conserved from yeast to neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2559–2563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain C. C., Trimble W. S., Lienhard G. E. Members of the VAMP family of synaptic vesicle proteins are components of glucose transporter-containing vesicles from rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11681–11684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderhead D. M., Kitagawa K., Tanner L. I., Holman G. D., Lienhard G. E. Insulin regulation of the two glucose transporters in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13801–13808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormont M., Tanti J. F., Grémeaux T., Van Obberghen E., Le Marchand-Brustel Y. Subcellular distribution of low molecular weight guanosine triphosphate-binding proteins in adipocytes: colocalization with the glucose transporter Glut 4. Endocrinology. 1991 Dec;129(6):3343–3350. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-6-3343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormont M., Tanti J. F., Zahraoui A., Van Obberghen E., Tavitian A., Le Marchand-Brustel Y. Insulin and okadaic acid induce Rab4 redistribution in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19491–19497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Buxton J. M. Insulin action on the internalization of the GLUT4 glucose transporter in isolated rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9187–9190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Jacot E., Jequier E., Maeder E., Wahren J., Felber J. P. The effect of insulin on the disposal of intravenous glucose. Results from indirect calorimetry and hepatic and femoral venous catheterization. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1000–1007. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Vecchio R. L., Pilch P. F. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase is a component of glucose transporter (GLUT 4)-containing vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13278–13283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaskar S. U., Mueckler M. M. The mammalian glucose transporters. Pediatr Res. 1992 Jan;31(1):1–13. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199201000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haney P. M., Slot J. W., Piper R. C., James D. E., Mueckler M. Intracellular targeting of the insulin-regulatable glucose transporter (GLUT4) is isoform specific and independent of cell type. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):689–699. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman G. D., Kozka I. J., Clark A. E., Flower C. J., Saltis J., Habberfield A. D., Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Cell surface labeling of glucose transporter isoform GLUT4 by bis-mannose photolabel. Correlation with stimulation of glucose transport in rat adipose cells by insulin and phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18172–18179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Brown R., Navarro J., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulatable tissues express a unique insulin-sensitive glucose transport protein. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):183–185. doi: 10.1038/333183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Jenkins A. B., Kraegen E. W. Heterogeneity of insulin action in individual muscles in vivo: euglycemic clamp studies in rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):E567–E574. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.5.E567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Lederman L., Pilch P. F. Purification of insulin-dependent exocytic vesicles containing the glucose transporter. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11817–11824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Pilch P. F. Fractionation of endocytic vesicles and glucose-transporter-containing vesicles in rat adipocytes. Biochem J. 1988 Dec 15;256(3):725–732. doi: 10.1042/bj2560725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhun B. H., Rampal A. L., Liu H., Lachaal M., Jung C. Y. Effects of insulin on steady state kinetics of GLUT4 subcellular distribution in rat adipocytes. Evidence of constitutive GLUT4 recycling. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17710–17715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandror K., Pilch P. F. Identification and isolation of glycoproteins that translocate to the cell surface from GLUT4-enriched vesicles in an insulin-dependent fashion. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):138–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotliar N., Pilch P. F. Expression of the glucose transporter isoform GLUT 4 is insufficient to confer insulin-regulatable hexose uptake to cultured muscle cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Mar;6(3):337–345. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.3.1584210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie S. M., Cain C. C., Lienhard G. E., Castle J. D. The glucose transporter GluT4 and secretory carrier membrane proteins (SCAMPs) colocalize in rat adipocytes and partially segregate during insulin stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):19110–19117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastick C. C., Aebersold R., Lienhard G. E. Characterization of a major protein in GLUT4 vesicles. Concentration in the vesicles and insulin-stimulated translocation to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):6089–6092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M., SCOW R. O., CHERNICK S. S. REMOVAL AND METABOLISM OF TRIGLYCERIDES BY PERFUSED LIVER. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:385–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh S., Nishimura H., Clark A. E., Kozka I. J., Vannucci S. J., Simpson I. A., Quon M. J., Cushman S. W., Holman G. D. Use of bismannose photolabel to elucidate insulin-regulated GLUT4 subcellular trafficking kinetics in rat adipose cells. Evidence that exocytosis is a critical site of hormone action. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17820–17829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibasaki Y., Asano T., Lin J. L., Tsukuda K., Katagiri H., Ishihara H., Yazaki Y., Oka Y. Two glucose transporter isoforms are sorted differentially and are expressed in distinct cellular compartments. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 1;281(Pt 3):829–834. doi: 10.1042/bj2810829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Yver D. R., Hissin P. J., Wardzala L. J., Karnieli E., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transporters in the isolated rat adipose cells: characterization of subcellular fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 19;763(4):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(83)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Gigengack S., James D. E., Lienhard G. E. Translocation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 in cardiac myocytes of the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7815–7819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Gigengack S., Lienhard G. E., James D. E. Immuno-localization of the insulin regulatable glucose transporter in brown adipose tissue of the rat. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):123–135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. M., Charron M. J., Shah N., Lodish H. F., Jarett L. Immunoelectron microscopic demonstration of insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transporters to the plasma membrane of isolated rat adipocytes and masking of the carboxyl-terminal epitope of intracellular GLUT4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6893–6897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoidis G., Kotliar N., Pilch P. F. Immunological analysis of GLUT4-enriched vesicles. Identification of novel proteins regulated by insulin and diabetes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11691–11696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzano A., Wilkinson W., Kotliar N., Thoidis G., Wadzinkski B. E., Ruoho A. E., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulated glucose uptake in rat adipocytes is mediated by two transporter isoforms present in at least two vesicle populations. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12358–12363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]