Abstract
Stable maintenance of the low-copy-number mini-F plasmid in Escherichia coli is dependent on a functional partition system. The sop partition region encodes proteins SopA and SopB and a cis-acting element sopC, which contains multiple sites to which SopB binds. We have found that SopB protein acting at sopC in vivo is associated with a marked effect on plasmid DNA supercoiling, which may reflect the formation of a wrapped nucleoprotein complex. In this study, we demonstrate that a functional partition complex can form with a single 43-bp SopB binding site. Our experiments suggest that SopB bound at a single site nucleates the binding of additional SopB protein and wrapping of adjacent DNA sequences, such that approximately equal numbers of supercoils are restrained regardless of the number of tandem sopC repeats present. It is likely that this unusual nucleoprotein complex allows interaction of the plasmid with the partition apparatus.
Full text
PDF


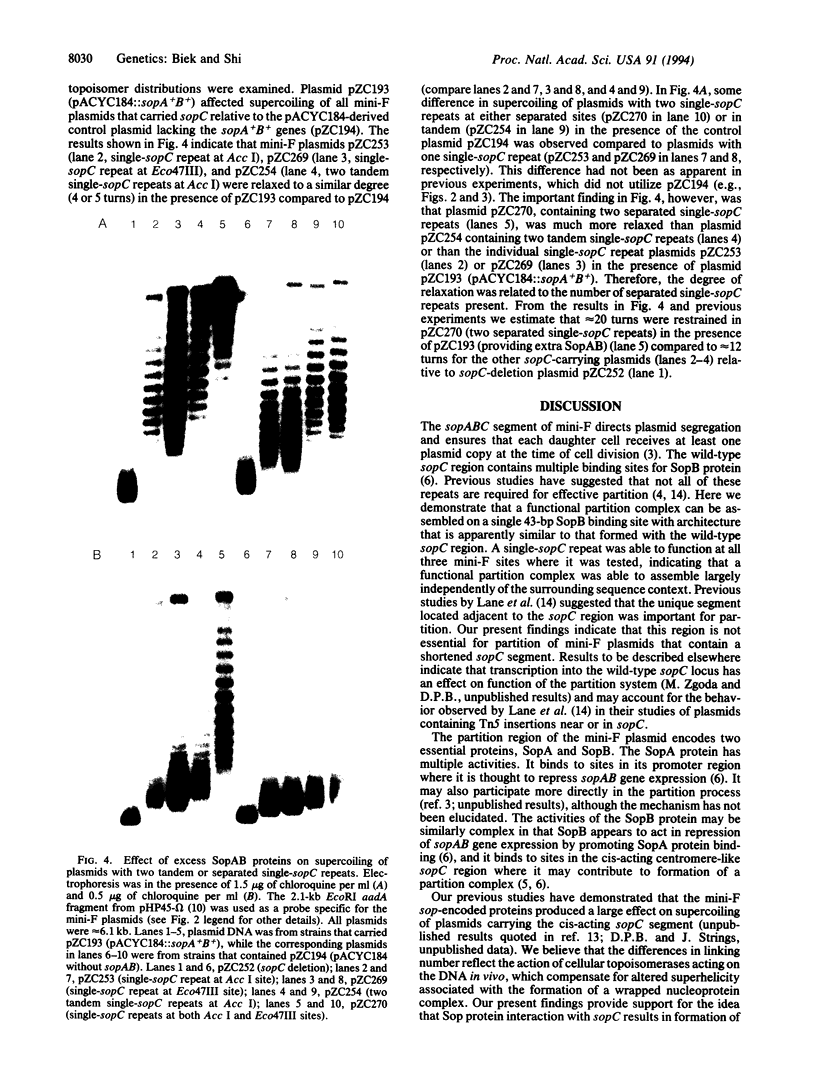

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeles A. L., Friedman S. A., Austin S. J. Partition of unit-copy miniplasmids to daughter cells. III. The DNA sequence and functional organization of the P1 partition region. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90402-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin S., Abeles A. Partition of unit-copy miniplasmids to daughter cells. II. The partition region of miniplasmid P1 encodes an essential protein and a centromere-like site at which it acts. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 15;169(2):373–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80056-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biek D. P., Cohen S. N. Identification and characterization of recD, a gene affecting plasmid maintenance and recombination in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):594–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.594-603.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. A., Martin K. A., Austin S. J. Specificity switching of the P1 plasmid centromere-like site. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):991–998. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08201.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame R., Bishop J. O. The number of sex-factors per chromosome in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(1):93–103. doi: 10.1042/bj1210093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. A., Austin S. J. The P1 plasmid-partition system synthesizes two essential proteins from an autoregulated operon. Plasmid. 1988 Mar;19(2):103–112. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(88)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funnell B. E., Gagnier L. The P1 plasmid partition complex at parS. II. Analysis of ParB protein binding activity and specificity. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3616–3624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez C., Freire R., Salas M., Hermoso J. M. Assembly of phage phi 29 genome with viral protein p6 into a compact complex. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):269–276. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06257.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa Y., Murotsu T., Matsubara K. Mini-F protein that binds to a unique region for partition of mini-F plasmid DNA. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):349–354. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.349-354.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraga S. Chromosome and plasmid partition in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:283–306. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.001435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline B. C. A review of mini-F plasmid maintenance. Plasmid. 1985 Jul;14(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusukawa N., Mori H., Kondo A., Hiraga S. Partitioning of the F plasmid: overproduction of an essential protein for partition inhibits plasmid maintenance. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jul;208(3):365–372. doi: 10.1007/BF00328125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D., Rothenbuehler R., Merrillat A. M., Aiken C. Analysis of the F plasmid centromere. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 May;207(2-3):406–412. doi: 10.1007/BF00331608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch A. S., Wang J. C. Use of an inducible site-specific recombinase to probe the structure of protein-DNA complexes involved in F plasmid partition in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 25;236(3):679–684. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manis J. J., Kline B. C. Restriction endonuclease mapping and mutagenesis of the F sex factor replication region. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Apr 29;152(3):175–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00268815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. A., Beaucage S. L., Cohen S. N. Role of DNA superhelicity in partitioning of the pSC101 plasmid. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):127–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90246-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Kondo A., Ohshima A., Ogura T., Hiraga S. Structure and function of the F plasmid genes essential for partitioning. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 5;192(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90459-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Mori Y., Ichinose C., Niki H., Ogura T., Kato A., Hiraga S. Purification and characterization of SopA and SopB proteins essential for F plasmid partitioning. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15535–15541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murotsu T., Matsubara K., Sugisaki H., Takanami M. Nine unique repeating sequences in a region essential for replication and incompatibility of the mini-F plasmid. Gene. 1981 Nov;15(2-3):257–271. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musgrave D. R., Sandman K. M., Reeve J. N. DNA binding by the archaeal histone HMf results in positive supercoiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10397–10401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström K., Austin S. J. Mechanisms that contribute to the stable segregation of plasmids. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:37–69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.000345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogura T., Hiraga S. Partition mechanism of F plasmid: two plasmid gene-encoded products and a cis-acting region are involved in partition. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):351–360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90454-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Krisch H. M. In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene. 1984 Sep;29(3):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano M., Salas M., Hermoso J. M. A novel nucleoprotein complex at a replication origin. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1012–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.2111580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmis K., Cabello F., Cohen S. N. Cloning, isolation, and characterization of replication regions of complex plasmid genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2242–2246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. Y., Liu L. F. DNA looping alters local DNA conformation during transcription. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jun 20;219(4):615–622. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90658-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]