Abstract
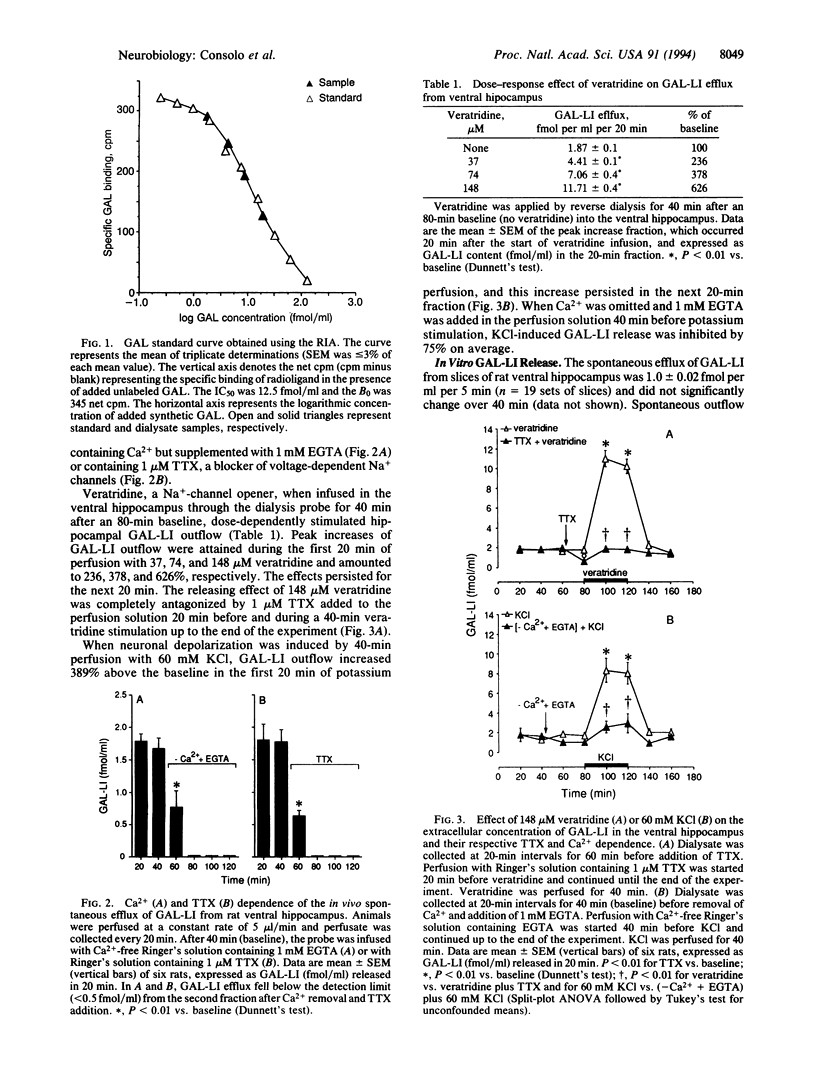
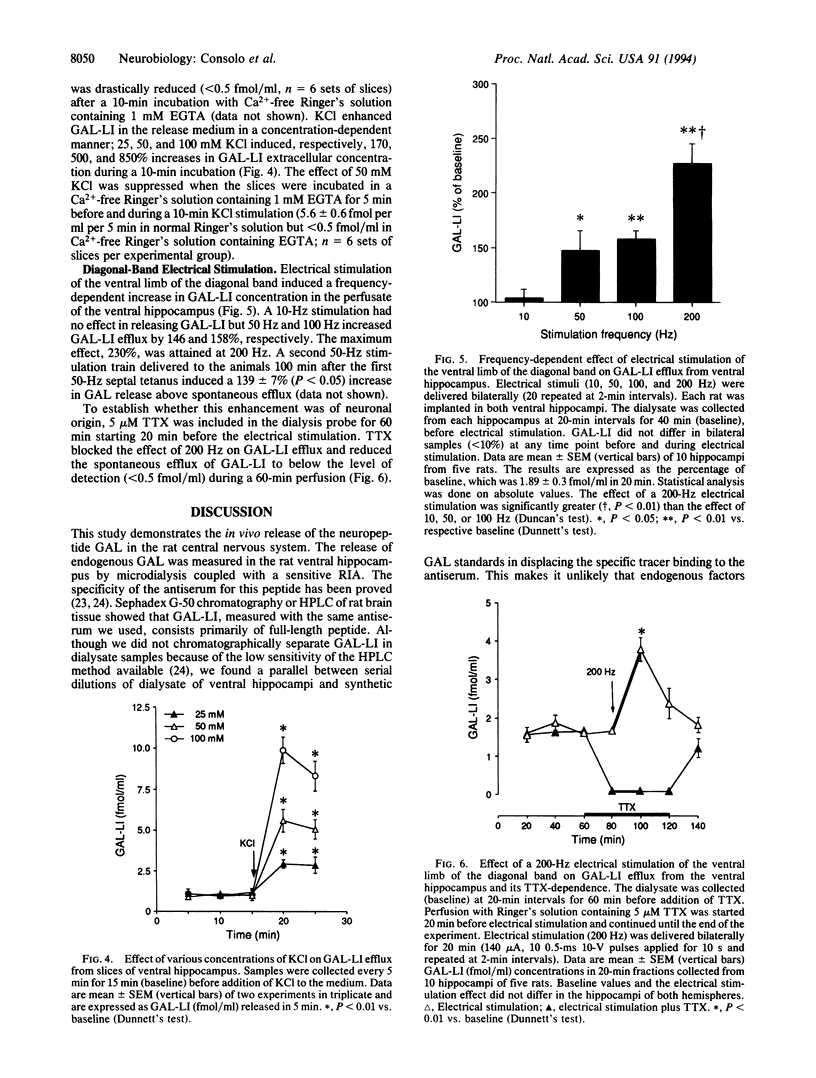
Using microdialysis and a sensitive RIA, we have studied the in vivo release of the neuropeptide galanin (GAL) from the ventral hippocampus of freely moving rats. The spontaneous outflow of GAL-like immunoreactivity (GAL-LI) (1.8 +/- 0.3 fmol per ml per 20 min) was dependent on the presence of extracellular Ca2+ and was inhibited by tetrodotoxin. Evoked release induced by infusion of KCl (60 mM) or veratridine (148 microM) was also Ca(2+)-dependent and sensitive to tetrodotoxin. Electrical stimulation of the ventral limb of the diagonal band nuclei induced a frequency-dependent (50-200 Hz) and tetrodotoxin-sensitive overflow of GAL-LI in the hippocampus. In vitro GAL-LI release (1.0 +/- 0.02 fmol per ml per 5 min), studied in slices of rat ventral hippocampus, was also Ca(2+)-dependent and was increased in a concentration-dependent manner by KCl depolarization. This study demonstrates the release of the neuropeptide GAL in the rat central nervous system. The in vivo release is related to the activity of the cholinergic GAL-LI-containing cells in the septal diagonal band nuclei. The results are discussed in relation to the coexistence of GAL and acetylcholine within the septal/diagonal band complex.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartfai T., Bedecs K., Land T., Langel U., Bertorelli R., Girotti P., Consolo S., Xu X. J., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z., Nilsson S. M-15: high-affinity chimeric peptide that blocks the neuronal actions of galanin in the hippocampus, locus coeruleus, and spinal cord. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10961–10965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartfai T., Fisone G., Langel U. Galanin and galanin antagonists: molecular and biochemical perspectives. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Aug;13(8):312–317. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90098-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartfai T., Hökfelt T., Langel U. Galanin--a neuroendocrine peptide. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1993;7(3-4):229–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartfai T., Iverfeldt K., Fisone G., Serfözö P. Regulation of the release of coexisting neurotransmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1988;28:285–310. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.28.040188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartfai T., Langel U., Bedecs K., Andell S., Land T., Gregersen S., Ahrén B., Girotti P., Consolo S., Corwin R. Galanin-receptor ligand M40 peptide distinguishes between putative galanin-receptor subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11287–11291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan-Palay V. Galanin hyperinnervates surviving neurons of the human basal nucleus of Meynert in dementias of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease: a hypothesis for the role of galanin in accentuating cholinergic dysfunction in dementia. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Jul 22;273(4):543–557. doi: 10.1002/cne.902730409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisone G., Bartfai T., Nilsson S., Hökfelt T. Galanin inhibits the potassium-evoked release of acetylcholine and the muscarinic receptor-mediated stimulation of phosphoinositide turnover in slices of monkey hippocampus. Brain Res. 1991 Dec 24;568(1-2):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91409-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisone G., Wu C. F., Consolo S., Nordström O., Brynne N., Bartfai T., Melander T., Hökfelt T. Galanin inhibits acetylcholine release in the ventral hippocampus of the rat: histochemical, autoradiographic, in vivo, and in vitro studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7339–7343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel S. M., Bierer L. M., Davidson M., Purohit D. P., Perl D. P., Harotunian V. Galanin-like immunoreactivity is increased in the postmortem cerebral cortex from patients with Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 1994 Apr;62(4):1516–1523. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62041516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel S. M., Koenig J. I., Washton D. L. Estrogen stimulation of galanin gene expression and galanin-like immunoreactivity in the rat and its blockade by the estrogen antagonist keoxifene (LY156758). Regul Pept. 1993 Jun 11;45(3):407–419. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(93)90367-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel S. M., Washton D. L., Roncancio J. R. Modulation of hypothalamic galanin gene expression by estrogen in peripubertal rats. Peptides. 1992 Jul-Aug;13(4):801–806. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(92)90190-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariano R. F., Groves P. M. A mechanism for the involvement of colocalized neuropeptides in the actions of antipsychotic drugs. Biol Psychiatry. 1989 Jul;26(3):303–314. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(89)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girotti P., Bertorelli R., Fisone G., Land T., Langel U., Consolo S., Bartfai T. N-terminal galanin fragments inhibit the hippocampal release of acetylcholine in vivo. Brain Res. 1993 May 28;612(1-2):258–262. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91670-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glavinović M., Ropert N., Krnjević K., Collier B. Hemicholinium impairs septo-hippocampal facilitatory action. Neuroscience. 1983 Jun;9(2):319–330. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90297-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsthemke B., Schulz M., Bauer K. Degradation of substance P by neurones and glial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 14;125(2):728–733. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90599-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz S. F., Kim T. Impact of a galanin antagonist on exogenous galanin and natural patterns of fat ingestion. Brain Res. 1992 Dec 18;599(1):148–152. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90863-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastropaolo J., Nadi N. S., Ostrowski N. L., Crawley J. N. Galanin antagonizes acetylcholine on a memory task in basal forebrain-lesioned rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9841–9845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Hökfelt T., Rökaeus A. Distribution of galaninlike immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Jun 22;248(4):475–517. doi: 10.1002/cne.902480404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander T., Staines W. A., Hökfelt T., Rökaeus A., Eckenstein F., Salvaterra P. M., Wainer B. H. Galanin-like immunoreactivity in cholinergic neurons of the septum-basal forebrain complex projecting to the hippocampus of the rat. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 23;360(1-2):130–138. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström O., Bartfai T. Muscarinic autoreceptor regulates acetylcholine release in rat hippocampus: in vitro evidence. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Apr;108(4):347–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogren S. O., Hökfelt T., Kask K., Langel U., Bartfai T. Evidence for a role of the neuropeptide galanin in spatial learning. Neuroscience. 1992 Nov;51(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90463-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palazzi E., Felinska S., Zambelli M., Fisone G., Bartfai T., Consolo S. Galanin reduces carbachol stimulation of phosphoinositide turnover in rat ventral hippocampus by lowering Ca2+ influx through voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels. J Neurochem. 1991 Mar;56(3):739–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb01986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senut M. C., Menetrey D., Lamour Y. Cholinergic and peptidergic projections from the medial septum and the nucleus of the diagonal band of Broca to dorsal hippocampus, cingulate cortex and olfactory bulb: a combined wheatgerm agglutinin-apohorseradish peroxidase-gold immunohistochemical study. Neuroscience. 1989;30(2):385–403. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90260-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skofitsch G., Jacobowitz D. M. Immunohistochemical mapping of galanin-like neurons in the rat central nervous system. Peptides. 1985 May-Jun;6(3):509–546. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström E., Archer T., Melander T., Hökfelt T. Galanin impairs acquisition but not retrieval of spatial memory in rats studied in the Morris swim maze. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Jun 7;88(3):331–335. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vezzani A., Ruiz R., Monno A., Rizzi M., Lindefors N., Samanin R., Brodin E. Extracellular somatostatin measured by microdialysis in the hippocampus of freely moving rats: evidence for neuronal release. J Neurochem. 1993 Feb;60(2):671–677. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weille J., Schmid-Antomarchi H., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. ATP-sensitive K+ channels that are blocked by hypoglycemia-inducing sulfonylureas in insulin-secreting cells are activated by galanin, a hyperglycemia-inducing hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1312–1316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



