Abstract
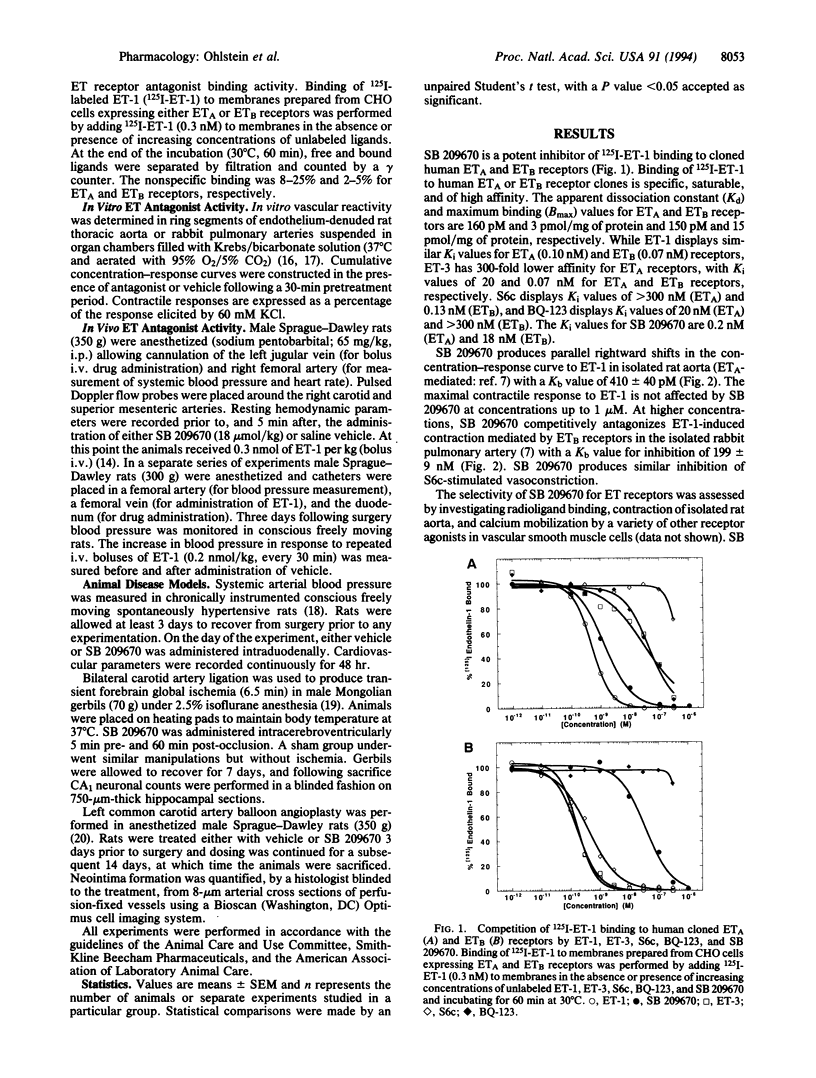
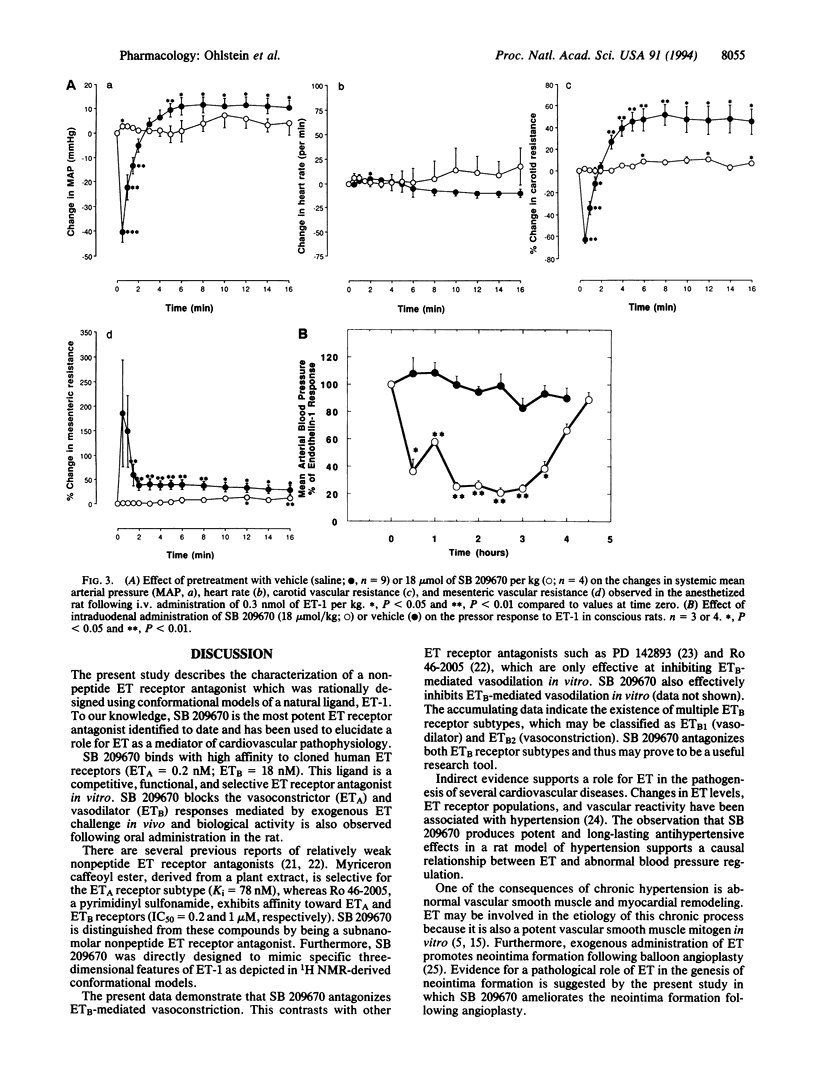
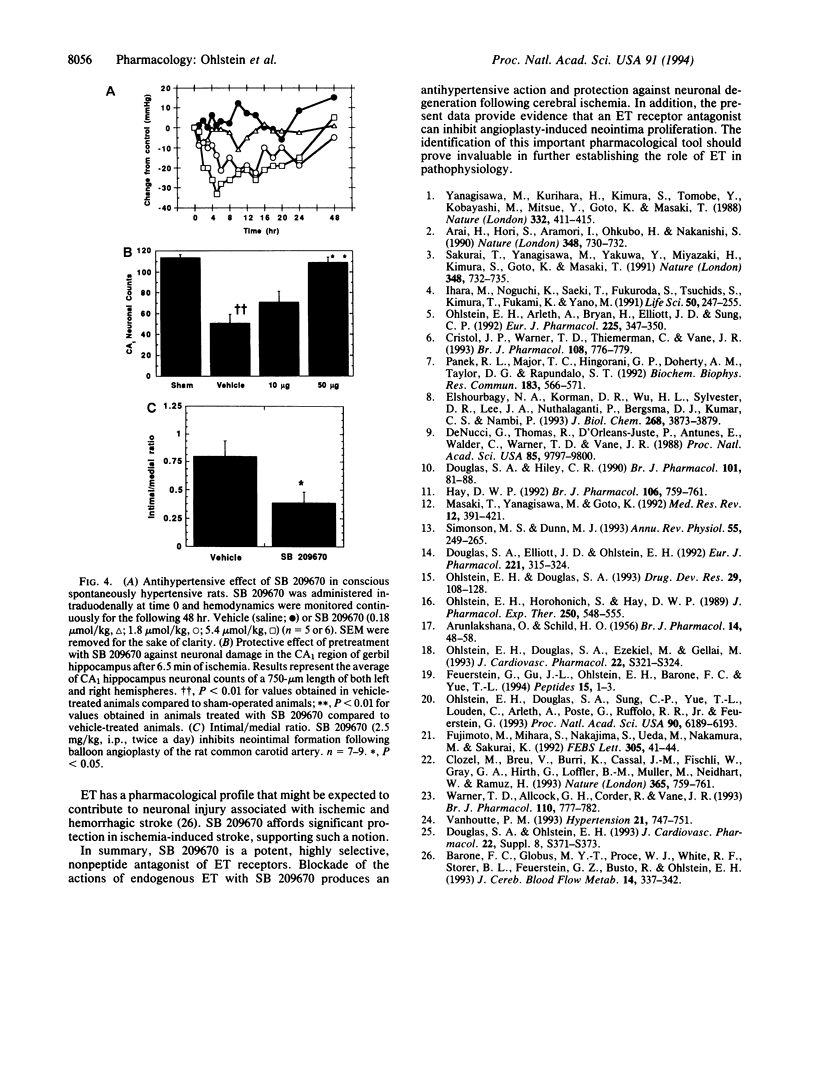
An extremely potent and highly specific non-peptide, subnanomolar endothelin (ET) receptor antagonist, SB 209670, has been synthesized and characterized. SB 209670, which was rationally designed using conformational models of ET-1, selectively inhibits binding of 125I-labeled ET-1 to cloned human ET receptor subtypes ETA and ETB (Ki = 0.2 and 18 nM, respectively). SB 209670 produces concentration-dependent inhibition of ET-1-mediated vasoconstriction in isolated vascular tissues and in vivo following either intravenous or intraduodenal administration. SB 209670 produces a dose-dependent reduction in blood pressure in hypertensive rats, protects from ischemia-induced neuronal degeneration in a gerbil stroke model, and attenuates neointima formation following rat carotid artery balloon angioplasty. SB 209670 will be useful in characterizing and classifying the physiological and pathophysiological effects of ET.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Hori S., Aramori I., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding an endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):730–732. doi: 10.1038/348730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barone F. C., Globus M. Y., Price W. J., White R. F., Storer B. L., Feuerstein G. Z., Busto R., Ohlstein E. H. Endothelin levels increase in rat focal and global ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1994 Mar;14(2):337–342. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1994.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clozel M., Breu V., Burri K., Cassal J. M., Fischli W., Gray G. A., Hirth G., Löffler B. M., Müller M., Neidhart W. Pathophysiological role of endothelin revealed by the first orally active endothelin receptor antagonist. Nature. 1993 Oct 21;365(6448):759–761. doi: 10.1038/365759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cristol J. P., Warner T. D., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Mediation via different receptors of the vasoconstrictor effects of endothelins and sarafotoxins in the systemic circulation and renal vasculature of the anaesthetized rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;108(3):776–779. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12877.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. A., Elliott J. D., Ohlstein E. H. Regional vasodilation to endothelin-1 is mediated by a non-ETA receptor subtype in the anaesthetized rat: effect of BQ-123 on systemic haemodynamic responses. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Oct 20;221(2-3):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90718-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. A., Hiley C. R. Endothelium-dependent vascular activities of endothelin-like peptides in the isolated superior mesenteric arterial bed of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;101(1):81–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12093.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. A., Ohlstein E. H. Endothelin-1 promotes neointima formation after balloon angioplasty in the rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993;22 (Suppl 8):S371–S373. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199322008-00097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Korman D. R., Wu H. L., Sylvester D. R., Lee J. A., Nuthalaganti P., Bergsma D. J., Kumar C. S., Nambi P. Molecular characterization and regulation of the human endothelin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):3873–3879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto M., Mihara S., Nakajima S., Ueda M., Nakamura M., Sakurai K. A novel non-peptide endothelin antagonist isolated from bayberry, Myrica cerifera. FEBS Lett. 1992 Jun 22;305(1):41–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80651-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gäde G., Janssens M. P., Kellner R. A novel peptide in the AKH/RPCH family isolated from the corpora cardiaca of the Emperor dragonfly, Anax imperator. Peptides. 1994 Jan;15(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(94)90162-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay D. W. Pharmacological evidence for distinct endothelin receptors in guinea-pig bronchus and aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;106(4):759–761. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara M., Noguchi K., Saeki T., Fukuroda T., Tsuchida S., Kimura S., Fukami T., Ishikawa K., Nishikibe M., Yano M. Biological profiles of highly potent novel endothelin antagonists selective for the ETA receptor. Life Sci. 1992;50(4):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90331-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masaki T., Yanagisawa M., Goto K. Physiology and pharmacology of endothelins. Med Res Rev. 1992 Jul;12(4):391–421. doi: 10.1002/med.2610120405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlstein E. H., Arleth A., Bryan H., Elliott J. D., Sung C. P. The selective endothelin ETA receptor antagonist BQ123 antagonizes endothelin-1-mediated mitogenesis. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr 10;225(4):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlstein E. H., Douglas S. A., Ezekiel M., Gellai M. Antihypertensive effects of the endothelin receptor antagonist BQ-123 in conscious spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993;22 (Suppl 8):S321–S324. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199322008-00084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlstein E. H., Douglas S. A., Sung C. P., Yue T. L., Louden C., Arleth A., Poste G., Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Feuerstein G. Z. Carvedilol, a cardiovascular drug, prevents vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, migration, and neointimal formation following vascular injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6189–6193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlstein E. H., Horohonich S., Hay D. W. Cellular mechanisms of endothelin in rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Aug;250(2):548–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panek R. L., Major T. C., Hingorani G. P., Doherty A. M., Taylor D. G., Rapundalo S. T. Endothelin and structurally related analogs distinguish between endothelin receptor subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 16;183(2):566–571. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90519-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai T., Yanagisawa M., Takuwa Y., Miyazaki H., Kimura S., Goto K., Masaki T. Cloning of a cDNA encoding a non-isopeptide-selective subtype of the endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):732–735. doi: 10.1038/348732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson M. S., Dunn M. J. Endothelin peptides and the kidney. Annu Rev Physiol. 1993;55:249–265. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.55.030193.001341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhoutte P. M. Is endothelin involved in the pathogenesis of hypertension? Hypertension. 1993 Jun;21(6 Pt 1):747–751. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.21.6.747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. D., Allcock G. H., Corder R., Vane J. R. Use of the endothelin antagonists BQ-123 and PD 142893 to reveal three endothelin receptors mediating smooth muscle contraction and the release of EDRF. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;110(2):777–782. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13879.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Nucci G., Thomas R., D'Orleans-Juste P., Antunes E., Walder C., Warner T. D., Vane J. R. Pressor effects of circulating endothelin are limited by its removal in the pulmonary circulation and by the release of prostacyclin and endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9797–9800. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



