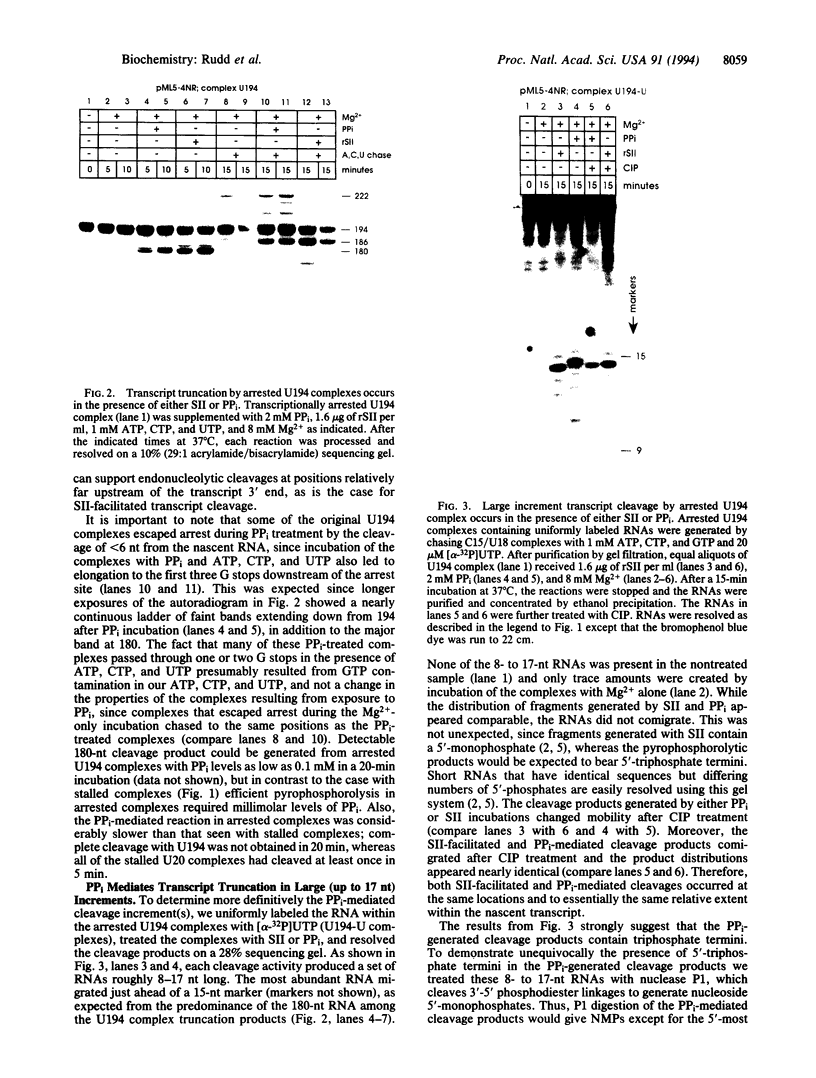
Abstract
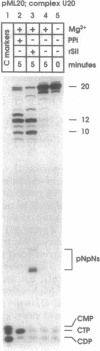
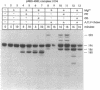
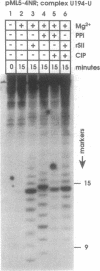
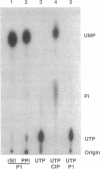
RNA polymerase II may become arrested during transcript elongation, in which case the ternary complex remains intact but further RNA synthesis is blocked. To relieve arrest, the nascent transcript must be cleaved from the 3' end. RNAs of 7-17 nt are liberated and transcription continues from the newly exposed 3' end. Factor SII increases elongation efficiency by strongly stimulating the transcript cleavage reaction. We show here that arrest relief can also occur by the addition of pyrophosphate. This generates the same set of cleavage products as factor SII, but the fragments produced with pyrophosphate have 5'-triphosphate termini. Thus, the active site of RNA polymerase II, in the presence of pyrophosphate, appears to be capable of cleaving phosphodiester linkages as far as 17 nt upstream of the original site of polymerization, leaving the ternary complex intact and transcriptionally active.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal K., Baek K. H., Jeon C. J., Miyamoto K., Ueno A., Yoon H. S. Stimulation of transcript elongation requires both the zinc finger and RNA polymerase II binding domains of human TFIIS. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 6;30(31):7842–7851. doi: 10.1021/bi00245a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmann C. R., Solow-Cordero D. E., Chamberlin M. J. RNA cleavage and chain elongation by Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in a binary enzyme.RNA complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3784–3788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borukhov S., Sagitov V., Goldfarb A. Transcript cleavage factors from E. coli. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J. New models for the mechanism of transcription elongation and its regulation. Harvey Lect. 1992 1993;88:1–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu W., Powell W., Mote J., Jr, Reines D. Nascent RNA cleavage by arrested RNA polymerase II does not require upstream translocation of the elongation complex on DNA. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25604–25616. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo H., Price D. H. Mechanism of DmS-II-mediated pause suppression by Drosophila RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18762–18770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izban M. G., Luse D. S. Factor-stimulated RNA polymerase II transcribes at physiological elongation rates on naked DNA but very poorly on chromatin templates. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13647–13655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izban M. G., Luse D. S. SII-facilitated transcript cleavage in RNA polymerase II complexes stalled early after initiation occurs in primarily dinucleotide increments. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12864–12873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izban M. G., Luse D. S. The RNA polymerase II ternary complex cleaves the nascent transcript in a 3'----5' direction in the presence of elongation factor SII. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1342–1356. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izban M. G., Luse D. S. The increment of SII-facilitated transcript cleavage varies dramatically between elongation competent and incompetent RNA polymerase II ternary complexes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12874–12885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izban M. G., Luse D. S. Transcription on nucleosomal templates by RNA polymerase II in vitro: inhibition of elongation with enhancement of sequence-specific pausing. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):683–696. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson T. L., Chamberlin M. J. Complexes of yeast RNA polymerase II and RNA are substrates for TFIIS-induced RNA cleavage. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakow J. S., Fronk E. Azotobacter vinelandii ribonucleic acid polymerase. 8. Pyrophosphate exchange. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5988–5993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn S. C., Luse D. S. RNA polymerase II elongation complexes paused after the synthesis of 15- or 35-base transcripts have different structures. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1508–1522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitra U., Hurwitz J. The role of deoxyribonucleic acid in ribonucleic acid synthesis. 13. Modified purification procedure and additional properties of ribonucleic acid polymerase from Escherichia coli W. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 10;242(21):4897–4907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroy G., Spencer E., Hurwitz J. Characteristics of reactions catalyzed by purified guanylyltransferase from vaccinia virus. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4490–4498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D. Elongation factor-dependent transcript shortening by template-engaged RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3795–3800. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reines D., Ghanouni P., Li Q. Q., Mote J., Jr The RNA polymerase II elongation complex. Factor-dependent transcription elongation involves nascent RNA cleavage. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15516–15522. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surratt C. K., Milan S. C., Chamberlin M. J. Spontaneous cleavage of RNA in ternary complexes of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and its significance for the mechanism of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):7983–7987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.7983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Hawley D. K. Identification of a 3'-->5' exonuclease activity associated with human RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):843–847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo O. J., Yoon H. S., Baek K. H., Jeon C. J., Miyamoto K., Ueno A., Agarwal K. Cloning, expression and characterization of the human transcription elongation factor, TFIIS. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1073–1079. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]