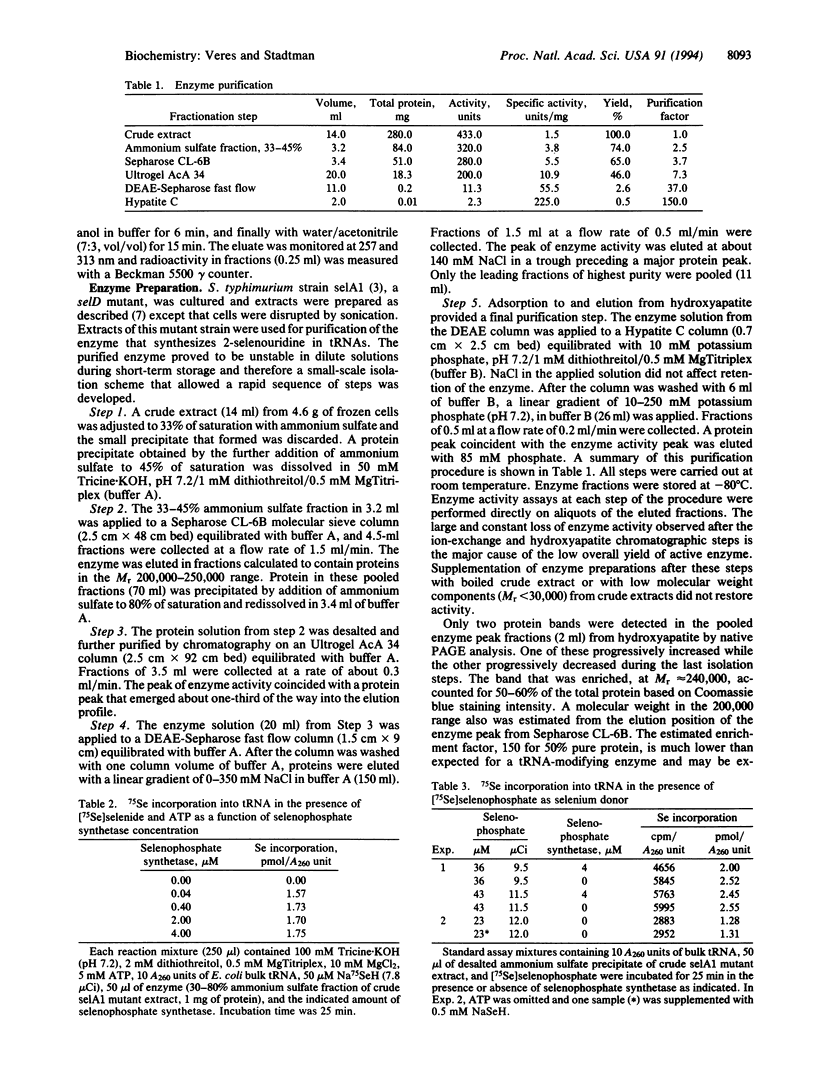
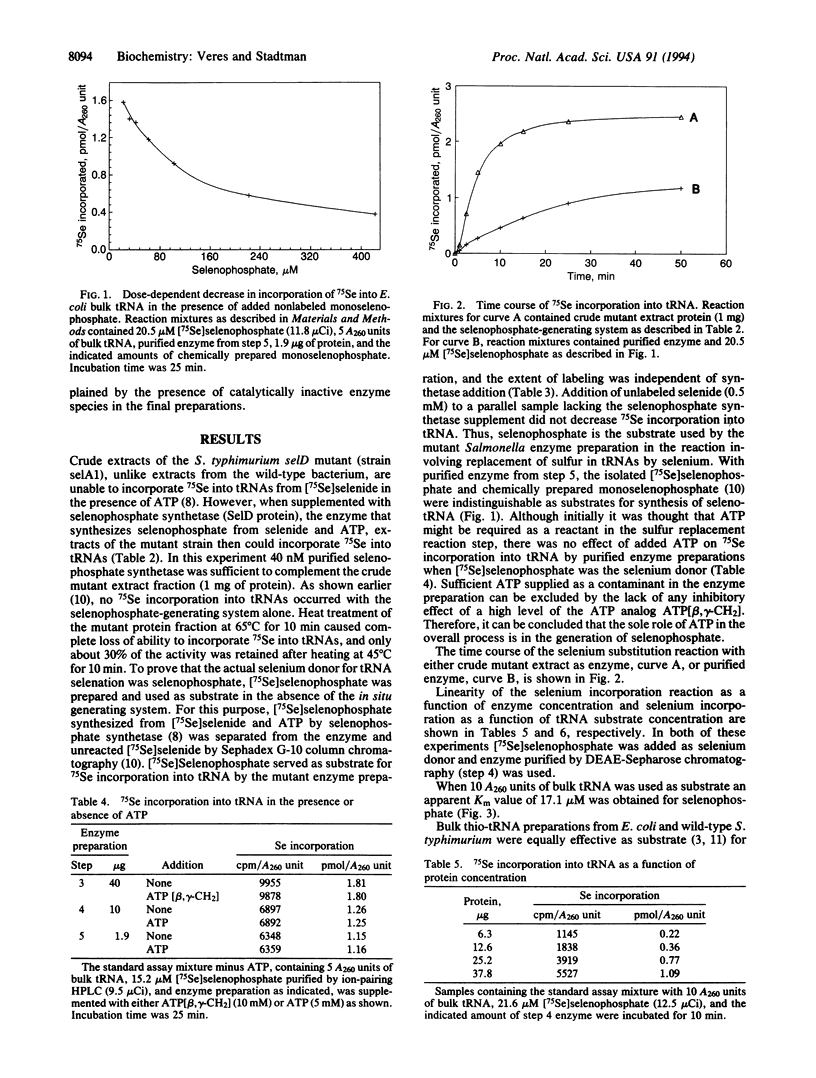
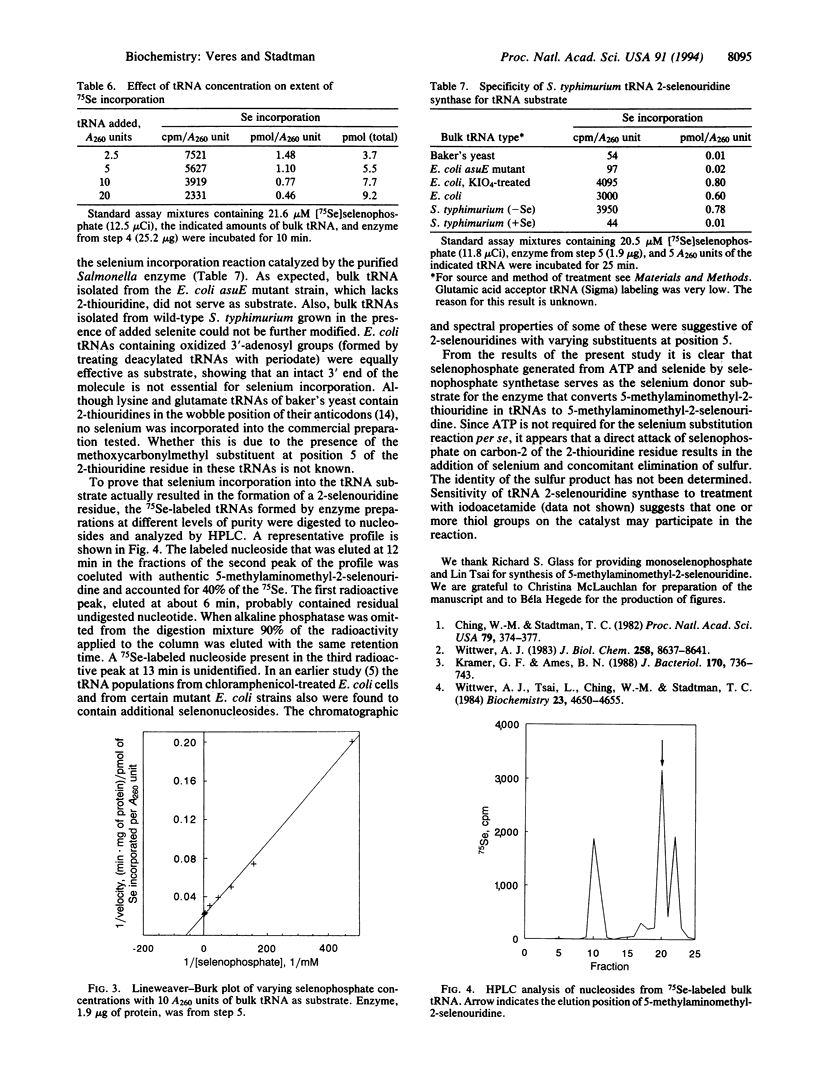
Abstract
A tRNA-modifying enzyme tentatively termed tRNA 2-selenouridine synthase was purified by a five-step procedure that resulted in 50-60% pure preparations. This enzyme catalyzes the conversion of a 5-methylaminomethyl-2-thiouridine residue in the tRNA substrate to 5-methylaminomethyl-2-selenouridine. The selenium donor substrate for this reaction is shown to be selenophosphate which is formed from ATP and selenide by selenophosphate synthetase. Replacement of sulfur with selenium in tRNAs catalyzed by tRNA 2-selenouridine synthase occurs in the absence of ATP. The dependence of reaction velocity on selenophosphate concentration obeys Michaelis-Menten kinetics indicating an apparent Km value of 17.1 microM. Bulk thio-tRNA preparations from Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium are equally effective as substrates for the selenium incorporation reaction. An intact 3' end of the tRNA molecule does not seem to be essential for selenium incorporation. Identity of the product of the reaction was confirmed by HPLC analysis of digests of [75Se]seleno-tRNAs labeled by incubation with the purified enzyme. A labeled compound in the nucleoside mixture was coeluted with authentic 5-methylaminomethyl-2-selenouridine.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baczynskyj L., Biemann K., Hall R. H. Sulfur-containing nucleoside from yeast transfer ribonucleic acid: 2-thio-5(or 6)-uridine acetic acid methyl ester. Science. 1968 Mar 29;159(3822):1481–1483. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3822.1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching W. M., Alzner-DeWeerd B., Stadtman T. C. A selenium-containing nucleoside at the first position of the anticodon in seleno-tRNAGlu from Clostridium sticklandii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):347–350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching W. M., Stadtman T. C. Selenium-containing tRNAGlu from Clostridium sticklandii: correlation of aminoacylation with selenium content. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):374–377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehrke C. W., Kuo K. C., McCune R. A., Gerhardt K. O., Agris P. F. Quantitative enzymatic hydrolysis of tRNAs: reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography of tRNA nucleosides. J Chromatogr. 1982 Jul 9;230(2):297–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass R. S., Singh W. P., Jung W., Veres Z., Scholz T. D., Stadtman T. C. Monoselenophosphate: synthesis, characterization, and identity with the prokaryotic biological selenium donor, compound SePX. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 30;32(47):12555–12559. doi: 10.1021/bi00210a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer G. F., Ames B. N. Isolation and characterization of a selenium metabolism mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):736–743. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.736-743.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remy P., Birmelé C., Ebel J. P. Purification of yeast phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase by affinity chromatography, on a tRNA(Phe)-sepharose column. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 15;27(1):134–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80426-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman T. C., Davis J. N., Zehelein E., Böck A. Biochemical and genetic analysis of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli mutants defective in specific incorporation of selenium into formate dehydrogenase and tRNAs. Biofactors. 1989 Mar;2(1):35–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan M. A., Cannon J. F., Webb F. H., Bock R. M. Antisuppressor mutation in Escherichia coli defective in biosynthesis of 5-methylaminomethyl-2-thiouridine. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):368–376. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.368-376.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veres Z., Tsai L., Politino M., Stadtman T. C. In vitro incorporation of selenium into tRNAs of Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6341–6344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veres Z., Tsai L., Scholz T. D., Politino M., Balaban R. S., Stadtman T. C. Synthesis of 5-methylaminomethyl-2-selenouridine in tRNAs: 31P NMR studies show the labile selenium donor synthesized by the selD gene product contains selenium bonded to phosphorus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2975–2979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittwer A. J. Specific incorporation of selenium into lysine- and glutamate- accepting tRNAs from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8637–8641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittwer A. J., Stadtman T. C. Biosynthesis of 5-methylaminomethyl-2-selenouridine, a naturally occurring nucleoside in Escherichia coli tRNA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Aug 1;248(2):540–550. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90507-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittwer A. J., Tsai L., Ching W. M., Stadtman T. C. Identification and synthesis of a naturally occurring selenonucleoside in bacterial tRNAs: 5-[(methylamino)methyl]-2-selenouridine. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 25;23(20):4650–4655. doi: 10.1021/bi00315a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



