Abstract
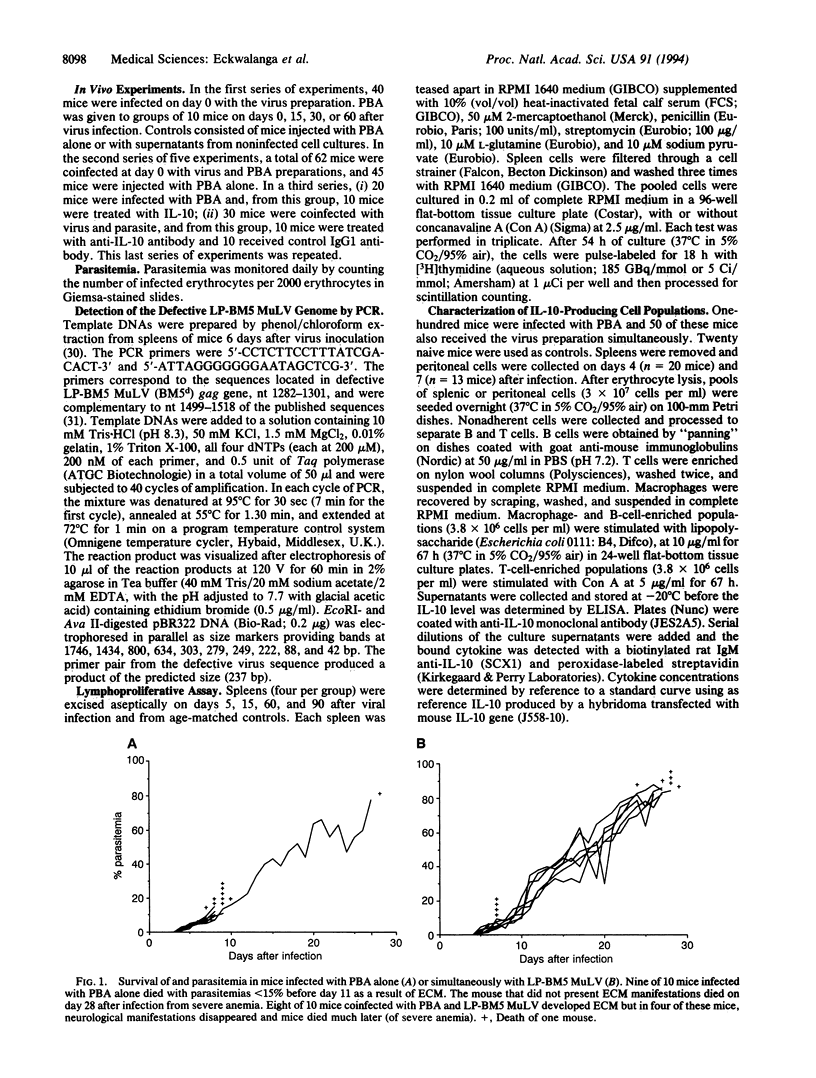
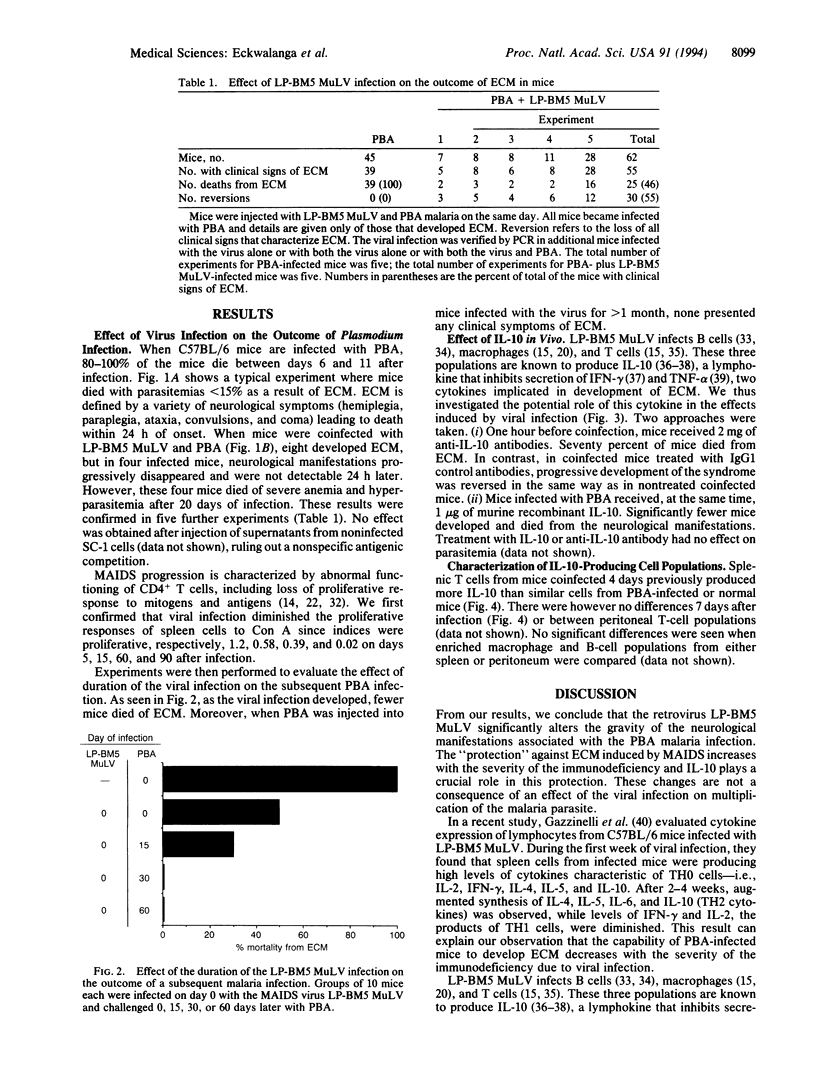
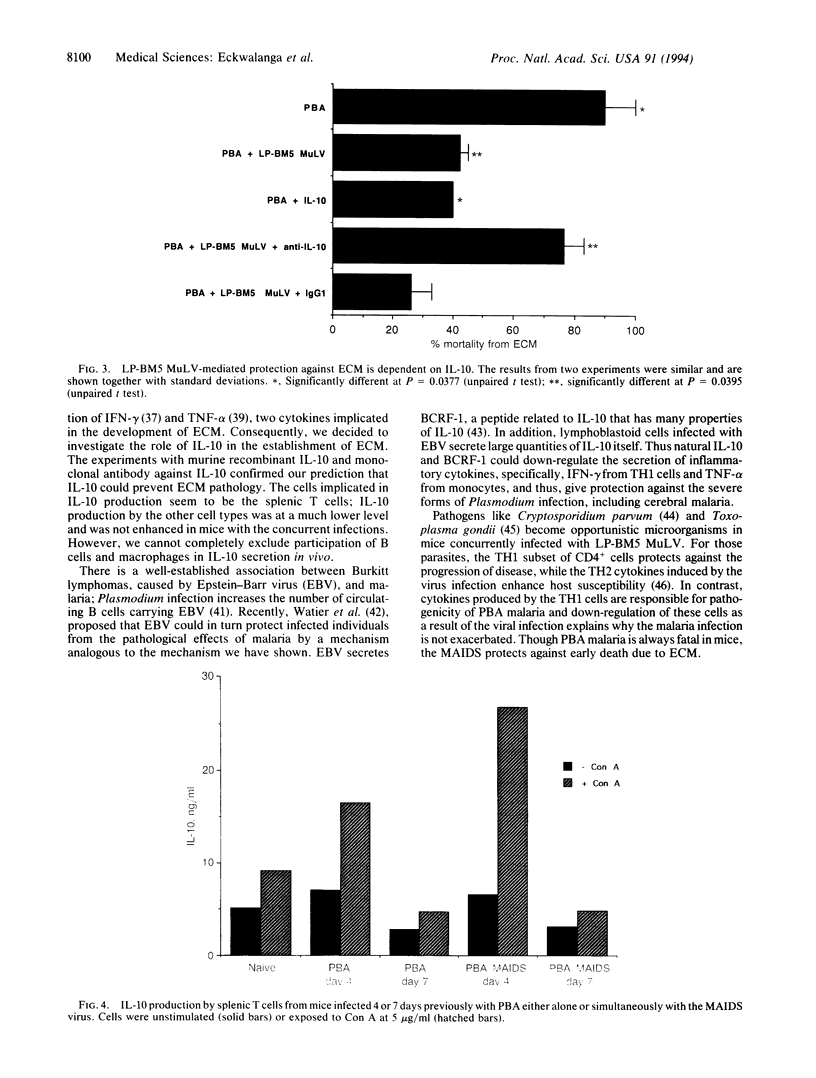
The retrovirus LP-BM5 murine leukemia virus induces murine AIDS in C57BL/6 mice that has many similarities with human AIDS; Plasmodium berghei ANKA causes experimental cerebral malaria in the same strain of mice. The outcome of malaria infection was studied in mice concurrently infected with the two pathogens. The retrovirus significantly reduced the gravity of the neurological manifestations associated with Plasmodium berghei ANKA infection. The protection against experimental cerebral malaria induced by murine AIDS increased with duration of viral infection and, hence, with the severity of the immunodeficiency. Interleukin 10, principally from splenic T cells, was shown to play a crucial role in this protection.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AIDS in Africa. N Engl J Med. 1991 Mar 21;324(12):847–848. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199103213241212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrams J. S., Roncarolo M. G., Yssel H., Andersson U., Gleich G. J., Silver J. E. Strategies of anti-cytokine monoclonal antibody development: immunoassay of IL-10 and IL-5 in clinical samples. Immunol Rev. 1992 Jun;127:5–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb01406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen S., Van de perre P., Serufilira A., Lepage P., Carael M., DeClercq A., Tice J., Black D., Nsengumuremyi F., Ziegler J. Human immunodeficiency virus and malaria in a representative sample of childbearing women in Kigali, Rwanda. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):67–71. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassin R. H., Tuttle N., Fischinger P. J. Rapid cell culture assay technic for murine leukaemia viruses. Nature. 1971 Feb 19;229(5286):564–566. doi: 10.1038/229564b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerny A., Hügin A. W., Hardy R. R., Hayakawa K., Zinkernagel R. M., Makino M., Morse H. C., 3rd B cells are required for induction of T cell abnormalities in a murine retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):315–320. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Morse H. C., 3rd, Makino M., Ruscetti S. K., Hartley J. W. Defective virus is associated with induction of murine retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3862–3866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Sengupta D. N., Fredrickson T. N., Morse H. C., 3rd, Hartley J. W. Characteristics and contributions of defective, ecotropic, and mink cell focus-inducing viruses involved in a retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome of mice. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4232–4241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4232-4241.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung S. C., Chattopadhyay S. K., Hartley J. W., Morse H. C., 3rd, Pitha P. M. Aberrant expression of cytokine genes in peritoneal macrophages from mice infected with LP-BM5 MuLV, a murine model of AIDS. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):121–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerici M., Shearer G. M. A TH1-->TH2 switch is a critical step in the etiology of HIV infection. Immunol Today. 1993 Mar;14(3):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerici M., Stocks N. I., Zajac R. A., Boswell R. N., Via C. S., Shearer G. M. Circumvention of defective CD4 T helper cell function in HIV-infected individuals by stimulation with HLA alloantigens. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3266–3271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colebunders R., Bahwe Y., Nekwei W., Ryder R., Perriens J., Nsimba K., Turner A., Francis H., Lebughe I., Van der Stuyft P. Incidence of malaria and efficacy of oral quinine in patients recently infected with human immunodeficiency virus in Kinshasa, Zaire. J Infect. 1990 Sep;21(2):167–173. doi: 10.1016/0163-4453(90)91701-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darban H., Enriquez J., Sterling C. R., Lopez M. C., Chen G., Abbaszadegan M., Watson R. R. Cryptosporidiosis facilitated by murine retroviral infection with LP-BM5. J Infect Dis. 1991 Oct;164(4):741–745. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.4.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentino D. F., Bond M. W., Mosmann T. R. Two types of mouse T helper cell. IV. Th2 clones secrete a factor that inhibits cytokine production by Th1 clones. J Exp Med. 1989 Dec 1;170(6):2081–2095. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentino D. F., Zlotnik A., Mosmann T. R., Howard M., O'Garra A. IL-10 inhibits cytokine production by activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3815–3822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzinelli R. T., Hartley J. W., Fredrickson T. N., Chattopadhyay S. K., Sher A., Morse H. C., 3rd Opportunistic infections and retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency: studies of acute and chronic infections with Toxoplasma gondii in mice infected with LP-BM5 murine leukemia viruses. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4394–4401. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4394-4401.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzinelli R. T., Makino M., Chattopadhyay S. K., Snapper C. M., Sher A., Hügin A. W., Morse H. C., 3rd CD4+ subset regulation in viral infection. Preferential activation of Th2 cells during progression of retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency in mice. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):182–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go N. F., Castle B. E., Barrett R., Kastelein R., Dang W., Mosmann T. R., Moore K. W., Howard M. Interleukin 10, a novel B cell stimulatory factor: unresponsiveness of X chromosome-linked immunodeficiency B cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1625–1631. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodgame R. W. AIDS in Uganda--clinical and social features. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 9;323(6):383–389. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008093230605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Bieler G., Pointaire P., De Kossodo S., Tacchini-Cotier F., Vassalli P., Piguet P. F., Lambert P. H. Significance of cytokine production and adhesion molecules in malarial immunopathology. Immunol Lett. 1990 Aug;25(1-3):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(90)90113-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P., Lambert P. H. Tumor-necrosis factor and other cytokines in cerebral malaria: experimental and clinical data. Immunol Rev. 1989 Dec;112:49–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A. E., Nsa W., Ryder R. W., Medi M., Nzeza M., Kitadi N., Baangi M., Malanda N., Davachi F., Hassig S. E. Plasmodium Falciparum malaria and perinatally acquired human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in Kinshasa, Zaire. A prospective, longitudinal cohort study of 587 children. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jul 11;325(2):105–109. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199107113250206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitoshi Y., Okada Y., Sonoda E., Tominaga A., Makino M., Suzuki K., Kinoshita J., Komuro K., Mizuochi T., Takatsu K. Delayed progression of a murine retrovirus-induced acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in X-linked immunodeficient mice. J Exp Med. 1993 Mar 1;177(3):621–626. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu D. H., de Waal Malefyt R., Fiorentino D. F., Dang M. N., Vieira P., de Vries J., Spits H., Mosmann T. R., Moore K. W. Expression of interleukin-10 activity by Epstein-Barr virus protein BCRF1. Science. 1990 Nov 9;250(4982):830–832. doi: 10.1126/science.2173142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M., Simard C., Kay D. G., Jolicoeur P. The majority of cells infected with the defective murine AIDS virus belong to the B-cell lineage. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6562–6571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6562-6571.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P. Murine acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (MAIDS): an animal model to study the AIDS pathogenesis. FASEB J. 1991 Jul;5(10):2398–2405. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.10.2065888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D., Hill A. V., Sambou I., Twumasi P., Castracane J., Manogue K. R., Cerami A., Brewster D. R., Greenwood B. M. TNF concentration in fatal cerebral, non-fatal cerebral, and uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Lancet. 1990 Nov 17;336(8725):1201–1204. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92827-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. M., Syed N., Whittle H., Crawford D. H. Circulating Epstein-Barr virus-carrying B cells in acute malaria. Lancet. 1991 Apr 13;337(8746):876–878. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Depper J. M., Greene W. C., Whalen G., Waldmann T. A., Fauci A. S. Qualitative analysis of immune function in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Evidence for a selective defect in soluble antigen recognition. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jul 11;313(2):79–84. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198507113130204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langhorne J. The role of CD4+ T-cells in the immune response to Plasmodium chabaudi. Parasitol Today. 1989 Nov;5(11):362–364. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(89)90113-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leaver R. J., Haile Z., Watters D. A. HIV and cerebral malaria. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Mar-Apr;84(2):201–201. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(90)90253-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. W., O'Garra A., de Waal Malefyt R., Vieira P., Mosmann T. R. Interleukin-10. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:165–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse H. C., 3rd, Chattopadhyay S. K., Makino M., Fredrickson T. N., Hügin A. W., Hartley J. W. Retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency in the mouse: MAIDS as a model for AIDS. AIDS. 1992 Jul;6(7):607–621. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199207000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse H. C., 3rd, Chattopadhyay S. K., Makino M., Fredrickson T. N., Hügin A. W., Hartley J. W. Retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency in the mouse: MAIDS as a model for AIDS. AIDS. 1992 Jul;6(7):607–621. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199207000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse H. C., 3rd, Yetter R. A., Via C. S., Hardy R. R., Cerny A., Hayakawa K., Hugin A. W., Miller M. W., Holmes K. L., Shearer G. M. Functional and phenotypic alterations in T cell subsets during the course of MAIDS, a murine retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):844–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Yetter R. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Functional T lymphocytes are required for a murine retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency disease (MAIDS). J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1737–1742. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller O., Moser R. The clinical and parasitological presentation of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Uganda is unaffected by HIV-1 infection. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1990 May-Jun;84(3):336–338. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(90)90306-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen-Dinh P., Greenberg A. E., Mann J. M., Kabote N., Francis H., Colebunders R. L., Huong A. Y., Quinn T. C., Davachi F., Lyamba B. Absence of association between Plasmodium falciparum malaria and human immunodeficiency virus infection in children in Kinshasa, Zaire. Bull World Health Organ. 1987;65(5):607–613. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Fauci A. S. The effect of cytokines and pharmacologic agents on chronic HIV infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Feb;8(2):191–197. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoi D., Stall A. M., Schwartz D., Merigan T. C., Herzenberg L. A., Basham T. Zidovudine (azido dideoxythymidine) inhibits characteristic early alterations of lymphoid cell populations in retrovirus-induced murine AIDS. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1705–1710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoï D., Viale A. C., Colle J. H. Abnormal selection of antibody repertoires in retrovirus-induced murine AIDS. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 1;151(9):5073–5080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher A., Gazzinelli R. T., Oswald I. P., Clerici M., Kullberg M., Pearce E. J., Berzofsky J. A., Mosmann T. R., James S. L., Morse H. C., 3rd Role of T-cell derived cytokines in the downregulation of immune responses in parasitic and retroviral infection. Immunol Rev. 1992 Jun;127:183–204. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb01414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai A., Cosentino M., Leitman-Klinman S. F., Klinman D. M. Human immunodeficiency virus infection induces both polyclonal and virus-specific B cell activation. J Clin Invest. 1992 Feb;89(2):561–566. doi: 10.1172/JCI115621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang Y., Fredrickson T. N., Chattopadhyay S. K., Hartley J. W., Morse H. C., 3rd Lymphomas in mice with retrovirus-induced immunodeficiency. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;182:395–398. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77633-5_50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinetz J. M., Kumar S., Good M. F., Fowlkes B. J., Berzofsky J. A., Miller L. H. Adoptive transfer of CD8+ T cells from immune animals does not transfer immunity to blood stage Plasmodium yoelii malaria. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 1;144(3):1069–1074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watier H., Auriault C., Capron A. Does Epstein-Barr virus infection confer selective advantage to malaria-infected children? Lancet. 1993 Mar 6;341(8845):612–613. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90364-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]