Abstract
Astrocytes in the brain release transmitters that actively modulate neuronal excitability and synaptic efficacy. Astrocytes also release vasoactive agents that contribute to neurovascular coupling. As reviewed in this article, Müller cells, the principal retinal glial cells, modulate neuronal activity and blood flow in the retina. Stimulated Müller cells release ATP which, following its conversion to adenosine by ectoenzymes, hyperpolarizes retinal ganglion cells by activation of A1 adenosine receptors. This results in the opening of G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium (GIRK) channels and small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (SK) channels. Tonic release of ATP also contributes to the generation of tone in the retinal vasculature by activation of P2X receptors on vascular smooth muscle cells. Vascular tone is lost when glial cells are poisoned with the gliotoxin fluorocitrate. The glial release of vasoactive metabolites of arachidonic acid, including prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), contributes to neurovascular coupling in the retina. Neurovascular coupling is reduced when neuronal stimulation of glial cells is interrupted and when the synthesis of arachidonic acid metabolites is blocked. Neurovascular coupling is compromised in diabetic retinopathy owing to the loss of glial-mediated vasodilation. This loss can be reversed by inhibiting inducible nitric oxide synthase. It is likely that future research will reveal additional important functions of the release of transmitters from glial cells.
Keywords: retina, gliotransmitters, neurovascular coupling, blood flow, astrocyte, diabetic retinopathy
1. Introduction
Glial cells have traditionally been viewed as passive elements in the central nervous system (CNS), providing structural and metabolic support for neurons but not actively interacting with other CNS cells or influencing neural activity. During the past three decades, however, it has become clear that glia interact actively with neurons and the vasculature in the CNS and have essential functions. Many of these functions involve the glial release of transmitters or other modulatory agents.
Astrocytes, the most common type of glial cell in the brain, release a number of transmitters [1]. These transmitters include many of the same molecules released from neurons and are termed gliotransmitters to emphasize their glial origin. Gliotransmitters include glutamate, ATP and d-serine. Release of these gliotransmitters results in increases and decreases in neuronal excitability and in modulation of synaptic transmission and synaptic plasticity [1]. Release of ATP from astrocytes, for instance, depresses synaptic transmission at the CA3 to CA1 synapse in the hippocampus and enhances long-term potentiation [2].
Astrocytes also release a number of vasoactive agents that dilate or constrict arteries and arterioles in the brain [3]. Release of these agents, including prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), 20-hydroxy-eicosatetraenoic acid (20-HETE) and K+, plays a key role in mediating neurovascular coupling, the modulation of blood flow in response to neuronal activity. The resulting functional hyperaemia response is the basis of functional brain imaging, measured using such techniques as BOLD fMRI (blood-oxygen-level-dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging).
In addition, glial cells release many neurotrophic and growth factors, including brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), interleukin 6 (IL-6), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) [4]. These signalling molecules play essential roles in providing trophic support for neurons, other glial cells and blood vessels in the brain.
Our laboratory has characterized the release of gliotransmitters and vasoactive agents from glial cells in the retina. Release of ATP from retinal glial cells results in the hyperpolarization of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and in reduced spike generation in these cells. Glial release of ATP also constricts retinal arterioles and is primarily responsible for generating tone in these vessels. In addition, stimulated glial cells release metabolites of arachidonic acid, including PGE2, EETs and 20-HETE, onto retinal vessels, mediating neurovascular coupling in the retina. The experiments demonstrating the modulation of neuronal activity and blood flow by glial cells in the retina are described in this article.
2. Glial cells of the retina
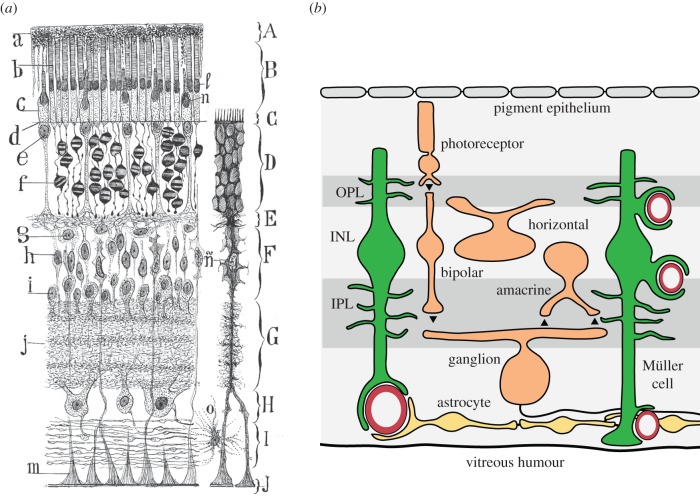
The retina is an integral part of the CNS and has a similar complement of glial cells as the brain [5,6]. The principal macroglial cell of the retina is the Müller cell, a radial glial cell that extends from the inner border of the retina at the vitreous humour to the photoreceptors in the outer retina (figure 1). Müller cells serve similar functions as astrocytes in the brain. Müller cell lamellae surround neuronal somata in the nuclear (cell body) layers and fine Müller cell processes contact synapses in the plexiform (synaptic) layers of the retina (figure 1a). Astrocytes are also present in the retina, but they are limited to the nerve fibre layer, the innermost retinal layer. Both Müller cells and astrocytes possess endfoot processes. Müller cell endfeet form the inner limiting membrane of the retina and surround blood vessels at the surface of the retina as well as vessels in deeper retinal layers (figure 1b). Surface blood vessels are also contacted by astrocyte endfeet (figure 1b). Both Müller cells and astrocytes express multiple transmitter receptors and are stimulated when transmitters are released from synapses [6].
Figure 1.
Glial cells of the retina. (a) A drawing by Ramon y Cajal illustrates the two macroglial cells of the retina. The Müller cell, n, a radial glial cell, is the principal retinal glial cell. The Müller cell functions as a type of astrocyte. True astrocytes, o, are restricted to the nerve fibre layer at the inner border of the retina. Layers of the retina include the photoreceptor outer segments, B, the outer nuclear layer, D, the outer plexiform layer, E, the inner nuclear layer, F, the inner plexiform layer, G, the ganglion cell layer, H and the nerve fibre layer, I. From Cajal [7]. (b) A schematic of the retina illustrating the contacts between glial cells and blood vessels. The endfoot processes of both astrocytes (yellow) and Müller cells (green) envelop blood vessels at the inner surface of the retina, adjacent to the vitreous humour. Deeper in the retina, Müller cell endfeet surround capillaries. From EA Newman and KR Biesecker 2015, unpublished. (Online version in colour.)
With processes in the synaptic layers and endfeet terminating on blood vessels, Müller cells are well situated to mediate neurovascular coupling. Release of transmitters from neurons stimulates Müller cells, resulting in cytosolic Ca2+ increases which lead to the release of vasoactive agents onto blood vessels. Müller cell Ca2+ increases also lead to the release of gliotransmitters from processes in the synaptic layers, resulting in the modulation of neuronal activity.
3. ATP release from glial cells inhibits retinal ganglion cells
The release of gliotransmitters from astrocytes modulates the efficacy of synaptic transmission in the brain [1]. Glial release of glutamate, ATP and d-serine leads to either the potentiation or depression of synaptic transmission and to changes in neuronal excitability in brain slice preparations.
In a similar fashion, release of the gliotransmitter ATP from Müller cells modulates the excitability of ganglion cells in the retina. Müller cell modulation of RGCs has been demonstrated in the acutely isolated retina of the rat [8,9]. When Müller cells are stimulated by the focal ejection of the non-hydrolysable ATP analogue ATPγS, neighbouring RGCs hyperpolarize. In cells displaying spontaneous spiking, this hyperpolarization results in a prolonged silencing of the cells (figure 2a).
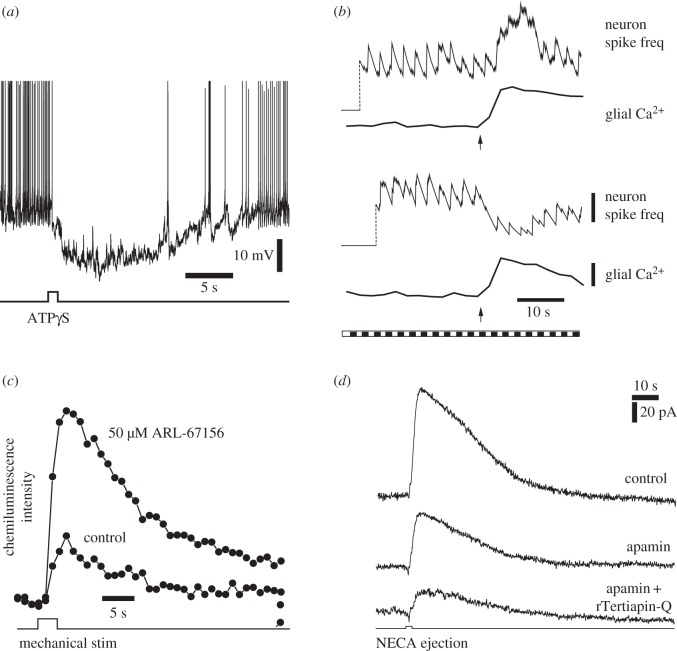
Figure 2.
ATP release from glial cells inhibits retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). (a) An intracellular recording from a RGC that displays spontaneous spiking. Stimulation of glial cells by ATPγS ejection results in prolonged hyperpolarization of the RGC and inhibition of spiking. From Newman [9]. (b) Mechanical stimulation of Müller cells (arrows) evokes Ca2+ increases in the glial cells and modulates light-evoked RGC activity. Müller cell stimulation potentiates neuronal activity in some cells (upper traces) and depresses activity in others (bottom traces). The retina was stimulated with a flickering light (bottom trace). Vertical scale bars: running average of neuron spike frequency, 3 spikes per s; glial Ca2+, 20% Δfluorescence/fluorescence. From Newman & Zahs [8]. (c) Mechanical stimulation of Müller cells evokes ATP release into the inner plexiform layer. Extracellular ATP is monitored by the luciferin-luciferase chemiluminescence assay. Addition of ARL-67156, which blocks the conversion of ATP to adenosine in the extracellular space, increases ATP levels. From Newman [9]. (d) Müller cell inhibition of RGCs is mediated by the opening of SK channels and GIRK channels. Ejection of NECA, an A1 adenosine receptor agonist, onto RGCs evokes an outward current in a voltage-clamped RGC. NECA mimics the activation of A1 receptors by ATP/adenosine released from Müller cells. Addition of the SK channel blocker apamin partially reduces the current while addition of apamin and the GIRK channel blocker rTeriapin-Q reduces the current further. From Clark et al. [10].
Müller cell stimulation can lead to either an increase or a decrease in RGC excitability [8]. Mechanical stimulation of Müller cells results in an increase in cytosolic Ca2+ (figure 2b, glia traces). Stimulation also leads to a modulation of flicker-evoked spiking. In some RGCs, flicker-evoked spiking is enhanced while in other RGCs spiking is depressed (figure 2b, neuron traces). Far more RGCs display depression than excitation in response to Müller cell stimulation. The mechanical stimuli used to initiate glial Ca2+ waves is not a physiological stimulus and could also stimulate neurons directly and alter their firing rate. This is unlikely, however. Identical mechanical stimuli applied to the same retinal location had different effects on neuronal firing, depending on whether the evoked Ca2+ wave reached the cell [8]. In addition, direct mechanical stimulation of a neuron would modulate neuronal activity within milliseconds rather than the several seconds observed.
Müller cell depression of RGC excitability is mediated by release of ATP. Direct release of ATP from Müller cells has been demonstrated using the luciferin-luciferase chemiluminescence assay [9]. A small volume of luciferin-luciferase-containing saline is injected into the inner plexiform (synaptic) layer of the retina while Müller cells are activated by a mechanical stimulus. An increase in chemiluminescence is observed, demonstrating that ATP is released from Müller cells into the inner plexiform layer (figure 2c). If the retina is treated with ARL-67156, a compound that blocks the activity of ecto-ATPases which hydrolyse ATP to ADP and AMP, the chemiluminescence signal is more than tripled (figure 2c). This result is consistent with previous findings that ATP, once released into the extracellular space, is rapidly (200 ms) converted to ADP, AMP and ultimately to adenosine. When, this hydrolysis is blocked, ATP accumulates in the extracellular space. The mechanism by which ATP is released from Müller cells, whether vesicular or through channels, remains to be determined.
Müller cell depression of RGCs is produced by activation of A1 adenosine receptors on the neurons [9,10]. Following release of ATP from Müller cells and its conversion to adenosine by ectoenzymes, activation of A1 receptors hyperpolarizes the RGCs. This hyperpolarization is mimicked by NECA, an A1 agonist. In addition, the glial-evoked hyperpolarization is blocked by the A1 receptor antagonist DPCPX but not by A2 receptor antagonists. Activation of A1 receptors results in an increase in RGC K+ conductance and in cell hyperpolarization. The K+ conductance increase is generated by the opening of G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying K+ (GIRK) channels and small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (SK) channels [10]. The GIRK channel blocker rTertiapin-Q diminishes NECA-evoked currents by 56%, while the SK channel blocker apamin decreases the currents by 42% (figure 2d).
The mechanism mediating Müller cell enhancement of RGC activity in those neurons displaying excitation is not known. The RGCs that display Müller cell-mediated excitation could lack the A1 receptors that mediate inhibition. In these cells, excitation may be mediated by P2X receptors stimulated by ATP before it is hydrolysed to adenosine. Alternately, Müller cells might release glutamate, which would stimulate RGC AMPA or NMDA receptors, or d-serine, which would potentiate NMDA responses [11].
4. Tonic release of ATP from glial cells generates vascular tone
Basal blood flow in the CNS is determined primarily by the tone of arteries and arterioles, defined as the degree of baseline vessel constriction. In the brain, several factors contribute to vessel tone, including autoregulatory mechanisms, which maintain constant blood flow in the face of variations in blood pressure, shear stress on vascular endothelial cells, extrinsic innervation from noradrenergic sympathetic terminals, intrinsic innervation from brainstem nuclei and from local interneurons, and release of vasoactive agents from vascular endothelial cells. However, the mechanisms that determine vascular tone in the CNS, particularly in penetrating arterioles, are not fully understood.
The retina is nourished by two independent vascular supplies [12]. The photoreceptors, which have an extremely high metabolic rate, are fed by the choroidal vasculature which lies directly behind the photoreceptors and the retinal pigment epithelium. The inner two-thirds of the retina, by contrast, is served by the intrinsic retinal vasculature. Blood enters the retinal vasculature from the central retinal artery at the optic disc and branches into primary retinal arterioles which project radially from the disc across the inner surface of the retina.
The mechanisms that control vascular tone in retinal arterioles are largely unexplored. Autonomic innervation is completely absent in the intrinsic retinal vasculature and does not contribute to the generation of vascular tone. Tone must be generated by intrinsic mechanisms, including the release of vasoactive agents from neurons, glial cells and vascular endothelial cells.
We have found that tonic release of ATP from glial cells could be responsible for generating tone in retinal arterioles [13]. Manipulation of endogenous ATP levels results in large changes in vascular tone. When endogenous ATP levels are reduced by addition of the ATP hydrolysing enzyme apyrase, primary arterioles dilate (figure 3a). Conversely, when ATP levels are increased by addition of the ecto-5-nucleotidase inhibitor AOPCP, which blocks the conversion of AMP to adenosine, vessels constrict. Addition of the non-hydrolysable ATP analogue ATPγS also results in rapid and large vasoconstrictions (figure 3b). The delayed dilation observed following ATPγS application is probably owing to activation of purinergic receptors on vascular endothelial cells, which results in nitric oxide (NO) production and vasodilation [14]. Overall, the results indicate that endogenous ATP acts on vascular smooth muscle cells to constrict retinal arterioles and generate vascular tone.
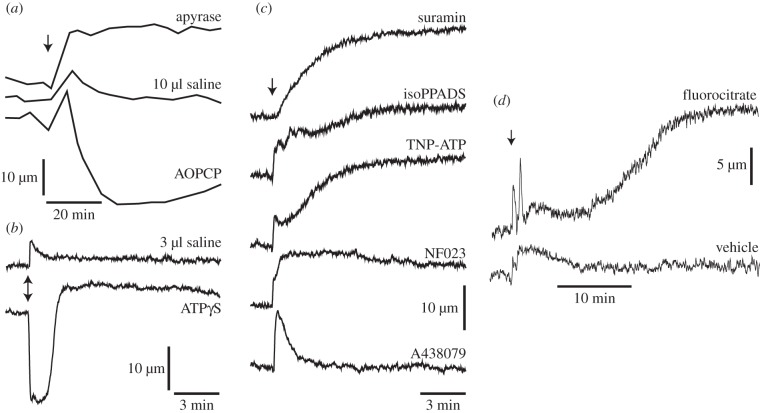
Figure 3.
Tonic release of ATP from glial cells generates tone in retinal vessels. Vascular tone is monitored by measuring the diameter of primary retinal arterioles in vivo. (a) Altering endogenous ATP levels changes vascular tone. Intravitreal injection of apyrase, which hydrolyses ATP and lowers ATP levels, dilates vessels. Injection of AOPCP, which prevents normal ATP hydrolysis and raises ATP levels, constricts vessels. Injection of vehicle (saline) in this and other panels, evokes a transient dilation (an artefact of the injection) but little sustained change in diameter. (b) Injection of the ATP analogue ATPγS onto the retinal surface constricts vessels. The delayed vessel dilation is probably owing to ATPγS stimulation of vascular endothelial cells. (c) ATP acts on P2X purinergic receptors to generate vessel tone. Injection of the non-selective purinergic antagonist suramin, the P2X antagonist isoPPADS, the P2X1, P2X2/3 and P2X3 antagonist TNP-ATP and the selective P2X1 antagonist NF023 all dilate retinal vessels. The P2X7 antagonist A438079 has no sustained effect on vessel tone. (d) Glial cells are a source of the vasoconstricting ATP. Injection of the selective gliotoxin fluorocitrate, which blocks ATP production in glial cells, dilates retinal vessels. All panels from Kur & Newman [13].
Endogenous ATP acts on P2X purinergic receptors to generate vascular tone [13]. Addition of non-selective P2X antagonists, including suramin and isoPPADS, reduces vascular tone, leading to a dilation of retinal arterioles (figure 3c). The specific P2X receptors responsible for generating tone were explored using more selective antagonists. TNP-ATP, a P2X1, P2X2/3 and P2X3 antagonist, dilates vessels as does the selective P2X1 antagonist NF023. However, the P2X7 antagonist A438079 has no effect on vessel tone. The results of these pharmacological studies demonstrate that endogenous ATP is acting, at least in part, on P2X1 receptors to generate vascular tone.
It is likely that one source of the endogenous ATP that generates vascular tone in the retina is glial cells. As discussed above and illustrated in figure 2c, Müller cells release ATP when stimulated by transmitters. In addition, brain astrocytes release ATP tonically. It has been estimated that release of ATP from astrocytes in brain slices results in a steady-state ATP level of 10 µM in the extracellular space [2].
We explored whether glial cells are the source of vasoconstricting ATP in the retina using the selective gliotoxin fluorocitrate [13]. Fluorocitrate is selectively taken up by glial cells in the CNS and blocks the tricarboxylic acid cycle by inhibiting aconitase. Thus, fluorocitrate blocks ATP production in glia. Addition of fluorocitrate dilates retinal arterioles after a delay of approximately 15 min (figure 3d). The magnitude of the dilation is large, similar to that observed following block of purinergic receptors. The results suggest that glial cells are a major source of the ATP that generates tone in retinal arterioles. Fluorocitrate could also be acting on neurons or on vascular cells to reduce vessel tone. This is unlikely, however, as the toxin is believed to act selectively on glial cells and reduces vascular tone in the retina by decreasing stimulation of P2 receptors [13]. The tonic release of ATP from Müller cells could also modulate the excitability of retinal neurons, for instance, inhibiting the firing of RGCs. This is an important topic for future investigation.
5. Glial release of arachidonic acid metabolites mediates neurovascular coupling in the retina
As discovered over a century ago, local increases in neuronal activity in the brain result in focal increases in blood flow, bringing additional oxygen and nutrients to the active neurons [15,16]. This haemodynamic response is termed functional hyperaemia. The signalling mechanisms linking neuronal activity to increased blood flow is named neurovascular coupling. Multiple mechanisms are thought to mediate neurovascular coupling in the brain [3]. Active neurons release NO and PGE2, both vasodilating agents. As discussed above, release of transmitters from active neurons also stimulates astrocytes, leading to increases in cytosolic Ca2+. Stimulation of astrocytes results in the release of vasoactive agents, including PGE2, EETs, 20-HETE and K+, directly onto vessels.
Functional hyperaemia is well developed in the retina. Flickering light evokes large and rapid vasodilations of retinal arterioles and increases in blood flow [17]. We have investigated the mechanisms mediating neurovascular coupling in the retina using the acutely isolated rat retina [18,19]. Neurovascular coupling remains intact in this preparation; when the retina is stimulated by flickering light, arterioles dilate rapidly (figure 4a,b), mimicking the response seen in vivo.
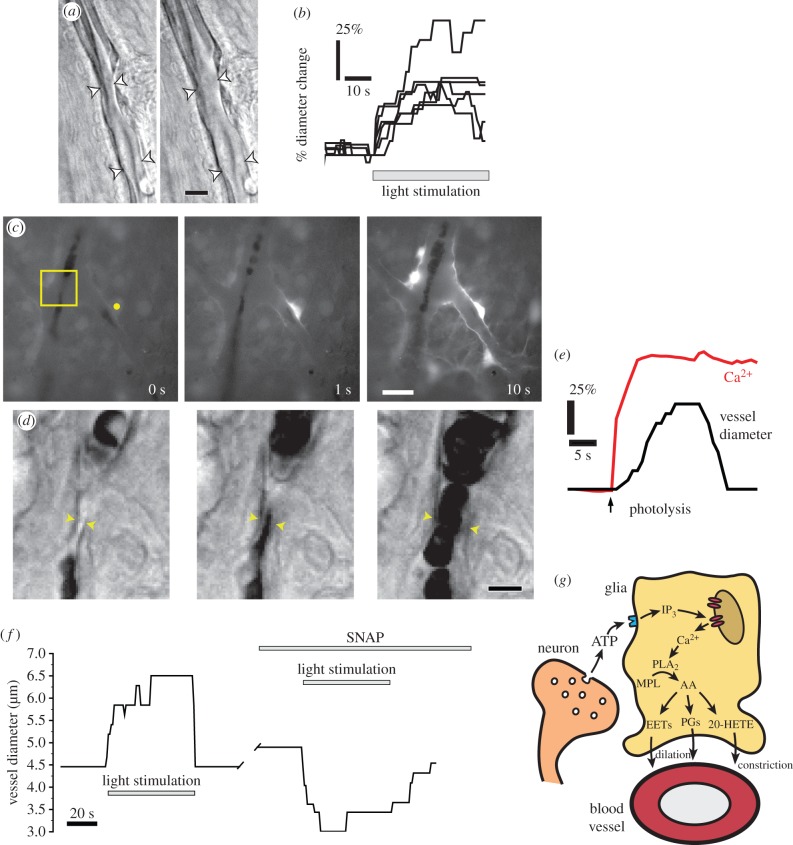
Figure 4.
Glial cell release of vasoactive arachidonic acid metabolites mediates neurovascular coupling in the retina. (a) Flicker stimulation dilates arterioles. Photomicrographs of an arteriole in an acutely isolated retina, before and during stimulation. Scale bar, 10 µm. (b) Dilation of retinal arterioles evoked by flicker stimulation. (c and d) Glial stimulation dilates arterioles. (c) Photolysis of caged Ca2+ (yellow dot) evokes a Ca2+ increase in the stimulated astrocyte and in adjacent glial cells. The boxed area is shown in d. Scale bar, 20 µm. (d) Glial cell stimulation results in arteriole dilation. Scale bar, 10 µm. (e) Analysis of the experiment shown in c and d. Photolysis of caged Ca2+ evokes a glial Ca2+ increase and an arteriole dilation. (f) Nitric oxide blocks light-evoked arteriole dilation, revealing a light-evoked constriction. Addition of the NO donor SNAP transforms a light-evoked dilation to a constriction. (g) Summary of glial-mediated neurovascular coupling in the retina. Synaptic release of ATP from neurons stimulates purinergic receptors on glial cells, leading to the production of IP3 and the release of Ca2+ from internal stores. Ca2+ activates phospholipase A2 (PLA2), which converts membrane phospholipids (MPL) to arachidonic acid (AA) which is subsequently metabolized to the vasodilators prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), and to the vasoconstrictor 20-hydroxy-eicosatetraenoic acid (20-HETE). (a–f) From Metea & Newman [18] and (g) adapted from Newman [20]. (Online version in colour.)
Neurovascular coupling in the retina is largely mediated by glial cells. In experiments on the rat retina, glial cells were selectively stimulated by photolysis of caged Ca2+ or caged inositol trisphosphate (IP3), which were bulk-loaded or injected into individual cells [18]. Uncaging of Ca2+ or IP3 resulted in increases in cytosolic Ca2+ in the stimulated glial cells and in glial cells coupled to them (figure 4c). Stimulation resulted in the dilation of adjacent arterioles (figure 4d,e). Glial-evoked vasodilation occurred independently of neuronal signalling. The response was unaffected when transmitter release from neurons was blocked with tetanus toxin. The results demonstrate that glial cells are able to signal directly to blood vessels, evoking vasodilation.
Light- and glial-evoked vasodilations in the retina are modulated by NO [18]. NO is a potent vasodilator that acts directly to relax vascular smooth muscle cells. Paradoxically, NO also acts to block glial-mediated vasodilation in the retina. When NO levels are raised by addition of the NO donor SNAP, light-evoked vasodilations are reduced, revealing a vasoconstricting response (figure 4f). Conversely, when NO levels are reduced by addition of the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor l-NAME or an NO scavenger, vasoconstrictions are reduced and vasodilations enhanced.
We have conducted a number of pharmacological experiments to elucidate the neurovascular coupling signalling mechanisms mediating glial-evoked vasodilation. As in the brain, metabolites of arachidonic acid mediate vasodilation in the retina. Both flicker- and glial-evoked vasodilations are reduced when the synthesis of PGE2 and EETs are blocked [18,19]. Flicker- and glial-evoked vasoconstrictions are mediated by another arachidonic acid metabolite, 20-HETE [18]. The net vascular response will be determined by the relative balance between vasodilating (PGE2 and EETs) and vasoconstricting (20-HETE) influences. In the healthy retina, vasodilating signalling will dominate and an increase in neuronal activity will result in vessel dilation and increased blood flow. However, when vasodilating EETs signalling is reduced by nitric oxide, which occurs under pathological conditions [21,22], or when PGE2 signalling is inhibited by hyperoxia [19,23], the vasoconstricting effects of 20-HETE will dominate and vessels will constrict in response to neuronal activity [18].
The mechanisms mediating neurovascular coupling in the retina are summarized in figure 4g. Flicker-evoked activation of retinal neurons leads to the release of ATP from synaptic terminals. The released ATP activates purinergic receptors on glial cells, resulting in the production of IP3 and the release of Ca2+ from internal stores. The rise in cytosolic Ca2+ activates phospholipase A2 (PLA2), which converts membrane phospholipids to arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid is further metabolized to PGE2 and EETs, which dilate vessels, and to 20-HETE, which constricts vessels. 20-HETE may also be produced in vascular smooth muscle cells following diffusion of arachidonic acid from the glial cells.
In support of this mechanism of neurovascular coupling, light-evoked vascular responses are blocked when signalling from neurons to glial cells is interrupted [18]. Suramin, a non-selective purinergic antagonist completely blocks light-evoked vasodilation and vasoconstriction. However, suramin does not block glial-evoked vasodilation. The results indicate that glial-mediated neurovascular coupling is the principal mechanism mediating functional hyperaemia in the retina. It should be noted that in the brain, glutamate, rather than ATP, is thought to be the principal transmitter mediating signalling from neurons to astrocytes [1].
The neurovascular coupling mechanism summarized above posits that the release of vasoactive agents from retinal glial cells is Ca2+-dependent. However, the nature of Ca2+ signalling in glial cells remains controversial. Flicker-evoked increases in Ca2+ signalling have been observed in Müller cells in the acutely isolated retina [24]. Stimulation-evoked Ca2+ signalling has also been observed in vivo in the cortex [25–27]. By contrast, other studies have reported a paucity of Ca2+ signalling in astrocytes following sensory stimulation that reliably elicits functional hyperaemia [28,29]. Calcium signals are observed in only a small percentage of astrocytes. When Ca2+ signals do occur, they are too slow to mediate vasodilation. In addition, normal functional hyperaemia is observed in IP3R2 null transgenic mice, where Ca2+ release from internal stores through IP3 type 2 receptors is blocked and most if not all astrocyte Ca2+ signalling is abolished [28–30].
These conflicting findings call into question the Ca2+-dependent, glial-mediated mechanism of neurovascular coupling. The importance of Ca2+-dependent glial cell signalling will only be clarified by additional experimentation. Specifically, we must resolve whether fast, reliable Ca2+ signalling occurs in glial cells in response to sensory stimulation and whether glial Ca2+ signalling is still present in IP3R2 null transgenic mice. The use of next-generation, membrane-tethered genetically encoded Ca2+ indicators will be key to resolving this important question. These Ca2+ indicators may reveal Ca2+ signalling in narrow glia cell processes that are not detectable with classical indicators.
6. Glial-mediated neurovascular coupling is compromised in diabetic retinopathy
Basal blood flow and activity-dependent increases in blood flow are compromised in many CNS pathologies including Alzheimer's disease, hypertension and stroke [31]. In the retina, neurovascular coupling is reduced in diabetic retinopathy. In both type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients, flicker-evoked vasodilation is substantially decreased [32–34]. This reduction in functional hyperaemia occurs in early stages of the disease, before overt signs of retinopathy are observed. The loss of neurovascular coupling may lead to retinal hypoxia and could be a causative factor in the development of retinopathy.
In addition to the loss of neurovascular coupling, many changes in neurons and glial cells are observed in early stages of diabetic retinopathy. There is a loss of neurons in the inner retina as well as a reduction in the electroretinogram, the field potential generated by light-evoked neuronal activity [35–37]. Changes in glial cells are also observed, including the upregulation of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) [21,38] and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) [21,39]. Increased iNOS expression results in raised NO levels in the retina [40].
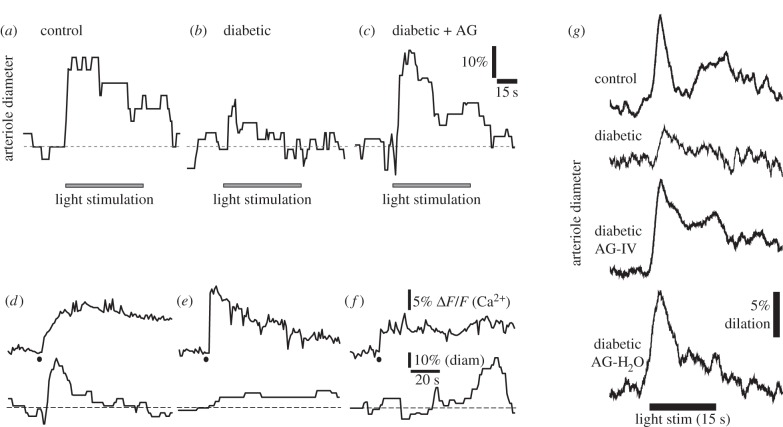
We have used the streptozotocin animal model of type 1 diabetes to investigate the loss of neurovascular coupling in diabetic retinopathy. Flicker-evoked increases in vessel diameter are reduced in diabetic rats (figure 5a,b), mimicking the loss of neurovascular coupling observed in diabetic patients [21]. The loss of neurovascular coupling is due largely to compromised signalling from glial cells to blood vessels. As described above, when glial cells are selectively stimulated by photolysis of caged Ca2+, neighbouring blood vessels dilate (figure 5d). This glial-evoked vessel dilation is substantially reduced in the diabetic retina (figure 5e) [21].
Figure 5.
Glial-mediated neurovascular coupling is compromised in diabetic retinopathy. (a) Flicker stimulation dilates an arteriole in an acutely isolated, age-matched control retina. (b) Vasodilations are reduced in the retinas of animals that have been diabetic for seven months. (c) The iNOS inhibitor aminoguanidine (AG) restores flicker-evoked vasodilation in a diabetic retina. (d) Stimulation of glial cells by photolysis of caged Ca2+ (black dot) evokes a glial Ca2+ increase (upper trace) and arteriole dilation (lower trace) in an acutely isolated aged-matched control retina. (e) The glial-evoked vasodilation, but not the glial Ca2+ increase, is reduced in a diabetic retina. (f) Aminoguanidine restores the glial-evoked vasodilation in a diabetic retina. (a–f) From Mishra & Newman [21]. (g) Aminoguanidine reverses the loss of flicker-evoked vasodilation in vivo. Both acute administration of aminoguanidine by IV injection (AG-IV) and chronic aminoguanidine administration through the drinking water (AG-H2O) reverses the loss of flicker-evoked vasodilation in diabetic animals. From Mishra & Newman [22].
The loss of glial-mediated neurovascular coupling in the diabetic retina may be due to the upregulation of iNOS and the resulting increase of NO levels. As noted above, NO blocks glial-mediated vasodilation (figure 4f). The loss of neurovascular coupling in the diabetic retina could be due to this action of NO. If this were the case, the loss of neurovascular coupling could be reversed by inhibiting iNOS and lowering NO levels. This proved to be the case. When the iNOS inhibitors aminoguanidine or 1400 W are added to the acutely isolated diabetic retina, both light- and glial-evoked vessel dilations are restored to control levels (figure 5c,f) [21]. Aminoguanidine also reverses the loss of neurovascular coupling in vivo. Light-evoked vasodilation is restored to control levels when the iNOS inhibitor is delivered either acutely or chronically (figure 5g) [22]. Aminoguanidine reduces the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) as well as inhibiting iNOS and its effect on the diabetic retina could be due to this action. However, the rapid reversal of the loss of neurovascular coupling, which can occur in 15 min, argues against this interpretation, as AGE levels change much more slowly.
The action of aminoguanidine in restoring normal neurovascular coupling in the diabetic retina may prevent retinal hypoxia and slow the progression of retinopathy. The use of aminoguanidine as a therapeutic agent is problematic, however, as prolonged administration at high doses can cause kidney damage [41]. The harmful systemic effects of aminoguanidine could be prevented if it were administrated topically.
7. Conclusion
We have shown that when stimulated experimentally, Müller cells and astrocytes can modulate neuronal activity and blood flow in the retina. A number of important questions regarding this modulation remain to be addressed.
— Stimulated Müller cells release ATP which can hyperpolarize RGCs. It remains to be determined how this glia to neuron signalling affects information processing in the retina. Do glial cells exert a tonic inhibitory influence on RGCs or does the modulation occur transiently? Under what conditions does modulation occur?
— Release of ATP from glial cells contributes to the generation of tone in the retinal vasculature. Astrocytes in the brain also release ATP and it is likely that this process contributes to the generation of tone in brain vessels. This conjecture remains to be tested.
— The release of vasoactive metabolites of arachidonic acid from glial cells contributes to neurovascular coupling in the retina. However, the importance of this glial signalling pathway, relative to other neurovascular coupling mechanisms in the retina and the brain, remains to be determined. The role of Ca2+ signalling in glial-mediated neurovascular coupling is controversial and must also be resolved.
— The loss of neurovascular coupling that occurs in animal models of diabetic retinopathy can be reversed by the iNOS inhibitor aminoguanidine. It remains to be determined whether iNOS inhibition can be used to develop an effective therapy for slowing the progression of diabetic retinopathy in patients.
The release of transmitters and vasoactive agents from glial cells, both in the brain and in the retina, undoubtedly have additional undescribed effects on neuronal activity and blood flow. Discovering these interactions will be an important goal of future research.
Acknowledgements
I thank Kyle Biesecker, Michael Burian, Tess Kornfield, Joanna Kur and Anja Srienc for their wisdom and advice on the manuscript.
Funding statement
Research in the Newman Lab is funded by NIH grants RO1 EY004077, R21 EY023216 and P30-EY11374, the Research to Prevent Blindness Foundation, the Winston and Maxine Wallin Neuroscience Discovery Fund and the Leducq Foundation.
Conflict of interests
The author has no competing interests.
Reference
- 1.Araque A, Carmignoto G, Haydon PG, Oliet SHR, Robitaille R, Volterra A. 2014. Gliotransmitters travel in time and space. Neuron 81, 728–739. ( 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.02.007) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pascual O, et al. 2005. Astrocytic purinergic signaling coordinates synaptic networks. Science 310, 113–116. ( 10.1126/science.1116916) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Attwell D, Buchan AM, Charpak S, Lauritzen M, MacVicar BA, Newman EA. 2010. Glial and neuronal control of brain blood flow. Nature 468, 232–243. ( 10.1038/nature09613) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Boddeke EWGM, Eggen BJL, Biber KPH. 2013. Cytokine, chemokine, and growth factor receptors and signaling. In Neuroglia (eds Kettenmann H, Ransom BR.), pp. 266–280, 3rd edn New York, NY: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bringmann A, Pannicke T, Grosche J, Francke M, Wiedemann P, Skatchkov SN, Osborne NN, Reichenbach A. 2006. Muller cells in the healthy and diseased retina. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 25, 397–424. ( 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2006.05.003) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Newman EA. 2009. Retinal glia. In Encyclopedia of neuroscience (ed. Squire LR.), pp. 225–232. Oxford, UK: Academic Press. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cajal SRy. 1995. Histology of the nervous system of man and vertebrates, pp. 1–805, 1st edn New York, NY: Oxford University Press. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Newman EA, Zahs KR. 1998. Modulation of neuronal activity by glial cells in the retina. J. Neurosci. 18, 4022–4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Newman EA. 2003. Glial cell inhibition of neurons by release of ATP. J. Neurosci. 23, 1659–1666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Clark BD, Kurth-Nelson ZL, Newman EA. 2009. Adenosine-evoked hyperpolarization of retinal ganglion cells is mediated by G-protein-coupled inwardly rectifying K+ and small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel activation. J. Neurosci. 29, 11 237–11 245. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2836-09.2009) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Stevens ER, Esguerra M, Kim PM, Newman EA, Snyder SH, Zahs KR, Miller RF. 2003. d-serine and serine racemase are present in the vertebrate retina and contribute to the physiological activation of NMDA receptors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 100, 6789–6794. ( 10.1073/pnas.1237052100) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kur J, Newman EA, Chan-Ling T. 2012. Cellular and physiological mechanisms underlying blood flow regulation in the retina and choroid in health and disease. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 31, 377–406. ( 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2012.04.004) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kur J, Newman EA. 2014. Purinergic control of vascular tone in the retina. J. Physiol. 592, 491–504. ( 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.267294) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Burnstock G. 2009. Purinergic regulation of vascular tone and remodelling. Auton. Autacoid Pharmacol. 29, 63–72. ( 10.1111/j.1474-8673.2009.00435.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mosso A. 1880. Sulla circolazione del sangue nel cervello dell'uomo. R. Accad. Lincei 5, 237–358. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Roy CS, Sherrington CS. 1890. On the regulation of the blood-supply of the brain. J. Physiol. 11, 85–108. ( 10.1113/jphysiol.1890.sp000321) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pournaras CJ, Rungger-Brandle E, Riva CE, Hardarson SH, Stefansson E. 2008. Regulation of retinal blood flow in health and disease. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 27, 284–330. ( 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2008.02.002) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Metea MR, Newman EA. 2006. Glial cells dilate and constrict blood vessels: a mechanism of neurovascular coupling. J. Neurosci. 26, 2862–2870. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4048-05.2006) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mishra A, Hamid A, Newman EA. 2011. Oxygen modulation of neurovascular coupling in the retina. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 17 827–17 831. ( 10.1073/pnas.1110533108) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Newman EA. 2013. Functional hyperemia and mechanisms of neurovascular coupling in the retinal vasculature. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 33, 1685–1695. ( 10.1038/jcbfm.2013.145) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mishra A, Newman EA. 2010. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase reverses the loss of functional hyperemia in diabetic retinopathy. Glia 58, 1996–2004. ( 10.1002/glia.21068) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mishra A, Newman EA. 2012. Aminoguanidine reverses the loss of functional hyperemia in a rat model of diabetic retinopathy. Front. Neuroenerg. 3, 10 ( 10.3389/fnene.2011.00010) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gordon GRJ, Choi HB, Rungta RL, Ellis-Davies GCR, MacVicar BA. 2008. Brain metabolism dictates the polarity of astrocyte control over arterioles. Nature 456, 745–749. ( 10.1038/nature07525) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Newman EA. 2005. Calcium increases in retinal glial cells evoked by light-induced neuronal activity. J. Neurosci. 25, 5502–5510. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1354-05.2005) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wang X, Lou N, Xu Q, Tian GF, Peng WG, Han X, Kang J, Takano T, Nedergaard M. 2006. Astrocytic Ca2+ signaling evoked by sensory stimulation in vivo. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 816–823. ( 10.1038/nn1703) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Winship IR, Plaa N, Murphy TH. 2007. Rapid astrocyte calcium signals correlate with neuronal activity and onset of the hemodynamic response in vivo. J. Neurosci. 27, 6268–6272. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4801-06.2007) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lind BL, Brazhe AR, Jessen SB, Tan FCC, Lauritzen MJ. 2013. Rapid stimulus-evoked astrocyte Ca2+ elevations and hemodynamic responses in mouse somatosensory cortex in vivo. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 110, E4678–E4687. ( 10.1073/pnas.1310065110) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nizar K, et al. 2013. In vivo stimulus-induced vasodilation occurs without IP3 receptor activation and may precede astrocytic calcium increase. J. Neurosci. 33, 8411–8422. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3285-12.2013) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bonder DE, McCarthy KD. 2014. Astrocytic Gq-GPCR-linked IP3R-dependent Ca2+ signaling does not mediate neurovascular coupling in mouse visual cortex in vivo. J. Neurosci. 34, 13 139–13 150. ( 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2591-14.2014) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Takata N, Nagai T, Ozawa K, Oe Y, Mikoshiba K, Hirase H. 2013. Cerebral blood flow modulation by basal forebrain or whisker stimulation can occur independently of large cytosolic Ca2+ signaling in astrocytes. PLoS ONE 8, e66525 ( 10.1371/journal.pone.0066525) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Girouard H, Iadecola C. 2006. Neurovascular coupling in the normal brain and in hypertension, stroke, and Alzheimer disease. J. Appl. Physiol. 100, 328–335. ( 10.1152/japplphysiol.00966.2005) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Garhofer G, Zawinka C, Resch H, Kothy P, Schmetterer L, Dorner GT. 2004. Reduced response of retinal vessel diameters to flicker stimulation in patients with diabetes. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 88, 887–891. ( 10.1136/bjo.2003.033548) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mandecka A, Dawczynski J, Blum M, Muller N, Kloos C, Wolf G, Vilser W, Hoyer H, Muller UA. 2007. Influence of flickering light on the retinal vessels in diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 30, 3048–3052. ( 10.2337/dc07-0927) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pemp B, Garhofer G, Weigert G, Karl K, Resch H, Wolzt M, Schmetterer L. 2009. Reduced retinal vessel response to flicker stimulation but not to exogenous nitric oxide in type 1 diabetes. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 50, 4029–4032. ( 10.1167/iovs.08-3260) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Barber AJ, Lieth E, Khin SA, Antonetti DA, Buchanan AG, Gardner TW. 1998. Neural apoptosis in the retina during experimental and human diabetes. Early onset and effect of insulin. J. Clin. Invest. 102, 783–791. ( 10.1172/JCI2425) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Harrison WW, Bearse MA, Jr, Ng JS, Jewell NP, Barez S, Burger D, Schneck ME, Adams AJ. 2011. Multifocal electroretinograms predict onset of diabetic retinopathy in adult patients with diabetes. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 52, 772–777. ( 10.1167/iovs.10-5931) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Luu CD, Szental JA, Lee SY, Lavanya R, Wong TY. 2010. Correlation between retinal oscillatory potentials and retinal vascular caliber in type 2 diabetes. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 51, 482–486. ( 10.1167/iovs.09-4069) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mizutani M, Kern TS, Lorenzi M. 1996. Accelerated death of retinal microvascular cells in human and experimental diabetic retinopathy. J. Clin. Invest. 97, 2883–2890. ( 10.1172/JCI118746) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Du Y, Smith MA, Miller CM, Kern TS. 2002. Diabetes-induced nitrative stress in the retina, and correction by aminoguanidine. J. Neurochem. 80, 771–779. ( 10.1046/j.0022-3042.2001.00737.x) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kowluru RA, Engerman RL, Kern TS. 2000. Abnormalities of retinal metabolism in diabetes or experimental galactosemia VIII. Prevention by aminoguanidine. Curr. Eye Res. 21, 814–819. ( 10.1076/ceyr.21.4.814.5545) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bolton WK, et al. 2004. Randomized trial of an inhibitor of formation of advanced glycation end products in diabetic nephropathy. Am. J. Nephrol. 24, 32–40. ( 10.1159/000075627) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]