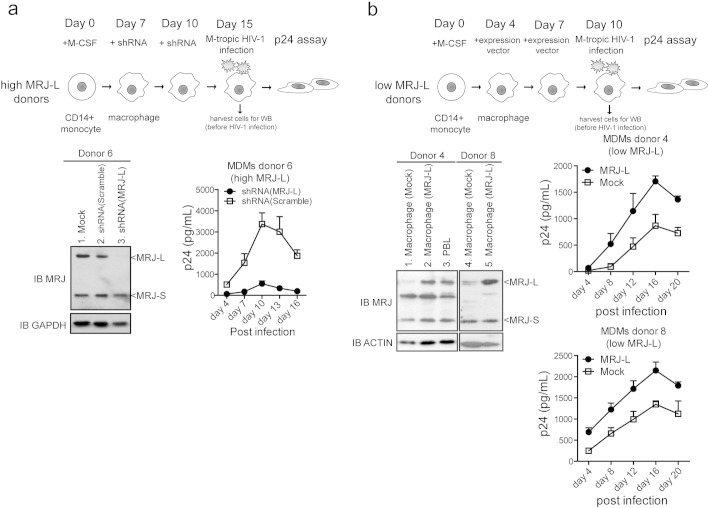
Fig. 4.
Expression of MRJ-L contributes to HIV-1 viral production. (a) (upper panel) Schematic diagram describing the experimental strategy for lentiviral shRNA depletion of MRJ-L in macrophages derived from monocytes of high MRJ-L healthy donors. The transduction efficiency was about 50–70% as evidenced by a GFP-expressing vector control (Supplementary Fig. 1). (Lower left) Knock down of endogenous MRJ-L in monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs) from a healthy donor (donor 6) examined by western blotting. Cells were harvested at day 8 after the shRNA treatment. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (Lower right) Virus output in MDMs (donor 6) treated with MRJ-L-shRNA measured by p24 ELISA at days 4, 7, 10, 13, and 16 post-HIV-1 (M-tropic) infection. Data shown represent mean ± SD from triplicate assays. (b) (upper panel) Schematic diagram describing the experimental strategy for lentiviral overexpression of MRJ-L in macrophages derived from monocytes of low MRJ-L healthy donors. (Lower left) Expression profile of MRJ-L by western blot. Cells were harvested at day 6 after vector transduction. (Lower right) Virus output in MDMs (donor 4 and donor 8) overexpressing MRJ-L by p24 ELISA at days 4, 8, 12, 16, and 20 post-HIV-1 (M-tropic) infection.