Abstract
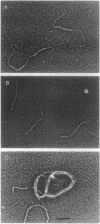
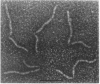
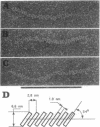
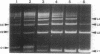
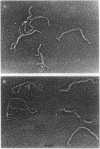
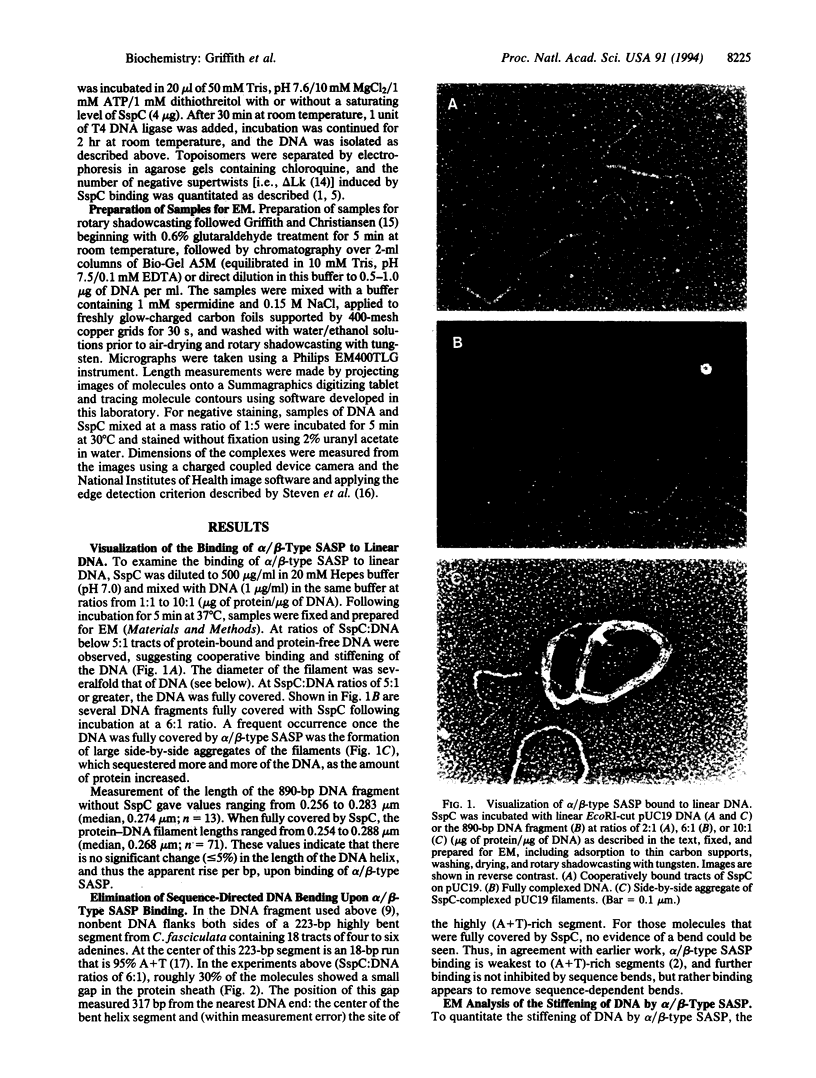
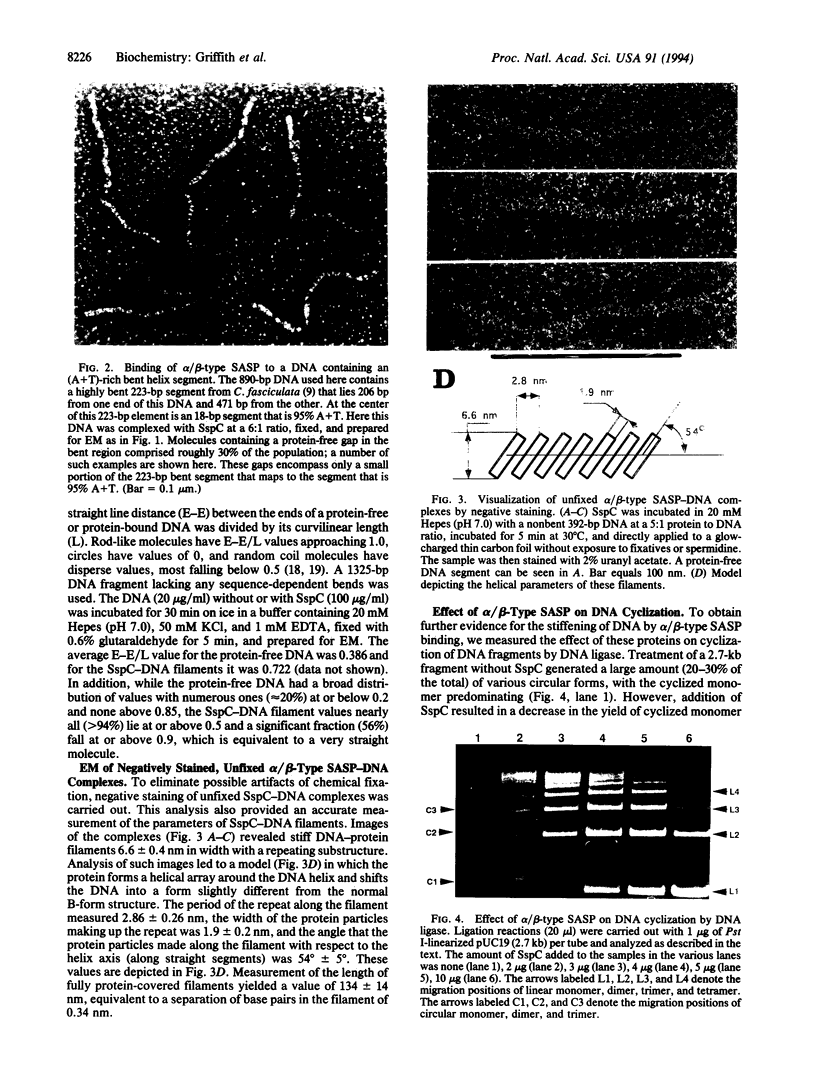
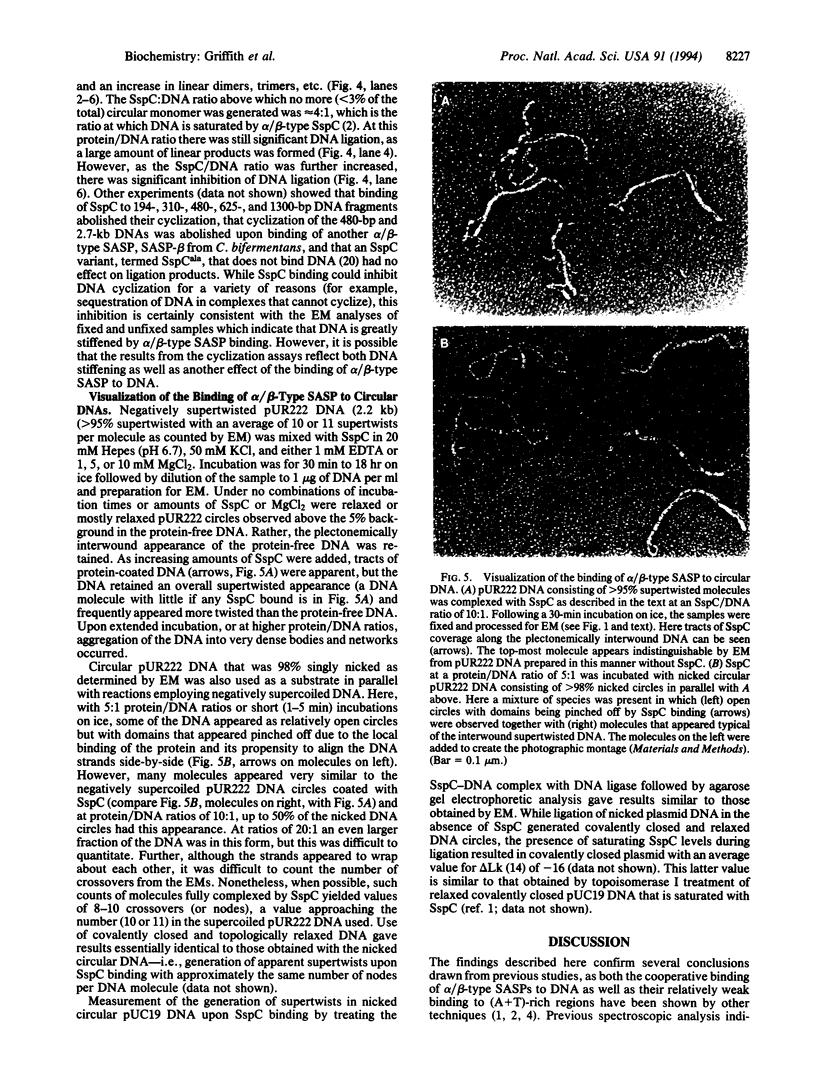
DNA within spores of Bacillus subtilis is complexed with a group of alpha/beta-type small acid-soluble spore proteins (alpha/beta-type SASPs), which have almost identical primary sequences and DNA binding properties. Here electron microscopic and cyclization studies were carried out on alpha/beta-type SASP-DNA complexes. When an alpha/beta-type SASP was incubated with linear DNA, the protein bound cooperatively, forming a helical coating 6.6 +/- 0.4 nm wide with a 2.9 +/- 0.3 nm periodicity. alpha/beta-Type SASP binding to an 890-bp DNA was weakest at an (A+T)-rich region that was highly bent, but binding eliminated the bending. alpha/beta-Type SASP binding did not alter the rise per bp in DNA but greatly increased the DNA stiffness as measured by both electron microscopic and cyclization assays. Addition of alpha/beta-type SASPs to negatively supertwisted DNA led to protein binding without significant alteration of the plectonemically interwound appearance of the DNA. Addition of alpha/beta-type SASPs to relaxed or nicked circular DNA led to molecules that by electron microscopy appeared similar to supertwisted DNA. The introduction of negative supertwists in nicked circular DNA by alpha/beta-type SASPs was confirmed by ligation of these molecules followed by topoisomer analyses using agarose gel electrophoresis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cabrera-Martinez R. M., Mason J. M., Setlow B., Waites W. M., Setlow P. Purification and amino acid sequence of two small, acid-soluble proteins from Clostridium bifermentans spores. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Oct 1;52(1-2):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charney E., Chen H. H., Rau D. C. The flexibility of A-form DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1991 Oct;9(2):353–362. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1991.10507917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrysogelos S., Register J. C., 3rd, Griffith J. The structure of recA protein-DNA filaments. 2 recA protein monomers unwind 17 base pairs of DNA by 11.5 degrees/base pair in the presence of adenosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate). J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12624–12631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield L., Simpson L., Kaplan D. Conversion of closed circular DNA molecules to single-nicked molecules by digestion with DNAase I in the presence of ethidium bromide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 15;407(3):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D., Christiansen G. Electron microscope visualization of chromatin and other DNA-protein complexes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:19–35. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges-Garcia Y., Hagerman P. J., Pettijohn D. E. DNA ring closure mediated by protein HU. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14621–14623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S., Sundaralingam M. Effect of crystal packing environment on conformation of the DNA duplex. Molecular structure of the A-DNA octamer d(G-T-G-T-A-C-A-C) in two crystal forms. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12780–12784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joanicot M., Revet B. DNA conformational studies from electron microscopy. I. Excluded volume effect and structure dimensionality. Biopolymers. 1987 Feb;26(2):315–326. doi: 10.1002/bip.360260211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laundon C. H., Griffith J. D. Cationic metals promote sequence-directed DNA bending. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 30;26(13):3759–3762. doi: 10.1021/bi00387a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr S. C., Sokolov N. V., He C. M., Setlow P. Binding of small acid-soluble spore proteins from Bacillus subtilis changes the conformation of DNA from B to A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):77–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson W. L., Setlow B., Setlow P. Binding of DNA in vitro by a small, acid-soluble spore protein from Bacillus subtilis and the effect of this binding on DNA topology. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6900–6906. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6900-6906.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson W. L., Setlow B., Setlow P. Ultraviolet irradiation of DNA complexed with alpha/beta-type small, acid-soluble proteins from spores of Bacillus or Clostridium species makes spore photoproduct but not thymine dimers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8288–8292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson W. L., Setlow P. Dramatic increase in negative superhelicity of plasmid DNA in the forespore compartment of sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):7–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.7-14.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revet B., Malinge J. M., Delain E., Le Bret M., Leng M. Electron microscopic measurement of chain flexibility of poly(dG-dC).poly(dG-dC) modified by cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II). Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8349–8362. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow B., Sun D., Setlow P. Interaction between DNA and alpha/beta-type small, acid-soluble spore proteins: a new class of DNA-binding protein. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2312–2322. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2312-2322.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakked Z., Guerstein-Guzikevich G., Eisenstein M., Frolow F., Rabinovich D. The conformation of the DNA double helix in the crystal is dependent on its environment. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):456–460. doi: 10.1038/342456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Langowski J., Baldwin R. L. DNA flexibility studied by covalent closure of short fragments into circles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4833–4837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stasiak A., Di Capua E., Koller T. Elongation of duplex DNA by recA protein. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):557–564. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steven A. C., Trus B. L., Maizel J. V., Unser M., Parry D. A., Wall J. S., Hainfeld J. F., Studier F. W. Molecular substructure of a viral receptor-recognition protein. The gp17 tail-fiber of bacteriophage T7. J Mol Biol. 1988 Mar 20;200(2):351–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90246-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. J., Bloomfield V. A. Chain flexibility and hydrodynamics of the B and Z forms of poly(dG-dC).poly(dG-dC). Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1919–1930. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thresher R. J., Griffith J. D. Intercalators promote the binding of RecA protein to double-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5056–5060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovar-Rojo F., Setlow P. Effects of mutant small, acid-soluble spore proteins from Bacillus subtilis on DNA in vivo and in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4827–4835. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4827-4835.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. H., Howard M. T., Griffith J. D. Phased adenine tracts in double-stranded RNA do not induce sequence-directed bending. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 4;30(22):5443–5449. doi: 10.1021/bi00236a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]