Figure 3.
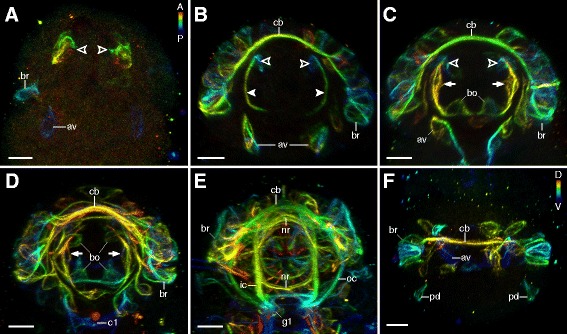
Details of neural development in the head region of Hypsibius dujardini. Maximum CLSM projections of embryos labeled for acetylated α-tubulin and depth-coded along the anteroposterior (in (A-E); orientation of depth-coding in (A)) or dorsoventral axis (in (F)). Dorsal is up in (A-E); anterior is up in (F). Hollow arrowheads indicate the first neurons of the stomodeal nervous system. Solid arrowheads demarcate stomodeal axons. Arrows point to neurons of the first stomodeal commissure. (A) Early-stage embryo showing the first three groups of neural cells. (B-E) Series of subsequent embryonic stages. Note that the first stomodeal neurons are posterior to the first brain commissure (=future central brain neuropil) but project axons anteriorly (in (B)). The ventral pair of buccal sensory organs arises before the dorsal pair (in (C), (D)). Also note that the neurons of the first stomodeal commissure are anterior to the brain and central brain neuropil (in (C)). (E) Late-stage embryo showing a complete circumbuccal nerve ring. (F) Dorsal view of the brain in an embryo of the same developmental stage as in (B). Notice the two pairs of posterodorsal cells (extracerebral neurons sensu ref. [23]) lying outside the anlage of the brain. Abbreviations: A, anterior; av, anteroventral cells; bo, buccal sensory organs; br, brain cells; c1, central commissure of the first trunk ganglion; cb, developing central brain neuropil (arising from a single commissure); D, dorsal; g1, first trunk ganglion anlage; ic, inner connective; nr, circumbuccal nerve ring; oc, outer connective; P, posterior; pd, posterodorsal cells; V, ventral. Scale bars: (A-F), 5 μm.
