Abstract
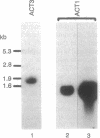
Actin filaments provide the internal scaffold of eukaryotic cells; they are involved in maintenance of cell shape, cytokinesis, organelle movement, and cell motility. The major component of these filaments, actin, is one of the most well-conserved eukaryotic proteins. Recently genes more distantly related to the conventional actins were cloned from several organisms. In the budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, one conventional actin gene, ACT1 (coding for the filament actin), and a so-called actin-like gene, ACT2 (of unknown function), have so far been identified. We report here the discovery of a third member of the actin gene family from this organism, which we named ACT3. The latter gene is essential for viability and codes for a putative polypeptide, Act3, of 489 amino acids (M(r) = 54,831). The deduced amino acid sequence of Act3 is less related to conventional actins than is the deduced amino acid sequence of Act2, mainly because of three unique hydrophilic [corrected] segments. These segments are found inserted into a part of the sequence corresponding to a surface loop of the known three-dimensional structure of the actin molecule. According to sequence comparison, the basal core structure of conventional actin may well be conserved in Act3. Our findings demonstrate that, unexpectedly, there exist three members of the diverse actin protein family in budding yeast that obviously provide different essential functions for survival.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amatruda J. F., Cooper J. A. Purification, characterization, and immunofluorescence localization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae capping protein. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(5):1067–1076. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.5.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3018–3025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bork P., Sander C., Valencia A. An ATPase domain common to prokaryotic cell cycle proteins, sugar kinases, actin, and hsp70 heat shock proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7290–7294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. W., Meyer D. I. Centractin is an actin homologue associated with the centrosome. Nature. 1992 Sep 17;359(6392):246–250. doi: 10.1038/359246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. H., Elzinga M. The primary structure of actin from rabbit skeletal muscle. Completion and analysis of the amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):5915–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. The major promoter element of rRNA transcription in yeast lies 2 kb upstream. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90473-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaherty K. M., McKay D. B., Kabsch W., Holmes K. C. Similarity of the three-dimensional structures of actin and the ATPase fragment of a 70-kDa heat shock cognate protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):5041–5045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.5041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Seidel R. Molecular cloning of the actin gene from yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):1043–1059. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Sures I. Structure of a split yeast gene: complete nucleotide sequence of the actin gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2546–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman I. M. Actin isoforms. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;5(1):48–55. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(05)80007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. C., Popp D., Gebhard W., Kabsch W. Atomic model of the actin filament. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):44–49. doi: 10.1038/347044a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Mannherz H. G., Suck D., Pai E. F., Holmes K. C. Atomic structure of the actin:DNase I complex. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):37–44. doi: 10.1038/347037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Vandekerckhove J. Structure and function of actin. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1992;21:49–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.21.060192.000405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees-Miller J. P., Helfman D. M., Schroer T. A. A vertebrate actin-related protein is a component of a multisubunit complex involved in microtubule-based vesicle motility. Nature. 1992 Sep 17;359(6392):244–246. doi: 10.1038/359244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees-Miller J. P., Henry G., Helfman D. M. Identification of act2, an essential gene in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe that encodes a protein related to actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):80–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin P. J., Gooch J. T., Mannherz H. G., Weeds A. G. Structure of gelsolin segment 1-actin complex and the mechanism of filament severing. Nature. 1993 Aug 19;364(6439):685–692. doi: 10.1038/364685a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A., Tatchell K. The structure of transposable yeast mating type loci. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):753–764. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Cooper J. A. Actin and actin-binding proteins. A critical evaluation of mechanisms and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:987–1035. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Holden H. M., Whittaker M., Yohn C. B., Lorenz M., Holmes K. C., Milligan R. A. Structure of the actin-myosin complex and its implications for muscle contraction. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):58–65. doi: 10.1126/science.8316858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Reizer A., Saier M. H., Jr, Bork P., Sander C. Exopolyphosphate phosphatase and guanosine pentaphosphate phosphatase belong to the sugar kinase/actin/hsp 70 superfamily. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jul;18(7):247–248. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90172-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutt C. E., Myslik J. C., Rozycki M. D., Goonesekere N. C., Lindberg U. The structure of crystalline profilin-beta-actin. Nature. 1993 Oct 28;365(6449):810–816. doi: 10.1038/365810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwob E., Martin R. P. New yeast actin-like gene required late in the cell cycle. Nature. 1992 Jan 9;355(6356):179–182. doi: 10.1038/355179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Li W. H. The codon Adaptation Index--a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1281–1295. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Actin amino-acid sequences. Comparison of actins from calf thymus, bovine brain, and SV40-transformed mouse 3T3 cells with rabbit skeletal muscle actin. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct 16;90(3):451–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12624.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A., Maciver S. F-actin capping proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;5(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(05)80009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]