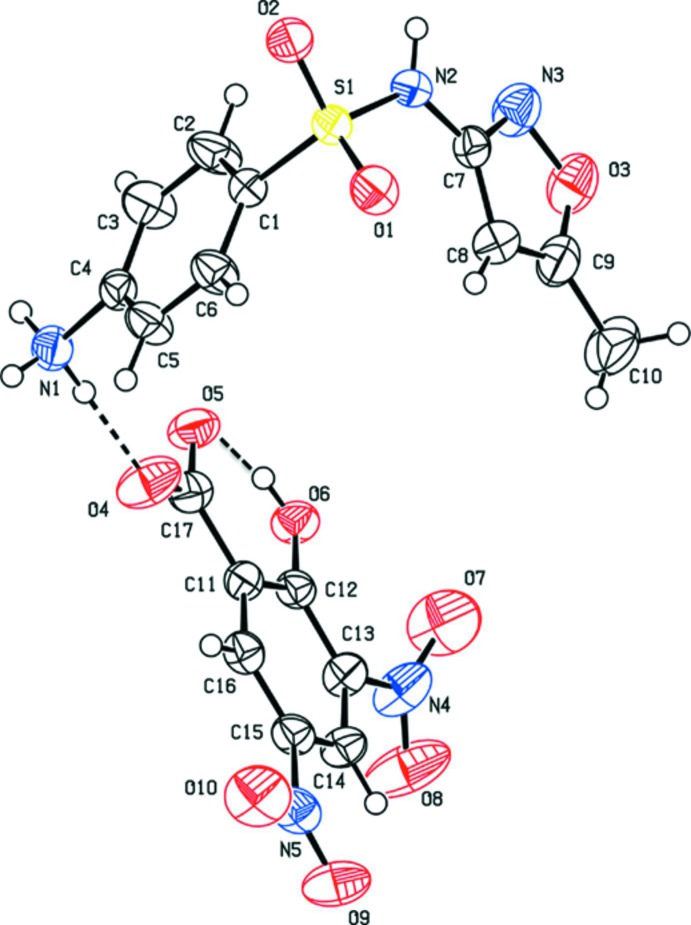
The title molecular salt, consists of a sulfamethoxazolium (SMZ) cation and a 3,5-dinitrosalicylate (DNS) anion, which are linked by an N—H⋯O hydrogen bond. In the crystal, the cations and anions are linked via N—H⋯O, N—H⋯N and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional framework.
Keywords: crystal structure; sulfamethoxazolium; 3,5-dinitrosalicylate; molecular salt; hydrogen bonding.
Abstract
The title molecular salt, C10H12N3O3S+·C7H3N2O7 −, protonation occurs at the amino N atom attached to the benzene ring of sulfamethoxazole. In the anion, there is an intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bond and the cation is linked to the anion by an N—H⋯O hydrogen bond. In the extended structure, the cations and anions are linked via N—H⋯O, N—H⋯N and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional framework.
Chemical context
Sulfamethoxazole, {4-[(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)aminosulfonyl]aniline} (SMZ) is a well-known antibacterial and antifungal sulfa drug (Ma et al., 2007 ▸; Hida et al., 2005 ▸). This drug prevents the formation of dihydrofolic acid, a compound that bacteria must be able to make in order to endure. The structural resemblance of p-amino benzoic acid to the sulfanilamide group enables sulfanilamide block folic acid synthesis in bacteria (Bock et al.,1974 ▸). SMZ is also known to be effective against gram positive and gram negative bacteria and some protozoans. In clinical practice, SMZ is used as a combinatorial drug along with Trimethoprim (TMP) to treat a variety of bacterial infections. In the last three and half decades, multiple crystalline forms of SMZ (Bettinetti et al., 1982 ▸; Maury et al., 1985 ▸; Price et al., 2005 ▸), metal complexes (Marques et al., 2006 ▸; Nakai et al., 1984 ▸) and salt forms (Nakai et al., 1984 ▸; Subashini et al., 2007 ▸) have been reported. We report herein on the crystal structure and supramolecular packing pattern of the title salt.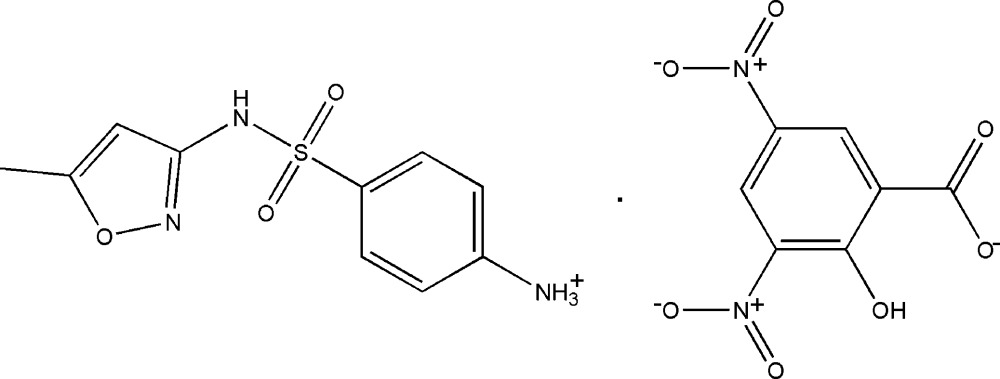
Structural commentary
The asymmetric unit of the title salt (SMZDNS), consists of a sulfamethoxazolium cation and a 3,5-dinitrosalicylate anion (Fig. 1 ▸). The SMZ cation is L-shaped with the dihedral angle between the oxazole and anilinium rings being 81.86 (10)°. The geometry around the sulfur atom is slightly distorted tetrahedral, which is evident from the O1—S1—O2 angle of 120.44 (8)°. Protonation occurs at the amino atom N1 of the benzene moiety of SMZ. In the cation there is an intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bond with an S(6) ring motif (Fig. 1 ▸ and Table 1 ▸). The cation is linked to the anion by an N—H⋯O hydrogen bond (Fig. 1 ▸ and Table 1 ▸), and the dihedral angle between the benzene rings of the cation and anion is 78.51 (8)°.
Figure 1.
A view of the molecular structure of the title molecular salt, showing the atom labelling. The displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. The hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 ▸ for details).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O6H6AO5 | 0.82 | 1.68 | 2.4296(19) | 151 |
| N2H2AO5 | 0.86 | 2.12 | 2.7852(18) | 134 |
| N1H1AO4i | 0.89 | 1.77 | 2.661(2) | 177 |
| N1H1BN3i | 0.89 | 2.24 | 3.041(2) | 150 |
| N1H1CO6ii | 0.89 | 2.21 | 3.064(2) | 160 |
| C5H5O6ii | 0.93 | 2.60 | 3.293(2) | 132 |
| C6H6O8iii | 0.93 | 2.60 | 3.176(2) | 121 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 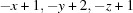 ; (ii)
; (ii) 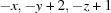 ; (iii)
; (iii) 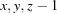 .
.
Supramolecular features
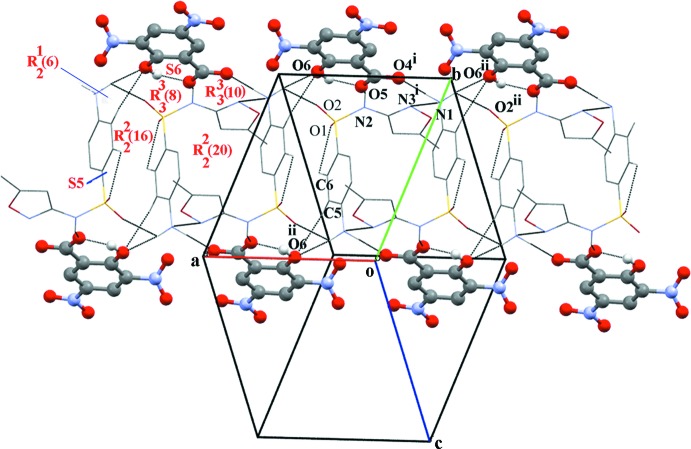
In the crystal of the title salt, there are various hydrogen bonds present linking the anions and cations and forming a three-dimensional network (Figs. 2 ▸ and 3 ▸, and Table 1 ▸). The ammonium ion of the cation generates a C(3) chain and two  (6) and
(6) and  (10) ring motifs (Bernstein et al., 1995 ▸). The primary interaction between the cation and anion happens through an N—H⋯O hydrogen bond and it forms a chain of C(3) graph set. The
(10) ring motifs (Bernstein et al., 1995 ▸). The primary interaction between the cation and anion happens through an N—H⋯O hydrogen bond and it forms a chain of C(3) graph set. The 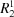 (6) motif is formed via N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds that link the ammonium N1 phenyl C5 group of SMZ and the hydroxy O6 group of the anion. The
(6) motif is formed via N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds that link the ammonium N1 phenyl C5 group of SMZ and the hydroxy O6 group of the anion. The 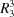 (10) ring motif is a result of the linking of two symmetry-related cations and one anion via a pair of N—H⋯O and N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds. This motif is formed by the interaction of symmetry-related imino N2, oxazole N3, ammonium N1 atoms of the cation and the carboxylate (O4 and O5) group of the anion. The
(10) ring motif is a result of the linking of two symmetry-related cations and one anion via a pair of N—H⋯O and N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds. This motif is formed by the interaction of symmetry-related imino N2, oxazole N3, ammonium N1 atoms of the cation and the carboxylate (O4 and O5) group of the anion. The 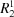 (6) and
(6) and 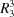 (10) motifs are linked by another ring motif with an
(10) motifs are linked by another ring motif with an 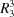 (8) graph set. This motif is formed by linking two symmetry-related cations with an anion via a pair of bifurcated N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The amalgamation of the above ring motifs leads to the formation of supramolecular sheets along the a axis (Fig. 2 ▸). The sheets thus formed are linked to adjacent ones through
(8) graph set. This motif is formed by linking two symmetry-related cations with an anion via a pair of bifurcated N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The amalgamation of the above ring motifs leads to the formation of supramolecular sheets along the a axis (Fig. 2 ▸). The sheets thus formed are linked to adjacent ones through 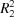 (16) and
(16) and 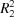 (20) motifs. The
(20) motifs. The 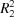 (16) motif is formed by interaction of ammonium atom N1 and atom O2 of the sulfate group of an inversion-related SMZ ion in an adjacent sheet via a pair of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The other motif, an
(16) motif is formed by interaction of ammonium atom N1 and atom O2 of the sulfate group of an inversion-related SMZ ion in an adjacent sheet via a pair of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The other motif, an 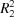 (20) ring, is formed by the linkage of two inversion-related cations along the b axis. Finally, through these arrangements a three-dimensional hydrogen-bonded architecture is formed.
(20) ring, is formed by the linkage of two inversion-related cations along the b axis. Finally, through these arrangements a three-dimensional hydrogen-bonded architecture is formed.
Figure 2.
A view of the graph set motifs formed in the crystal of the title salt, via N—H⋯O, N—H⋯N and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (dashed lines; see Table 1 ▸ for details). The cations are drawn in wire mode and the anions in ball-and-stick mode.
Figure 3.
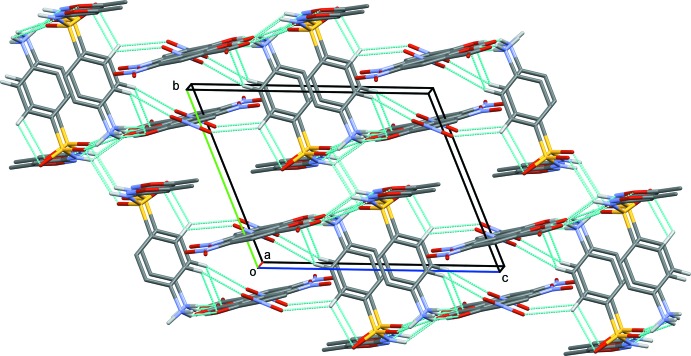
A view along the a axis of the crystal packing of the title salt. The hydrogen bonds are drawn as dashed lines (see Table 1 ▸ for details). H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (Version 5.36; Groom & Allen, 2014 ▸) for 4-[(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)aminosulfonyl]aniline revealed the presence of only two structures of the protonated form. These include, catena-[bis(sulfamethoxazolium)(μ2-chlorido)trichloridocadmium(II) monohydrate] [RISZAV; Subashini et al., 2008 ▸] and 4-[(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)aminosulfonyl]anilinium chloride (also known as sulfamethoxazole chloride; SIMJEE; Subashini et al., 2007 ▸). The dihedral angles between the oxazole ring and anilinium ring is found to be ca 88° in RISZAV, similar to the value of 81.86 (10)° in the title salt, and ca 58° in SIMJEE.
Synthesis and crystallization
20 ml of a hot ethanolic solution of sulfamethoxazole (63 mg) and 3.5 dinitrosalicylic acid (57 mg) were mixed and warmed at 323 K for 30 min over a water bath. The mixture was then allowed to cool slowly at room temperature. Three weeks later, light-yellow prismatic crystals were obtained.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. All H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model: O—H = 0.82 Å, N—H = 0.86–0.89 Å, and C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C,O,N) for methyl, hydroxy and ammonium H atoms and 1.2U eq(C,N) for aromatic and other H atoms.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C10H12N3O3S+C7H3N2O7 |
| M r | 481.41 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P
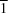
|
| Temperature (K) | 296 |
| a, b, c () | 8.5551(1), 10.5000(2), 12.7576(3) |
| , , () | 106.463(1), 100.913(1), 108.272(1) |
| V (3) | 993.72(3) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo K |
| (mm1) | 0.23 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.20 0.20 0.16 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.955, 0.964 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2(I)] reflections | 24261, 6718, 4911 |
| R int | 0.030 |
| (sin /)max (1) | 0.758 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.048, 0.139, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 6718 |
| No. of parameters | 301 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| max, min (e 3) | 0.40, 0.40 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008701/su5130sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008701/su5130Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008701/su5130Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1063245
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the DST–India (FIST programme) for the use of the Bruker SMART APEXII diffractometer at the School of Chemistry, Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, India. JSN thanks the UGC–SAP, India, for the award of an RFSMS.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C10H12N3O3S+·C7H3N2O7− | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 481.41 | F(000) = 496 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.609 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.5551 (1) Å | Cell parameters from 6718 reflections |
| b = 10.5000 (2) Å | θ = 1.8–32.6° |
| c = 12.7576 (3) Å | µ = 0.23 mm−1 |
| α = 106.463 (1)° | T = 296 K |
| β = 100.913 (1)° | Prism, yellow |
| γ = 108.272 (1)° | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.16 mm |
| V = 993.72 (3) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 6718 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 4911 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.030 |
| ω and φ scan | θmax = 32.6°, θmin = 1.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004) | h = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.955, Tmax = 0.964 | k = −15→15 |
| 24261 measured reflections | l = −19→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.139 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0667P)2 + 0.2293P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 6718 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 301 parameters | Δρmax = 0.40 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement on F2 for ALL reflections except those flagged by the user for potential systematic errors. Weighted R-factors wR and all goodnesses of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The observed criterion of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating -R-factor-obs etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | −0.02011 (5) | 0.65153 (4) | 0.38510 (3) | 0.0339 (1) | |
| O1 | −0.12139 (15) | 0.56291 (12) | 0.26954 (11) | 0.0467 (4) | |
| O2 | −0.09563 (16) | 0.65425 (13) | 0.47595 (11) | 0.0464 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.47464 (18) | 0.55503 (17) | 0.32047 (14) | 0.0620 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.29162 (18) | 1.24424 (14) | 0.38400 (13) | 0.0425 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.13876 (17) | 0.60279 (14) | 0.42019 (12) | 0.0379 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.3923 (2) | 0.57678 (19) | 0.40572 (15) | 0.0531 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.07470 (18) | 0.82911 (15) | 0.38933 (13) | 0.0317 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.2170 (2) | 0.93167 (19) | 0.47915 (16) | 0.0503 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.2877 (2) | 1.06900 (19) | 0.47852 (16) | 0.0512 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.21460 (19) | 1.10143 (15) | 0.38930 (14) | 0.0346 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.0702 (2) | 1.00106 (18) | 0.30178 (15) | 0.0436 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.0001 (2) | 0.86347 (18) | 0.30136 (15) | 0.0419 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.24792 (19) | 0.58288 (15) | 0.35500 (14) | 0.0351 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.2303 (2) | 0.5656 (2) | 0.23927 (16) | 0.0473 (6) | |
| C9 | 0.3764 (3) | 0.55030 (19) | 0.22403 (18) | 0.0508 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.4458 (3) | 0.5285 (3) | 0.1246 (2) | 0.0749 (10) | |
| O4 | 0.51673 (18) | 0.76879 (19) | 0.75742 (13) | 0.0650 (5) | |
| O5 | 0.24957 (17) | 0.72400 (14) | 0.65907 (10) | 0.0492 (4) | |
| O6 | 0.03386 (14) | 0.74389 (13) | 0.75511 (10) | 0.0423 (3) | |
| O7 | −0.1353 (2) | 0.8493 (3) | 0.89565 (18) | 0.0976 (9) | |
| O8 | −0.1205 (2) | 0.7661 (3) | 1.02988 (15) | 0.0952 (8) | |
| O9 | 0.4658 (2) | 0.9039 (2) | 1.25864 (12) | 0.0710 (6) | |
| O10 | 0.66328 (19) | 0.9064 (2) | 1.17615 (14) | 0.0731 (6) | |
| N4 | −0.06166 (19) | 0.8072 (2) | 0.96064 (14) | 0.0581 (6) | |
| N5 | 0.51517 (19) | 0.88887 (16) | 1.17389 (13) | 0.0476 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.31809 (18) | 0.78573 (15) | 0.85972 (13) | 0.0322 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.14695 (18) | 0.77861 (15) | 0.85294 (13) | 0.0326 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.10795 (19) | 0.80780 (18) | 0.95755 (14) | 0.0386 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.2252 (2) | 0.84029 (18) | 1.06109 (14) | 0.0398 (4) | |
| C15 | 0.38950 (19) | 0.84785 (16) | 1.06265 (13) | 0.0361 (4) | |
| C16 | 0.43768 (18) | 0.82182 (16) | 0.96381 (14) | 0.0352 (4) | |
| C17 | 0.3688 (2) | 0.75745 (17) | 0.75231 (14) | 0.0391 (4) | |
| H1A | 0.35880 | 1.24140 | 0.33870 | 0.0640* | |
| H1B | 0.35470 | 1.30800 | 0.45420 | 0.0640* | |
| H1C | 0.20820 | 1.27010 | 0.35590 | 0.0640* | |
| H2 | 0.26480 | 0.90860 | 0.53940 | 0.0600* | |
| H2A | 0.15640 | 0.58830 | 0.48370 | 0.0450* | |
| H3 | 0.38410 | 1.13910 | 0.53810 | 0.0610* | |
| H5 | 0.02000 | 1.02560 | 0.24320 | 0.0520* | |
| H6 | −0.09710 | 0.79410 | 0.24200 | 0.0500* | |
| H8 | 0.13930 | 0.56490 | 0.18580 | 0.0570* | |
| H10A | 0.55580 | 0.60560 | 0.14430 | 0.1120* | |
| H10B | 0.36680 | 0.52770 | 0.05980 | 0.1120* | |
| H10C | 0.45950 | 0.43820 | 0.10560 | 0.1120* | |
| H6A | 0.07860 | 0.73090 | 0.70370 | 0.0630* | |
| H14 | 0.19440 | 0.85670 | 1.12830 | 0.0480* | |
| H16 | 0.54970 | 0.82850 | 0.96720 | 0.0420* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0360 (2) | 0.0322 (2) | 0.0349 (2) | 0.0131 (1) | 0.0121 (1) | 0.0137 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0460 (6) | 0.0366 (6) | 0.0424 (7) | 0.0088 (5) | 0.0010 (5) | 0.0093 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0511 (6) | 0.0500 (7) | 0.0531 (8) | 0.0239 (5) | 0.0301 (6) | 0.0265 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0505 (7) | 0.0712 (9) | 0.0659 (10) | 0.0312 (7) | 0.0241 (7) | 0.0152 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0506 (7) | 0.0353 (7) | 0.0509 (9) | 0.0180 (6) | 0.0277 (7) | 0.0199 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0475 (7) | 0.0421 (7) | 0.0347 (7) | 0.0238 (6) | 0.0164 (6) | 0.0198 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0485 (8) | 0.0614 (10) | 0.0492 (9) | 0.0275 (7) | 0.0145 (7) | 0.0134 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0344 (6) | 0.0310 (6) | 0.0310 (7) | 0.0136 (5) | 0.0102 (5) | 0.0120 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0576 (10) | 0.0412 (9) | 0.0381 (9) | 0.0092 (7) | −0.0054 (7) | 0.0189 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0529 (9) | 0.0367 (8) | 0.0428 (10) | 0.0026 (7) | −0.0037 (8) | 0.0132 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0397 (7) | 0.0318 (7) | 0.0399 (8) | 0.0169 (6) | 0.0203 (6) | 0.0156 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0465 (8) | 0.0430 (8) | 0.0434 (9) | 0.0185 (7) | 0.0060 (7) | 0.0228 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0393 (7) | 0.0390 (8) | 0.0403 (9) | 0.0115 (6) | 0.0000 (6) | 0.0165 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0409 (7) | 0.0272 (6) | 0.0368 (8) | 0.0132 (5) | 0.0132 (6) | 0.0106 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0559 (10) | 0.0513 (10) | 0.0423 (10) | 0.0243 (8) | 0.0220 (8) | 0.0198 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0598 (10) | 0.0385 (8) | 0.0567 (12) | 0.0173 (8) | 0.0324 (9) | 0.0136 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0892 (17) | 0.0710 (15) | 0.0808 (18) | 0.0340 (13) | 0.0583 (15) | 0.0270 (13) |
| O4 | 0.0475 (7) | 0.0968 (12) | 0.0513 (8) | 0.0267 (7) | 0.0256 (6) | 0.0230 (8) |
| O5 | 0.0571 (7) | 0.0597 (8) | 0.0306 (6) | 0.0233 (6) | 0.0132 (5) | 0.0160 (6) |
| O6 | 0.0395 (5) | 0.0529 (7) | 0.0314 (6) | 0.0198 (5) | 0.0039 (4) | 0.0138 (5) |
| O7 | 0.0692 (10) | 0.171 (2) | 0.0830 (13) | 0.0813 (13) | 0.0218 (9) | 0.0526 (13) |
| O8 | 0.0515 (8) | 0.167 (2) | 0.0550 (10) | 0.0286 (11) | 0.0271 (8) | 0.0321 (12) |
| O9 | 0.0746 (10) | 0.0941 (12) | 0.0313 (7) | 0.0259 (9) | 0.0026 (7) | 0.0211 (8) |
| O10 | 0.0468 (7) | 0.0981 (12) | 0.0612 (10) | 0.0296 (8) | −0.0061 (7) | 0.0238 (9) |
| N4 | 0.0382 (7) | 0.0850 (12) | 0.0393 (9) | 0.0244 (8) | 0.0082 (6) | 0.0079 (8) |
| N5 | 0.0474 (8) | 0.0447 (8) | 0.0376 (8) | 0.0141 (6) | −0.0053 (6) | 0.0128 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0333 (6) | 0.0298 (6) | 0.0305 (7) | 0.0109 (5) | 0.0073 (5) | 0.0098 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0348 (6) | 0.0304 (6) | 0.0288 (7) | 0.0116 (5) | 0.0041 (5) | 0.0102 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0327 (7) | 0.0451 (8) | 0.0349 (8) | 0.0158 (6) | 0.0079 (6) | 0.0114 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0407 (7) | 0.0452 (8) | 0.0294 (8) | 0.0154 (6) | 0.0084 (6) | 0.0109 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0361 (7) | 0.0346 (7) | 0.0299 (7) | 0.0112 (6) | −0.0004 (6) | 0.0105 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0321 (6) | 0.0336 (7) | 0.0369 (8) | 0.0124 (5) | 0.0057 (6) | 0.0122 (6) |
| C17 | 0.0403 (7) | 0.0394 (8) | 0.0365 (8) | 0.0134 (6) | 0.0128 (6) | 0.0140 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| S1—O1 | 1.4224 (13) | C2—C3 | 1.381 (3) |
| S1—O2 | 1.4276 (14) | C3—C4 | 1.373 (3) |
| S1—N2 | 1.6264 (16) | C4—C5 | 1.370 (2) |
| S1—C1 | 1.7651 (17) | C5—C6 | 1.378 (3) |
| O3—N3 | 1.408 (2) | C7—C8 | 1.408 (2) |
| O3—C9 | 1.331 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.351 (3) |
| O4—C17 | 1.221 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.490 (3) |
| O5—C17 | 1.288 (2) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| O6—C12 | 1.300 (2) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| O7—N4 | 1.210 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| O8—N4 | 1.212 (3) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| O9—N5 | 1.221 (2) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| O10—N5 | 1.215 (2) | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| O6—H6A | 0.8200 | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| N1—C4 | 1.464 (2) | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| N2—C7 | 1.388 (2) | C11—C16 | 1.382 (2) |
| N3—C7 | 1.311 (3) | C11—C17 | 1.493 (2) |
| N1—H1B | 0.8900 | C11—C12 | 1.427 (2) |
| N1—H1C | 0.8900 | C12—C13 | 1.410 (2) |
| N1—H1A | 0.8900 | C13—C14 | 1.377 (2) |
| N2—H2A | 0.8600 | C14—C15 | 1.379 (3) |
| N4—C13 | 1.457 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.381 (2) |
| N5—C15 | 1.463 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.380 (2) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C6 | 1.378 (2) | ||
| O1—S1—O2 | 120.44 (8) | C8—C9—C10 | 133.9 (2) |
| O1—S1—N2 | 108.84 (8) | O3—C9—C8 | 110.33 (19) |
| O1—S1—C1 | 107.28 (8) | C1—C2—H2 | 120.00 |
| O2—S1—N2 | 104.18 (8) | C3—C2—H2 | 120.00 |
| O2—S1—C1 | 109.04 (8) | C2—C3—H3 | 120.00 |
| N2—S1—C1 | 106.25 (8) | C4—C3—H3 | 120.00 |
| N3—O3—C9 | 108.82 (18) | C6—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| C12—O6—H6A | 109.00 | C4—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| S1—N2—C7 | 124.67 (12) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| O3—N3—C7 | 104.87 (15) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| H1B—N1—H1C | 109.00 | C9—C8—H8 | 128.00 |
| C4—N1—H1A | 109.00 | C7—C8—H8 | 128.00 |
| C4—N1—H1B | 109.00 | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.00 |
| C4—N1—H1C | 109.00 | C9—C10—H10B | 109.00 |
| H1A—N1—H1B | 109.00 | C9—C10—H10C | 110.00 |
| H1A—N1—H1C | 110.00 | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.00 |
| S1—N2—H2A | 118.00 | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.00 |
| C7—N2—H2A | 118.00 | C9—C10—H10A | 109.00 |
| O7—N4—O8 | 123.4 (2) | C12—C11—C16 | 121.17 (14) |
| O7—N4—C13 | 118.79 (19) | C12—C11—C17 | 118.90 (14) |
| O8—N4—C13 | 117.80 (18) | C16—C11—C17 | 119.92 (15) |
| O10—N5—C15 | 117.66 (15) | O6—C12—C13 | 122.61 (15) |
| O9—N5—O10 | 123.92 (17) | C11—C12—C13 | 116.05 (14) |
| O9—N5—C15 | 118.42 (17) | O6—C12—C11 | 121.32 (14) |
| S1—C1—C2 | 121.18 (13) | N4—C13—C12 | 120.47 (15) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.80 (16) | C12—C13—C14 | 123.04 (16) |
| S1—C1—C6 | 118.00 (13) | N4—C13—C14 | 116.48 (15) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.21 (17) | C13—C14—C15 | 118.34 (15) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.55 (17) | N5—C15—C16 | 120.25 (15) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.35 (16) | C14—C15—C16 | 121.92 (15) |
| N1—C4—C5 | 118.03 (15) | N5—C15—C14 | 117.80 (14) |
| N1—C4—C3 | 120.61 (16) | C11—C16—C15 | 119.46 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.34 (17) | O4—C17—C11 | 119.62 (16) |
| C1—C6—C5 | 119.70 (16) | O5—C17—C11 | 115.95 (16) |
| N3—C7—C8 | 112.03 (16) | O4—C17—O5 | 124.43 (17) |
| N2—C7—C8 | 130.75 (16) | C13—C14—H14 | 121.00 |
| N2—C7—N3 | 117.21 (15) | C15—C14—H14 | 121.00 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 103.93 (17) | C11—C16—H16 | 120.00 |
| O3—C9—C10 | 115.7 (2) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.00 |
| O1—S1—N2—C7 | 49.04 (16) | C2—C3—C4—N1 | −177.26 (16) |
| O2—S1—N2—C7 | 178.71 (14) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.5 (3) |
| C1—S1—N2—C7 | −66.19 (15) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −2.1 (3) |
| O1—S1—C1—C2 | −161.03 (14) | N1—C4—C5—C6 | 176.66 (16) |
| O1—S1—C1—C6 | 20.36 (16) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.7 (3) |
| O2—S1—C1—C2 | 67.01 (16) | N2—C7—C8—C9 | −179.86 (19) |
| O2—S1—C1—C6 | −111.60 (14) | N3—C7—C8—C9 | −0.7 (2) |
| N2—S1—C1—C2 | −44.74 (16) | C7—C8—C9—O3 | 1.0 (2) |
| N2—S1—C1—C6 | 136.65 (14) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −179.8 (3) |
| N3—O3—C9—C8 | −0.9 (2) | C16—C11—C12—O6 | −179.60 (16) |
| C9—O3—N3—C7 | 0.4 (2) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | −1.1 (2) |
| N3—O3—C9—C10 | 179.7 (2) | C17—C11—C12—O6 | 2.1 (2) |
| S1—N2—C7—N3 | 164.49 (14) | C17—C11—C12—C13 | −179.40 (15) |
| S1—N2—C7—C8 | −16.4 (3) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 1.7 (3) |
| O3—N3—C7—N2 | 179.46 (15) | C17—C11—C16—C15 | 179.96 (16) |
| O3—N3—C7—C8 | 0.2 (2) | C12—C11—C17—O4 | 177.09 (18) |
| O7—N4—C13—C14 | 144.2 (2) | C12—C11—C17—O5 | −1.9 (2) |
| O8—N4—C13—C12 | 146.3 (2) | C16—C11—C17—O4 | −1.2 (3) |
| O7—N4—C13—C12 | −34.7 (3) | C16—C11—C17—O5 | 179.75 (16) |
| O8—N4—C13—C14 | −34.7 (3) | O6—C12—C13—N4 | −3.2 (3) |
| O9—N5—C15—C14 | 5.4 (3) | O6—C12—C13—C14 | 177.93 (17) |
| O9—N5—C15—C16 | −176.34 (18) | C11—C12—C13—N4 | 178.36 (17) |
| O10—N5—C15—C16 | 3.9 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.5 (3) |
| O10—N5—C15—C14 | −174.40 (19) | N4—C13—C14—C15 | −177.38 (17) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.9 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 1.6 (3) |
| S1—C1—C6—C5 | 179.87 (14) | C13—C14—C15—N5 | 177.28 (17) |
| S1—C1—C2—C3 | 179.55 (14) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −1.0 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.3 (3) | N5—C15—C16—C11 | −178.83 (16) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.5 (3) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | −0.6 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O6—H6A···O5 | 0.82 | 1.68 | 2.4296 (19) | 151 |
| N2—H2A···O5 | 0.86 | 2.12 | 2.7852 (18) | 134 |
| N1—H1A···O4i | 0.89 | 1.77 | 2.661 (2) | 177 |
| N1—H1B···N3i | 0.89 | 2.24 | 3.041 (2) | 150 |
| N1—H1C···O6ii | 0.89 | 2.21 | 3.064 (2) | 160 |
| C5—H5···O6ii | 0.93 | 2.60 | 3.293 (2) | 132 |
| C6—H6···O8iii | 0.93 | 2.60 | 3.176 (2) | 121 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+2, −z+1; (ii) −x, −y+2, −z+1; (iii) x, y, z−1.
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Bettinetti, G. P., Giordano, F., La Manna, A., Giuseppetti, G. & Tadini, C. (1982). Cryst. Struct. Commun. 11, 821–828.
- Bock, L., Miller, G. H., Schaper, K. J. & Seydel, J. K. (1974). J. Med. Chem. 17, 23–28. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2004). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cason, C. J. (2004). POV-RAY for Windows. Persistence of Vision, Raytracer Pty Ltd, Victoria, Australia. URL: http://www.povray.org.
- Groom, C. R. & Allen, F. H. (2014). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 662–671. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hida, S., Yoshida, M., Nakabayashi, I., Miura, N. N., Adachi, Y. & Ohno, N. (2005). Biol. Pharm. Bull. 28, 773–778. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.-L., Cheng, Y.-Y., Xu, Z.-H., Xu, P., Qu, H.-O., Fang, Y.-J., Xu, T.-W. & Wen, L. (2007). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 42, 93–98. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Marques, L. L., de Oliveira, G. M. & Schulz Lang, E. (2006). Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 632, 2310–2314.
- Maury, L., Rambaud, J., Pauvert, B., Lasserre, Y., Berge, G. & Audran, M. (1985). Can. J. Chem. 63, 3012–3018.
- Nakai, H., Takasuka, M. & Shiro, M. (1984). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. 1459–1464.
- Price, C. P., Grzesiak, A. L. & Matzger, A. J. (2005). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 5512–5517. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Subashini, A., Muthiah, P. T., Bocelli, G. & Cantoni, A. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o4312–o4313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Subashini, A., Muthiah, P. T., Bocelli, G. & Cantoni, A. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, m250–m251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008701/su5130sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008701/su5130Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008701/su5130Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1063245
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report