In the crystal of title molecular salt, the protonated N atom of the 4-methylmorpholin-4-ium cation forms a hydrogen bond with a carbonyl O atom of the barbiturate anion. This N—H⋯O hydrogen bond contributes to the good stability of the reported salt, which exhibits noticeable anticonvulsant and hypnotic activity.
Keywords: crystal structure, anticonvulsant activity, hypnotic activity, barbiturate, molecular salt, hydrogen bonding
Abstract
The title molecular salt, C5H12NO+·C12H8N5O9 − [common name: 4-methylmorpholin-4-ium 1,3-dimethyl-5-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl)barbiturate], possesses noticeable anticonvulsant and hypnotic activity. In the anion, the 1,3-dimethylbarbituric acid ring and the symmetrically substituted trinitrophenyl ring, linked via a C—C bond, are not coplanar but subtend an angle of 44.88 (7)°. The six-membered ring of the 4-methylmorpholin-4-ium cation has a chair conformation. In the crystal, the cation and anion are linked via an N—H⋯O hydrogen bond. The cation–anion units are linked by a number of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional network.
Chemical context
In biological systems, pyrimidine derivatives play a significant role. Substituted barbituric acid (barbiturates) are pyrimidine derivatives which have been used as hypnotic drugs and in the treatment of epilepsy. Morpholines also have pharmacological properties and are used in organic synthesis as bases, catalysts and chiral auxiliaries (Dave & Sasaki, 2004 ▸; Mayer & List, 2006 ▸; Mossé et al., 2006 ▸; Nelson & Wang, 2006 ▸; Qin & Pu, 2006 ▸). The molecular salts previously synthesized in our laboratory from chloronitroaromatics, barbituric acid and amines containing tertiary nitrogen atoms possess noticeable anticonvulsant/hypnotic activity (Kalaivani & Buvaneswari, 2010 ▸; Buvaneswari & Kalaivani, 2013 ▸). In this context, we report herein on the crystal structure of a new molecular salt isolated from ethanolic solutions of 1-chloro-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene (TNCB), 1,3-dimethyl barbituric acid and 4-methylmorpholine.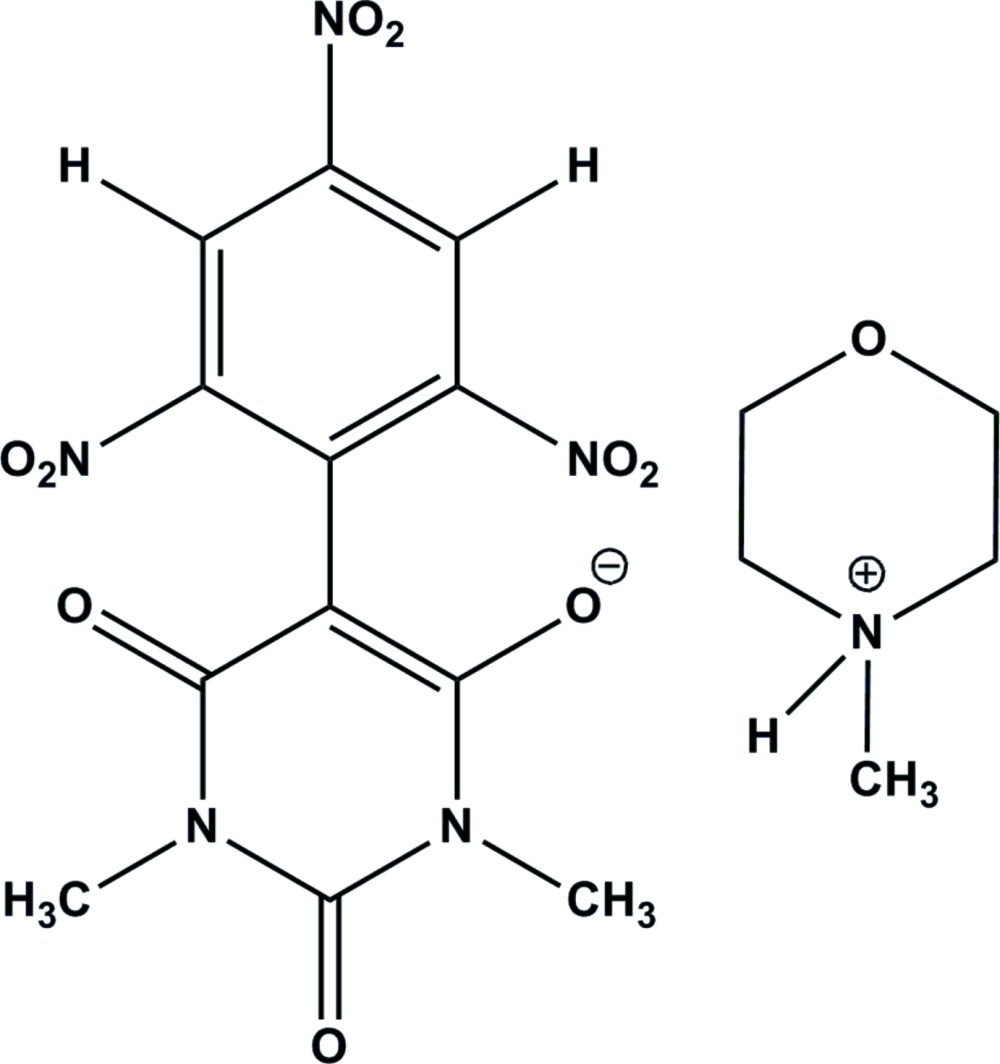
Structural commentary
The molecular structure of the title molecular salt is depicted in Fig. 1 ▸. The protonated nitrogen atom of the N-methylmorpholinium cation forms a hydrogen bond with the carbonyl group O atom of the 1,3-dimethyl-5-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) barbiturate anion (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 2 ▸). This N—H⋯O hydrogen bond may well be the driving force for the formation of the title molecular salt. All the bond lengths and bond angles are normal and comparable with those observed in related barbiturates (Gunaseelan & Doraisamyraja, 2014 ▸; Vaduganathan & Doraisamyraja, 2014 ▸). The six-membered morpholin-4-ium ring has a chair conformation. In the anion, the 1,3-dimethyl barbituric acid ring and the symmetrically substituted trinitrophenyl ring, linked via the C4—C7 bond, are not co-planar but subtend an angle of 44.88 (7)°. The planes of the nitro groups substituted in the aromatic ring ortho with respect to the ring junction of the anion deviate to a greater extent than that of the para nitro group [dihedral angles of 42.66 (10) and 45.44 (9°) for the ortho nitro groups and 12.5 (8)° for the para nitro group]. Thus the para nitro group is more involved in delocalizing the charge of the anion than the ortho nitro groups, which imparts a red colour for the title molecular salt.
Figure 1.
A view of the molecular structure of the title molecular salt, showing the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 40% probability level.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N6H6AO9i | 0.90(1) | 1.81(2) | 2.6790(17) | 162(2) |
| C12H12BO1ii | 0.96 | 2.53 | 3.270(3) | 134 |
| C13H13BO8iii | 0.97 | 2.42 | 3.046(2) | 122 |
| C15H15AO7iv | 0.97 | 2.57 | 3.529(2) | 169 |
| C17H17AO7 | 0.96 | 2.43 | 3.297(2) | 151 |
| C17H17BO4 | 0.96 | 2.40 | 3.344(2) | 168 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Figure 2.
A view along the b axis of the crystal packing of the title molecular salt. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines (see Table 1 ▸ for details).
Supramolecular features
In the crystal, in addition to the N—H⋯O hydrogen bond linking the cation and anion, there are a number of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds present, leading to the formation of a three-dimensional network, enclosing two sizable  (11) and
(11) and  (10) ring motifs (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 2 ▸).
(10) ring motifs (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 2 ▸).
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (Version 5.36, February 2015; Groom & Allen, 2014 ▸) for 5-phenyl-1,3-dimethyl barbiturates gave seven hits with various tertiary amines as cations. Two of these compounds involve 2,4-dinitrophenyl (CORWUD; Gunaseelan & Doraisamyraja, 2014 ▸; YAVSOF; Sridevi & Kalaivani, 2012 ▸), two involve 5-chloro-2,4-dinitrophenyl (DOQCUJ; Vaduganathan & Doraisamyraja, 2014 ▸), and the final three involve 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl, as in the title barbiturate anion. These three compounds include the N,N-dimethylanilinium salt (JOKGIB: Babykala et al., 2014 ▸), the quinolinium salt (JOKGUN: Babykala et al., 2014 ▸) and the triethylammonium salt (LEGWIF; Rajamani & Kalaivani, 2012 ▸). In these compounds, the benzene ring is inclined to the plane of the 1,3-dimethyl barbiturate ring by 44.34, 42.88 and 46.88°, respectively, compared to 44.88 (7)° in the title salt.
Pharmacological activity
Epilepsy is a medical condition that produces seizures affecting a variety of mental and physical functions. Barbituric acid derivatives are potential anti-epileptic agents. The title molecular salt is a derivative of 1,3-dimethylbarbituric acid and possesses anticonvulsant activity even at low dosage (25 mg kg−1), inferred from the Maximal Electro Shock method on albino rats (Misra et al., 1973 ▸; Kulkarni, 1999 ▸). The therapeutic dose (100 mg kg−1) induces hypnosis in albino mice (Dewas, 1953 ▸) and the molecular salt is non-cytotoxic on human embryonic kidney cell-HEK 293 (Mosmann, 1983 ▸).
Synthesis and crystallization
1-Chloro-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene (TNCB: 2.5 g, 0.01 mol) dissolved in 30 ml of absolute ethanol was mixed with 1,3-dimethylbarbituric acid (1.6 g, 0.01 mol) in 30 ml of absolute ethanol. After mixing these two solutions, 3 ml of N-methylmorpholine (0.03 mol) was added and the mixture was shaken vigorously for 6 to 7 h. The solution was filtered and the filtrate was kept at room temperature. After a period of four weeks, dark shiny maroon–red-coloured crystals formed from the solution. The crystals were filtered and washed with 30 ml of dry ether and recrystallized from absolute ethanol (yield: 70%; m.p.: 483 K).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The NH H atom was located from a difference Fourier map and freely refined. The C-bound H atoms were included in calculated positions and refined as riding: C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å with U iso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms and 1.2U eq(C) for other H atoms.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C5H12NO+C12H8N5O9 |
| M r | 468.39 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, b, c () | 12.0335(2), 12.5495(2), 14.2095(3) |
| () | 110.619(1) |
| V (3) | 2008.38(6) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo K |
| (mm1) | 0.13 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.35 0.35 0.30 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.944, 0.979 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2(I)] reflections | 17785, 3531, 3100 |
| R int | 0.022 |
| (sin /)max (1) | 0.594 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.033, 0.094, 1.02 |
| No. of reflections | 3531 |
| No. of parameters | 303 |
| No. of restraints | 1 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| max, min (e 3) | 0.29, 0.19 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015010075/su5140sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015010075/su5140Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015010075/su5140Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1006239
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the DST–SERB for financial support and the SAIF, IIT Madras, for the single-crystal XRD data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C5H12NO+·C12H8N5O9− | F(000) = 976 |
| Mr = 468.39 | Dx = 1.549 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 5001 reflections |
| a = 12.0335 (2) Å | θ = 2.4–31.0° |
| b = 12.5495 (2) Å | µ = 0.13 mm−1 |
| c = 14.2095 (3) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 110.619 (1)° | Block, red |
| V = 2008.38 (6) Å3 | 0.35 × 0.35 × 0.30 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3531 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3100 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.022 |
| ω and φ scan | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004) | h = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.944, Tmax = 0.979 | k = −14→14 |
| 17785 measured reflections | l = −14→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.033 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.094 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0481P)2 + 0.8436P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.02 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3531 reflections | Δρmax = 0.29 e Å−3 |
| 303 parameters | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0055 (8) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.43707 (13) | 0.03855 (13) | 0.25436 (11) | 0.0302 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.38283 (12) | 0.12808 (12) | 0.27338 (11) | 0.0289 (3) | |
| H2 | 0.3864 | 0.1927 | 0.2425 | 0.035* | |
| C3 | 0.32290 (12) | 0.11897 (11) | 0.33969 (10) | 0.0260 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.31666 (12) | 0.02532 (11) | 0.39227 (10) | 0.0243 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.37585 (12) | −0.06119 (11) | 0.36784 (10) | 0.0255 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.43254 (13) | −0.05755 (12) | 0.29902 (11) | 0.0293 (3) | |
| H6 | 0.4667 | −0.1183 | 0.2833 | 0.035* | |
| C7 | 0.25695 (12) | 0.01764 (11) | 0.46538 (10) | 0.0258 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.27868 (13) | 0.09763 (12) | 0.53973 (10) | 0.0276 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.15786 (14) | −0.00393 (13) | 0.61560 (12) | 0.0351 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.18464 (12) | −0.07197 (11) | 0.46323 (11) | 0.0266 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.06174 (16) | −0.16822 (14) | 0.54379 (14) | 0.0426 (4) | |
| H11A | 0.0535 | −0.2146 | 0.4880 | 0.064* | |
| H11B | −0.0151 | −0.1428 | 0.5396 | 0.064* | |
| H11C | 0.0974 | −0.2066 | 0.6056 | 0.064* | |
| C12 | 0.23622 (19) | 0.16819 (15) | 0.68544 (14) | 0.0512 (5) | |
| H12A | 0.2844 | 0.2243 | 0.6744 | 0.077* | |
| H12B | 0.2732 | 0.1402 | 0.7521 | 0.077* | |
| H12C | 0.1592 | 0.1958 | 0.6781 | 0.077* | |
| C13 | −0.12719 (15) | 0.08388 (12) | 0.08075 (13) | 0.0376 (4) | |
| H13A | −0.0888 | 0.0936 | 0.0317 | 0.045* | |
| H13B | −0.1145 | 0.1478 | 0.1215 | 0.045* | |
| C14 | −0.25795 (15) | 0.06698 (14) | 0.02738 (14) | 0.0455 (4) | |
| H14A | −0.2972 | 0.0616 | 0.0763 | 0.055* | |
| H14B | −0.2913 | 0.1274 | −0.0159 | 0.055* | |
| C15 | −0.23768 (16) | −0.11649 (14) | 0.03294 (14) | 0.0455 (4) | |
| H15A | −0.2566 | −0.1813 | −0.0068 | 0.055* | |
| H15B | −0.2785 | −0.1189 | 0.0808 | 0.055* | |
| C16 | −0.10612 (15) | −0.11112 (12) | 0.08864 (12) | 0.0371 (4) | |
| H16A | −0.0816 | −0.1708 | 0.1347 | 0.045* | |
| H16B | −0.0648 | −0.1161 | 0.0412 | 0.045* | |
| C17 | 0.05704 (14) | 0.00254 (14) | 0.19529 (13) | 0.0408 (4) | |
| H17A | 0.0886 | −0.0586 | 0.2367 | 0.061* | |
| H17B | 0.0741 | 0.0656 | 0.2362 | 0.061* | |
| H17C | 0.0928 | 0.0083 | 0.1448 | 0.061* | |
| N1 | 0.50516 (12) | 0.04650 (12) | 0.18734 (11) | 0.0415 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.26003 (11) | 0.21678 (9) | 0.34983 (9) | 0.0300 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.39089 (11) | −0.16271 (10) | 0.42314 (9) | 0.0287 (3) | |
| N4 | 0.22370 (12) | 0.08312 (10) | 0.61182 (9) | 0.0346 (3) | |
| N5 | 0.13701 (11) | −0.07774 (10) | 0.54094 (10) | 0.0320 (3) | |
| N6 | −0.07361 (11) | −0.00932 (10) | 0.14601 (10) | 0.0285 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.53911 (14) | −0.03584 (12) | 0.16052 (11) | 0.0625 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.52504 (14) | 0.13486 (12) | 0.16192 (13) | 0.0680 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.31154 (11) | 0.30113 (9) | 0.35283 (9) | 0.0441 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.15911 (10) | 0.20924 (9) | 0.35025 (8) | 0.0373 (3) | |
| O5 | 0.37978 (11) | −0.24515 (9) | 0.37513 (9) | 0.0412 (3) | |
| O6 | 0.41853 (10) | −0.15902 (9) | 0.51449 (8) | 0.0362 (3) | |
| O7 | 0.16068 (9) | −0.14407 (8) | 0.40033 (8) | 0.0336 (3) | |
| O8 | 0.34225 (10) | 0.17649 (8) | 0.54788 (8) | 0.0358 (3) | |
| O9 | 0.11726 (13) | −0.01616 (11) | 0.68304 (10) | 0.0554 (4) | |
| O10 | −0.27783 (11) | −0.02750 (11) | −0.03090 (9) | 0.0518 (3) | |
| H6A | −0.1019 (14) | −0.0097 (13) | 0.1966 (12) | 0.033 (4)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0272 (7) | 0.0396 (9) | 0.0254 (7) | −0.0018 (6) | 0.0114 (6) | 0.0027 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0295 (7) | 0.0289 (8) | 0.0265 (8) | −0.0053 (6) | 0.0078 (6) | 0.0037 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0282 (7) | 0.0240 (7) | 0.0246 (7) | −0.0022 (6) | 0.0078 (6) | −0.0017 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0258 (7) | 0.0248 (7) | 0.0204 (7) | −0.0042 (5) | 0.0058 (5) | −0.0020 (5) |
| C5 | 0.0282 (7) | 0.0241 (7) | 0.0231 (7) | −0.0021 (6) | 0.0076 (6) | 0.0008 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0298 (7) | 0.0313 (8) | 0.0271 (8) | 0.0026 (6) | 0.0102 (6) | −0.0003 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0319 (7) | 0.0243 (7) | 0.0231 (7) | 0.0011 (6) | 0.0121 (6) | 0.0010 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0328 (8) | 0.0271 (8) | 0.0227 (7) | 0.0037 (6) | 0.0094 (6) | 0.0020 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0393 (8) | 0.0402 (9) | 0.0310 (8) | 0.0067 (7) | 0.0187 (7) | 0.0053 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0283 (7) | 0.0267 (8) | 0.0259 (7) | 0.0042 (6) | 0.0110 (6) | 0.0040 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0441 (9) | 0.0396 (9) | 0.0531 (11) | −0.0032 (7) | 0.0282 (8) | 0.0068 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0744 (13) | 0.0478 (11) | 0.0387 (10) | 0.0034 (9) | 0.0288 (9) | −0.0116 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0439 (9) | 0.0263 (8) | 0.0447 (9) | 0.0015 (7) | 0.0184 (8) | 0.0067 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0424 (10) | 0.0432 (10) | 0.0501 (10) | 0.0077 (8) | 0.0153 (8) | 0.0108 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0506 (10) | 0.0381 (10) | 0.0482 (10) | −0.0104 (8) | 0.0180 (8) | −0.0111 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0481 (9) | 0.0256 (8) | 0.0386 (9) | −0.0002 (7) | 0.0166 (7) | −0.0072 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0376 (9) | 0.0427 (10) | 0.0384 (9) | 0.0004 (7) | 0.0088 (7) | −0.0066 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0377 (7) | 0.0522 (9) | 0.0408 (8) | 0.0049 (7) | 0.0214 (6) | 0.0110 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0398 (7) | 0.0241 (7) | 0.0267 (7) | −0.0009 (5) | 0.0127 (5) | 0.0017 (5) |
| N3 | 0.0305 (6) | 0.0262 (7) | 0.0303 (7) | 0.0015 (5) | 0.0116 (5) | 0.0023 (5) |
| N4 | 0.0475 (8) | 0.0340 (7) | 0.0266 (7) | 0.0033 (6) | 0.0186 (6) | −0.0028 (5) |
| N5 | 0.0367 (7) | 0.0325 (7) | 0.0327 (7) | −0.0003 (5) | 0.0197 (6) | 0.0032 (5) |
| N6 | 0.0370 (7) | 0.0260 (7) | 0.0256 (6) | −0.0001 (5) | 0.0147 (5) | −0.0027 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0751 (10) | 0.0663 (9) | 0.0688 (10) | 0.0253 (8) | 0.0537 (8) | 0.0156 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0828 (11) | 0.0593 (9) | 0.0880 (11) | −0.0058 (8) | 0.0624 (10) | 0.0168 (8) |
| O3 | 0.0609 (8) | 0.0232 (6) | 0.0526 (7) | −0.0081 (5) | 0.0252 (6) | −0.0014 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0385 (6) | 0.0355 (6) | 0.0407 (7) | 0.0057 (5) | 0.0175 (5) | 0.0028 (5) |
| O5 | 0.0580 (7) | 0.0246 (6) | 0.0446 (7) | 0.0008 (5) | 0.0224 (6) | −0.0032 (5) |
| O6 | 0.0435 (6) | 0.0368 (6) | 0.0264 (6) | 0.0030 (5) | 0.0100 (5) | 0.0074 (5) |
| O7 | 0.0404 (6) | 0.0290 (6) | 0.0342 (6) | −0.0065 (4) | 0.0166 (5) | −0.0050 (5) |
| O8 | 0.0457 (6) | 0.0293 (6) | 0.0325 (6) | −0.0058 (5) | 0.0137 (5) | −0.0057 (5) |
| O9 | 0.0725 (9) | 0.0674 (9) | 0.0433 (7) | −0.0055 (7) | 0.0417 (7) | −0.0029 (6) |
| O10 | 0.0483 (7) | 0.0606 (9) | 0.0375 (7) | −0.0019 (6) | 0.0040 (6) | −0.0023 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C6 | 1.373 (2) | C12—H12B | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.373 (2) | C12—H12C | 0.9600 |
| C1—N1 | 1.462 (2) | C13—N6 | 1.491 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.378 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.502 (2) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C13—H13A | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.409 (2) | C13—H13B | 0.9700 |
| C3—N2 | 1.4753 (18) | C14—O10 | 1.417 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.407 (2) | C14—H14A | 0.9700 |
| C4—C7 | 1.4597 (19) | C14—H14B | 0.9700 |
| C5—C6 | 1.376 (2) | C15—O10 | 1.412 (2) |
| C5—N3 | 1.4742 (18) | C15—C16 | 1.502 (2) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C15—H15A | 0.9700 |
| C7—C8 | 1.413 (2) | C15—H15B | 0.9700 |
| C7—C10 | 1.416 (2) | C16—N6 | 1.4917 (19) |
| C8—O8 | 1.2311 (18) | C16—H16A | 0.9700 |
| C8—N4 | 1.4134 (19) | C16—H16B | 0.9700 |
| C9—O9 | 1.2291 (19) | C17—N6 | 1.486 (2) |
| C9—N4 | 1.362 (2) | C17—H17A | 0.9600 |
| C9—N5 | 1.363 (2) | C17—H17B | 0.9600 |
| C10—O7 | 1.2325 (18) | C17—H17C | 0.9600 |
| C10—N5 | 1.4137 (18) | N1—O2 | 1.2158 (19) |
| C11—N5 | 1.462 (2) | N1—O1 | 1.220 (2) |
| C11—H11A | 0.9600 | N2—O3 | 1.2198 (16) |
| C11—H11B | 0.9600 | N2—O4 | 1.2201 (16) |
| C11—H11C | 0.9600 | N3—O5 | 1.2203 (16) |
| C12—N4 | 1.465 (2) | N3—O6 | 1.2221 (16) |
| C12—H12A | 0.9600 | N6—H6A | 0.897 (14) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 121.94 (13) | H13A—C13—H13B | 108.1 |
| C6—C1—N1 | 118.92 (14) | O10—C14—C13 | 110.15 (14) |
| C2—C1—N1 | 119.11 (14) | O10—C14—H14A | 109.6 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 117.77 (13) | C13—C14—H14A | 109.6 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 121.1 | O10—C14—H14B | 109.6 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 121.1 | C13—C14—H14B | 109.6 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 124.77 (13) | H14A—C14—H14B | 108.1 |
| C2—C3—N2 | 114.05 (12) | O10—C15—C16 | 111.21 (14) |
| C4—C3—N2 | 121.16 (12) | O10—C15—H15A | 109.4 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 112.75 (12) | C16—C15—H15A | 109.4 |
| C5—C4—C7 | 122.91 (12) | O10—C15—H15B | 109.4 |
| C3—C4—C7 | 124.33 (12) | C16—C15—H15B | 109.4 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 124.77 (13) | H15A—C15—H15B | 108.0 |
| C6—C5—N3 | 114.14 (12) | N6—C16—C15 | 110.58 (13) |
| C4—C5—N3 | 120.87 (12) | N6—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 117.90 (14) | C15—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 121.0 | N6—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 121.0 | C15—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C10 | 122.06 (13) | H16A—C16—H16B | 108.1 |
| C8—C7—C4 | 118.51 (12) | N6—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C10—C7—C4 | 119.34 (12) | N6—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O8—C8—C7 | 125.91 (13) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O8—C8—N4 | 117.99 (13) | N6—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—N4 | 116.08 (13) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O9—C9—N4 | 121.84 (15) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O9—C9—N5 | 120.48 (15) | O2—N1—O1 | 123.84 (14) |
| N4—C9—N5 | 117.69 (13) | O2—N1—C1 | 118.02 (15) |
| O7—C10—N5 | 118.24 (13) | O1—N1—C1 | 118.14 (14) |
| O7—C10—C7 | 125.72 (13) | O3—N2—O4 | 124.16 (13) |
| N5—C10—C7 | 116.04 (13) | O3—N2—C3 | 116.98 (12) |
| N5—C11—H11A | 109.5 | O4—N2—C3 | 118.78 (12) |
| N5—C11—H11B | 109.5 | O5—N3—O6 | 124.13 (12) |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 | O5—N3—C5 | 117.77 (12) |
| N5—C11—H11C | 109.5 | O6—N3—C5 | 118.02 (12) |
| H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 | C9—N4—C8 | 124.01 (13) |
| H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 | C9—N4—C12 | 118.14 (14) |
| N4—C12—H12A | 109.5 | C8—N4—C12 | 117.84 (14) |
| N4—C12—H12B | 109.5 | C9—N5—C10 | 123.98 (13) |
| H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 | C9—N5—C11 | 116.88 (13) |
| N4—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C10—N5—C11 | 119.14 (13) |
| H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C17—N6—C13 | 111.63 (12) |
| H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C17—N6—C16 | 111.94 (12) |
| N6—C13—C14 | 110.49 (13) | C13—N6—C16 | 111.05 (12) |
| N6—C13—H13A | 109.6 | C17—N6—H6A | 105.1 (11) |
| C14—C13—H13A | 109.6 | C13—N6—H6A | 107.4 (11) |
| N6—C13—H13B | 109.6 | C16—N6—H6A | 109.4 (11) |
| C14—C13—H13B | 109.6 | C15—O10—C14 | 109.69 (13) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.1 (2) | C6—C1—N1—O1 | 11.8 (2) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −177.70 (13) | C2—C1—N1—O1 | −170.27 (15) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 2.4 (2) | C2—C3—N2—O3 | −40.93 (17) |
| C1—C2—C3—N2 | −175.69 (13) | C4—C3—N2—O3 | 140.92 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.9 (2) | C2—C3—N2—O4 | 135.91 (13) |
| N2—C3—C4—C5 | 176.08 (12) | C4—C3—N2—O4 | −42.23 (19) |
| C2—C3—C4—C7 | 177.42 (13) | C6—C5—N3—O5 | −44.54 (17) |
| N2—C3—C4—C7 | −4.6 (2) | C4—C5—N3—O5 | 140.67 (13) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.1 (2) | C6—C5—N3—O6 | 132.46 (13) |
| C7—C4—C5—C6 | 179.58 (13) | C4—C5—N3—O6 | −42.33 (18) |
| C3—C4—C5—N3 | 173.08 (12) | O9—C9—N4—C8 | 175.76 (15) |
| C7—C4—C5—N3 | −6.2 (2) | N5—C9—N4—C8 | −4.8 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −2.8 (2) | O9—C9—N4—C12 | −5.7 (2) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | 174.99 (13) | N5—C9—N4—C12 | 173.71 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 3.4 (2) | O8—C8—N4—C9 | −175.43 (14) |
| N3—C5—C6—C1 | −171.15 (13) | C7—C8—N4—C9 | 3.2 (2) |
| C5—C4—C7—C8 | 132.29 (14) | O8—C8—N4—C12 | 6.0 (2) |
| C3—C4—C7—C8 | −46.92 (19) | C7—C8—N4—C12 | −175.31 (14) |
| C5—C4—C7—C10 | −44.30 (19) | O9—C9—N5—C10 | −177.15 (15) |
| C3—C4—C7—C10 | 136.49 (14) | N4—C9—N5—C10 | 3.4 (2) |
| C10—C7—C8—O8 | 178.39 (14) | O9—C9—N5—C11 | 2.1 (2) |
| C4—C7—C8—O8 | 1.9 (2) | N4—C9—N5—C11 | −177.34 (14) |
| C10—C7—C8—N4 | −0.2 (2) | O7—C10—N5—C9 | 179.21 (14) |
| C4—C7—C8—N4 | −176.65 (12) | C7—C10—N5—C9 | −0.6 (2) |
| C8—C7—C10—O7 | 179.15 (14) | O7—C10—N5—C11 | 0.0 (2) |
| C4—C7—C10—O7 | −4.4 (2) | C7—C10—N5—C11 | −179.82 (13) |
| C8—C7—C10—N5 | −1.0 (2) | C14—C13—N6—C17 | 176.77 (14) |
| C4—C7—C10—N5 | 175.41 (12) | C14—C13—N6—C16 | 51.09 (18) |
| N6—C13—C14—O10 | −57.98 (18) | C15—C16—N6—C17 | −175.33 (14) |
| O10—C15—C16—N6 | 55.94 (19) | C15—C16—N6—C13 | −49.82 (17) |
| C6—C1—N1—O2 | −167.86 (16) | C16—C15—O10—C14 | −63.10 (18) |
| C2—C1—N1—O2 | 10.0 (2) | C13—C14—O10—C15 | 63.87 (18) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N6—H6A···O9i | 0.90 (1) | 1.81 (2) | 2.6790 (17) | 162 (2) |
| C12—H12B···O1ii | 0.96 | 2.53 | 3.270 (3) | 134 |
| C13—H13B···O8iii | 0.97 | 2.42 | 3.046 (2) | 122 |
| C15—H15A···O7iv | 0.97 | 2.57 | 3.529 (2) | 169 |
| C17—H17A···O7 | 0.96 | 2.43 | 3.297 (2) | 151 |
| C17—H17B···O4 | 0.96 | 2.40 | 3.344 (2) | 168 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (iii) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (iv) x−1/2, −y−1/2, z−1/2.
References
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C. & Guagliardi, A. (1993). J. Appl. Cryst. 26, 343–350.
- Babykala, R., Rajamani, K., Muthulakshmi, S. & Kalaivani, D. (2014). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 44, 243–254.
- Bruker (2004). APEX2, SAINT, XPREP and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Buvaneswari, M. & Kalaivani, D. (2013). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 43, 561–567.
- Dave, R. & Sasaki, N. A. (2004). Org. Lett. 6, 15–18. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dewas, P. B. (1953). Br. J. Pharmacol. 6, 46–48.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Groom, C. R. & Allen, F. H. (2014). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 662–671. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gunaseelan, S. & Doraisamyraja, K. (2014). Acta Cryst. E70, o1102–o1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Kalaivani, D. & Buvaneswari, M. (2010). Recent. Adv. Clin. Med. pp. 255–260 Cambridge, UK: WSEAS Publications.
- Kulkarni, S. K. (1999). Handbook of experimental pharmacology, p. 131. Mumbai: Vallabh Prakashan.
- Macrae, C. F., Bruno, I. J., Chisholm, J. A., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Rodriguez-Monge, L., Taylor, R., van de Streek, J. & Wood, P. A. (2008). J. Appl. Cryst. 41, 466–470.
- Mayer, S. & List, B. (2006). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 4193–4195. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Misra, A. K., Dandiya, P. C. & Kulkarni, S. K. (1973). Indian J. Pharmacol. 5, 449–450.
- Mosmann, T. (1983). J. Immunol. Methods, 65, 55–63. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mossé, S., Laars, M., Kriis, K., Kanger, T. & Alexakis, A. (2006). Org. Lett. 8, 2559–2562. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nelson, S. G. & Wang, K. (2006). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 4232–4233. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y. & Pu, L. (2006). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 273–277.
- Rajamani, K. & Kalaivani, D. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o2395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sridevi, G. & Kalaivani, D. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Vaduganathan, M. & Doraisamyraja, K. (2014). Acta Cryst. E70, 256–258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015010075/su5140sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015010075/su5140Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015010075/su5140Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1006239
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




