The title arylsulfonyl glycinyl hydrazone Schiff base compound crystallizes as a monohydrate. In the crystal, a series of O—H⋯O and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds leads to the formation of corrugated sheets lying parallel to (100).
Keywords: crystal structure, synthesis, arylsulfonyl glycinyl hydrazone, hydrogen bonding
Abstract
The molecule of the title compound, C16H16ClN3O3S·H2O, is L-shaped being bent at the S atom; the S—N—C—C torsion angle is 132.0 (3)°. The central part of the molecule, C—C—N—N=C, is almost linear, with the C—C—N—N and C—N—N=C torsion angles being −174.1 (2) and 176.0 (2)°, respectively. The dihedral angle between the p-toluenesulfonyl ring and the S—N—C—C(=O) segment is 67.5 (4)°, while that between the two aromatic rings is 52.17 (11)°. In the crystal, the water H atom is involved in O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds with a sulfonamide O atom and the carbonyl O atom. The water O atom is itself hydrogen bonded to both NH hydrogen atoms. These four hydrogen bonds lead to the formation of corrugated sheets lying parallel to (100). There are also weak C—H⋯O contacts present within the sheets.
Chemical context
Hydrazones are an important class of organic compounds in the Schiff base family. The latter display various biological activities such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticonvulsant, analgesic, anticancer, antiparasitic, cardioprotective, antidepressant, antitubercular and anti-HIV activities. The hydrazone Schiff bases of aroyl, acyl, and heteroaroyl compounds are more versatile and flexible due to the presence of the C=O group, an additional donor site. N-Acylhydrazones containing a glycine residue have been investigated extensively in recent years for their biological and medical activities (Tian et al., 2011 ▸). Acylhydrazone derivatives which contain an amino acid moiety and an electron-donating substituent in the sulfonyl phenyl ring have been demonstrated to possess good antiviral activity (Tian et al., 2009 ▸).
In view of the biological activities of these Schiff bases, which are related to structural aspects, and as part of our studies on the effects of substituents on the structures of N-(aryl)-amides (Gowda et al., 2000 ▸; Rodrigues et al., 2011 ▸), N-chloroarylamides (Jyothi & Gowda, 2004 ▸) and N-bromoaryl-sulfonamides (Usha & Gowda, 2006 ▸), we report herein on the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound. This acylhydrazone derivative contains an amino acid moiety and an electron-donating substituent in the p-toluenesulfonyl ring.
Structural commentary
The molecular structure of the title compound is illustrated in Fig. 1 ▸. The conformations of the N—H and C—H bonds in the hydazone part are syn to each other, while the N—H and C=O bonds in the central part and the sulfonamide N—H and C—H bonds in the glycine segment are anti to each other. The C8—O3 bond length of 1.222 (3) Å indicates that the molecule exists in the keto form in the solid state. The C9—N3 bond length of 1.266 (3) Å confirms its significant double-bond character. The N2—N3 and C8—N2 bond distances are 1.384 (3) and 1.337 (3) Å, respectively, which indicate significant delocalization of the π-electron density over the hydrazone portion of the molecule. The molecule is bent at the S-atom with a S1—N1—C7—C8 torsion angle of 132.0 (2)°. The other central part of the molecule is almost linear with the C7—C8—N2—N3, C8—N2—N3—C9 and N2—N3—C9—C10 torsion angles being −174.1 (2), 176.0 (2) and −176.7 (2)°, respectively. The orientation of the sulfonamide group with respect to the attached p-toluenesulfonyl ring (C1–C6) is given by torsion angles C2—C1—S1—N1 = −99.8 (2)° and C6—C1—S1—N1 = 76.6 (2)°, while that of the hydrazone group with the attached benzene ring (C10-C15) is given by torsion angles C11—C10—C9—N3 = 9.9 (4)° and C15—C10—C9—N3 = −172.1 (2)°. The dihedral angles between the mean plane of the central segment [O3/N2/N3/C7–C9; maximum deviation = 0.065 (3) Å for atom N2] and the benzene rings (C1–C6 and C10–C15) are 65.22 (15) and 13.06 (14)°, respectively. The two benzene rings are inclined to one another by 52.16 (14)°.
Figure 1.
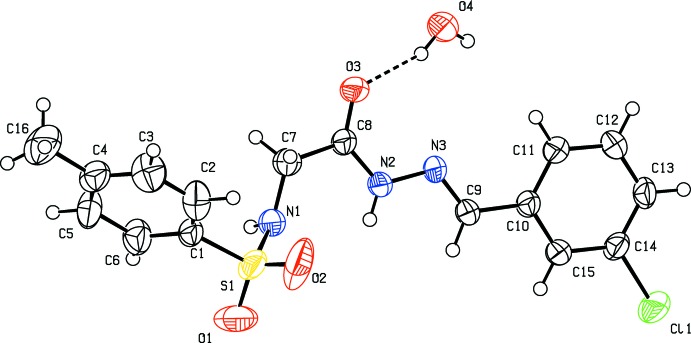
Molecular structure of the title compound, showing the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Supramolecular features
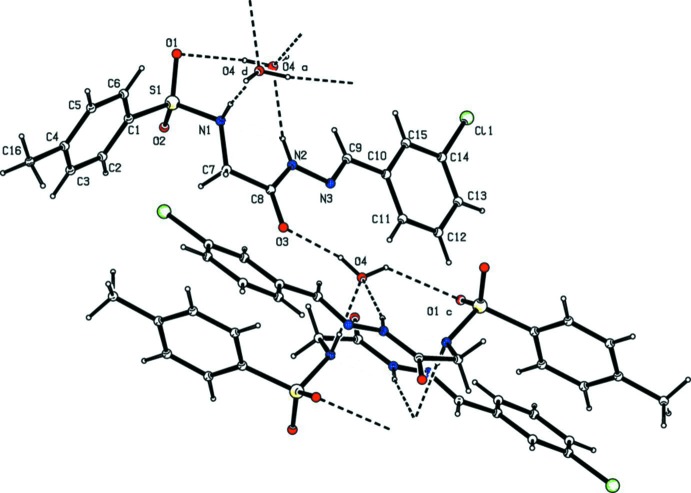
In the crystal, the water O-atom, O4, shows bifurcated hydrogen bonding with the amino-H atom of the hydrazide segment (N2) and the sulfonamide-H atom (N1); see Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 2 ▸. One of the H atoms of the water molecule is hydrogen bonded with a sulfonyl O atom, O1, generating  (6) and
(6) and 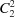 (7) chains. The other H atom shows hydrogen bonding with the carbonyl O atom, O3. These four hydrogen bonds lead to the formation of corrugated sheets lying parallel to (100); see Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 3 ▸. There are also weak C—H⋯O contacts present within the sheets (Table 1 ▸).
(7) chains. The other H atom shows hydrogen bonding with the carbonyl O atom, O3. These four hydrogen bonds lead to the formation of corrugated sheets lying parallel to (100); see Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 3 ▸. There are also weak C—H⋯O contacts present within the sheets (Table 1 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (, ).
| DHA | DH | HA | D A | DHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O4H41O3 | 0.85(3) | 1.94(3) | 2.752(3) | 159(3) |
| O4H42O1i | 0.85(3) | 2.60(3) | 3.274(3) | 138(3) |
| N1H1NO4ii | 0.84(3) | 2.06(3) | 2.895(4) | 171(3) |
| N2H2NO4iii | 0.84(2) | 2.29(2) | 3.107(3) | 167(2) |
| C13H13O2iv | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.366(3) | 161 |
| C15H15O3iii | 0.93 | 2.59 | 3.450(3) | 155 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 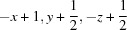 ; (ii)
; (ii) 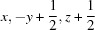 ; (iii)
; (iii) 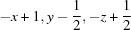 ; (iv)
; (iv) 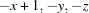 .
.
Figure 2.
Hydrogen bonding pattern in the title compound [see Table 1 ▸ for details; symmetry codes: (a) −x + 1, y −  , −z +
, −z +  ; (c) −x + 1, y +
; (c) −x + 1, y +  , −z +
, −z +  ; (d) x, −y +
; (d) x, −y +  , z +
, z +  ].
].
Figure 3.
A view along the c axis of the crystal packing of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines (see Table 1 ▸ for details), and C-bound H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (Version 5.36; Groom & Allen, 2014 ▸) for the fragment, viz. –NH–CH2–C(=O)–NH–N=CH–, yielded only one hit, namely N-(2-hydroxy-1-naphthylmethylene)-N′-(N-phenylglycyl)hydrazine (MEMTOO; Gudasi et al., 2006 ▸).
Synthesis and crystallization
The title compound was synthesized in a number of steps. Firstly p-toluenesulfonyl chloride (0.01 mol) was added to glycine (0.02 mol) dissolved in an aqueous solution of potassium carbonate (0.06 mol, 50 ml). The reaction mixture was stirred at 373 K for 6 h, then left overnight at room temperature, filtered and then treated with dilute hydrochloric acid. The solid N-(4-methylbenzenesulfonyl)glycine (L1) obtained was crystallized from aqueous ethanol.
Sulfuric acid (0.5 ml) was added to L1 (0.02 mol) dissolved in ethanol (30 ml) and the mixture was refluxed. The reaction was monitored by TLC at regular intervals. After completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was concentrated to remove excess ethanol. The product, N-(4-methylbenzenesulfonyl)glycine ethyl ester (L2) obtained was poured into water, neutralized with sodium bicarbonate and recrystallized from acetone.
The pure L2 (0.01 mol) was then added in small portions to a stirred solution of 99% hydrazine hydrate (10 ml) in 30 ml ethanol and the mixture was refluxed for 6 h. After cooling to room temperature, the resulting precipitate was filtered, washed with cold water and dried to obtain N-(4-methylbenzenesulfonyl)glycinyl hydrazide (L3).
A mixture of L3 (0.01 mol) and 3-chlorobenzaldehyde (0.01 mol) in anhydrous methanol (30 ml) and two drops of glacial acetic acid was refluxed for 8 h. After cooling, the precipitate was collected by vacuum filtration, washed with cold methanol and dried. It was recrystallized to constant melting point from methanol (457–458 K). The purity of the title compound was checked and characterized by its IR spectrum. The characteristic absorptions observed are 3253.9, 1680.0, 1597.1, 1334.7 and 1161.2 cm−1 for the stretching bands of N—H, C—O, C—N, S—O asymmetric and S—O symmetric, respectively.
Prism-like colourless single crystals of the title compound were grown from a DMF solution by slow evaporation of the solvent.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The water H atoms were located in a difference Fourier map and refined with the O—H distances restrained to 0.85 (2) Å, and with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(O). The U eq of atoms O1 and O2 were restrained to approximate isotropic behaviour. The NH H atoms were also located in a difference Fourier map and refined with Uiso(H) = 1.2U eq(N). The C-bound H atoms were positioned with idealized geometry and refined using a riding model: C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C) for methyl H atoms and 1.2U eq(C) for other H atoms.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C16H16ClN3O3SH2O |
| M r | 383.84 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, b, c () | 12.576(1), 12.769(2), 12.481(1) |
| () | 115.58(1) |
| V (3) | 1807.8(3) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo K |
| (mm1) | 0.35 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.48 0.40 0.36 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Sapphire CCD detector |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.849, 0.884 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2(I)] reflections | 11031, 3307, 2408 |
| R int | 0.026 |
| (sin /)max (1) | 0.602 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.041, 0.106, 1.04 |
| No. of reflections | 3307 |
| No. of parameters | 239 |
| No. of restraints | 17 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| max, min (e 3) | 0.24, 0.29 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008506/su5128sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008506/su5128Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008506/su5128Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1062518
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
HP thanks the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, New Delhi, for a research fellowship under its INSPIRE Program. BTG thanks the University Grants Commission, Government of India, New Delhi for a special grant under the UGC–BSR one-time grant to faculty.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C16H16ClN3O3S·H2O | F(000) = 800 |
| Mr = 383.84 | Dx = 1.410 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 3002 reflections |
| a = 12.576 (1) Å | θ = 3.1–27.8° |
| b = 12.769 (2) Å | µ = 0.35 mm−1 |
| c = 12.481 (1) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 115.58 (1)° | Prism, colourless |
| V = 1807.8 (3) Å3 | 0.48 × 0.40 × 0.36 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Sapphire CCD detector diffractometer | 3307 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2408 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.026 |
| ω scans | θmax = 25.4°, θmin = 3.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2009) | h = −11→15 |
| Tmin = 0.849, Tmax = 0.884 | k = −14→15 |
| 11031 measured reflections | l = −14→15 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.041 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.106 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0426P)2 + 0.8977P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3307 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 239 parameters | Δρmax = 0.24 e Å−3 |
| 17 restraints | Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.17126 (8) | −0.13298 (6) | −0.26071 (6) | 0.0738 (3) | |
| S1 | 0.76144 (8) | −0.01311 (5) | 0.61570 (6) | 0.0673 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.7033 (2) | −0.09611 (16) | 0.6464 (2) | 0.1062 (9) | |
| O2 | 0.8221 (3) | −0.0340 (2) | 0.54459 (19) | 0.1084 (10) | |
| O3 | 0.61344 (16) | 0.28736 (12) | 0.34493 (15) | 0.0527 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.6578 (2) | 0.06969 (17) | 0.54323 (18) | 0.0531 (6) | |
| H1N | 0.609 (2) | 0.075 (2) | 0.572 (3) | 0.064* | |
| N2 | 0.55088 (19) | 0.11910 (15) | 0.30730 (17) | 0.0429 (5) | |
| H2N | 0.550 (2) | 0.0597 (15) | 0.335 (2) | 0.052* | |
| N3 | 0.48871 (18) | 0.13740 (15) | 0.18666 (16) | 0.0411 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.8618 (2) | 0.04984 (19) | 0.7459 (2) | 0.0455 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.9647 (3) | 0.0911 (3) | 0.7515 (3) | 0.0625 (8) | |
| H2 | 0.9845 | 0.0822 | 0.6884 | 0.075* | |
| C3 | 1.0386 (3) | 0.1459 (3) | 0.8509 (3) | 0.0679 (8) | |
| H3 | 1.1078 | 0.1745 | 0.8538 | 0.081* | |
| C4 | 1.0120 (3) | 0.1590 (2) | 0.9455 (2) | 0.0558 (7) | |
| C5 | 0.9090 (3) | 0.1164 (2) | 0.9388 (2) | 0.0642 (8) | |
| H5 | 0.8899 | 0.1244 | 1.0025 | 0.077* | |
| C6 | 0.8329 (3) | 0.0622 (2) | 0.8393 (2) | 0.0598 (8) | |
| H6 | 0.7631 | 0.0344 | 0.8358 | 0.072* | |
| C7 | 0.6874 (3) | 0.1691 (2) | 0.5065 (2) | 0.0592 (8) | |
| H7A | 0.7692 | 0.1669 | 0.5196 | 0.071* | |
| H7B | 0.6800 | 0.2240 | 0.5566 | 0.071* | |
| C8 | 0.6120 (2) | 0.19752 (18) | 0.3780 (2) | 0.0404 (6) | |
| C9 | 0.4390 (2) | 0.05767 (18) | 0.12515 (19) | 0.0397 (6) | |
| H9 | 0.4432 | −0.0058 | 0.1634 | 0.048* | |
| C10 | 0.3749 (2) | 0.06248 (17) | −0.00476 (19) | 0.0373 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.3796 (2) | 0.14931 (18) | −0.0694 (2) | 0.0437 (6) | |
| H11 | 0.4218 | 0.2083 | −0.0301 | 0.052* | |
| C12 | 0.3216 (2) | 0.1485 (2) | −0.1919 (2) | 0.0485 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.3257 | 0.2068 | −0.2346 | 0.058* | |
| C13 | 0.2575 (2) | 0.0619 (2) | −0.2517 (2) | 0.0474 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.2185 | 0.0614 | −0.3343 | 0.057* | |
| C14 | 0.2526 (2) | −0.02361 (18) | −0.1869 (2) | 0.0440 (6) | |
| C15 | 0.3108 (2) | −0.02469 (18) | −0.0641 (2) | 0.0415 (6) | |
| H15 | 0.3070 | −0.0834 | −0.0217 | 0.050* | |
| C16 | 1.0936 (3) | 0.2202 (3) | 1.0535 (3) | 0.0944 (12) | |
| H16A | 1.1740 | 0.2051 | 1.0699 | 0.142* | |
| H16B | 1.0796 | 0.2005 | 1.1206 | 0.142* | |
| H16C | 1.0790 | 0.2937 | 1.0385 | 0.142* | |
| O4 | 0.4852 (2) | 0.38922 (15) | 0.13369 (18) | 0.0643 (6) | |
| H41 | 0.516 (3) | 0.344 (2) | 0.189 (3) | 0.096* | |
| H42 | 0.425 (2) | 0.364 (3) | 0.077 (3) | 0.096* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0936 (6) | 0.0521 (4) | 0.0468 (4) | −0.0165 (4) | 0.0030 (4) | −0.0128 (3) |
| S1 | 0.0968 (6) | 0.0392 (4) | 0.0341 (4) | 0.0075 (4) | −0.0016 (4) | −0.0071 (3) |
| O1 | 0.136 (2) | 0.0424 (11) | 0.0708 (14) | −0.0240 (11) | −0.0207 (13) | 0.0124 (10) |
| O2 | 0.132 (2) | 0.117 (2) | 0.0522 (13) | 0.0494 (17) | 0.0169 (14) | −0.0300 (13) |
| O3 | 0.0696 (12) | 0.0340 (9) | 0.0400 (10) | −0.0012 (8) | 0.0100 (9) | 0.0021 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0679 (16) | 0.0407 (12) | 0.0300 (11) | −0.0059 (11) | 0.0014 (10) | 0.0019 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0535 (13) | 0.0349 (11) | 0.0267 (10) | −0.0036 (9) | 0.0044 (9) | 0.0030 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0498 (12) | 0.0383 (11) | 0.0253 (10) | 0.0000 (9) | 0.0068 (9) | 0.0012 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0573 (17) | 0.0396 (13) | 0.0295 (12) | 0.0061 (12) | 0.0092 (12) | −0.0005 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0617 (19) | 0.082 (2) | 0.0438 (16) | 0.0111 (16) | 0.0229 (15) | −0.0023 (14) |
| C3 | 0.0481 (17) | 0.087 (2) | 0.0607 (19) | −0.0048 (16) | 0.0166 (15) | 0.0003 (17) |
| C4 | 0.0548 (18) | 0.0494 (15) | 0.0440 (16) | 0.0016 (13) | 0.0032 (13) | −0.0043 (12) |
| C5 | 0.073 (2) | 0.082 (2) | 0.0377 (15) | −0.0082 (17) | 0.0235 (15) | −0.0154 (14) |
| C6 | 0.0578 (18) | 0.0744 (19) | 0.0430 (15) | −0.0159 (15) | 0.0179 (14) | −0.0065 (14) |
| C7 | 0.075 (2) | 0.0436 (14) | 0.0333 (14) | −0.0112 (13) | −0.0013 (13) | 0.0017 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0464 (14) | 0.0353 (13) | 0.0310 (12) | 0.0009 (11) | 0.0088 (11) | −0.0005 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0461 (14) | 0.0368 (12) | 0.0285 (12) | 0.0009 (11) | 0.0088 (11) | 0.0039 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0402 (13) | 0.0364 (12) | 0.0293 (12) | 0.0029 (10) | 0.0092 (10) | −0.0002 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0521 (15) | 0.0377 (13) | 0.0364 (13) | −0.0043 (11) | 0.0143 (11) | −0.0029 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0609 (17) | 0.0452 (14) | 0.0346 (13) | 0.0018 (12) | 0.0160 (12) | 0.0074 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0575 (16) | 0.0508 (15) | 0.0258 (12) | 0.0086 (13) | 0.0102 (11) | 0.0011 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0494 (15) | 0.0374 (12) | 0.0336 (12) | 0.0015 (11) | 0.0069 (11) | −0.0073 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0492 (15) | 0.0351 (12) | 0.0339 (12) | 0.0009 (11) | 0.0120 (11) | 0.0021 (10) |
| C16 | 0.097 (3) | 0.082 (2) | 0.065 (2) | −0.019 (2) | −0.0017 (19) | −0.0223 (18) |
| O4 | 0.0862 (16) | 0.0459 (11) | 0.0450 (12) | 0.0082 (10) | 0.0134 (11) | 0.0081 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C14 | 1.741 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| S1—O2 | 1.423 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.512 (3) |
| S1—O1 | 1.430 (3) | C7—H7A | 0.9700 |
| S1—N1 | 1.618 (2) | C7—H7B | 0.9700 |
| S1—C1 | 1.763 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.468 (3) |
| O3—C8 | 1.222 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C7 | 1.452 (3) | C10—C15 | 1.386 (3) |
| N1—H1N | 0.833 (18) | C10—C11 | 1.387 (3) |
| N2—C8 | 1.337 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.381 (3) |
| N2—N3 | 1.384 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| N2—H2N | 0.836 (18) | C12—C13 | 1.382 (4) |
| N3—C9 | 1.266 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.370 (4) | C13—C14 | 1.376 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.373 (4) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.377 (4) | C14—C15 | 1.385 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.369 (4) | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.374 (4) | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C4—C16 | 1.512 (4) | O4—H41 | 0.85 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.382 (4) | O4—H42 | 0.844 (19) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | ||
| O2—S1—O1 | 120.10 (18) | N1—C7—H7B | 108.6 |
| O2—S1—N1 | 107.06 (14) | C8—C7—H7B | 108.6 |
| O1—S1—N1 | 104.62 (15) | H7A—C7—H7B | 107.6 |
| O2—S1—C1 | 107.26 (16) | O3—C8—N2 | 124.6 (2) |
| O1—S1—C1 | 109.67 (13) | O3—C8—C7 | 119.3 (2) |
| N1—S1—C1 | 107.51 (11) | N2—C8—C7 | 116.0 (2) |
| C7—N1—S1 | 119.6 (2) | N3—C9—C10 | 121.9 (2) |
| C7—N1—H1N | 113 (2) | N3—C9—H9 | 119.1 |
| S1—N1—H1N | 112 (2) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.1 |
| C8—N2—N3 | 119.05 (19) | C15—C10—C11 | 119.5 (2) |
| C8—N2—H2N | 120.8 (18) | C15—C10—C9 | 118.1 (2) |
| N3—N2—H2N | 120.2 (18) | C11—C10—C9 | 122.4 (2) |
| C9—N3—N2 | 115.02 (19) | C12—C11—C10 | 120.2 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.2 (2) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.9 |
| C2—C1—S1 | 120.5 (2) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.9 |
| C6—C1—S1 | 119.2 (2) | C11—C12—C13 | 120.7 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.8 (3) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.1 | C13—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.1 | C14—C13—C12 | 118.7 (2) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.2 (3) | C14—C13—H13 | 120.6 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.4 | C12—C13—H13 | 120.6 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.4 | C13—C14—C15 | 121.5 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.3 (3) | C13—C14—Cl1 | 119.37 (18) |
| C3—C4—C16 | 120.5 (3) | C15—C14—Cl1 | 119.12 (19) |
| C5—C4—C16 | 121.2 (3) | C14—C15—C10 | 119.4 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.5 (3) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.3 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.3 | C10—C15—H15 | 120.3 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.3 | C4—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 119.1 (3) | C4—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.5 | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.5 | C4—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—C8 | 114.6 (2) | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—H7A | 108.6 | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7A | 108.6 | H41—O4—H42 | 110 (3) |
| O2—S1—N1—C7 | −56.6 (2) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.6 (5) |
| O1—S1—N1—C7 | 174.9 (2) | S1—N1—C7—C8 | 132.0 (2) |
| C1—S1—N1—C7 | 58.4 (2) | N3—N2—C8—O3 | 3.4 (4) |
| C8—N2—N3—C9 | 176.0 (2) | N3—N2—C8—C7 | −174.1 (2) |
| O2—S1—C1—C2 | 15.1 (3) | N1—C7—C8—O3 | 165.3 (3) |
| O1—S1—C1—C2 | 147.0 (2) | N1—C7—C8—N2 | −17.0 (4) |
| N1—S1—C1—C2 | −99.8 (2) | N2—N3—C9—C10 | −176.7 (2) |
| O2—S1—C1—C6 | −168.5 (2) | N3—C9—C10—C15 | −172.1 (2) |
| O1—S1—C1—C6 | −36.5 (3) | N3—C9—C10—C11 | 9.9 (4) |
| N1—S1—C1—C6 | 76.6 (2) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | −0.6 (4) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.5 (4) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 177.4 (2) |
| S1—C1—C2—C3 | 175.8 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.6 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.8 (5) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.0 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.4 (5) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.5 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C16 | −179.4 (3) | C12—C13—C14—Cl1 | 179.4 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.4 (5) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | 0.4 (4) |
| C16—C4—C5—C6 | 178.7 (3) | Cl1—C14—C15—C10 | −179.45 (19) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.2 (4) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | 0.1 (4) |
| S1—C1—C6—C5 | −176.6 (2) | C9—C10—C15—C14 | −177.9 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O4—H41···O3 | 0.85 (3) | 1.94 (3) | 2.752 (3) | 159 (3) |
| O4—H42···O1i | 0.85 (3) | 2.60 (3) | 3.274 (3) | 138 (3) |
| N1—H1N···O4ii | 0.84 (3) | 2.06 (3) | 2.895 (4) | 171 (3) |
| N2—H2N···O4iii | 0.84 (2) | 2.29 (2) | 3.107 (3) | 167 (2) |
| C13—H13···O2iv | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.366 (3) | 161 |
| C15—H15···O3iii | 0.93 | 2.59 | 3.450 (3) | 155 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (iii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (iv) −x+1, −y, −z.
References
- Gowda, B. T., Kumar, B. H. A. & Fuess, H. (2000). Z. Naturforsch. Teil A, 55, 721–728.
- Groom, C. R. & Allen, F. H. (2014). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 662–671. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gudasi, K. B., Patil, M. S., Vadavi, R. S., Shenoy, R. V., Patil, S. A. & Nethaji, M. (2006). Transition Met. Chem. 31, 580–585.
- Jyothi, K. & Gowda, B. T. (2004). Z. Naturforsch. Teil A, 59, 64–68.
- Oxford Diffraction (2009). CrysAlis CCD and CrysAlis RED. Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, England.
- Rodrigues, V. Z., Foro, S. & Gowda, B. T. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o2179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tian, B., He, M., Tan, Z., Tang, S., Hewlett, I., Chen, S., Jin, Y. & Yang, M. (2011). Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 77, 189–198. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tian, B., He, M., Tang, S., Hewlett, I., Tan, Z., Li, J., Jin, Y. & Yang, M. (2009). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19, 2162–2167. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Usha, K. M. & Gowda, B. T. (2006). J. Chem. Sci. 118, 351–359.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008506/su5128sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008506/su5128Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015008506/su5128Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1062518
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report