Abstract
Background:
Macrosolen parasiticus (L.) Danser belonging to Loranthaceaea (mistletoe family) is a parasitic plant that grows on different host plants such as mango, jack fruit, peepal, neem tree, etc., This study was aimed to investigate the anti-cancer activity of methanolic and aqueous extract of stem of M. parasiticus.
Objectives:
To investigate the in vitro cytotoxic potential of the methanolic and aqueous extracts from stems of M. parasiticus against MCF-7 breast cancer cells by brine shrimp lethality (BSL) bioassay, MTT assay and sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay.
Materials and Methods:
The extracts were tested in human breast cancer cell lines in vitro for percentage cytotoxicity, apoptosis by acridine orange/ethidium bromide staining, LD50 and IC50 values after treatment with M. parasiticus extracts.
Results:
In BSL bioassay, aqueous extract showed more significant (P < 0.01) cytotoxicity with LD50 82.79 ± 2.67 μg/mL as compared to methanolic extract with LD50 125 ± 3.04 μg/mL. The methanolic extract of M. parasiticus showed IC50 97.33 ± 3.75 μg/mL (MTT) (P < 0.05) and 94.58 ± 3.84 μg/mL (SRB) (P < 0.01) assays against MCF-7. The aqueous extract of M. parasiticus demonstrated higher activity with IC50 59.33 ± 3.3 μg/mL (MTT) (P < 0.01) and 51.9 ± 1.87 μg/mL (SRB)(P < 0.01) assays, after 48 h of exposure and thus showed significant dose-dependent cytotoxic activity.
Conclusion:
The finding demonstrated that both extracts of M. parasiticus showed significant cytotoxic activity, however aqueous extract demonstrated higher activity against MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
Keywords: Apoptosis, breast cancer, cytotoxicity, Macrosolen parasiticus extracts
INTRODUCTION
Cancer is considered as one of the most terrified diseases and it's a class of diseases or disorders characterized by uncontrolled cell proliferation and tissue invasion or metastasis of abnormal cell in the body.[1] breast cancer is the second leading cause of death in women[2] and in breast cancer bone, lungs, liver, chest wall, and central nervous system are mainly affected by metastasis.[3] At present, chemotherapeutic agents, surgery and radiation are the commonly used treatment strategies in cancer; however they are not fully effective against the high prevalence or low survival rate. Hence, there is a great interest in the development of safe, low-cost anti-cancer agents from natural sources.[4]
Many plants and plant derived agents have been used for cancer treatment since 1950.[5] The phytoconstituents present in the plants are mainly responsible for its cytotoxic activity. The isolation of vincristine and vinblastine from vinca and podophyllotoxins from Podophyllum hexandrum are considered as milestones in the development of anti-cancer agents.[6,7] This led to the discovery of other compounds in cancer treatment such as taxanes, camptothecins, and combretastatins.[8,9]
Plant-derived agents act by modulating various signaling pathways in cancer cells. Plant-products are known to modulate multiple signaling pathways simultaneously; hence, they can be very effective in inhibiting uncontrolled cell proliferation of cancer cells, which have multiple survival strategies. Naturally herbs are curative, whereas chemotherapy and cytotoxic drugs are inherently destructive.[10]
Macrosolen parasiticus L. Danser (Loranthaceae) also known as Elytranthe parasiticus or Parasite Honeysuckle is a parasitic shrub, found in the Western Ghats. M. parasiticus commonly grows on mango, peepal and jack trees.[11] phytochemical investigation of the plant revealed the presence of phytosterols, saponins, phenolic compounds and flavonoids.[12] M. parasiticus has been reported to have significant anti-oxidant activity and anti-tumor activity against Ehrlich ascites carcinoma.[13,14] The present study was aimed to investigate the in vitro cytotoxic potential of methanolic and aqueous extracts from stem of M. parasiticus against MCF-7 breast cancer cells (estrogen receptor [ER] positive) by brine shrimp lethality (BSL) bioassay, MTT assay and sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant material
The stems of M. parasiticus were collected from Manipal, Karnataka, India in the month of September 2009 and were authenticated by Dr. Gopalakrishna Bhat, Taxonomist, Department of Botany, Poorna Prajna College, Udupi, Karnataka, India. A voucher specimen (PP 565) has been deposited in the museum of Department of Pharmacognosy, Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences (Manipal, India).
Reagents
All chemicals and solvents (analytical grade) were obtained from Nice Chemicals, Mumbai. Dulbecco's minimum essential medium (DMEM) media, 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and MTT reagent was purchased from Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, USA. Tissue culture flasks and 96 well plates were procured from Tarson and Nunc, USA). Trypsin phosphate versene glucose (TPVG) solution (Himedia, Mumbai) were used in the present study.
Plant extract
The shade dried, coarsely powdered M. parasiticus stem (500 g) was extracted with methanol (3 L × 1 L) using soxhlet extractor. For aqueous extract, 500 g of the powdered stem was macerated with water: Chloroform (99:1) for 7 days. The extracts were concentrated and dried in vacuo to get the percentage yield of methanolic and aqueous extracts 11.9 and 14.4% w/w, respectively.
Cell line and culture medium
Human breast cancer cells (MCF-7) were procured from National Centre for Cell Science Pune, India. MCF-7 cells were grown in 75 cm2 tissue culture flasks containing DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, TPVG solution at 37°C in CO2 incubator in an atmosphere of humidified 5% CO2 and 95% air. The cells were maintained by routine sub culturing in 75 cm2 tissue culture flasks.
Brine shrimp lethality bioassay
A total of 100 mg of eggs roughly represents 2.5–3.0 1000 of eggs. Hatching chamber was fabricated as per the design used by Meyer et al.[15] The chamber was made of glass, with aluminum lid on top. The chamber was divided into two equal parts with the help of a laminated plywood divider having a number of holes of 2 mm size. One of the compartments was illuminated with a lamp (60 W) while the other was darkened. Both the chambers were aerated.
Stock solution was prepared by dissolving 5 mg of sample extracts with 5 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (1000 μg/mL). From this stock 50 μL, 250 μL and 500 μL were taken and volume was made up to 5 mL (in 7 mL vial capacity) with solution which contain specific volume of brine and yeast suspension to get the final drug concentration of 10 ppm, 50 ppm and 100 ppm. The dilutions were made in triplicates for each dose level. Nauplii was collected using a pipette and transferred 10 such shrimps to each sample vial. The artificial sea water prepared according to the composition given by Dr. Vasudevappa, Research Officer, FRS, Hesaraghatta, Bengaluru. A volume of 5 mL of water and a drop of dry yeast suspension were added to each vial. survivors were counted after 24 h, and LC50 values were calculated.
MTT assay
100 μl of cell suspension of density 1 × 104 cells/well was placed into each well of 96-well plates and incubated for 24 h. Plant extracts were dissolved in DMSO and added (31.25–250 μg/mL) to cultured cells in 96 well plates and incubated for 24 h. Then, the medium was removed and washed with 200 μl phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Added 100 μL of the tetrazolium dye (MTT) solution (1 mg/mL in PBS) to each well of 96 well plates and incubated for 4 h at 37°C. MTT reagent was discarded by inverting the microplates. Formed formazan crystals were dissolved by adding 100 μL of DMSO. The plate was placed in a plate shaker for 5 min. then optical density was read on a microplate reader (BioTek, USA) at 540 nm.[16,17] The experiment was performed in triplicates. Results were expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) values.
Sulforhodamine B assay
100 μl of cell suspension of density 1 × 104 cells/well was placed into each well of 96-well plates and incubated for 24 h. A range of concentrations (31.25–250 μg/mL) of extracts was made in the culture medium. 100 μl of test sample of each concentration was added to every well except control wells. only 0.1% DMSO was added in the control group. After 48 h, the cells were fixed with ice-cold trichloroacetic acid (100 μl/well, 10% w/v) for 1 h at 4°C. To the washed and dried plates, added 100 μL SRB (0.057% w/v in 1% aqueous acetic acid) solution and kept at room temperature for 30 min. The unbound SRB solution was removed by washing the plates 5 times with 1% v/v acetic acid. Washed plates were then dried. 200 μL of 10 mM Tris Base (pH 10.5) was added to each well to solubilize the bound SRB. It was then placed in a shaker for 5–10 min. Then, the plates were read in a 96-well plate reader with working wavelength of 570 nm and optical density was noted.[18]
Acridine orange/ethidium bromide staining
Cancer cells were seeded in T-25 flasks and allowed to grow for 24 h. The extracts were added and incubated, then stained with acridine orange (AO), followed by ethidium bromide (EB). The cells were observed under a fluorescent microscope (Polywar, Reinchard Jung).[19]
Statistical analysis
All the experiments were performed in triplicates. Data were represented as mean ± SEM values. The IC50 or LD50 values were obtained by nonlinear regression using Microsoft Excel spread sheet application. Statistical analysis of the data were performed by one-way ANOVA (GraphPad Prism 5.02, GraphPad Software, Inc., California) followed by Tukey's test.
RESULTS
Brine shrimp lethality bioassay
Both methanolic and aqueous extracts of M. parasiticus screened for BSL bioassay were found to be effective. The LD50 of methanolic and aqueous extracts was found to be 125 ± 3.04 μg/mL and 82.79 ± 2.67 μg/mL, respectively [Figure 1].
Figure 1.
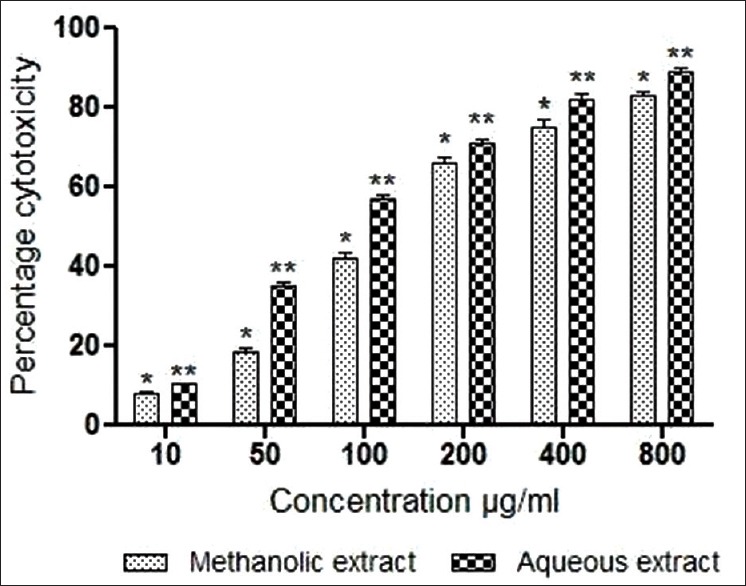
Effect of various extracts of stem of Macrosolen. parasiticus on brine shrimp lethality. Results were expressed as mean values ± standard deviation of independent experiments performed in triplicate. The values were significant at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 (indicated by single asterisk [*] and a double asterisk [**] respectively) compared to control using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test
Acridine orange/ethidium bromide staining
Figure 2 shows the morphological examination of MCF-7 cells with dual staining using AO/EB. Cells, which endured apoptosis showed nuclear shrinking and apoptotic bodies. AO gave green color to live nuclei, and dead cells were stained red with EB.
Figure 2.
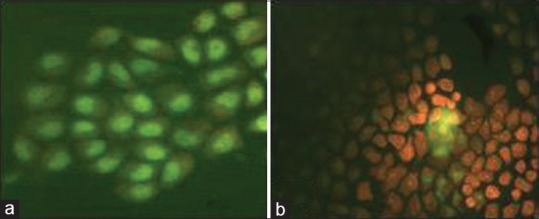
Fluorescence microscopy of MCF-7 stained with acridine orange/ethidium bromide after treatment with Macrosolen parasiticus extract. (a) Normal cell; (b) Treatment with extracts led to nuclear shrinking and formation of apoptotic bodies
MTT and sulforhodamine B assay
The percentage cell growth inhibition by M. parasiticus stem extracts at a concentration range of 31.25–250 μg/mL was determined after 48 h. The methanolic and aqueous extracts showed significant activity against MCF-7 breast cancer cells using MTT assay [Figure 3]. Both the extracts demonstrated a dose-dependent inhibition with IC50 values of 97.33 ± 3.75 μg/mL and 59.33 ± 3.3 μg/mL, respectively. Results of the SRB assay are presented in Figure 4. As evident from this figure, aqueous and methanolic extracts demonstrated dose-dependent inhibition of cell survival with IC50 values of 94.58 ± 3.84 μg/mL and 51.9 ± 1.87 μg/mL respectively. In general, extracts demonstrated cytotoxic activity in a dose depending manner, aqueous extract of M. parasiticus was found to be significantly (P < 0.01) more effective in both assays compared to methanolic extract. However, methanolic extract demonstrated significant values (P < 0.01) against MCF-7 breast cancer cells by SRB assay, compared to MTT assay (P < 0.05).
Figure 3.
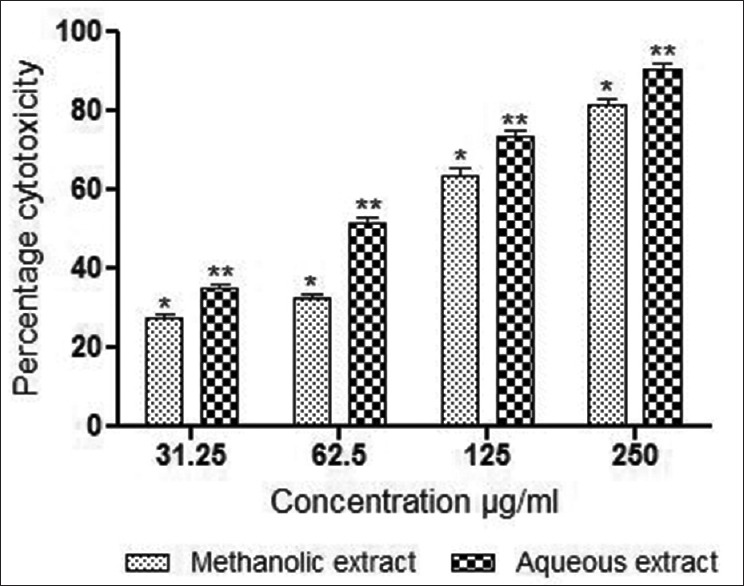
In vitro cytotoxic activity of methanolic and aqueous extracts of stem of M. parasiticus in MCF-7 breast cancer cells (estrogen receptor positive) by MTT assay at 48 h of exposure. Results were expressed as mean values ± standard deviation of independent experiments performed in triplicate. The values were significant at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 (indicated by single asterisk [*] and double asterisk [**] respectively) compared to control using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test
Figure 4.
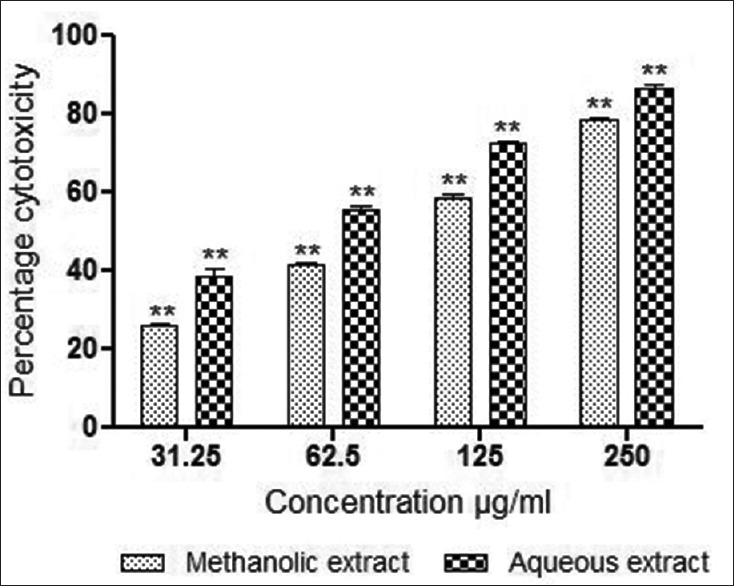
In vitro cytotoxic activity of methanolic and aqueous extracts of stem of Macrosolen parasiticus in MCF-7 breast cancer cells (estrogen receptor positive) by sulforhodamine B assay at 48 h of exposure. Results were expressed as mean values ± standard deviation of independent experiments performed in triplicate. The values were significant at P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 (indicated by single asterisk [*] and double asterisk [**] respectively) compared to control using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test
DISCUSSION
According to a recent survey by GLOBOCAN project, it was found that nearly 1, 55, 000 new cases of breast cancer will be diagnosed in 2015 and almost 76000 women in India are likely to die of the disease.[20] As such, we chose to screen M. parasiticus extracts for cytotoxicity against MCF-7, an ER positive breast cancer cell line. In general, breast cancer cell lines can be classified as either ER positive or ER negative.[21] The major goal in anti-cancer treatment is the development of molecules with improved therapeutic activity and selectivity. plant derived agents are used in cancer therapy as a cytotoxic agent. Use of nonherbal cytotoxic drug and chemotherapy is often destructive and not curative. Development of cytotoxic drug or formulation using plant products reduces the risk of side effects.
M. parasiticus, known locally as Bandanekke in Kannada is a parasitic plant that belongs to the family Loranthaceae. There are numerous plants in this family such as Viscum album, Scurrula ferruginea, Helixanthera parasiticus, Viscum album coloratum, Dendrophthoe Falcata etc., that are reported to have remarkable anti-cancer potential both in vitro and in vivo.[22,23,24,25,26,27] M. parasiticus extract showed anti-oxidant properties against in vitro models and also possess anti-cancer properties against Ehrlich ascites carcinoma.[11,12,13] The major components of M. parasiticus are polyphenols, flavonoids, and saponins, which have anti-oxidant and anti-cancer activity. Plants with anti-oxidant activity show anti-cancer properties by inhibiting the proliferation of multiple human cancer cells.[14] In animals the dietary polyphenol exhibits anti-carcinogenic activity.[28]
Moderate level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) are required for cell proliferation, and differentiation, but high levels produce oxidative damage to DNA resulting in mutation; leading to cancer. flavonoids are responsible for preventing the generation of enzymes required for the production of ROS, thus inhibiting over production of ROS and progression of carcinogenesis. Saponins are reported to have antitumor, anti-oxidant and anti-mutagenic activity. Saponins produce cytotoxicity by preventing the growth of cells, which are cancerous, thereby reducing the risk of human cancer. Polyphenols have free radical scavenging activity and protect DNA damage caused by ROS. It also induces apoptosis and inhibits angiogenesis.
The present study suggests that the main compounds such as polyphenols, flavonoids and saponins could be responsible for its cytotoxic activity against MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. screening of cytotoxicity in cultured cancer cells and in the animal model are necessary to evaluate the anti-cancer potential of plants prior to clinical trials.[29] Breast cancer cell lines are either ER positive or ER negative. Hence, developing an anti-cancer herbal agent, which is effective to both ER positive and ER negative breast cancer is important to reduce the risk level of breast cancer.
CONCLUSION
Significant activity has been observed in both aqueous and methanolic extracts of M. parasiticus. Methanolic and aqueous extract of M. parasiticus contains phenolic compounds, saponins, and flavonoid.[11] Cytotoxicity may be due to the presence of chemopreventive constituents in the plant extracts. Further studies on M. parasiticus will be carried out to identify the exact compounds responsible for the cytotoxicity and its mechanism of action.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors would like to thank Manipal University and Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Manipal, Karnataka, India for providing the necessary facilities to carry out this work.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Kaufman D, Chabner BA. Clinical strategies for cancer treatment: The role of drugs. Cancer Chemotherapy and Biotherapy: Principles and Practice. In: Chabner BA, Longo DL, editors. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven; 1996. pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nor-Aini AS, Merrina A, Stanslas J, Sreeramanan S. Cytotoxic potential on breast cancer cells using selected forest species found in Malaysia. Int J Cancer Res. 2008;4:103–9. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zia MK, Rmali KA, Mansel RE, Jiang WG. Level of expression of parathyroid hormone related protein and its receptor in human breast cancer and its correlation with the clinical outcome. Int J Cancer Res. 2007;3:92–102. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Moongkarndi P, Kosem N, Kaslungka S, Luanratana O, Pongpan N, Neungton N. Antiproliferation, antioxidation and induction of apoptosis by Garcinia mangostana (mangosteen) on SKBR3 human breast cancer cell line. J Ethnopharmacol. 2004;90:161–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2003.09.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Publishers; 2002. Introduction. The Genetic Basis of Human Cancer. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Cragg GM, Kingston DG, Newman DJ. USA (FL): Brunner-Routledge Psychology Press, Taylor and Francis Group; 2005. Anticancer Agents from Natural Products. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Newman DJ, Cragg GM, Snader KM. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the period 1981-2002. J Nat Prod. 2003;66:1022–37. doi: 10.1021/np030096l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cassady JM, Dourus JD. 2nd ed. New York: Academic Press; 1980. Anticancer Agents Based on Natural Product Models. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pinney KG, Jelinak C, Edvardsen K, Chaplin DJ, Petit GR. The Discovery and Development of the Combrestatins. In: Cragg GM, Kingston DG, Newman DJ, editors. Anticancer Agents from Natural Products. Boca Raton (FL): Brunner-Routledge Psychology Press, Taylor and Francis Group. 2005. pp. 5–22. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hopking AN. The Use of Herbs and Natural Plant Compounds in the Fight against Cancer. Cancer support association, Information, Wellness and Healing. [Last accessed on 2014 Feb 21]. Available from: http://www.cancersupportwa.org.au/newsletter_article.php?news_ id=270 .
- 11.Bhat KG. Manipal: Manipal Press Limited; 2003. Flora of Udupi. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sodde V, Dashora N, Prabhu K, Bhagat J, Lobo R. Histological and physico-chemical studies of Macrosolen parasiticus (L.) Danser stem – A common parasitic medicinal plant. Pharm Sin. 2011;2:217–21. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sodde V, Dashora N, Prabhu K, Lobo R. Antioxidant activities of methanolic and aqueous extract of Macrosolen parasiticus (L.) Danser. Int J Res Ayurveda Pharm. 2011;2:207–10. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sodde V, Dashora N, Prabhu K, Lobo R. Evaluation of anticancer activity of Macrosolen parasiticus (L.) Danser on Enrlich's ascites carcinoma treated mice. Int Cancer Res. 2011;7:135–43. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Meyer BN, Ferrigni NR, Putnam JE, Jacobsen LB, Nichols DE, McLaughlin JL. Brine shrimp: A convenient general bioassay for active plant constituents. Planta Med. 1982;45:31–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983;65:55–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dua P, Gude RP. Antiproliferative and antiproteolytic activity of pentoxifylline in cultures of B16F10 melanoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2006;58:195–202. doi: 10.1007/s00280-005-0155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Houghton P, Fang R, Techatanawat I, Steventon G, Hylands PJ, Lee CC. The sulphorhodamine (SRB) assay and other approaches to testing plant extracts and derived compounds for activities related to reputed anticancer activity. Methods. 2007;42:377–87. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Amarante-Mendes GP, Bossy-Wetzel E, Brunner T, Green DR. Apoptosis assay. In: Spector DL, Goldman RD, Leinwand LA, editors. Cell: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Manual on Cell Biology. New York: Cold Spring Harbor; pp. 15.1–15.24. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, et al. GLOBOCAN 2012. v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC Cancer Base No. 11. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. [Last accessed on 2014 Dec 11]. Available from: http://www.globocan.iarc.fr .
- 21.Swami S, Raghavachari N, Muller UR, Bao YP, Feldman D. Vitamin D growth inhibition of breast cancer cells: Gene expression patterns assessed by cDNA microarray. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2003;80:49–62. doi: 10.1023/A:1024487118457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Graham JG, Quinn ML, Fabricant DS, Farnsworth NR. Plants used against cancer – An extension of the work of Jonathan Hartwell. J Ethnopharmacol. 2000;73:347–77. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(00)00341-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lohézic-Le Dévéhat F, Tomasi S, Fontanel D, Boustie J. Flavonols from Scurrula ferruginea Danser (Loranthaceae) Z Naturforsch C. 2002;57:1092–5. doi: 10.1515/znc-2002-11-1224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lirdprapamongkol K, Mahidol C, Thongnest S, Prawat H, Ruchirawat S, Srisomsap C, et al. Anti-metastatic effects of aqueous extract of Helixanthera parasitica. J Ethnopharmacol. 2003;86:253–6. doi: 10.1016/s0378-8741(03)00072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yoon TJ, Yoo YC, Kang TB, Baek YJ, Huh CS, Song SK, et al. Prophylactic effect of Korean mistletoe (Viscum album coloratum) extract on tumor metastasis is mediated by enhancement of NK cell activity. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1998;20:163–72. doi: 10.1016/s0192-0561(98)00024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lobo R, Dashora N, Sodde V, Bhagat J, Prabhu KS. Antitumor activity of Dendrophthoe falcata against Ehrlich ascites carcinoma in Swiss albino mice. Pharm Crops. 2011;2:1–7. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kodithala S, Yoganandam G, Kiranmai M. Pharmacognostical, phytochemical and anticancer studies of Dendrophthoe falcata (l.f.) ettingsh. (Loranthaceae) growing on the host plant Azadirachta indica (Meliaceae) Int J Pharm Biol Sci. 2004;74:1013–26. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ju EM, Lee SE, Hwang HJ, Kim JH. Antioxidant and anticancer activity of extract from Betula platyphylla var. Japonica. Life Sci. 2004;74:1013–26. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2003.07.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Singh AV, Xiao D, Lew KL, Dhir R, Singh SV. Sulforaphane induces caspase-mediated apoptosis in cultured PC-3 human prostate cancer cells and retards growth of PC-3xenografts in vivo. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25:83–90. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgg178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


