Abstract
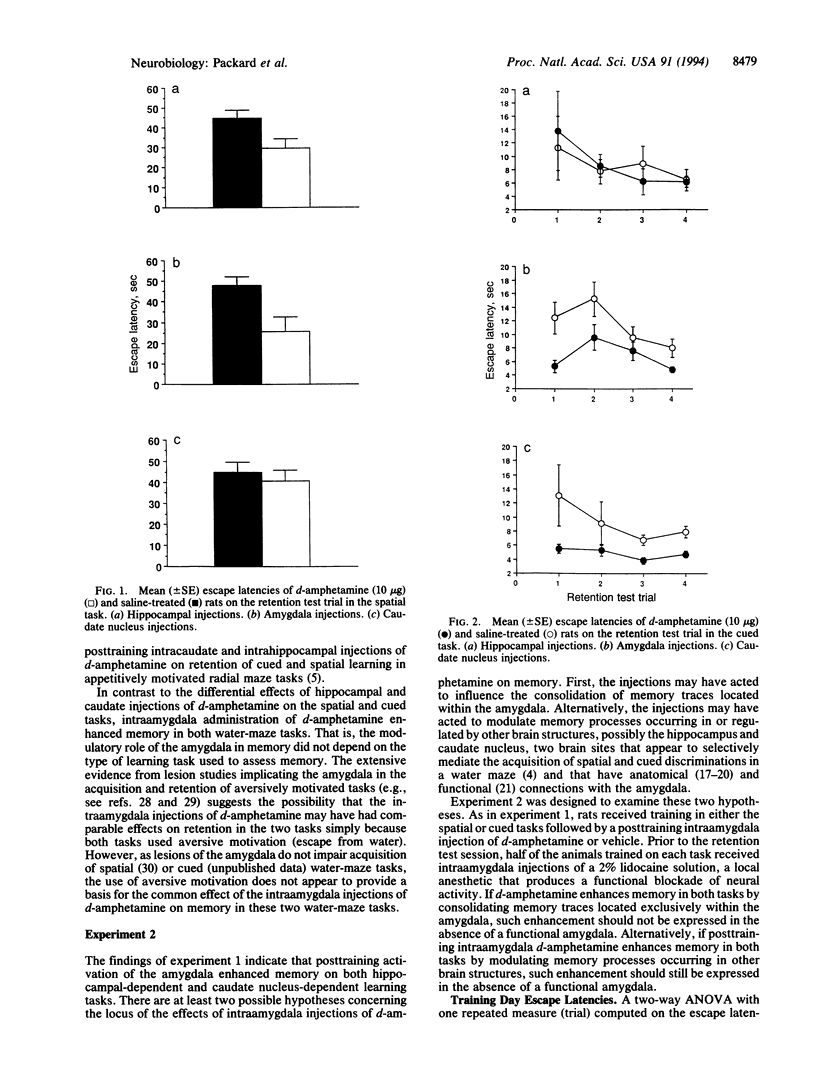
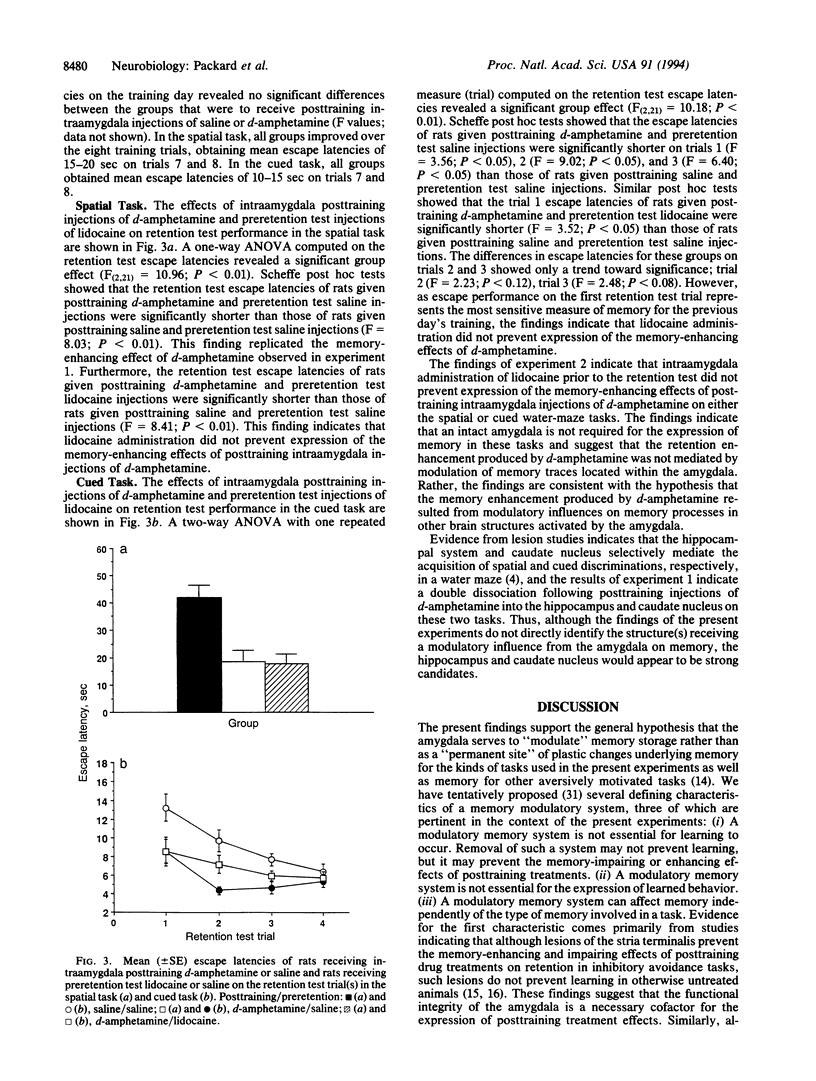
These experiments investigated the effects, on memory, of injections of d-amphetamine (10 micrograms/0.5 microliter) administered into the amygdala, hippocampus, or caudate nucleus immediately after training in cued or spatial water-maze tasks. In experiment 1, rats received an eight-trial training session on one of the two tasks followed by injections of d-amphetamine or saline. Retention was tested 24 hr later. On the spatial task, intrahippocampal, but not intracaudate, injections of d-amphetamine facilitated retention. In contrast, on the cued task intracaudate, but not intrahippocampal, injections of d-amphetamine facilitated retention. Posttraining intraamygdala injections of d-amphetamine enhanced retention of both tasks. In experiment 2, lidocaine (2% solution; 1.0 microliter) injected intraamygdally prior to the retention test did not block the memory enhancement induced by posttraining intraamygdala injections of d-amphetamine. The findings (i) provide further evidence of a dissociation between the roles of the hippocampus and caudate nucleus in different forms of memory, (ii) indicate that the modulatory role of the amygdala is not limited to either of the two different forms of memory represented in spatial and cued discriminations in a water maze, and (iii) are consistent with previous findings indicating that amygdala influences on memory storage are not mediated by lasting neural changes located within the amygdala.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cohen N. J., Squire L. R. Preserved learning and retention of pattern-analyzing skill in amnesia: dissociation of knowing how and knowing that. Science. 1980 Oct 10;210(4466):207–210. doi: 10.1126/science.7414331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. The role of the amygdala in fear and anxiety. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1992;15:353–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.15.030192.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everitt B. J., Cador M., Robbins T. W. Interactions between the amygdala and ventral striatum in stimulus-reward associations: studies using a second-order schedule of sexual reinforcement. Neuroscience. 1989;30(1):63–75. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch D. M., Wong E. E., Derian E. L., Chen X. H., Nowlin-Finch N. L., Brothers L. A. Neurophysiology of limbic system pathways in the rat: projections from the amygdala to the entorhinal cortex. Brain Res. 1986 Apr 9;370(2):273–284. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90482-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf P., Schacter D. L. Implicit and explicit memory for new associations in normal and amnesic subjects. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn. 1985 Jul;11(3):501–518. doi: 10.1037//0278-7393.11.3.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiroi N., White N. M. The lateral nucleus of the amygdala mediates expression of the amphetamine-produced conditioned place preference. J Neurosci. 1991 Jul;11(7):2107–2116. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-07-02107.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsh R. The hippocampus and contextual retrieval of information from memory: a theory. Behav Biol. 1974 Dec;12(4):421–444. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6773(74)92231-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley A. E., Domesick V. B., Nauta W. J. The amygdalostriatal projection in the rat--an anatomical study by anterograde and retrograde tracing methods. Neuroscience. 1982 Mar;7(3):615–630. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(82)90067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita H., Kitai S. T. Amygdaloid projections to the frontal cortex and the striatum in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Aug 1;298(1):40–49. doi: 10.1002/cne.902980104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krettek J. E., Price J. L. Amygdaloid projections to subcortical structures within the basal forebrain and brainstem in the rat and cat. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Mar 15;178(2):225–254. doi: 10.1002/cne.901780204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeDoux J. E., Iwata J., Cicchetti P., Reis D. J. Different projections of the central amygdaloid nucleus mediate autonomic and behavioral correlates of conditioned fear. J Neurosci. 1988 Jul;8(7):2517–2529. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-07-02517.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang K. C., McGaugh J. L. Lesions of the stria terminalis attenuate the enhancing effect of post-training epinephrine on retention of an inhibitory avoidance response. Behav Brain Res. 1983 Jul;9(1):49–58. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(83)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald R. J., White N. M. A triple dissociation of memory systems: hippocampus, amygdala, and dorsal striatum. Behav Neurosci. 1993 Feb;107(1):3–22. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.107.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGaugh J. L. Drug facilitation of learning and memory. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1973;13:229–241. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.13.040173.001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGaugh J. L., Introini-Collison I. B., Nagahara A. H., Cahill L., Brioni J. D., Castellano C. Involvement of the amygdaloid complex in neuromodulatory influences on memory storage. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1990 Winter;14(4):425–431. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7634(05)80065-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R. G., Garrud P., Rawlins J. N., O'Keefe J. Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):681–683. doi: 10.1038/297681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packard M. G., Hirsh R., White N. M. Differential effects of fornix and caudate nucleus lesions on two radial maze tasks: evidence for multiple memory systems. J Neurosci. 1989 May;9(5):1465–1472. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-05-01465.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packard M. G., McGaugh J. L. Double dissociation of fornix and caudate nucleus lesions on acquisition of two water maze tasks: further evidence for multiple memory systems. Behav Neurosci. 1992 Jun;106(3):439–446. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.106.3.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packard M. G., White N. M. Dissociation of hippocampus and caudate nucleus memory systems by posttraining intracerebral injection of dopamine agonists. Behav Neurosci. 1991 Apr;105(2):295–306. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.105.2.295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packard M. G., White N. M. Memory facilitation produced by dopamine agonists: role of receptor subtype and mnemonic requirements. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1989 Jul;33(3):511–518. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(89)90378-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R. J., Kolb B., Whishaw I. Q. Spatial mapping: definitive disruption by hippocampal or medial frontal cortical damage in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Aug 31;31(3):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90032-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R. J., McDonald R. J. Hippocampus, amygdala, and memory deficits in rats. Behav Brain Res. 1990 Feb 12;37(1):57–79. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(90)90072-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrington E. K., Weiskrantz L. Amnesia: a disconnection syndrome? Neuropsychologia. 1982;20(3):233–248. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(82)90099-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zola-Morgan S., Squire L. R., Mishkin M. The neuroanatomy of amnesia: amygdala-hippocampus versus temporal stem. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1337–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.6890713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



