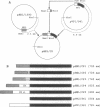
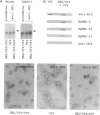
Abstract
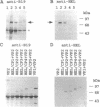
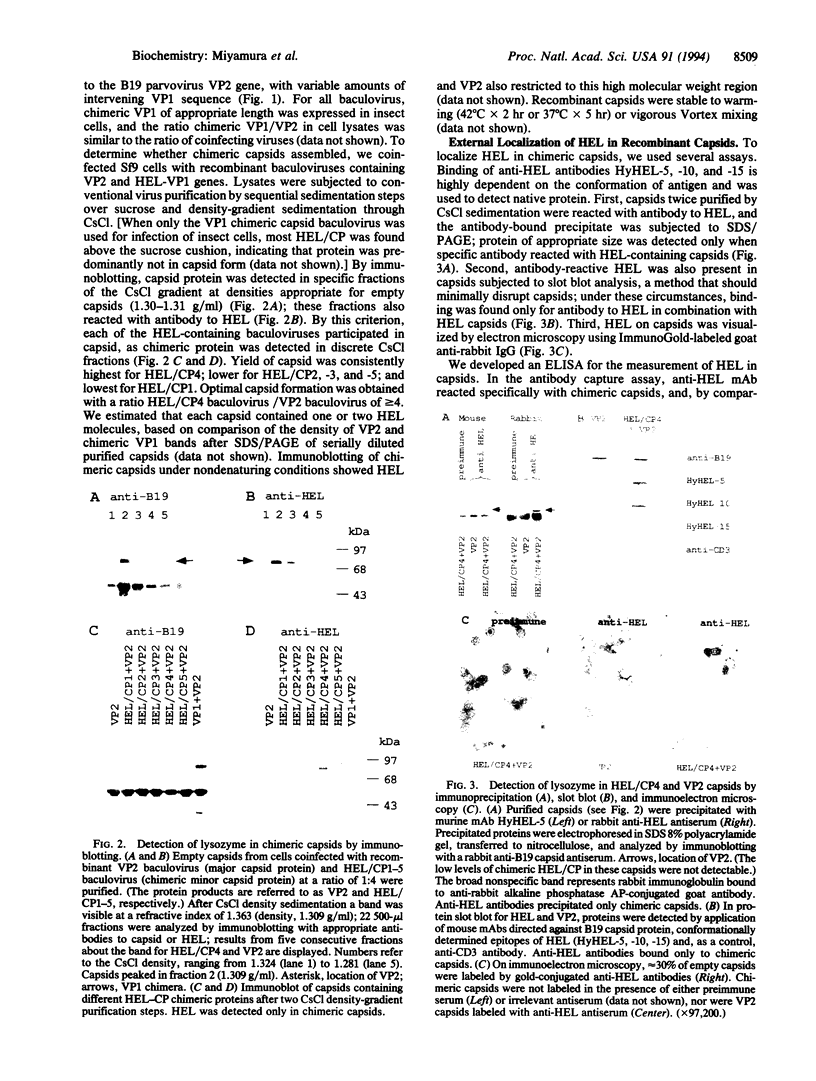
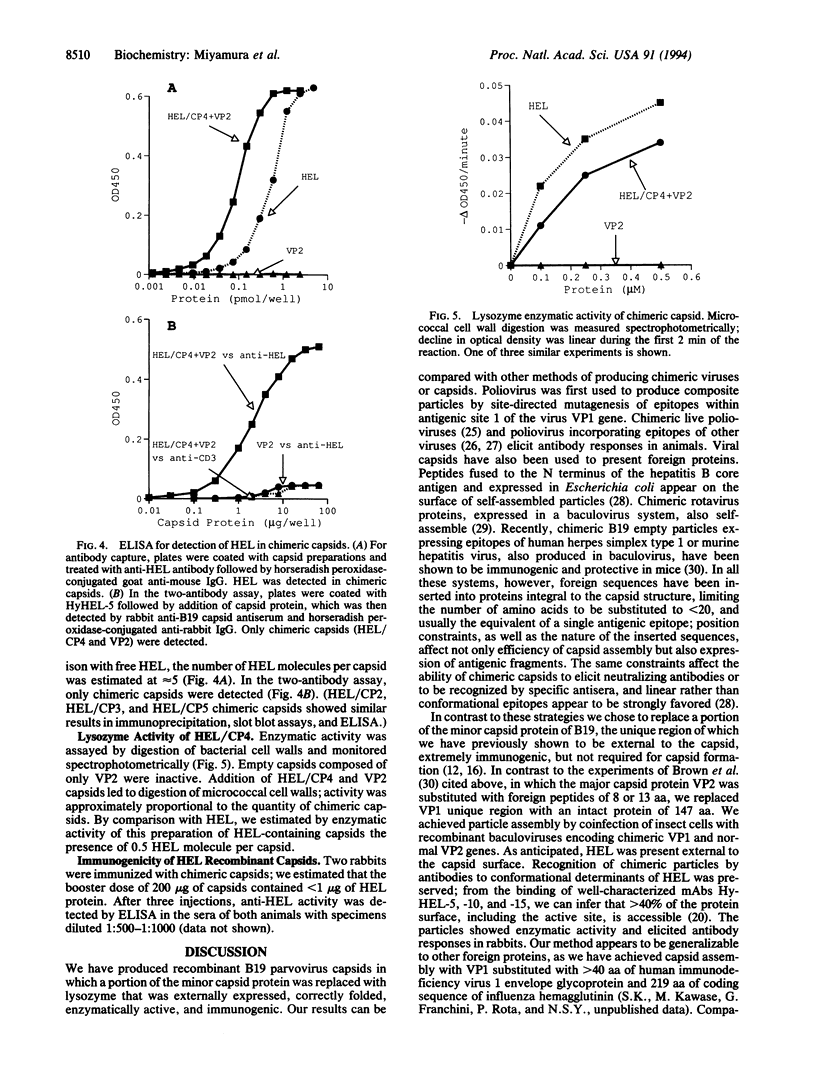
Empty capsids of the human pathogenic parvovirus B19 can be produced in a baculovirus system. B19 capsids are composed mainly of major capsid protein (VP2) and a small amount of minor capsid protein (VP1); VP1 is identical to VP2 but contains an additional 227-aa N-terminal region ("unique" region). A portion of that region of VP1 is external to the capsid, and VP1 is not required for capsid formation. We substituted the unique region with a sequence encoding the 147 aa of hen egg white lysozyme (HEL) and constructed recombinant baculoviruses with variable amounts of retained VP1 sequence joined to the VP2 backbone. After cotransfection with VP2 baculovirus and expression in insect cells, capsids were purified by density sedimentation. Purified recombinant capsids contained HEL. External presentation of HEL was demonstrated by immunoprecipitation, ELISA, and immune electron microscopy using anti-lysozyme monoclonal antibodies or specific rabbit antisera. Empty particles showed enzymatic activity in a micrococcal cell wall digestion assay. Rabbits inoculated with capsids made antibodies to HEL. Intact heterologous protein can be incorporated in B19 particles and presented on the capsid surface, properties that may be useful in vaccine development, cell targeting, and gene therapy.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agbandje M., McKenna R., Rossmann M. G., Kajigaya S., Young N. S. Preliminary X-ray crystallographic investigation of human parvovirus B19. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):170–174. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90833-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmeyer R., Murdin A. D., Harber J. J., Wimmer E. Construction and characterization of a poliovirus/rhinovirus antigenic hybrid. Virology. 1991 Oct;184(2):636–644. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90433-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bansal G. P., Hatfield J. A., Dunn F. E., Kramer A. A., Brady F., Riggin C. H., Collett M. S., Yoshimoto K., Kajigaya S., Young N. S. Candidate recombinant vaccine for human B19 parvovirus. J Infect Dis. 1993 May;167(5):1034–1044. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.5.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. S., Welling-Wester S., Feijlbrief M., Van Lent J. W., Spaan W. J. Chimeric parvovirus B19 capsids for the presentation of foreign epitopes. Virology. 1994 Feb;198(2):477–488. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. E., Anderson S. M., Young N. S. Erythrocyte P antigen: cellular receptor for B19 parvovirus. Science. 1993 Oct 1;262(5130):114–117. doi: 10.1126/science.8211117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke K. L., Dunn G., Ferguson M., Minor P. D., Almond J. W. Antigen chimaeras of poliovirus as potential new vaccines. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):81–82. doi: 10.1038/332081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke B. E., Brown A. L., Grace K. G., Hastings G. Z., Brown F., Rowlands D. J., Francis M. J. Presentation and immunogenicity of viral epitopes on the surface of hybrid hepatitis B virus core particles produced in bacteria. J Gen Virol. 1990 May;71(Pt 5):1109–1117. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-5-1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F., Tenenbaum L., Guo L. P., Spegelaere P., Zeicher M., Rommelaere J. Use of an autonomous parvovirus vector for selective transfer of a foreign gene into transformed human cells of different tissue origins and its expression therein. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1397–1406. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1397-1406.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung A., Sippel A. E., Grez M., Schütz G. Exons encode functional and structural units of chicken lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajigaya S., Fujii H., Field A., Anderson S., Rosenfeld S., Anderson L. J., Shimada T., Young N. S. Self-assembled B19 parvovirus capsids, produced in a baculovirus system, are antigenically and immunogenically similar to native virions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4646–4650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang A. S., Barbas C. F., Janda K. D., Benkovic S. J., Lerner R. A. Linkage of recognition and replication functions by assembling combinatorial antibody Fab libraries along phage surfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4363–4366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keisu M., Wiholm B. E., Ost A., Mortimer O. Acetazolamide-associated aplastic anaemia. J Intern Med. 1990 Dec;228(6):627–632. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1990.tb00290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzman G. J., Cohen B. J., Field A. M., Oseas R., Blaese R. M., Young N. S. Immune response to B19 parvovirus and an antibody defect in persistent viral infection. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1114–1123. doi: 10.1172/JCI114274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. M., Green S. W., Shimada T., Young N. S. A block in full-length transcript maturation in cells nonpermissive for B19 parvovirus. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4686–4692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4686-4692.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm B. A., Rosenberg S., Corey M. J., Allen J. S., de Baetselier A., Kirsch J. F. Site-directed mutagenesis of the catalytic residues Asp-52 and Glu-35 of chicken egg white lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):133–137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. A., Mainhart C. R., Mallett C. P., Lavoie T. B., Smith-Gill S. J. Patterns of antibody specificity during the BALB/c immune response to hen eggwhite lysozyme. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 15;149(10):3260–3272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa K., Kurtzman G., Young N. Productive infection by B19 parvovirus of human erythroid bone marrow cells in vitro. Blood. 1987 Aug;70(2):384–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa K., Young N. Characterization of capsid and noncapsid proteins of B19 parvovirus propagated in human erythroid bone marrow cell cultures. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2627–2630. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2627-2630.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. J., Yoshimoto K., Kajigaya S., Anderson S., Young N. S., Field A., Warrener P., Bansal G., Collett M. S. Unique region of the minor capsid protein of human parvovirus B19 is exposed on the virion surface. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jun;89(6):2023–2029. doi: 10.1172/JCI115812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. J., Hawkins R. E., Winter G. Retroviral vectors displaying functional antibody fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1081–1085. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saikawa T., Anderson S., Momoeda M., Kajigaya S., Young N. S. Neutralizing linear epitopes of B19 parvovirus cluster in the VP1 unique and VP1-VP2 junction regions. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3004–3009. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3004-3009.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shade R. O., Blundell M. C., Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P., Astell C. R. Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of human parvovirus B19 isolated from the serum of a child during aplastic crisis. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):921–936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.921-936.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith-Gill S. J., Wilson A. C., Potter M., Prager E. M., Feldmann R. J., Mainhart C. R. Mapping the antigenic epitope for a monoclonal antibody against lysozyme. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):314–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosser G., Labbé M., Brémont M., Cohen J. Expression of the major capsid protein VP6 of group C rotavirus and synthesis of chimeric single-shelled particles by using recombinant baculoviruses. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):5825–5831. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.5825-5831.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao J., Chapman M. S., Agbandje M., Keller W., Smith K., Wu H., Luo M., Smith T. J., Rossmann M. G., Compans R. W. The three-dimensional structure of canine parvovirus and its functional implications. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1456–1464. doi: 10.1126/science.2006420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vella C., Minor P. D., Weller I. V., Jenkins O., Evans D., Almond J. Recognition of poliovirus/HIV chimaeras by antisera from individuals with HIV infection. AIDS. 1991 Apr;5(4):425–430. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199104000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E., Zatloukal K., Cotten M., Kirlappos H., Mechtler K., Curiel D. T., Birnstiel M. L. Coupling of adenovirus to transferrin-polylysine/DNA complexes greatly enhances receptor-mediated gene delivery and expression of transfected genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6099–6103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. E., Liu J. M., Xiao X., Young N. S., Nienhuis A. W., Samulski R. J. Regulated high level expression of a human gamma-globin gene introduced into erythroid cells by an adeno-associated virus vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7257–7261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S., Momoeda M., Field A., Kajigaya S., Young N. S. Formation of empty B19 parvovirus capsids by the truncated minor capsid protein. J Virol. 1994 Jul;68(7):4690–4694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.7.4690-4694.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]