Abstract
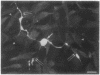
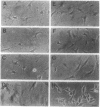
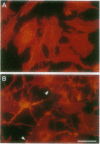
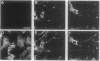
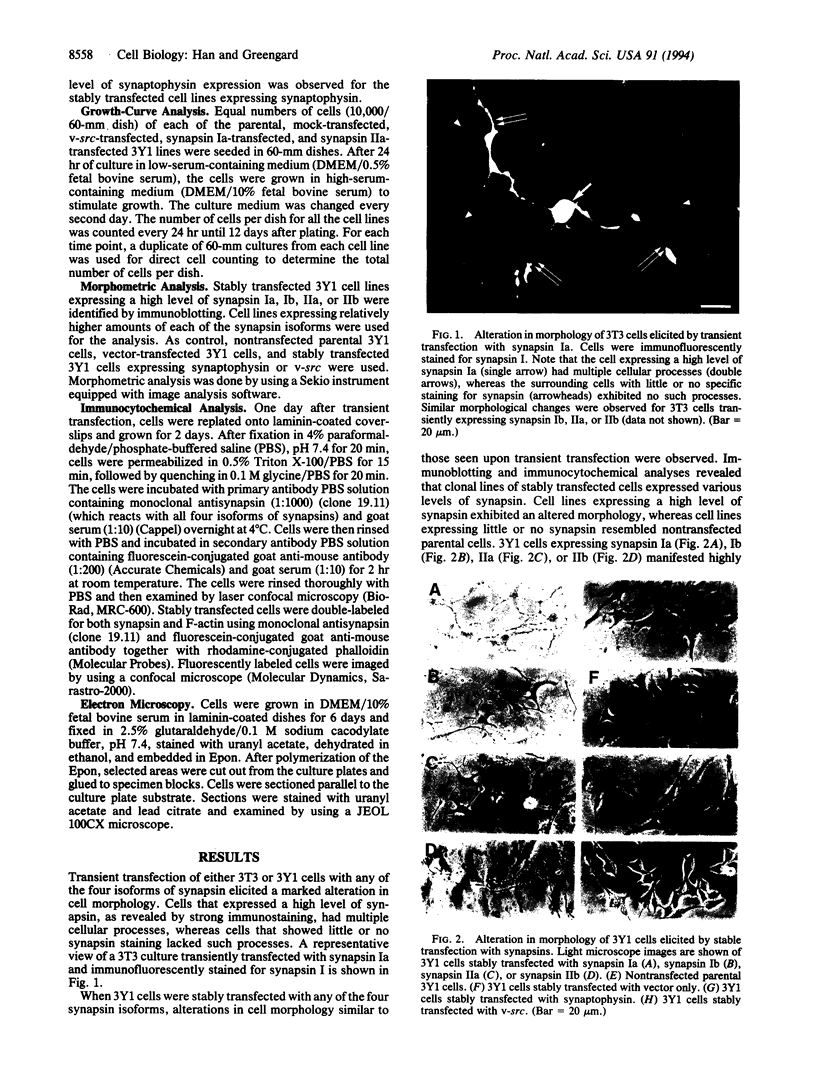
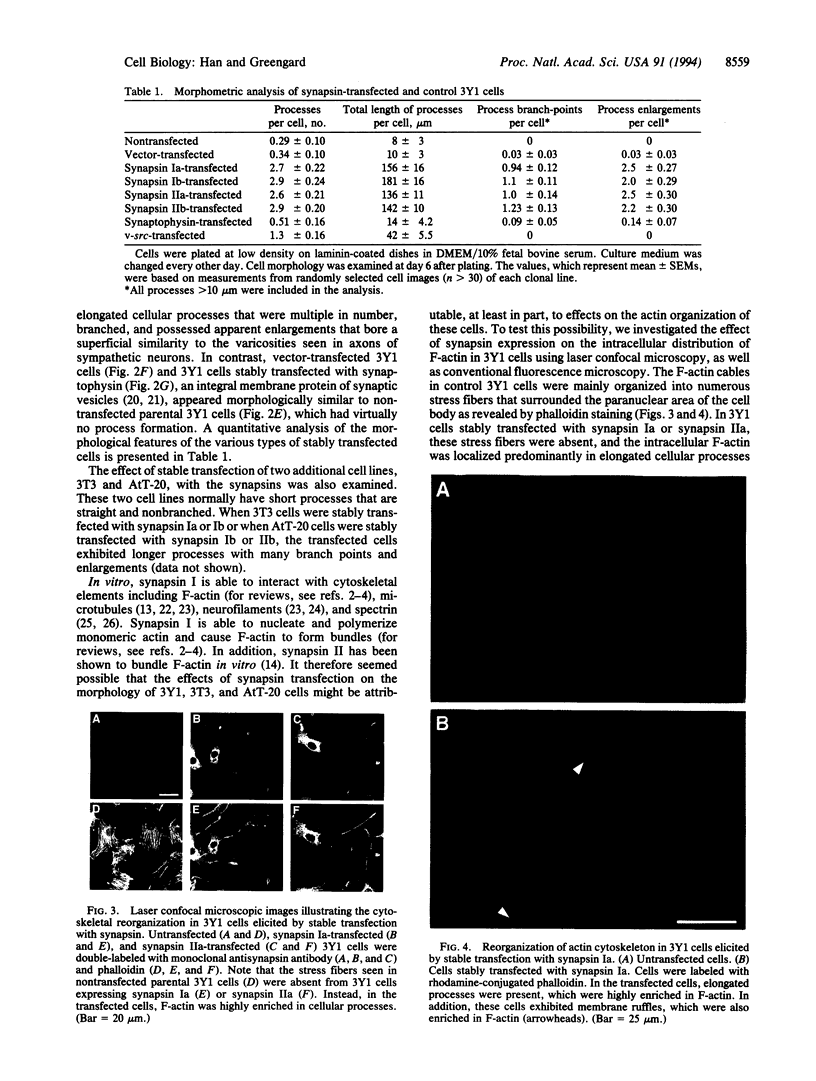
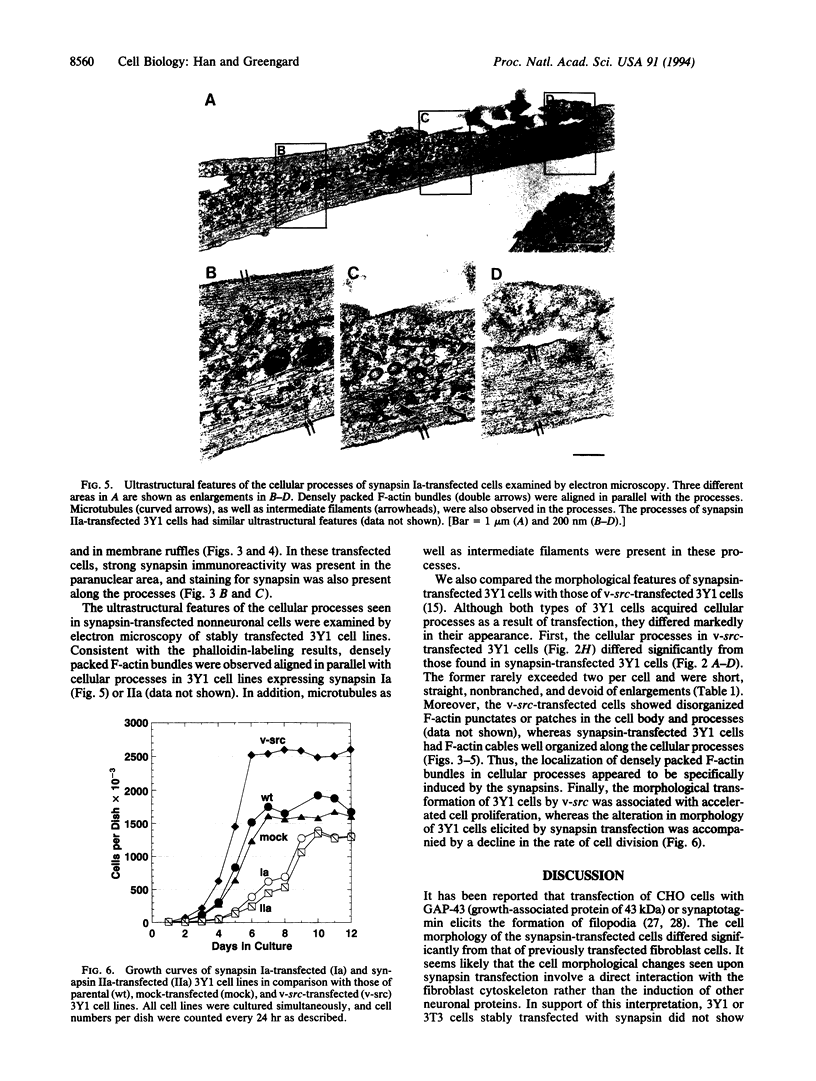
The synapsins, a family of neuron-specific phosphoproteins, have been implicated in the functional and structural maturation of synapses. The cell biological basis for these effects is unknown. In vitro, the synapsins interact with cytoskeletal elements including actin. To examine, in vivo, the possible effect of the synapsins on cytoskeletal organization and cell morphology, we have transfected each of the four known members of the synapsin family into nonneuronal cells. We report here that synapsin expression in fibroblast cells gives rise to an alteration in cell morphology that is associated with formation of highly elongated processes. This morphological change is accompanied by a reorganization of filamentous actin (F-actin) characterized by disruption of existing stress fibers and formation of bundles of actin cables in the elongated processes. These results suggest that interactions of the synapsins with actin, and possibly with other cytoskeletal elements, may play a role in the morphological differentiation of neurons.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson P., Goldfarb M. P., Weinberg R. A. A defined subgenomic fragment of in vitro synthesized Moloney sarcoma virus DNA can induce cell transformation upon transfection. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):63–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baines A. J., Bennett V. Synapsin I is a microtubule-bundling protein. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):145–147. doi: 10.1038/319145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baines A. J., Bennett V. Synapsin I is a spectrin-binding protein immunologically related to erythrocyte protein 4.1. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):410–413. doi: 10.1038/315410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bähler M., Greengard P. Synapsin I bundles F-actin in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):704–707. doi: 10.1038/326704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Benfenati F., Valtorta F., Greengard P. The synapsins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:433–460. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsmore J. H., Solomon F. Inhibition of MAP2 expression affects both morphological and cell division phenotypes of neuronal differentiation. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):817–826. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90510-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURTH J., GADSEN E. L., UPTON A. C. ACTH secreting transplantable pituitary tumors. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Oct;84(1):253–254. doi: 10.3181/00379727-84-20607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feany M. B., Buckley K. M. The synaptic vesicle protein synaptotagmin promotes formation of filopodia in fibroblasts. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):537–540. doi: 10.1038/364537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira A., Kosik K. S., Greengard P., Han H. Q. Aberrant neurites and synaptic vesicle protein deficiency in synapsin II-depleted neurons. Science. 1994 May 13;264(5161):977–979. doi: 10.1126/science.8178158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friederich E., Huet C., Arpin M., Louvard D. Villin induces microvilli growth and actin redistribution in transfected fibroblasts. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):461–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenring J. R., Lasher R. S., Vallano M. L., Ueda T., Naito S., Sternberger N. H., Sternberger L. A., DeLorenzo R. J. Association of synapsin I with neuronal cytoskeleton. Identification in cytoskeletal preparations in vitro and immunocytochemical localization in brain of synapsin I. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8495–8504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P., Valtorta F., Czernik A. J., Benfenati F. Synaptic vesicle phosphoproteins and regulation of synaptic function. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):780–785. doi: 10.1126/science.8430330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett J. T., Cochran S. L., Greenfield L. J., Jr, Brosius D. C., Ueda T. Synapsin I injected presynaptically into goldfish mauthner axons reduces quantal synaptic transmission. J Neurophysiol. 1990 Apr;63(4):701–706. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.63.4.701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han H. Q., Nichols R. A., Rubin M. R., Bähler M., Greengard P. Induction of formation of presynaptic terminals in neuroblastoma cells by synapsin IIb. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):697–700. doi: 10.1038/349697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Schiebler W., Ouimet C., Greengard P. A 38,000-dalton membrane protein (p38) present in synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4137–4141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston P. A., Cameron P. L., Stukenbrok H., Jahn R., De Camilli P., Südhof T. C. Synaptophysin is targeted to similar microvesicles in CHO and PC12 cells. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2863–2872. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08434.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs K. E., Prouty S. M., Zagon I. S., Goodman S. R. Structural and functional relationship of red blood cell protein 4.1 to synapsin I. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 1):C500–C505. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.4.C500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Ivanov I. E., Lee G. H., Cowan N. J. Organization of microtubules in dendrites and axons is determined by a short hydrophobic zipper in microtubule-associated proteins MAP2 and tau. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):498–505. doi: 10.1038/342498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., McGuinness T. L., Leonard C. S., Sugimori M., Greengard P. Intraterminal injection of synapsin I or calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alters neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3035–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu B., Greengard P., Poo M. M. Exogenous synapsin I promotes functional maturation of developing neuromuscular synapses. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90280-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R. A., Chilcote T. J., Czernik A. J., Greengard P. Synapsin I regulates glutamate release from rat brain synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1992 Feb;58(2):783–785. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb09788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrucci T. C., Morrow J. S. Synapsin I: an actin-bundling protein under phosphorylation control. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1355–1363. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer E., Alder J., Greengard P., Poo M. M. Synapsin IIa accelerates functional development of neuromuscular synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3882–3886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner J. P., Ling E., Bennett V. Nearest neighbor analysis for brain synapsin I. Evidence from in vitro reassociation assays for association with membrane protein(s) and the Mr = 68,000 neurofilament subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):905–914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg D. W., Scholz G., Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Activation of a histone H1 kinase by tyrosine phosphorylation in v-src-transformed fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):323–330. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05660.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Czernik A. J., Kao H. T., Takei K., Johnston P. A., Horiuchi A., Kanazir S. D., Wagner M. A., Perin M. S., De Camilli P. Synapsins: mosaics of shared and individual domains in a family of synaptic vesicle phosphoproteins. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1474–1480. doi: 10.1126/science.2506642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valtorta F., Benfenati F., Greengard P. Structure and function of the synapsins. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7195–7198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann B., Franke W. W. Identification and localization of synaptophysin, an integral membrane glycoprotein of Mr 38,000 characteristic of presynaptic vesicles. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1017–1028. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuber M. X., Goodman D. W., Karns L. R., Fishman M. C. The neuronal growth-associated protein GAP-43 induces filopodia in non-neuronal cells. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1193–1195. doi: 10.1126/science.2658062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]