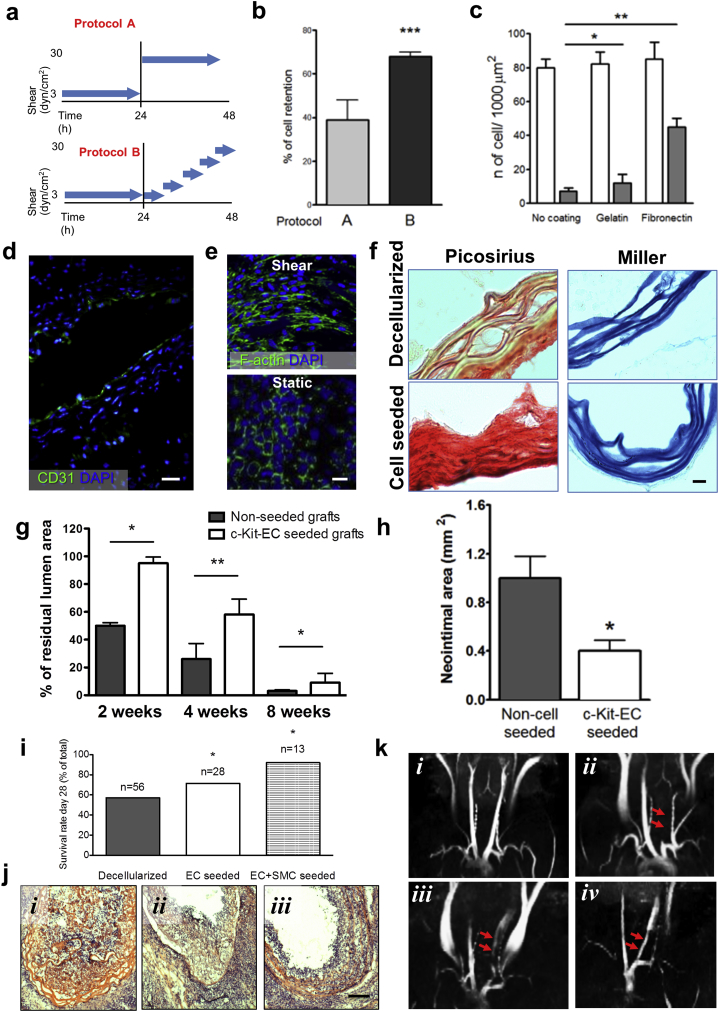
Fig. 2.
Ex vivo seeding of decellularised vessel scaffolds and in vivo grafting. Two protocols were followed to increase the shear from 3 to 30 dyn/cm2 in the tissue engineered grafts after luminal seeding of ECs: ‘daily step-wise’ (protocol A) or ‘hourly step-wise’ (protocol B) (a); cell retention was quantified in (b). Effect of PBS or gelatin or fibronectin coating on cell retention in static (empty bars) and shear (grey bars) was quantified in (c). c-Kit+ ECs formed a homogeneous CD31+ luminal monolayer on the decellularised vessel (d) and elongate in response to shear (e). Picosirius staining for collagen and Miler's elastin staining of decellularised vessels showed improved matrix deposition after cell seeding (f). In vivo implantation of vessels seeded with c-Kit+ ECs showed improved lumen patency (g) and reduced neointima formation (h). Both the seeding with ECs and with the combination of ECs and SMCs (ECs+ SMCs) increased the survival of grafted animals (i) and reduced vessel obstruction (j). MRI detection of the blood flow in the normal carotid (k, i), an occluded carotid grafted with a decellularised vessel (k, ii) and a patent carotid grafted with ECs+ SMCs seeded scaffolds at Day 2 (k, iii), and 2 weeks (k, iv). Red arrows indicate the position of the grafts. Scale bars: 50 μm (d, f, l) and 100 μm (e). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)