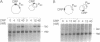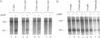Abstract
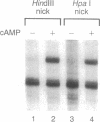
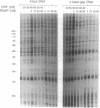
The mechanism by which the cAMP receptor protein (CRP) activates transcription has been investigated using the lac promoter of Escherichia coli. For transcription activation, an interaction between DNA-bound CRP and RNA polymerase is not sufficient. CRP must bind to a site in the same DNA and close to the promoter. CRP action requires an intact spacer DNA to provide a rigid support in building a CRP-RNA polymerase protein bridge or to allow a conformational change in the DNA to be transmitted to the lac promoter using the protein bridge as a structural support.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Garges S. Positive control. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10797–10800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beabealashvily R. S., Ivanov V. I., Minchenkova L. E., Savotchkina L. P. RNA polymerase-DNA complexes. I. The study of the conformation of nucleic acids at the growing point of RNA in an RNA polymerase-DNA system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 18;259(1):35–40. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90471-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckle M., Buc H., Travers A. A. DNA deformation in nucleoprotein complexes between RNA polymerase, cAMP receptor protein and the lac UV5 promoter probed by singlet oxygen. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2619–2625. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05327.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd J. F., Wartell R. M., Dodgson J. B., Wells R. D. Transmission of stability (telestability) in deoxyribonucleic acid. Physical and enzymatic studies on the duplex block polymer d(C15A15) - d(T15G15). J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5109–5113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Shang C., Ptashne M. A single glutamic acid residue plays a key role in the transcriptional activation function of lambda repressor. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1163–1171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90514-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy H. E., Adhya S. RNA polymerase idling and clearance in gal promoters: use of supercoiled minicircle DNA template made in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):472–476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. C., Abelson J., Barnes W. M., Reznikoff W. S. Genetic regulation: the Lac control region. Science. 1975 Jan 10;187(4171):27–35. doi: 10.1126/science.1088926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H., Ebright Y. W., Gunasekera A. Consensus DNA site for the Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein (CAP): CAP exhibits a 450-fold higher affinity for the consensus DNA site than for the E. coli lac DNA site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 25;17(24):10295–10305. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.24.10295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson E. L., Scheffler I. E., Baldwin R. L. Helix formation by d(TA) oligomers. 3. Electrostatic effects. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 28;54(3):401–415. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. DNA sequence determinants of CAP-induced bending and protein binding affinity. Nature. 1988 Jun 30;333(6176):824–829. doi: 10.1038/333824a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giladi H., Gottesman M., Oppenheim A. B. Integration host factor stimulates the phage lambda pL promoter. J Mol Biol. 1990 May 5;213(1):109–121. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80124-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giladi H., Igarashi K., Ishihama A., Oppenheim A. B. Stimulation of the phage lambda pL promoter by integration host factor requires the carboxy terminus of the alpha-subunit of RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):985–990. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90514-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Messer W. Localized DNA melting and structural pertubations in the origin of replication, oriC, of Escherichia coli in vitro and in vivo. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1579–1584. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyduk T., Lee J. C., Ebright Y. W., Blatter E. E., Zhou Y., Ebright R. H. CAP interacts with RNA polymerase in solution in the absence of promoter DNA. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):548–549. doi: 10.1038/364548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Ptashne M. Cooperative binding of lambda repressors to sites separated by integral turns of the DNA helix. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):681–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90833-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A. Protein-protein communication within the transcription apparatus. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2483–2489. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2483-2489.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov V. I., Minchenkova L. E., Minyat E. E., Schyolkina A. K. Cooperative transitions in DNA with no separation of strands. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):243–250. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Meyer B. J., Ptashne M. Interactions between DNA-bound repressors govern regulation by the lambda phage repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5061–5065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Busby S., Buc H., Garges S., Adhya S. Transcriptional regulation by cAMP and its receptor protein. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:749–795. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Igarashi K., Ishihama A., Lavigne M., Buckle M., Buc H. E. coli RNA polymerase, deleted in the C-terminal part of its alpha-subunit, interacts differently with the cAMP-CRP complex at the lacP1 and at the galP1 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 25;21(2):319–326. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. M., Krakow J. S. Monoclonal antibodies that inhibit activation of transcription by the Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3448–3453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malan T. P., Kolb A., Buc H., McClure W. R. Mechanism of CRP-cAMP activation of lac operon transcription initiation activation of the P1 promoter. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):881–909. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meiklejohn A. L., Gralla J. D. Activation of the lac promoter and its variants. Synergistic effects of catabolite activator protein and supercoiling in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jun 20;207(4):661–673. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90236-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Gellert M., Weisberg R. A., Nash H. A. Catenation and supercoiling in the products of bacteriophage lambda integrative recombination in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1980 Aug 25;141(4):485–494. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay G., Carr K. M., Kaguni J. M., Chattoraj D. K. Open-complex formation by the host initiator, DnaA, at the origin of P1 plasmid replication. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4547–4554. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagel J. M., Winkelman J. W., Adams C. W., Hatfield G. W. DNA topology-mediated regulation of transcription initiation from the tandem promoters of the ilvGMEDA operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1992 Apr 20;224(4):919–935. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90460-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkney M., Hoggett J. G. Binding of the cyclic AMP receptor protein of Escherichia coli to RNA polymerase. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 15;250(3):897–902. doi: 10.1042/bj2500897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riftina F., DeFalco E., Krakow J. S. Effects of an anti-alpha monoclonal antibody on interaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with lac promoters. Biochemistry. 1990 May 8;29(18):4440–4446. doi: 10.1021/bi00470a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Gosink K. K., Salomon J., Igarashi K., Zou C., Ishihama A., Severinov K., Gourse R. L. A third recognition element in bacterial promoters: DNA binding by the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1407–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.8248780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Thompson J. F., Newlands J. T., Gourse R. L. E.coli Fis protein activates ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro and in vivo. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3733–3742. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S., Kim J., Adhya S., Garges S. Pivotal role of amino acid at position 138 in the allosteric hinge reorientation of cAMP receptor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):75–79. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano M., Barthelemy I., Salas M. Transcription activation at a distance by phage phi 29 protein p4. Effect of bent and non-bent intervening DNA sequences. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jun 5;219(3):403–414. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Porter S., Kustu S., Echols H. DNA-looping and enhancer activity: association between DNA-bound NtrC activator and RNA polymerase at the bacterial glnA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedel A., Weiss D. S., Popham D., Dröge P., Kustu S. A bacterial enhancer functions to tether a transcriptional activator near a promoter. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):486–490. doi: 10.1126/science.1970441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. Catabolite activator protein-induced DNA bending in transcription initiation. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 20;219(2):201–215. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90562-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]