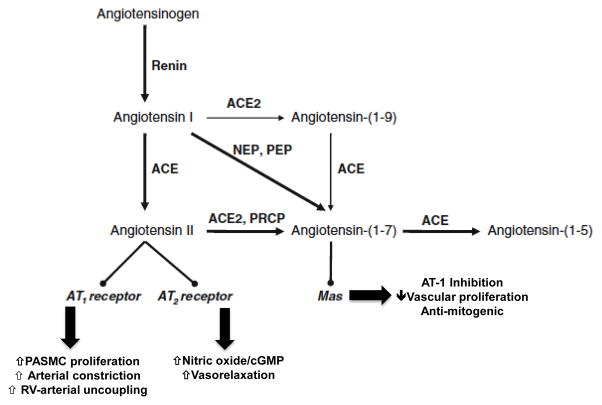
Figure 5.
Angiotensin II and related metabolites. Angiotensin II is generated from angiotensin I via the actions of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin I and II may also be metabolized to the vasoactive heptapeptides angiotensin-(1-9) and angiotensin-(1-7) through the actions of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and neutral endopeptidsase (NEP) and prolylendopeptidase (PEP). Angiotensin II may stimulate angiotensin type-1 (AT-1) receptors to increase pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell (PASMC) proliferation, vasoconstriction, and disrupt right ventricular (RV)-arterial coupling. By contrast, stimulation of angiotensin II receptor type 2 (AT-2) or the Mas receptor by angiotensin II or angiotensin-(1-7) is associated with vasculoprotective effects, including increased nitric oxide generation and a decrease in cell proliferation and vasodilation. PRCP, prolylcarboxypeptidase. Adapted with modifications from reference 55.