Abstract
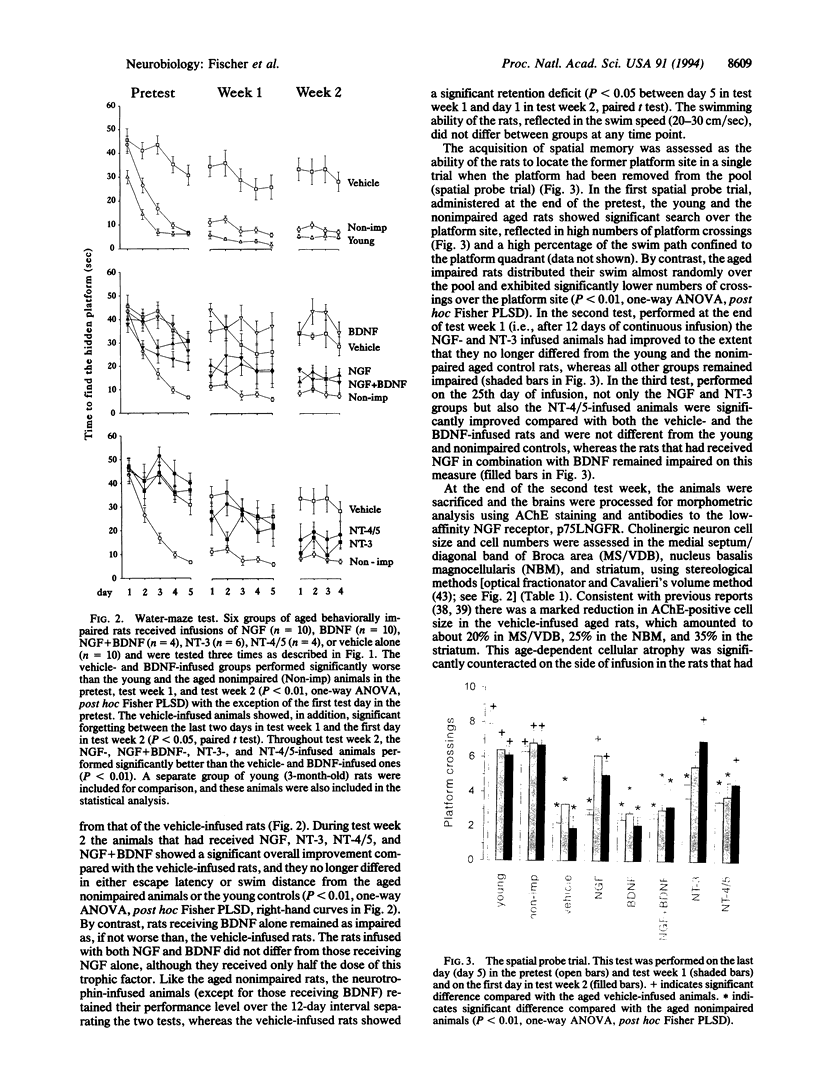
Aged rats, displaying impairments in spatial learning and memory associated with marked cellular atrophy of forebrain cholinergic neurons, received intracerebroventricular infusions of one of the four neurotrophins nerve growth factor (NGF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), neurotrophin 3 (NT-3), or neurotrophin 4/5 (NT-4/5), or a combination of NGF and BDNF, or vehicle. During the 4-week infusion period rats receiving NGF, NT-3, or NT-4/5 showed improved acquisition and retention of spatial memory. With NGF and NT-3, but not NT-4/5, this was accompanied by a significant reduction in cholinergic neuron atrophy in septum, nucleus basalis, and striatum. BDNF, in contrast, was without effect either alone or in combination with NGF. These results show that memory deficits associated with aging can be reversed by several members of the neurotrophin family and that this effect may be mediated through activation of multiple neurotrophin receptors associated with cholinergic and possibly noncholinergic systems in the brain.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderson R. F., Alterman A. L., Barde Y. A., Lindsay R. M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor increases survival and differentiated functions of rat septal cholinergic neurons in culture. Neuron. 1990 Sep;5(3):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90166-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altar C. A., Criden M. R., Lindsay R. M., DiStefano P. S. Characterization and topography of high-affinity 125I-neurotrophin-3 binding to mammalian brain. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):733–743. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00733.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altavista M. C., Rossi P., Bentivoglio A. R., Crociani P., Albanese A. Aging is associated with a diffuse impairment of forebrain cholinergic neurons. Brain Res. 1990 Jan 29;508(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91116-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor P. E., Armstrong D. M., Blaker S. N., Gage F. H. Nerve growth factor receptor and choline acetyltransferase colocalization in neurons within the rat forebrain: response to fimbria-fornix transection. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Jun 8;284(2):187–204. doi: 10.1002/cne.902840204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao M. V. Neurotrophin receptors: a window into neuronal differentiation. Neuron. 1992 Oct;9(4):583–593. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collazo D., Takahashi H., McKay R. D. Cellular targets and trophic functions of neurotrophin-3 in the developing rat hippocampus. Neuron. 1992 Oct;9(4):643–656. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90028-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker M. W. The effects of aging on hippocampal and cortical projections of the forebrain cholinergic system. Brain Res. 1987 Nov;434(4):423–438. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(87)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiStefano P. S., Friedman B., Radziejewski C., Alexander C., Boland P., Schick C. M., Lindsay R. M., Wiegand S. J. The neurotrophins BDNF, NT-3, and NGF display distinct patterns of retrograde axonal transport in peripheral and central neurons. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):983–993. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90213-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Björklund A., Chen K., Gage F. H. NGF improves spatial memory in aged rodents as a function of age. J Neurosci. 1991 Jul;11(7):1889–1906. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-07-01889.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Chen K. S., Gage F. H., Björklund A. Progressive decline in spatial learning and integrity of forebrain cholinergic neurons in rats during aging. Neurobiol Aging. 1992 Jan-Feb;13(1):9–23. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(92)90003-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Wictorin K., Björklund A., Williams L. R., Varon S., Gage F. H. Amelioration of cholinergic neuron atrophy and spatial memory impairment in aged rats by nerve growth factor. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):65–68. doi: 10.1038/329065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer Walter, Gage Fred H., Björklund Anders. Degenerative Changes in Forebrain Cholinergic Nuclei Correlate with Cognitive Impairments in Aged Rats. Eur J Neurosci. 1989 Jan;1(1):34–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1989.tb00772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage F. H., Kelly P. A., Björklund A. Regional changes in brain glucose metabolism reflect cognitive impairments in aged rats. J Neurosci. 1984 Nov;4(11):2856–2865. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-11-02856.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher M., Burwell R. D., Kodsi M. H., McKinney M., Southerland S., Vella-Rountree L., Lewis M. H. Markers for biogenic amines in the aged rat brain: relationship to decline in spatial learning ability. Neurobiol Aging. 1990 Sep-Oct;11(5):507–514. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(90)90111-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnahn H., Hefti F., Heumann R., Schwab M. E., Thoenen H. NGF-mediated increase of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) in the neonatal rat forebrain: evidence for a physiological role of NGF in the brain? Brain Res. 1983 Jul;285(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(83)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen H. J., Bagger P., Bendtsen T. F., Evans S. M., Korbo L., Marcussen N., Møller A., Nielsen K., Nyengaard J. R., Pakkenberg B. The new stereological tools: disector, fractionator, nucleator and point sampled intercepts and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS. 1988 Oct;96(10):857–881. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1988.tb00954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedreen J. C., Bacon S. J., Price D. L. A modified histochemical technique to visualize acetylcholinesterase-containing axons. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Feb;33(2):134–140. doi: 10.1177/33.2.2578498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefti F., Hartikka J., Eckenstein F., Gnahn H., Heumann R., Schwab M. Nerve growth factor increases choline acetyltransferase but not survival or fiber outgrowth of cultured fetal septal cholinergic neurons. Neuroscience. 1985 Jan;14(1):55–68. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefti F. Nerve growth factor promotes survival of septal cholinergic neurons after fimbrial transections. J Neurosci. 1986 Aug;6(8):2155–2162. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-08-02155.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson C. E., Camu W., Mettling C., Gouin A., Poulsen K., Karihaloo M., Rullamas J., Evans T., McMahon S. B., Armanini M. P. Neurotrophins promote motor neuron survival and are present in embryonic limb bud. Nature. 1993 May 20;363(6426):266–270. doi: 10.1038/363266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman D. M., Li Y., Parada L. F., Kinsman S., Chen C. K., Valletta J. S., Zhou J., Long J. B., Mobley W. C. p140trk mRNA marks NGF-responsive forebrain neurons: evidence that trk gene expression is induced by NGF. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):465–478. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90184-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornberger J. C., Buell S. J., Flood D. G., McNeill T. H., Coleman P. D. Stability of numbers but not size of mouse forebrain cholinergic neurons to 53 months. Neurobiol Aging. 1985 Winter;6(4):269–275. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(85)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman C., Hofer M., Barde Y. A., Juhasz M., Yancopoulos G. D., Squinto S. P., Lindsay R. M. BDNF is a neurotrophic factor for dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra. Nature. 1991 Mar 21;350(6315):230–232. doi: 10.1038/350230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman C., Juhasz M., Jackson C., Wright P., Ip N. Y., Lindsay R. M. Overlapping and distinct actions of the neurotrophins BDNF, NT-3, and NT-4/5 on cultured dopaminergic and GABAergic neurons of the ventral mesencephalon. J Neurosci. 1994 Jan;14(1):335–347. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-01-00335.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Li Y., Yancopoulos G. D., Lindsay R. M. Cultured hippocampal neurons show responses to BDNF, NT-3, and NT-4, but not NGF. J Neurosci. 1993 Aug;13(8):3394–3405. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-08-03394.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Stitt T. N., Tapley P., Klein R., Glass D. J., Fandl J., Greene L. A., Barbacid M., Yancopoulos G. D. Similarities and differences in the way neurotrophins interact with the Trk receptors in neuronal and nonneuronal cells. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):137–149. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90306-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Parada L. F., Coulier F., Barbacid M. trkB, a novel tyrosine protein kinase receptor expressed during mouse neural development. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3701–3709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08545.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knüsel B., Winslow J. W., Rosenthal A., Burton L. E., Seid D. P., Nikolics K., Hefti F. Promotion of central cholinergic and dopaminergic neuron differentiation by brain-derived neurotrophic factor but not neurotrophin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):961–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh S., Chang P., Collier T. J., Loy R. Loss of NGF receptor immunoreactivity in basal forebrain neurons of aged rats: correlation with spatial memory impairment. Brain Res. 1989 Oct 2;498(2):397–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh S., Loy R. Age-related loss of nerve growth factor sensitivity in rat basal forebrain neurons. Brain Res. 1988 Feb 9;440(2):396–401. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kromer L. F. Nerve growth factor treatment after brain injury prevents neuronal death. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):214–216. doi: 10.1126/science.3798108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamballe F., Klein R., Barbacid M. trkC, a new member of the trk family of tyrosine protein kinases, is a receptor for neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):967–979. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor 35 years later. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1154–1162. doi: 10.1126/science.3306916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markram H., Segal M. Regional changes in NGF receptor immunohistochemical labeling in the septum of the aged rat. Neurobiol Aging. 1990 Jul-Aug;11(4):481–484. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(90)90017-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meakin S. O., Shooter E. M. The nerve growth factor family of receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Sep;15(9):323–331. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90047-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlio J. P., Ernfors P., Jaber M., Persson H. Molecular cloning of rat trkC and distribution of cells expressing messenger RNAs for members of the trk family in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1992 Dec;51(3):513–532. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90292-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse J. K., Wiegand S. J., Anderson K., You Y., Cai N., Carnahan J., Miller J., DiStefano P. S., Altar C. A., Lindsay R. M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) prevents the degeneration of medial septal cholinergic neurons following fimbria transection. J Neurosci. 1993 Oct;13(10):4146–4156. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-10-04146.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawa H., Bessho Y., Carnahan J., Nakanishi S., Mizuno K. Regulation of neuropeptide expression in cultured cerebral cortical neurons by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurochem. 1993 Feb;60(2):772–775. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer J. E., Koh S., Tayrien M. W., Loy R. Basal forebrain magnocellular neurons stain for nerve growth factor receptor: correlation with cholinergic cell bodies and effects of axotomy. J Neurosci Res. 1987;17(2):111–118. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490170204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H. The changing scene of neurotrophic factors. Trends Neurosci. 1991 May;14(5):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90097-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela D. M., Maisonpierre P. C., Glass D. J., Rojas E., Nuñez L., Kong Y., Gies D. R., Stitt T. N., Ip N. Y., Yancopoulos G. D. Alternative forms of rat TrkC with different functional capabilities. Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):963–974. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. R., Varon S., Peterson G. M., Wictorin K., Fischer W., Bjorklund A., Gage F. H. Continuous infusion of nerve growth factor prevents basal forebrain neuronal death after fimbria fornix transection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9231–9235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong V., Arriaga R., Ip N. Y., Lindsay R. M. The neurotrophins BDNF, NT-3 and NT-4/5, but not NGF, up-regulate the cholinergic phenotype of developing motor neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1993 May 1;5(5):466–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00513.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]