Abstract
Membrane adhesion is essential to many vital biological processes. Sites of membrane adhesion are often associated with heterogeneities in the lipid and protein composition of the membrane. These heterogeneities are thought to play functional roles by facilitating interactions between proteins. However, the causal links between membrane adhesion and membrane heterogeneities are not known. Here we survey the state of the field and indicate what we think are understudied areas ripe for development.
Introduction
The close approach and subsequent adherence and fusion of one membrane with another is a frequent event that underlies the organization of all eukaryotic cells. Membrane adhesion can be found in structures that range in scale from the entire plasma membrane of a 50 micron cell as it adheres to a substratum to an individual 50 nm secretory vesicle that adheres to a target organelle in the cell interior. The past decade has led to an increasing understanding of the heterogeneous arrangement of lipids and proteins in membranes. Less frequently considered is how membrane adhesion and heterogeneity influence each other. Consideration of this interplay can lead to new mechanistic insights in how cell membranes function and also aid the design of lipid carriers for delivery of therapeutics.
This Perspective is a review article that considers how membrane adhesion and membrane heterogeneity interact. We begin by highlighting cellular events where membrane adhesion and heterogeneity are key factors in cellular functions. We then consider how these events are studied in experimental model membranes where the components can be defined. Finally while both the specific adhesion of lipid membranes to targets and the formation of lateral heterogeneities in membranes have been advanced as means of making “smarter,” more responsive membrane-based therapeutics, to our knowledge these two streams of investigation have not yet been combined. We conclude with a consideration of how the intersection of these topics could advance membrane functionality in technologies for drug delivery and biosensing.
Biology
Cellular adhesion and signaling
Membrane adhesion and heterogeneity is best understood for the plasma membrane, the outermost membrane composed of lipids and proteins that encompasses all eukaryotic cells. The plasma membrane is known to be composed of groupings of specific lipids and proteins clustered into microdomains. This ordered arrangement of membrane components creates functional membrane domains specialized for cell substrate and cell-cell interactions 1–7.
A specialized microdomain that has received abundant consideration from both cell biologists and biophysicists is the raft 8–12. This concentration of specific lipids, largely sphingolipids and cholesterol, along with particular proteins is thought to provide a structural basis for biological function by clustering together specific components for controlled functional interactions 8, 9, 13–16. From a biophysical perspective, membrane rafts are often thought of as phase-separated domains or fluctuations in composition associated with lipid phase separation 16–21.
These phase-separated domains play key roles in several functions of the plasma membrane. Rafts can concentrate and even order specific proteins suggesting that this microdomain can regulate protein-protein interactions 22. The capacity of rafts to organize and thereby confer regulation to proteins has been shown in living cells where integrins, cell membrane proteins that function in cell-substrate interactions, can change conformation to adopt a higher affinity state for their ligand when in the appropriate lipid microenvironment 23, 24.
SNARES, proteins that function in the fusion of a vesicle with a membrane also appear to function withiin specialized lipid microenvironments. The association of SNARES in rafts may control their ability to function in the recognition and promotion of the fusion of a specific vesicle with its target, the plasma membrane 25–28.
The concept that organization into heterogeneious specialized microdomains regulate protein function extends beyond rafts. For example specialized microdomains on the plasma membrane also play a role in immunological synapses, a structure where two immune cells interact. Immunological synapses have been shown to be sites of protein reorganization and clustering that are associated with the exchange of information between immune cells 29, 30. This organization has important ramifications for the organism: aging is associated with changes in the lipid composition and the behavior of lipid rafts in T-cells as well as altered signaling response; it has been suggested that alterations in lipid rafts promote immune dysregulation 31.
While most examples of functional clustering of lipids and proteins into heterogeneous microdomains have been studied on the plasma membrane, the idea that ordered arrays of lipid microenvironments regulate protein function is probably true for the rest of the membranes in cells. SNARE proteins function in the fusion of vesicles with a target membrane at the plasma membrane, but also at multiple sites of membrane fusion important for organelles, including the fusion of ER-derived secretory vesicles with the cis-Golgi and other membrane fusion events in the secretory pathway. Thus it is likely that SNARES are similarly organized and regulated in microdomains in intracellular organelles. Microdomains of ordered membranes are known to provide a platform for organizing proteins into step-wise signaling cascades; organized signaling events occur throughout organelles in the cell interior. Microdomains on the intracellular membranes could well regulate the conformation affinity and function of proteins in intracellular organelles similarly to how they regulate events on the plasma membrane.
Model systems
It is difficult, and perhaps impossible, to understand how membrane adhesion and the heterogeneous organization of membranes influence each other using living systems alone, because of the multiplicity of biological processes involved. Despite widespread observation of the importance of membrane adhesion and heterogeneities, how they are causally linked is unknown. Indeed, the origins, character, and function of heterogeneities in biological membranes independent of adhesion still have many open associated questions. Reductionist model systems provide a way around this, by allowing the effects of one to a few interactions to be carefully characterized. To better understand these intricate systems, biophysical and biochemical researchers often use model lipid bilayers. Typical model membranes contain one to a few lipid species and zero to a few protein or protein-like species, depending on the purpose of the investigation.
Model systems for membrane adhesion
In Figure 1 we summarize the effects that adhesion could have on a simple bilayer membrane. Note that some effects, such as adhesion-induced tension, are expected to apply across the whole membrane, whereas other effects are localized to the adhering region or even to single proteins. Although there are exceptions, as a general rule of thumb the more global effects arise from generic physics and the more localized effects arise from molecular specificity.
Figure 1. Effects of adhesion on a spherical membrane.
(Tension) The area of membrane adhesion will increase until binding proteins are saturated or the free energy benefit to forming one more bond is balanced by the free energy penalty for tensing the membrane by the amount necessary to form one more bond. Assuming constraint on the membrane’s internal volume, this will result in increasing the tension in the membrane. (Altered curvature) For the case of an initially-spherical membrane adhering to a flat, rigid target, as shown, the membrane curvature in the adhered region will be zero (grey), the membrane curvature in the non-adhered membrane may decrease or may be essentially unaltered from the initial curvature (black), and the membrane just off the adhering area will be highly curved (red). Adhesion to non-flat or non-rigid targets can also result in changes in curvature. (Proximity to target) Many biological membranes and model membranes contain polymers in the bilayer that prevent nonspecific adhesion (not shown). In addition, membranes are subject to thermally-driven undulations by the same principle as Brownian motion. Both these act to increase the average distance from the membrane to any adhesion target. Upon adhesion, the proximity to the target is both reduced and stabilized. (Undulation suppression) Thermally-driven membrane undulations will be suppressed in the adhering region, because adhesion acts to increase the free energy cost for separating the membrane from the target. (Receptor clustering) If the availability of targets is sufficiently high, and the free energy of binding sufficiently large, the receptors in the membrane will demix from their initially-isotropic distribution and become clustered at the adhesion site. This will result in the adhering part of the membrane being enriched in receptors, and the non-adhering part of the membrane being depleted in receptors. (Receptor conformational change) In biological systems, adhesion to a ligand often induces a change in the receptor that makes it more susceptible to phosphorylation or some other change on the cytoplasmic side. This is often the basis for signal transduction. It has been speculated that membrane rafts may be stabilized by changes in receptors that alter their affinity for specific lipid species or for generic characteristics of phase structure.
The artificial giant unilamellar vesicle (GUV) has been widely used to mimic cell membranes. GUVs are typically 5–50 μm in diameter—the size of a typical eukaryotic cell. Supported lipid bilayers (SLBs) are widely used as targets for GUV adhesion. Adhesion can be mediated either by nonspecific, generic interactions or by specific protein-protein binding. It is our view that for model systems to truly yield insight into the relationship between membrane adhesion, protein heterogeneities, and lipid heterogeneities, mixed-lipid membranes near a phase transition should adhere to a target via proteins or model proteins. A substantial body of work using GUV and SLB systesms with binding proteins, both model (e.g. biotin-avidin, RGD-capped lipids 32, 33, DNA-capped lipids 34, 35) and real (e.g. cadherin 36), has examined the biophysics underlying the static stucutre and the dynamic distribution and redistribution of membrane proteins at adhesion sites 37–53.
Microscopy techniques suitable for studing specific adhesion in model systems have developed in parallel with experimental models. Reflection interference contrast microscopy (RICM) has been widely used to study specifically adhering membranes. 37–56 RICM uses the lipid membrane as one reflecting surface of an interferometer and the adhesion target substrate as the other reflecting surface. This allows RICM to measure target-membrane separations with a spatial resolution set by the wavelength of illuminating light. RICM was originally adapted for imagining lipid membranes54 and has been well reviewed by earlier writers53.
Epi-fluorescence studies of specific adhesion often rely on exciting fluorescent dye molecules conjugated to binding proteins (typically advin) and using this as a way to visualize the location of binding proteins.37 Total internal reflection fluorescence microcopy (TIRF) is another fluorescence-based technique suitable for measuring membrane adhesion.57 TIRF uses the evanescent wave of a totally-reflected laser beam to excite fluorophores. Because the evanescent wave decays exponentially with distance above the reflecting surface, this provides a sensitive measure of membrane-target separation. These and other fluorescence-based techniques are reviewed in detail by Groves et al. 58
The literature studying how adhesion processes lead to heterogeneities in the distribution of binding proteins commonly refers to the formation of protein-dense regions at the adhesion site as “phase separation”. This terminology may be confusing to the reader new to the field, since this is not the lipid phase separation discussed in the section below. This field of work has primarily studied the roles of membrane mechanics, binder density, and adhesion energies, and how these interplay 37–52, 56, 59–63.
Adhesion statics
Studies using RICM and epi-fluorescence microscopy to measure model systems consisting of protein-decorated GUVs adhered to SLBs has revealed that adhesion is mediated by the formation and growth of adhesion plaques, i.e. regions where protein binders are dense (biotin-avidin 1–5%37) and intermembrane distances are small (for biotin-avidin the intermembrane distance is 1–5nm,59 and for RGD-integrin the intermembrane distance is 5–10nm60). In mature adhered membranes—membranes whose adhesion zone has stopped growing—there are two primary regimes characterized by 1) complete adhesion zones composed of a single uniform adhesion plaque and 2) incomplete adhesion zones composed of adhesion plaques coexisting with regions of low binder density and large intermembrane distances (for biotin-avidin the intermembrane distance is 10–20nm37, 59 The two regimes of mature membrane adhesion can be controlled by binder concentrations. For biotin-neutravidin binding Fenz et al. 37 found incomplete adhesion for initial neutravidin concentrations on the SLB less than 1% and complete adhesion for concentrations greater than 1%.
Membrane adhesion impacts the effective strength of molecular bonds. For biotin-avidin in free solution, the binding energy is about -35 kBT. In incompletely-adhered membranes, the biotin-avidin binding energy is only about -10 kBT. A reduction in the size of the bond energy associated with incorporating the protein binders into a membrane, compared with free solution, has also been observed in the intrinsically weaker bonding pair sialyl-LewisX—E-selectin. 39
Adhesion dynamics
The kinetics of growth of adhesion zones give rise to adhesion dynamics. Puech et al. 43 were able to switch between two growth regimes by varying the initial tension, and thus the excess membrane area, in GUVs before adhesion. When initially-tense (tension 10−5-10−4 N/m) membranes were adhered to an SLB via biotin-streptavidin binding, they nucleated a single adhesion plaque which proceded to a state of complete adhesion. The radial growth of the adhesion zone scaled as time0.2 and the growth of adhesion zones stopped after about 800s. When initially-floppy vesicles (tension 10−7-10−6 N/m) were adhered under otherwise identical conditions, many adhesion plaques nucleated and then coalesced. In this case, radial growth of the adhesion zone scaled as time1 and the adhesion zones stopped growing after about 400s. This is a striking demonstration that membrane mechanics can impact the kinetics of adhesion, in addition to the equilibrated adhered state.
The growth rates of adhesion zones have also been observed in systems where GUVs containing RGD proteins adhered to stationary integrins adsorbed onto a glass substrate.60 This contrasts with the biotin-avidin mediated adhesion discussed above, in which avidin binders were mobile in the SLB substrate. Boulbich et al.60 found that when the RGD contentrations in the GUVs were low (less than 0.08–0.1 mol%) the radial growth of the adhesion zone grew as time1/2 and the adhesion region stopped growing after 1500–2000s. However, when RGD concentrations in the GUVs were high (0.2–2 mol%) the radial growth of the adhesion zone grew as time1 and adhesion arrested after 30s. The slow-growth regime was limited by RGD proteins on the GUV membrane diffusing into the adhesion front on the vesicle while the fast-growth regime was limited by the RGD-integrin binding rate. This is an example of how the chemical properties of the membrane, here in the form of the chemical potential of the RGD proteins, can impact the kinetics of adhesion.
In Figure 2, we summarize the changes in the physics and chemistry of a lipid bilayer membrane that could arise from the effects of adhesion described in Figure 1.
Figure 2. Impacts of adhesion on membrane chemistry and physics.
(Tension) Work by Evan Evans and co-workers has shown that there are two regimes of membrane tension – a low-tension regime in which tension primarily acts to reduce thermally-driven membrane undulations, and a high-tension regime in which tension acts to increase the area per lipid. Membrane undulations increase the number of microstates available to any given macroscopic configurations, and therefore increase membrane entropy. Therefore, suppressing membrane undulations will decrease the membrane’s entropy. Membrane undulations can also be suppressed directly as a result of adhesion, as indicated in Figure 1. This will also reduce the membrane’s entropy in the adhered region. In the high-tension regime, increasing area/lipid is analogous to increasing volume/molecule in a gas or liquid. It increases the membrane’s free energy by exposing hydrophobic lipid tails to water. (Altered curvature) The greatest change (per unit membrane area) in bending energy will happen in the rim membrane just off the adhering area. This rim is shown in red. Depending on the curvature of the initial, non-adhered membrane, the change in curvature from the spherical region (black) to the flat region (grey) may also result in a comparable change in bending energy. The rim region (red) will have a higher bending energy than the non-adhered, spherical membrane, and the adhered region (grey) will have a lower bending energy than the non-adhered, spherical membrane. (Proximity to target) Lipid headgroups are either zwitterionic or charged, as are the materials in their binding environment. This opens up the possibility of electrostatic interactions, the strength of which depends on the distance between membrane lipids and the target or other objects. For physiological conditions or work done using biological buffers, it is also necessary to account for the screening of electrostatic interactions that arises from salt concentration. The Bjerrum length gives the lengthscale at which the electrostatic interaction between two objects is comparable in magnitude to randomizing thermal energies. It depends inversely on the dielectric constant of the medium, which will be impacted by the number density and valance of salt ions. (Receptor clustering) The chemical potential of a species is determined by both its number density and its activity, which can be thought of as proportional to its energy level. Here we consider only the effect of concentration. Entropy maximization requires minimization of chemical potential, such that each species is isotropically distributed and at the same average number density everywhere in the system. If favourable binding energies cause receptors to concentrate in the adhering area and be depleted in the non-adhering membrane, the membrane’s entropy will be reduced. Moreover, the receptor concentration will result in an increased chemical potential for the receptor species in the adhering area. (Receptor conformational change) Changes in receptor conformation could alter the receptor’s molecular affinity for specific lipid species.
Model systems for lipid phase separation
Biophysical work motivated by the desire to better understand rafts in the plasma membrane has elucidated the formation of lipid sub/super-micron sized heterogeneities by lipid phase separation in artificial and biological membranes 64–75. The liquid-ordered phase LO is widely considered as a model phase for membrane rafts because it is rich in cholesterol and detergent insoluble lipid species.. Model systems for lipid phase separation are typically ternary, containing a low-melting phospholipid, a high-melting sphingolipid (or phospholipid), and cholesterol or another sterol. The phase diagrams of such systems contain a region where LO coexists with the fluid-disordered phase, Ld, which is widely considered as a model phase for the non-raft portion of the plasma membrane.
Synthetic model membranes are typically made with a well-defined mixture of lipids and are made at temperatures above the chain-melting temperature of the highest-melting lipid in the system. Electroformation is probably the most widely-used method for forming GUVs, because it produces a high yield of unilamellar vesicles that are tens of microns in diameter, and therefore well-sized for study with optical microscopy.76 However, electroformation can change the molecular structure of the membrane constituents, which in turn can change the phase behaviour of the system. Moreover, electroformation does not work well if the membranes are to be formed in a salt-containing biological buffer or another electrolyte solution. To circumvent these concerns, rehydration of a dried lipid film is also sometimes used.76 For visualization of phase separation using fluorescence microscopy, fluorescent dyes are incorporated into the membrane at trace amounts (typically 0.1–0.5 mol%). These dyes are preferentially excluded from or included into the lipid phases that form, according to the molecular compatibility of the dye with the lipid phase structure.77
In other studies, researchers have investigated lipid phase separation in giant plasma membranes vesicles (GPMVs) harvested from living cells. GPMVs maintain much of the chemical complexity of living cells. A recent protocol by Sezgin et al.64 details how to isolate, fluorescently label, and induce phase separation in GPMVs.
Upon a temperature quench, GUVs and GPMVs can undergo Ld-Lo phase separation. In their seminal work, Veatch and Keller experimentally mapped the full three-component phase diagram for DPPC/DOPC/Chol membranes.74 This work and other work on other ternary systems75, 78 serve as a basic library for other researchers investigating phase separation in ternary GUVs. Included in these works are the phase coordinates of the associated thermodynamic critical points where compositional fluctuations exist at the submicron scale. Suprisingly, GPMVs exist near a compositional critical point.79 The submicron scale of composition fluctuations in GUVs and GPMVs is the same scale as lipid rafts. This suggests biology may use critical lipid compositions as a mechanism for small scale membrane heterogeneity.
The rapidity of the temperature quench that takes membranes from isotropic Ld to coexisting Ld and Lo can impact the dynamics of phase separation by changing whether the system is in the binodal decomposition region, in which there is an energy barrier to nucleating an ordered domain, or the spinodal decomposition region, in which there is no energy barrier to ordered-phase nucleation. In the binodal region, one to a few ordered-phase domains will nucleate and then grow in size; in the spinodal region fluctuation-like, small domains of ordered phase will appear immediately and then grow by coalescence. A quench into the spinodal region can also result in the formation of a metastable lipid phase, according to the Ostwald Rule of Stages.77 These are examples of controlling the kinetics of lipid phase separation by controlling the speed of the temperature quench.
Recently, Stanich et al. studied the dynamics of phase separation in membranes that all underwent a rapid temperature quench.80 They measured the growth of LO domains in membranes near a miscibility boundary for membranes at both critical and noncritical compositions. They found that in critical membranes the radius of ordered-phase domains grew as time0.5 while in noncritical membranes the radius grew as time0.28. This is an example of controlling the kinetics of lipid phase separation by controlling the system’s location on a phase diagram.
Membrane mechanics and phase separation
Coarse-grained approximations that treat the membrane as a continuum are often used to calculate membrane mechanics. The elastic energy cost to bend a membrane is described by the Helfrich Hamiltonian.81 This elastic energy cost will depend on the radius of curvature R and on the bending modulus κ(Figure 2). The bending modulus is higher for ordered lipid phases than for disordered lipid phases. In addition, Brodchard et al. describes the energy cost for stretching the membrane.82 Ordered lipid phases lower area/lipid ratios than disordererd lipid phases. Taken together, these findings suggest that altering membrane mechanics could alter the phase separation behaviour of membranes.
Recent publications have reported seemingly-contradictory effects of increasing membrane tension on the Lo-Ld demixing temperature 21, 83, 84. Namely, membranes that were tensed by micropipette aspiration experienced a consequent reduction in demixing temperature, but membranes that were tensed by osmotic stress experienced a consequent increase in demixing temperature. We suggest that these two sets of observations may not, in fact, contradict each other, but rather correspond to the two different regimes of membrane tension 85. Lower tension corresponds to suppressing membrane undulations, which we expect86 to increase the demixing temperature by decreasing the system’s entropy. Higher tension increases the membrane area per lipid, which we expect disfavour ordered-phase formation and thus decrease the demixing temperature. Understanding the role of membrane tension in phase separation is relevant to biology because tension has been suggested as a possible cause of the apparent size-limitation of phase-separated domains in living cells 87.
Other researchers have studied how altering gross (micron-scale) curvature affects the spatial segregation of pre-formed lipid phases. They formed supported bilayer membranes on corrugated solid substrates that had periodically-varying radii of curvature, and showed that Lo domains segregated to regions of lower curvature, leaving the higher-curvature regions covered with the softer Ld phase.88
In our previous work86, we suggested that the suppression of thermally-driven membrane undulations should favour the formation of ordered phases when the membrane is near a demixing transition. For typical GUV sizes (10 μm radius), we estimated that the shift in the free energy of demixing due to undulation suppression was of the order kBT while the shift in the free energy of demixing due to gross curvature modulation was much smaller, of the order 10−4 kBT.86 However, the two effects become comparable when the vesicle’s radius becomes about 100nm. This suggests, as Parthasarathy et al. point out, 88 that the submicron scale of lipid rafts may make rafts susceptible to curvature modulation of phase separation.
Model systems for lipid phase separation combined with adhesion
Other researchers have shown that the distribution of molecular species in adhering membranes can be controlled by whether binding agents preferentially partition into the LO or Ld phases 89. More recently, Zhao et al. have found that, near a critical point in the lipid phase diagram, adhesion produces heterogeneities in membrane components that is specific to the molecular affinity of the binder-conjugated lipids 90. In our lab, we have found that adhesion can form dual, simultaneous heterogeneities that have protein and lipid composition distinct from each other and from the non-adhered portion of the membrane (manuscript submitted to PCCP simultaneously with this review). We suggest that this likely results form an interplay between generic features of adhesion, which will locally suppress membrane undulations, reduce curvature, and modify tension, with a specific molecular affinity of protein-conjugated lipids for one or more components of the lipid membrane and a disaffinity of the ordered phase structure for protein-conjugated lipids that causes these lipids to be excluded as impurities.
In addition to the experiments summarized in the previous paragraph, there are theoretical models examining the effects of adhesion on lipid phase separation in membranes91, 92. One reason that theory is powerful is that it allows the behavior of a complex system to be described as a function of only the salient parameters. Unfortunately, in the case of the interaction between adhesion and phase separation, what controlling parameters are relevant for specific cases is not known. What parameters matter is likely to depend sensitively on details such as the molecular structure of lipid species in the membrane, the system’s location on its phase diagram, the molecular structure and mechanical compliance of adhesion-mediating binding proteins, the topography and compliance of the target for adhesion, and the mobility of binding proteins in the membrane and the target.
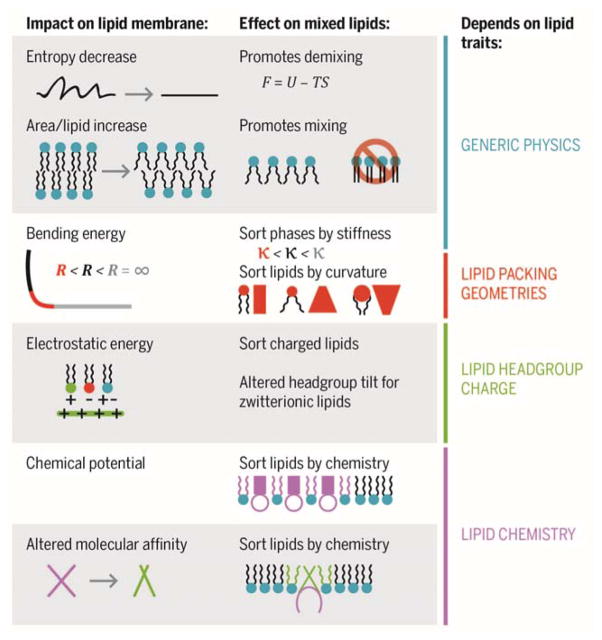
Figure 3 summarizes different ways that adhesion could impact demixing in a mixed-lipid membrane. These ideas are grounded in fundamental principles of lipid chemistry and physics and, to some degree, by empirical studies. However, we emphasize that these ideas are speculative and the degree to which the described effects will impact specific systems very much remains to be determined.
Figure 3. Potential of adhesion on lipid demixing.
(Entropy decrease) Systems demix when this will minimize their free energy, F = U − TS. Thus, for equilibrium physics, the conditions determining whether a membrane will be mixed are demixed are set by a competition between energetic and entropic terms. We have previously argued that suppressing undulations should act to favour demixing by reducing the entropic cost of demixing to form a stiffer lipid phase. (Increased area/lipid) By Le Chatelier’s principle, which states that an equilibrated system will respond to an externally-imposed change in such a way as to oppose the change and achieve a new equilibrium, we expect area/lipid dilation to promote mixing because the area per lipid is greatest for the fluid-disordered Ld phase, and lower for Lo and other ordered lipid phases. (Altered curvature) Work by others has suggested that changes in curvature alone could cause the membrane to phase separate and localize stiffer phases in regions of low curvature, and softer phases in regions of high curvature. (Proximity to target) Minimization of electrostatic energy will sort species of the opposite charge sign to be near the target, and species of the same charge sign to be away from the target. Dipole interactions could alter the tilt of lipid headgroups. Since different lipid phase structures have different headgroup tilts, in principle this could favour demixing. (Receptor clustering) If the receptors have a specific affinity for a particular lipid species, that species could be concentrated in the adhesion region of the membrane. This has recently been shown by Sarah Veatch and co-workers. (Receptor conformational change) If a receptor undergoes a change upon adhesion that alters its affinity for a particular lipid species, that could promote demixing on a very local, molecular lengthscale. We note that this effect does not depend on adhesion to a large or solid target, but could happen even for receptor binding to a small, soluble ligand. Therefore, while it may be challenging to achieve in a model or technological system, this likely under-reflects its biological importance.
Technology
Encapsulation and controlled release of therapeutic agents
In the clinic and home, lipids and lipid-like amphiphiles are widely used in technologies for controlled encapsulation and release 93–99. Liposomes can significantly improve circulation times and can overcome many of the biophysical barriers to drug uptake and effectiveness. In liposome-based systems, delivery is often triggered when the membrane phase separates laterally, into co-existing fluid and solid phases 100. How phase transitions promote release is not generally understood.
Phases vary in their lipid packing density, and so may have varying permeability to drugs, or domain boundaries may have more defects and therefore be more permeable than continuous regions of any phase 100–104. It has also been proposed that physiologically-present proteins act at domain boundaries to disrupt the liposome and increase release 105. These mechanisms would tend to favour slow, diffusive release, while the disruption in the membrane inherent to the phase transition itself could allow a transitory “burst” of release.
Thermally-triggered phase transitions in the membranes of vesicles delivering drugs to hyperthermic cancer sites 106, 107 have gone to clinical trials 108. Typically, the targeted site must be at 43 °C, whereas normal human body temperature is 37 °C. Since body temperatures above 40 °C can be life-threatening, induced hyperthermia at the target site must be spatially minimized and carefully controlled. This has been one of the significant obstacles to overcome for this type of therapy, and has limited its application to sites that can withstand elevated temperature, and where such elevation in temperature can be restricted to the target area only.
Much work exists to target delivery from membrane-based encapsulation systems by incorporating specifically-binding proteins into the membrane. Specifically-binding proteins bind to a particular ligand or target profile. Tumors may be targeted by EGF 109, 110, transferrin and its receptor 111–113, the RGD sequence 114, or the metastasis-asociated Eph A2-EphrinA1 pair 115. Other binders include T cell receptors and their cognate ligands 115, collagen-binding block copolymers 116 and peptides 117, artificial extracellular matrix proteins 118, cadherins 36, and lipids capped with RGD 32, 33 or DNA 34, 35. To date, systems of specifically-adhering membranes for drug delivery have not examined the formation of heterogeneities in the delivering membrane. However, since membrane adhesion is associated with the formation of heterogeneities in protein and lipid composition and phase, we suggest that there is likely technological potential for membranes that respond to adhesion by forming heterogeneities without requiring harmful elevations in temperature.
Biosensing
By containing many signalling molecules, lipid vesicles have the ability to transduce a signal from one or a few binding events into a many-molecule signal. This approach is widely used in biosensors 119 in which liposome binding to a specific region on a strip is controlled by analyte concentration. Subsequent processing, typically involving washing-away or lysis of liposomes, results in a readable signal. Liposome-based sensors have been used to detect a variety of harmful agents and disease markers 120–146 and often have good sensitivity and easy readout. Reducing the number of steps involved in a biosensor assay improves that assay’s efficiency and ease of use. Thus, it is desirable to have liposomes that respond to binding per se by some detectable signal. One avenue toward such responsive liposomes may come from phase separation of bilayer membranes, as in the previous section. Therefore, controlling the characteristics of adhesion-induced phase separation presents a possible way to control signal amplification in biosensors.
Figure 4 summarizes some speculative avenues by which the release of encapsulated contents might be tuned by changing either the perimeter/area ratio of ordered phase and/or the timescale of lipid phase separation, using some of the biophysical ideas discussed previously and shown in Figures 1–3. For ease of reference, a supplementary Figure S1 summarizes the most salient points of Figures 1–3.
Figure 4. Potential avenues for tuning the release of encapsulated contents by tuning the perimeter/area ratio of ordered domains and/or the speed of the phase transition.
These suggestions are based on the impact of mechanical and compositional parameters on membrane adhesion and lipid phase separation, as discussed in the text. In addition, we note that the speed of a phase transition can also be changed if the composition of the membrane can be adjusted such that a first-order transition is replaced with a second-order transition, or vice versa. A second-order transition will be slower than a first-order transition.
Figure 4 focuses on cases in which the encapsulating membrane stays intact, but poration or lysis of the membrane could also be a good strategy for content release. Lateral clustering of negative-curvature or fusogenic lipids may favour membrane poration, lysis, and fusion 147–154.
Conclusions
The interplay between protein-mediated adhesion and lipid phase separation is greatly under-studied and ripe for growth. Extant streams of work that separately examine membrane physics, protein-mediated adhesion, and lipid phase behavior have laid a firm foundation for a new research area that synthesizes these streams. A better understanding of how specific adhesion and lipid phase separation interact has the potential to advance both biology and technology. Both the generic physics of a flexible membrane and the specific chemistry and molecular structure of the protein and lipid species involved are likely to play important roles, as is the mechanics and molecular specificity of the target for adhesion. This rich landscape of parameters provides a biophysical and biochemical rationale for the different types of membrane heterogeneities found at adhesion sites of biological membranes. This review has focused primarily on adhesion to external structures, but the scaffolding cytoskeleton is an internal structure that also has the potential to impact membrane structure. Adhesion to a soluble ligand could also produce some of the same biophysical interactions discussed here.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by startup funds from UT Austin and a gift from ExxonMobile to VDG and by NIH R01 R01 GM089896 to T.J.O.
Notes and references
- 1.Lajoie P, Goetz JG, Dennis JW, Nabi IR. Journal of Chemical Biology. 2009;185:381–385. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200811059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Viola A, Gupta N. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2007;7:889–896. doi: 10.1038/nri2193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Balasubramanian N, Scott DW, Castle JD, Casanova JE, Schwartz MA. Nature Cell Biology. 2007;9:1381–1391. doi: 10.1038/ncb1657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sheetz MP, Sable JE, Sobereiner HG. Annual Review of Biophysics and Biomolecular Structure. 2006;35:417–434. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.35.040405.102017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Manes S, Viola A. Molecular Membrane Biology. 2006;23:59–69. doi: 10.1080/09687860500430069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yu Y, Fay N, Smoligovets A, Wu HJ, Groves J. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e30704. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nair P, Salaita K, Petit R, Groves J. Nature Protocols. 2011;6:523–539. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2011.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Simons K, Ikonen E. Nature. 1997;387:569–572. doi: 10.1038/42408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lingwood D, Simons K. Science. 2010;327:46–50. doi: 10.1126/science.1174621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Edidin M. Annual Reviews in Biophysics and Biomolecular Structure. 2003;32:257–283. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.142439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Simons K, Vaz W. Annual Reviews in Biophysics and Biomolecular Structure. 2004;33:269–295. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.141803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pike L. Journal of Lipid Research. 2006;47:1597–1598. doi: 10.1194/jlr.E600002-JLR200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Engleman DM. Nature. 2005;438:578–580. doi: 10.1038/nature04394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Manz B, Jackson B, Petit R, Dustin M, Groves J. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 2011;108:9089–9094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018771108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Groves J. Angewandte Chemie. 2005;44:3524–3538. doi: 10.1002/anie.200461014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Levental I, Grzybek M, Simons K. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 2011;108:11411–11416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1105996108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Baumgart T, Hammond A, Sengupta P, Hess S, Holowka D, Baird B, Webb W. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 2007;104:3165–3170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611357104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Veatch S, Cicuta P, Sengupta P, Honerkamp-Smith A, Holowka D, Baird B. ACS Chemical Biology. 2008;16:287–293. doi: 10.1021/cb800012x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Honerkamp-Smith A, Veatch S, Keller S. Biochemica Biophysica Acta. 2009;1788:53–63. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.09.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lingwood D, Ries J, Schwille P, Simons K. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 2008;105:10005–10010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804374105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ayuyan A, Cohen F. Biophysical Journal. 2008;94:2654–2666. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.118596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sharma P, Varma R, Sarasij R, Ira, Gousset K, Krishnamoorthy G, Rao M, Mayor S. Cell. 2004;116:577–589. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00167-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Porter J, Hogg N. Trends in Cell Biology. 1998;8:390–396. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(98)01344-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Decker L, ffrench-Constant C. The Journal of Neuroscience. 2004;24:3816–3825. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5725-03.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Salaun C, Gould G, Chamberlain L. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2005;280:19449–19453. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M501923200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chamberlain L, Burgoyne R, Gould G. PNAS. 2001;98:5619–5624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.091502398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Puri N, Roche P. Traffic. 2006;7:1482–1494. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2006.00490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Reverter M, Rentero C, de Muga S, Alvarez-Guaita A, Mulay V, Cairns R, Wood P, Monastyrskaya K, Pol A, Tebar F, Blasi J, Grewal T, Enrich C. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 2011;22:4108–4123. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-04-0332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dustin M, Groves J. Annual Review of Biophysics. 2012;41:543–556. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-042910-155238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Dustin M, Chakraborty A, Shaw A. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives on Biology. 2010;15:a002311. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Fulop T, Le Page A, Garneau H, Azimi N, Baehl S, Dupuis G, Pawelec G, Larbi A. Longevity & Healthspan. 2012;2012:1. doi: 10.1186/2046-2395-1181-1186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Purrucker O, Gonnenwein S, Fortig A, Jordan R, Rusp M, Barmann M, Moroder L, Sackmann E, Tanaka M. Soft Matter. 2007;3:333–336. doi: 10.1039/b612069e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Smith AS, Sengupta K, Goennenwein S, Seifert U, Sackmann E. PNAS. 2008;105:6906–6911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801706105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chung M, Lowe RD, Chan YHM, Ganesan PV, Boxer SG. Journal of Structural Biology. 2009;168:190–199. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2009.06.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.van Lengerich B, Rawle RJ, Boxer SG. Langmuir. 26:8666–8672. doi: 10.1021/la904822f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Perez TD, Nelson WJ, Boxer SG, Kam L. Langmuir. 2005;21:11963–11968. doi: 10.1021/la052264a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fenz S, Smith AS, Merkel R, Sengupta K. Soft Matter. 2011;7:952–962. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Smith AS, Sackmann E. ChemPhysChem. 2009;10:66–78. doi: 10.1002/cphc.200800683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Reister-Gottfried E, Sengupta K, Lorz B, Sackmann E, Seifert U, Smith AS. Physical Review Letters. 2008;101:208103. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.208103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Monzel C, Fenz S, Merkel R, Sengupta K. ChemPhysChem. 2009;10:2828–2838. doi: 10.1002/cphc.200900645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sengupta K, Limozin L. ChemPhysChem. 2010;10:2752–2768. doi: 10.1002/cphc.200900601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Cuvelier D, Nassoy P. Physical Review Letters. 2004;93:228101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.228101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Puech PH, Askovic V, de Gennes PG, Brochard-Wyart F. Biophysical Reviews and Letters. 2006;1:85–95. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Puech P, Feracci H, Brochard-Wyart F. Langmuir. 2004;20:9763–9768. doi: 10.1021/la048682h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sackmann E, Bruinsma R. ChemPhysChem. 2002;12:262–269. doi: 10.1002/1439-7641(20020315)3:3<262::AID-CPHC262>3.0.CO;2-U. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Fenz S, Bihr T, Merkel R, Seifert U, Sengupta K, Smith AS. Advanced Materials. 2011;23:2622–2626. doi: 10.1002/adma.201004097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Krobath H, Rozycki B, Lipowsky R, Weikl T. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e23284. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Weikl T, Groves J, Lipowsky R. Europhysics Letters. 2002;59:916–922. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Weikl T, Asfaw M, Krobath H, Rozycki B, Lipowsky R. Soft Matter. 2009;5:3213–3224. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Krobath H, Schutz G, Lipowsky R, Weikl T. Europhysics Letters. 2007;78:38003. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Rozycki B, Lipowsky R, Weikl T. New Journal of Physics. 2010;12:095003. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Krobath H, Rozycki B, Lipowsky R, Weikl T. Soft Matter. 2009;5:3354–3361. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Limozin L, Sengupta K. Chemphyschem. 2009;16:2752–2768. doi: 10.1002/cphc.200900601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Radler J, Sackmann E. Journal de Physique II. 1993;3:727–748. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Fenz S, Merkel R, Sengupta K. Langmuir. 2009;25:1074–1085. doi: 10.1021/la803227s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Smith AS, Sengupta K, Goennenwein S, Seifert U, Sackmann E. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 2008;105:6906–6911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801706105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Axelrod D. Journal of Cell Biology. 1981;89:141–145. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Groves J, Parthasarathy R, Forstner M. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering. 2008;10:311–338. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bioeng.10.061807.160431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Albersdörfer A, Feder T, Sackmann E. Biophysical Journal. 1997;73:245–257. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(97)78065-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Boulbitch A, Guttenberg Z, Sackmann E. Biophysical Journal. 2001;81:2743–2751. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(01)75917-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kloboucek A, Behrisch A, Faix J, Sackmann E. Biophysical Journal. 1999;77:2311–2328. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77070-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Tanaka M, Sackmann E. Nature. 2005;437:656–663. doi: 10.1038/nature04164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Smith AS, Lorz BG, Seifert U, Sackmann E. Biophysical Journal. 2006;90:1064–1080. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.062166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Sezgin E, Kaiser HJ, Baumgart T, Schwille P, Simons K, Levental I. Nature Protocols. 2012;7:1042–1051. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2012.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Sullan R, Li J, Hao C, Walker G, Zou S. Biophysical Journal. 2010;99:507–516. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.04.044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kaiser HJ, Lingwood D, Levental I, Sampaio J, Kalvodova L, Rajendran L, Simons K. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 2009;106:16645–16650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908987106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Levental I, Byfield F, Chowdhury P, Gai F, Baumgart T, Janmey P. Biochemical Journal. 2009;424:163–167. doi: 10.1042/BJ20091283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Veatch S. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology. 2007;18:573–582. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2007.08.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Feigenson G. Annual Review of Biophysics and Biomolecular Structure. 2007;36:63–77. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.36.040306.132721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Veatch S, Keller S. Physical Review Letters. 2005;94:148101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.148101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Beattie M, Veatch S, Stottrup B, Keller S. Biophysical Journal. 2005;89:1760–1768. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.049635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.McConnell H, Vrljic M. Annual Review of Biophysics and Biomolecular Structure. 2003;32:469–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.141704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Veatch S, Keller S. Physical Review Letters. 2002;89:268101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.89.268101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Veatch S, Keller S. Biophysical Journal. 2003;85:3074–3083. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74726-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Veatch S. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology. 2007;18:573–582. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2007.08.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Manley S, Gordon V. Current Protocols in Cell Biology. 2008;24:3. doi: 10.1002/0471143030.cb2403s40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Gordon V, Beales P, Zhao Z, Blake C, MacKintosh F, Olmsted P, Cates M, Egelhaaf S, Poon W. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 2006;18:L415–L420. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/18/32/L02. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Veatch S, Gawrisch K, Keller S. Biophysical Journal. 2006;90:4428–4436. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.080283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Veatch S, Cicuta P, Sengupta P, Honerkamp-Smith A, Holowka D, Baird B. ACS Chemical Biology. 2008;3:287–293. doi: 10.1021/cb800012x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Stanich C, Honerkamp-Smith A, Putzel G, Warth C, Lamprecht A, Mandal P, Mann E, Hua TAD, Keller S. Biophysical Journal. 2013;105:444–454. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.06.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Helfrich W. Zeitschrift fur Naturforschung C. 1973;28:693–703. doi: 10.1515/znc-1973-11-1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Brochard F, de Gennes P, Pfeuty P. Journal de Physique. 1976;37:1099–1104. [Google Scholar]
- 83.Portet T, Gordon S, Keller S. Biophysical Journal. 2012;103:L35–L37. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.08.061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Hamada T, Kishimoto Y, Nagasaki T, Takagi M. Soft Matter. 2011;7:9061–9068. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Evans E, Rawicz W. Physical Review Letters. 1990;64:2094–2097. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.64.2094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Gordon V, Deserno M, Andrew C, Egelhaaf S, Poon W. Europhysics Letters. 2008;84:48003. [Google Scholar]
- 87.Uline M, Schick M, Szleifer I. Biophysical Journal. 2012;102:517–522. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.12.050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Parthasarathy R, Yu CH, Groves J. Langmuir. 2006;22:5095–5099. doi: 10.1021/la060390o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Beales P, Vanderlick T. Soft Matter. 2011;7:1747–1755. [Google Scholar]
- 90.Zhao J, Wu J, Veatch S. Biophysical Journal. 2013;105:444–454. [Google Scholar]
- 91.Zhao Y, Das S, Du Q. Physical Review E. 2010;81:041919. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.81.041919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Rouhiparkouhi T, Weikl T, Discher D, Lipowsky R. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013;14:2203–2229. doi: 10.3390/ijms14012203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Lian T, Ho RJY. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2001;90:667–680. doi: 10.1002/jps.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Shah JC, Sadhale Y, Chilukuri DM. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2001;47:229–250. doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(01)00108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Langer R. Nature. 1998;392:5–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Cevc G. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2004;56:675–711. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2003.10.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Huang SL, MacDonald RC. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2004;1665:134–141. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Discher DE, Eisenberg A. Science. 2002;297:967–973. doi: 10.1126/science.1074972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Anyarambhatla GR, Needham D. Journal of Liposome Research. 1999;9:491–506. [Google Scholar]
- 100.Sparr E, Aberg C, Nilsson P, Wennerstrom H. Soft Matter. 2009;5:3225–3233. [Google Scholar]
- 101.Lee AG. Biochimica Biophysica Acta. 1977;472:237–281. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(77)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Papahadjopoulos D, Jacobson K, Nir S, Isac T. Biochimica Biophysica Acta. 1973;311:330–348. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Blok MC, van der Neut-Kok ECM, van Deenen LLM, de Gier J. Biochimica Biophysica Acta. 1975;406:187–196. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Risbo J, Jorgensen K, Sperotto MM, Mouritsen OH. Biochimica Biophysica Acta. 1997;1329:85–96. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2736(97)00091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Kong G, Dewhirst MW. Int J Hyperthermia. 1999;15:345–370. doi: 10.1080/026567399285558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Yatvin MB, Weinstein JN, Dennis WH, Blumenthal R. Science. 1978;202:1290–1293. doi: 10.1126/science.364652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Weinstein JN, MRL, Yatvin MB, Zaharko DS. Science. 1979;204:188–191. doi: 10.1126/science.432641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Puri A, Loomis K, Smith B, Lee JH, Yavlovich A, Heldman E, Blumenthal R. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2009;26:523–580. doi: 10.1615/critrevtherdrugcarriersyst.v26.i6.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Mamot C, Drummond DC, Greiser U, Hong K, Kirpotin DB, Marks JD, Park JW. Cancer Research. 2003;63:3154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Kullberg EB, Bergstrand N, Carlsson J, Edwards K, Johnsson M, Sjoberg S, Gedda L. Bioconjugate Chemistry. 2002;13:737–743. doi: 10.1021/bc0100713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Wagner E, Curiel D, Cotten M. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 1994;14:113–135. [Google Scholar]
- 112.Qian ZM, Li H, Sun H, Ho K. Pharmacological Reviews. 2002;54:561–587. doi: 10.1124/pr.54.4.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Kakudo T, Chaki S, Futaki S, Nakase I, Asaji K, Kawakami T, Maruyama K, Kamiya H, Harashima H. Biochemistry. 2004;43:5618–5628. doi: 10.1021/bi035802w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Colin M, Maurice M, Trugnan G, Kornprobsl M, Harbottle RP, Knight A, Cooper RG, Miller AD, Capeau J, Coutelle C, Brahimi-Horn MC. Gene Therapy. 2000;7:139–152. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3301056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Yu CH, Groves JT. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2010;48:955–963. doi: 10.1007/s11517-010-0634-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.O’Neil CP, van der Vlies AJ, Velluto D, Wandrey C, Demurtas D, Dubochet J, Hubbell JA. Journal of Controlled Release. 2009;137:146–151. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.03.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Rothenfluh DA. Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 118.Liu JC, Tirrell DA. Biomacromolecules. 2008;9:2984–2988. doi: 10.1021/bm800469j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Liu Q, Boyd B. Analyst. 2013;138:391–409. doi: 10.1039/c2an36140j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Wen HW, Borejsza-Wysocki W, DeCory T, Durst R. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2005;382:1217–1226. doi: 10.1007/s00216-005-3292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Wen HW, Borejsza-Wysocki W, DeCory T, Baeumner A, Durst R. European Food Research and Technology. 2005;221:564–569. [Google Scholar]
- 122.Reefes S, Siebert S, Roberts M, Durst R. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry. 1995;14:351–355. [Google Scholar]
- 123.Ahn-Yoon S, DeCory T, Durst R. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2004;378:68–75. doi: 10.1007/s00216-003-2365-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Ahn S, Durst R. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2008;391:473–478. doi: 10.1007/s00216-007-1551-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Park S, Durst R. Analytical Biochemistry. 2000;280:151–158. doi: 10.1006/abio.2000.4481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Shukla S, Bang J, Heu S, Kim M. European Food Research and Technology. 2012;234:53–59. [Google Scholar]
- 127.Kim M, Oh S, Durst R. Journal of Microbiol Biotechnol. 2003;13:509–516. [Google Scholar]
- 128.Ho JAA, Zeng SC, Tseng WH, Lin YJ, Chen CH. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2008;391:479–485. doi: 10.1007/s00216-008-1875-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Ho JAA, Hsu HW. Analytical Chemistry. 2003;75:4330–4334. doi: 10.1021/ac0343580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Baeumner A, Leonard B, McElwee J, Montagna R. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2004;380:15–23. doi: 10.1007/s00216-004-2726-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Hartley H, Baeumner A. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 2003;376:319–327. doi: 10.1007/s00216-003-1939-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Baeumner A, Schlesinger N, Slutzki N, Romano J, Lee E, Montagna R. Analytical Chemistry. 2002;74:1442–1448. doi: 10.1021/ac015675e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Kumanan V, Nugen S, Baeumner A, Chang YF. Journal of Veterinary Science. 2009;10:35–42. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2009.10.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Horie M, Yanagisawa H, Sugawara M. Analytical Biochemistry. 2007;369:192–201. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2007.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Banerjee J, Hanson A, Nyren-Erickson E, Ganguli B, Wagh A, Muhonen W, Shabb BLJ, Srivastava D, Mallik S. Chemical Communications. 2010;46:3209–3211. doi: 10.1039/b926554f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Rongen H, van der Horst H, Hugenholtz G, Bult A, van Bennekom W. Analytica Chimica Acta. 1994;287:191–199. [Google Scholar]
- 137.Rongen H, van Nierop T, van der Horst H, Rombouts R, van der Meide P, Bult A, van Bennekom W. Fluorimetry. 1995;306:333–341. [Google Scholar]
- 138.Edwards K, March J. Analytical Biochemistry. 2007;368:39–48. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2007.04.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Ho J-AA, Wu L-C, Huang M-R, Lin Y-J, Baeumner A, Durst R. Analytical Chemistry. 2007;79:246–250. doi: 10.1021/ac060889n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Ho JAA, Hsu HW, Huang MR. Analytical Biochemistry. 2004;330:342–349. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2004.03.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Viswanathan S, Wu LC, Huang MR, Ho JA. Analytical Chemistry. 2006;78:1115–1121. doi: 10.1021/ac051435d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Qu B, Guo L, Chu X, Wu DH, Shen GL, Yu RQ. Analytica Chimica Acta. 2010;663:147–152. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2010.01.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Egashira N, Morita SI, Hifumi E, Mitoma Y, Uda T. Analytical Chemistry. 2008;80:4020–4025. doi: 10.1021/ac702625d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Chen H, Zheng Y, Jiang JH, Wu HL, Shen GL, Yu RQ. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2008;24:684–689. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2008.06.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Zheng Y, Chen H, Liu XP, Jiang JH, Luo Y, Shen GL, Yu RQ. Talanta. 2008;77:809–814. [Google Scholar]
- 146.Thet N, Hong S, Marshall S, Laabei M, Toby A, Jenkins A. Biosensors and Bioelectronics. 2013;41:538–543. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2012.09.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Cevc G, Richardsen H. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 1999;38:207–232. doi: 10.1016/s0169-409x(99)00030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Ellens H, Benz J, Szoka FC. Biochemistry. 1984;23:1532–1538. doi: 10.1021/bi00302a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Connor J, Yatvin MB, Huang L. PNAS. 1984;81:1715–1718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Collins D, Litzinger DC, Huang L. Biochimica Biophysica Acta. 1990;1025:234–242. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90102-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Ho RJY, Rouse BT, Huang L. Biochemistry. 1986;25:5500–5506. doi: 10.1021/bi00367a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Pinnaduwage P, Huang L. Biochemistry. 1992;31:2850–2855. doi: 10.1021/bi00126a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Ho RJY, Rouse BT, Huang L. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1987;31:13973–13978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Cevc G. Journal of Lipid Research. 1996;6:643–663. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.