Figure 3. Lentivirus-mediated shRNA knockdown of NIBP inhibits the colony formation of cancer cells in vitro.
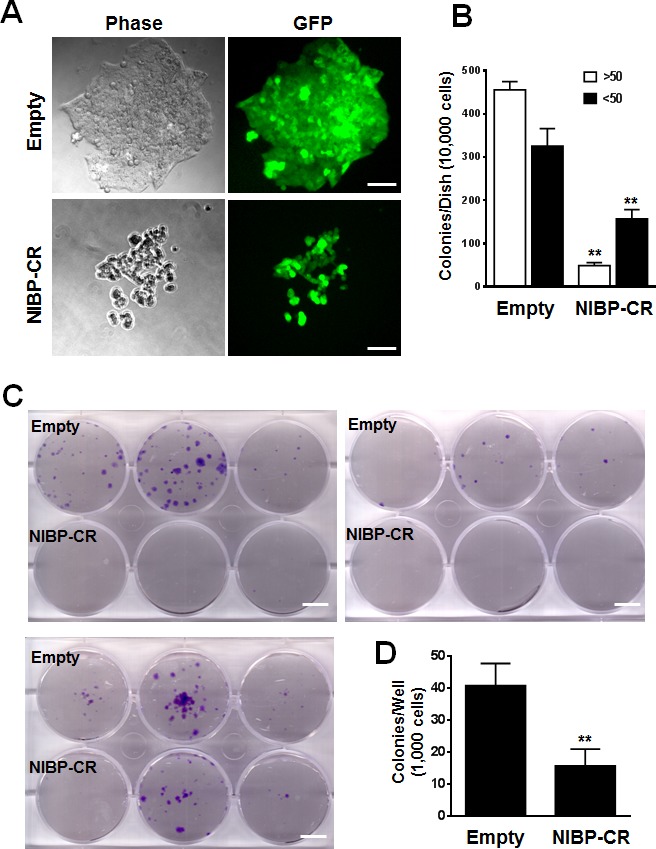
(A, B) Anchorage-dependent colony formation was significantly inhibited in NIBP-CR shRNA transduced HCT116 cells (passage 5). An equal number of exponentially growing cancer cells with or without stable NIBP shRNA knockdown were seeded in a 6-well tissue culture plate and incubated for 2 weeks. All colonies with at least 10 cells were counted under a standard inverted fluorescent microscope. The values (B) represent mean ± SD of three independent experiments each with triplicate wells. (C, D) Anchorage-independent growth was significantly reduced in NIBP-CR shRNA transduced MDA-MB-231 cells (passage 4). Equal numbers of cancer cells were resuspended in 1 ml of 0.3% top agar and plated on 2 ml of 0.8% bottom agar in each well of a 6-well plate. After 3 weeks, cell colonies were visualized by crystal violet staining (C) and quantified by counting the colony number (D). ** p<0.01 indicates a significant decrease in NIBP-CR shRNA knockdown as compared with corresponding empty vector control. Scale bar = 50 μm (A) or 10 mm (C).
