Abstract
Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are common imaging methods to detect cervical lymph node metastasis of head and neck cancer. We aimed to assess the diagnostic efficacy of CT and MRI in detecting cervical lymph node metastasis, and to establish unified diagnostic criteria via systematic review and meta-analysis. A systematic literature search in five databases until January 2014 was carried out. All retrieved studies were reviewed and eligible studies were qualitatively summarized. Besides pooling the sensitivity (SEN) and specificity (SPE) data of CT and MRI, summary receiver operating characteristic curves were generated. A total of 63 studies including 3,029 participants were involved. The pooled results of meta-analysis showed that CT had a higher SEN (0.77 [95% confidence interval {CI} 0.73–0.87]) than MRI (0.72 [95% CI 0.70–0.74]) when node was considered as unit of analysis (P<0.05); MRI had a higher SPE (0.81 [95% CI 0.80–0.82]) than CT (0.72 [95% CI 0.69–0.74]) when neck level was considered as unit of analysis (P<0.05) and MRI had a higher area under concentration-time curve than CT when the patient was considered as unit of analysis (P<0.05). With regards to diagnostic criteria, for MRI, the results showed that the minimal axial diameter of 10 mm could be considered as the best size criterion, compared to 12 mm for CT. Overall, MRI conferred significantly higher SPE while CT demonstrated higher SEN. The diagnostic criteria for MRI and CT on size of metastatic lymph nodes were suggested as 10 and 12 mm, respectively.
Keywords: computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, metastasis, head and neck cancer, meta-analysis
Introduction
The occurrence of cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with head and neck cancers are very common.1 The presence of cervical lymph node metastasis may affect the optimal treatment choice as well as prognosis in patients.2 Management of patients presenting with cervical lymph node metastasis includes selective or radical neck dissection, followed by radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy depending on the pathological findings of the nodes.3–5 Besides, the detection of cervical lymph node metastasis is very important for predicting prognosis in patients with head and neck cancers.6–8
Many imaging techniques exist for identifying cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with head and neck cancers.9–12 Among them, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are the most widely used tools.13 Both of them have improved accuracy of nodal staging over clinical palpation and the nodes which are clinically occulted can be visualized through these techniques.14 Usually the cervical lymph nodes demonstrate similar density as muscle on pre-contrast images of CT examination, and they can be separated from adjacent vessels by their differential enhancement after contrast administration.15 On the other hand, MRI is considered to have similar accuracy for identifying the cervical lymph node metastasis of head and neck cancer.16,17 Because of the intrinsic high soft-tissue discrimination, MRI has become the preferred method for evaluating the soft tissues of the head and neck recently.18 Under current health care settings, the routine practice for evaluating patients with head and neck cancer is to perform either CT or MRI, but not both.19 Thus, to determine whether one of the two techniques is superior to the other is critical for providing guidance for clinical practice. Besides, since relevant studies utilized very different diagnostic criteria, it is warranted to determine the unified criteria that are most appropriate. A systematic review to assess all available evidence is thus needed for providing a comprehensive evaluation for these aims.
The aim of this study was thus to compare CT and MRI for detecting cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with head and neck cancer and to establish the unified diagnostic criteria by performing a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
Inclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: a) types of study: diagnostic accuracy test studies designed as cohort studies; b) participants: patients with biopsy proven head and neck cancers who would undergo neck dissection; c) index tests: CT and/or MRI; d) target condition: cervical lymph node metastasis; e) reference standard: histopathology examination; f) outcome: rates of true positive, false positive, false negative, and true negative or related data that could be used to calculate them.
Literature search
With no language restriction, the following databases were searched for retrieving studies: MEDLINE (1948 to 25 January 2014), EMBASE (1980 to 25 January 2014), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (1994 to 25 January 2014), VIP Chinese Journal Database (1989 to 25 January 2014), and Chinainfo (1998 to 25 January 2014).
The search strategy was optimized for all consulted databases, taking into account the differences in the various controlled vocabularies as well as the differences of database-specific technical variations.20 Once relevant articles were identified, their reference lists were searched for additional articles. Both Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) and free text words were used in the search strategy with the following MeSH terms: “head and neck neoplasm”, “neoplasm metastases”, “SEN and SPE”, “Tomography, Spiral Computed” and “Magnetic Resonance Imaging”.
Study selection
Two reviewers independently examined the titles and abstracts of each search record to remove obviously irrelevant ones, and then retrieved the full text articles for potentially eligible articles. The full-texts were further examined according to the inclusion criteria. Discrepancies were resolved by consensus.
Data extraction
A standardized data extraction form was used by two authors independently for data extraction from included studies. Discrepancies were resolved by discussion, with input from a third author. The contents of the form included: name of first author, publication year, country, participants’ age, sex, number of included patients, tumor location, unit, details of CT and/or MRI, study design (prospective or retrospective).
Quality assessment
The methodological quality of included studies was assessed by The Quality Assessment Diagnostic Accuracy Studies statement-2 (QUADAS-2),21 which included four domains: patient selection, index test, reference standard, and flow and timing. Each domain was assessed in terms of risk of bias and the first three were assessed in terms of concerns regarding applicability. Signaling questions were included to assist judgments on risk of bias. The signaling questions in the QUADAS-2 were presented as shown in Table 1. The result for each item was categorized as yes (Y), unclear (U), or no (N). The summary risk of bias for each study was categorized as low (A), unclear (B), or high (C).
Table 1.
Signaling questions in the QUADAS-2
| Domain | Patient selection | Index test | Reference standard | Flow and timing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signaling questions (yes/no/unclear) | 1 Was a consecutive or random sample of patients enrolled? | 4 Were the index test results inter preted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard? | 5 Is the reference standard likely to correctly classify the target condition? | 7 Was there an appropriate interval between index test(s) and reference standard? |
| 2 Was a case-control design avoided? | 6 Were the reference standard results interpreted without know ledge of the results of the index test? | 8 Did all patients receive a reference standard? | ||
| 3 Did the study avoid inappropriate exclusions? | 9 Were all patients included in the analysis? |
Abbreviation: QUADAS-2, The Quality Assessment Diagnostic Accuracy Studies statement-2.
Meta-analysis
Measures of diagnostic efficacy of CT and/or MRI included sensitivity (SEN), specificity (SPE), positive likelihood ratio (+LR), negative likelihood ratio (−LR), accuracy (ACC), and diagnostic odds ratios (DOR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curves were then drawn. The area under the curve (AUC) and Q* (the point where SEN is equal to SPE on the SROC curve) were calculated.
To detect any differences for SEN, SPE, AUC, and Q* between CT and MRI, a Z-test was conducted (Z= (VAL1–VAL2)/SQRT (SE12+SE22). The test standard was set at α=0.05. VAL indicates the mean of SEN, SPE, AUC or Q* of the CT or MRI and SE indicates the standard error of the corresponding variable.
Heterogeneity analysis
Heterogeneity between studies was evaluated by I2 statistic.22,23 If I2≤50% and P≥0.10, the heterogeneity was considered not significant and in such case the fixed-effects model would be used in meta-analysis. Otherwise, the random-effects model would be used.24,25
Meta-regression
Meta-regression was used to determine any potential source of heterogeneity that might influence the overall assessment. The test standard for meta-regression was set at α=0.10. Relevant variables which might cause heterogeneities were tested, and any suggested sources of heterogeneity were considered as proof for a subgroup analysis. Variables detected by meta-regression included publication year (0= published before 2000; 1= published in or after 2000), race (0= Mongolia; 1= Caucasian), study type (0= retrospective; 1= prospective), risk of bias (0= high; 1= unclear; 2= low), blinding of the radiologists (0= no or unclear; 1= yes) and blinding of the pathologists (0= no or unclear; 1= yes). Meta-disc 1.4 and STATA 11.0 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX, USA) were used to perform the statistical analyses.26,27
Results
Selection of literature
The computerized and manual search retrieved a total of 306 articles. After assessing the titles and abstracts, 144 articles were found to be potentially relevant. After the full text assessment, 63 studies met the inclusion criteria and were included in this meta-analysis (Figure 1).28–90
Figure 1.
Flow chart of the literature search and selection.
Abbreviations: CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
Study characteristics
Of the 63 included studies, 24 were retrospective and 39 were prospective. A total of 3,029 participants were involved in these studies. Among those patients, 1,044 underwent both CT and MRI examination, 2,395 underwent MRI examination, and 1,678 underwent CT examination. Three kinds of unit of analysis were used, including node, neck level (the neck was classified as five levels according to anatomical landmarks), and patients. When node was considered as the unit of analysis, available studies involved 22 with CT and 30 with MRI. When neck level was considered as the unit of analysis, eight studies with CT and 16 with MRI were available. When patient was considered as the unit of analysis, available studies included eight with CT and eleven with MRI. The tumor locations included floor of mouth, nasopharynx, retromolar trigonum, mandibule, maxilla, supra-glottic larynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx, hypopharynx, parotid gland, submandibular gland, tonsil, thyroid gland, cervical esophageal, paranasal sinuses et al. The characteristics of included studies are listed in Table 2.
Table 2.
Study characteristics and included data sets for CT and MRI of the included articles
| Study ID | Country | Study type | Patients (M/F) | Age (yr), mean (range) | Tumor location | Imaging modality | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adams et al28 1998 | Germany | P | 60 (16/44) | 58.3 (38–76) | Tongue, FOM, Palate, MAN, MAX | MRI, CT | node |
| Akoglu et al29 2005 | Turkey | P | 23 (19/4) | 58.3 (40–78) | Head and neck | MRI, CT | node |
| Anzai et al30 1994 | USA | P | 12 (7/5) | 39–78 | EAC, MAN, BCC, RMT, Lip, Oral cavity, Larynx | MRI | node |
| Ao et al31 1998 | Japan | R | 42 (9/33) | 60 (39–78) | Larynx | MRI, CT | node |
| Bondt et al32 2009 | The Netherlands | P | 16 (9/7) | 40–77 | Tongue, NP, RMT, SMG, Cheek, RMT, SP, Nose | MRI, CT | neck level |
| Braams et al33 1996 | The Netherlands | P | 11 (7/4) | 62.3 (46–73) | FOM, RMT, Cheek, Gingiva | MRI, CT | node |
| Braams et al34 1995 | The Netherlands | P | 12 (8/4) | 65.3 (48–85) | Tongue, Lip, Gingiva, RMT, FOM | MRI | node |
| Bruschini et al35 2003 | Italy | P | 22 (19/3) | 62.3 (46–79) | Larynx, OP, Oral cavity, Skin | CT | node |
| Curtin et al36 1997 | Canada | R | 213 (150/63) | 59.6 (18–84) | Oral cavity, OP, HP, Larynx | MRI, CT | neck level |
| Dammann et al37 2005 | Germany | P | 64 (43/21) | 56 (26–83) | Oral cavity, OP | MRI, CT | neck level |
| Ding et al38 2005 | People’s Republic of China | P | 92 (58/34) | 53 (24–81) | Tongue | MRI | neck level |
| Dirix et al39 2010 | Sweden | P | 22 (13/9) | 60 (41–83) | Oral cavity, Larynx, HP | MRI | node |
| Eida et al40 2003 | Japan | P | 111 (74/37) | FOM, Tongue, Palate, Gingiva, Cheek | CT | node | |
| Fan et al41 2006 | People’s Republic of China | R | 42 (37/5) | 53.6 (45–70) | OP, HP, Cervical esophageal | CT | patient |
| Fukunari et al42 2010 | Japan | R | 20 | 58 (23–81) | Tongue, Gingiva, Buccal, MAN, FOM | MRI | node |
| Gross et al43 2001 | USA | R | 26 (8/18) | 40 (10–80) | Thyroid | MRI | node |
| Gu et al44 2000 | People’s Republic of China | P | 62 | 58 (44–77) | Head and neck | MRI | node |
| Guenzel et al45 2013 | Germany | P | 120 (95/25) | 41–85 | OP, Larynx | MRI | node |
| Guo et al46 2006 | People’s Republic of China | R | 48 (28/20) | 56 (21–66) | Tongue, Buccal, Gingiva, FOM, Palate | MRI | node |
| Hannah et al47 2002 | Australia | P | 48 (34/14) | 61 (26–92) | Oral cavity, OP, SGL, HP | CT | neck level |
| Hao et al48 2000 | People’s Republic of China | P | 60 | Tongue, Gingiva, FOM, Palate, RMT, Buccal, Larynx, HP | MRI | node | |
| Hafidh et al49 2006 | Ireland | R | 48 (42/6) | 56 (32–80) | Oral cavity, OP, HP, Paranasal sinuses, Ear(skin) | MRI, CT | node |
| Hlawitschka et al50 2002 | Germany | P | 38 (28/10) | 59 (41–89) | Tongue, Buccal, Palate, MAX | MRI, CT | node |
| Hoffman et al51 2000 | USA | P | 9 (6/3) | 43–76 | Oral cavity, OP, Lip | MRI | node, neck level |
| Jeong et al52 2007 | Greece | R | 47 (41/6) | 56.3 | Oral cavity, Larynx, OP, HP, PG | CT | neck level |
| Kau et al53 1999 | Germany | P | 111 (95/16) | 29–78 | Larynx, OP, LP, Lip, Ear | MRI, CT | node, neck level |
| Kawai et al54 2005 | Japan | P | 29 (23/6) | 60 (28–81) | Tongue, OP, NP, Larynx, Buccal, Palate, PG, Gingiva | MRI | neck level |
| Ke et al55 2006 | People’s Republic of China | R | 20 (15/5) | 54.5 (31–69) | Tongue, Larynx, Thyroid gland | CT | node |
| Krabbe et al56 2008 | The Netherlands | P | 38 (21/17) | 59 (53–680) | Tongue, Gingiva, FOM, Tonsillar fossa | MRI, CT | node |
| Laubenbacher et al57 1994 | Germany | P | 22 (20/2) | 54.4 (38–70) | OP, HP | MRI | node, neck level |
| Lee et al58 2013 | People’s Republic of China | P | 22 (21/1) | 49.8 (26–66) | Tongue, Buccal, OP, FOM, HP, Palate, RMT, epiglottis, Pyriform sinus | MRI | patient |
| Lu et al59 2007 | People’s Republic of China | P | 13 (11/2) | 58 (47–71) | Oral cavity, HP, OP, Larynx | CT | node |
| Lwin et al60 2012 | UK | R | 102 (68/34) | 59 (23–89) | Tongue, FOM, Palate, Buccal, RMT, Tonsil, Gingiva | MRI | patient |
| Mcguirt et al61 1995 | UK | P | 49 | Oral cavity, OP, HP | CT | node | |
| Nakamoto et al62 2009 | Japan | R | 65 (50/15) | 62 (27–81) | Larynx, HP, MAX, Tongue, OP, PG, Gingiva, FOM, NP, Ethmoid, EAM, Thyoid | MRI | patient |
| Nishimura et al63 2006 | Japan | P | 16 (13/3) | 65.8 (37–76) | Cervical Esophageal | MRI | node |
| Olmos et al64 1999 | The Netherlands | P | 12 (6/6) | 61.8 (44–73) | OP, Larynx, HP, Tongue, MAX | MRI | neck level |
| Ou et al65 2007 | People’s Republic of China | R | 24 (19/5) | 50 (23–80) | Tongue, OP, Palate, Cheek, Maxillary sinus, Branchial cleft | MRI | node |
| Paulus et al66 1998 | Belgium | R | 25 (21/4) | 48–74 | SGL, Tongue, Glottis, Palate, RMT, FOM, HP, Vocal cord, Vestibule, Pyriform sinus | CT | node |
| Perrone et al67 2011 | Italy | R | 17 (10/7) | 63 (15–85) | Head and neck | MRI | patient |
| Peters et al68 2013 | The Netherlands | R | 149 (120/29) | 62 (40–78) | SGL, Glottis, NP, Cervical Esophageal | MRI, CT | patient |
| Pohar et al69 2006 | USA | R | 25 (17/8) | 63.4 | Oral cavity, OP, HP, Larynx, Nasal cavity | CT | node, neck level |
| Ren et al70 2000 | People’s Republic of China | P | 20 (18/2) | 45–68 | SGL | CT | node |
| Schwartz et al71 2004 | USA | P | 20 (20/0) | 61 (42–78) | Oral cavity, OP | CT | node |
| Semedo et al72 2006 | Portugal | P | 20 (20/0) | 57.3 (36–78) | HP, Larynx, OP | MRI | node |
| Seitz et al73 2009 | Germany | R | 66 (39/27) | 63 (25–89) | Oral cavity, OP | MRI | node, patient |
| Stokkel et al74 2000 | The Netherlands | P | 54 (31/23) | 60 (34–81) | Tongue, FOM, Gingiva, RMT, OP | CT | node |
| Stuckensen et al75 2000 | Germany | P | 106 (89/17) | 59.6 (33–87) | FOM, Tongue, RMT, MAN, MAX, Buccal | MRI, CT | neck level |
| Sumi et al76 2007 | Japan | R | 38 (32/6) | 65 | HP, Gingiva, OP, Tongue, Larynx, FOM | MRI, CT | node |
| Sumi et al77 2006 | Japan | P | 26 | OP, Gingiva, Larynx, Tongue | MRI | node | |
| Sumi et al78 2003 | Japan | P | 32 | 24–80 | OP, Gingiva, FOM, Tongue, Buccal, EAC | MRI | node |
| Sun et al79 2013 | People’s Republic of China | R | 114 (60/54) | 51.2 (34–70) | Thyroid gland, Larynx, NP, HP, Tongue, PG, Cervical Esophageal, Maxillary sinus, Ear | CT | node |
| Sun et al79 2013 | People’s Republic of China | R | 86 (45/41) | 52.7 (35–75) | Thyroid gland, Larynx, NP, HP, Tongue, PG, Cervical Esophageal, Maxillary sinus, Ear | MRI | node |
| Tai et al80 2002 | People’s Republic of China | P | 40 (24/16) | 25–65 | NP | MRI | patient |
| Takashima et al81 1997 | Japan | R | 50 (13/37) | 57 (24–81) | Thyroid | MRI | node |
| Tuli et al82 2008 | India | P | 20 (12/8) | 54.75 (30–85) | Tongue | MRI, CT | patient |
| Van den Brekel et al83 1991 | The Netherlands | P | 100 | 63±12.8 | Tongue, FOM, SP, Lip, Tonsil, Pharyngeal wall, Ear, Tonsil, PS, SGL, Gingiva | MRI | patient |
| Vandecaveye et al84 2008 | Belgium | P | 36 | 41–81 | Nasal cavity, SGL, FOM, OP, Glottis, Tongue, HP | MRI | node, neck level, patient |
| Wang et al85 1999 | Japan | P | 14 (10/4) | 46 (26–71) | Thyroid | MRI | node |
| WIDE et al86 1999 | UK | R | 58 | 58.1 (32–82) | Tongue, FOM, Buccal, RMT, OP, Gingiva | MRI | neck level |
| Wilson et al87 1994 | UK | P | 12 | FOM, Tongue, Tonsillar, Skin, Pinna, PG, Thyroid | MRI | neck level | |
| Wu et al88 2010 | People’s Republic of China | R | 24 (23/1) | 53.6 (45–85) | Larynx, HP | CT | node |
| Yoon et al89 2008 | Korea | R | 67 (58/9) | 60 (24–85) | Larynx, Pharynx, Tonsil, Tongue, Oral cavity, Skin, MAX | MRI, CT | neck level |
| Yuan et al90 2000 | People’s Republic of China | R | 19 (12/7) | 42–66 | Larynx | MRI | neck level |
Abbreviations: M, male; F, female; R, Retrospective; P, Prospective; EAC, external auditory canal; BCC, branchial cleft cyst; PS, piriform sinus; SGL, supra-glottic larynx; TGL, trans-glottic larynx; CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; FOM, floor of mouth; MAN, mandibule; MAX, maxilla; RMT, retro-molar trigonum; NP, nasopharynx; SMG, submandibular gland; OP, oropharynx; HP, hypopharynx; LP, laryngopharynx; PG, parotid gland; SP, supropharynx; yr, years.
Quality of included studies
All included studies had fairly good applicability. For the risk of bias assessment, only two studies had a low risk of bias, five had a high risk, and 56 had an unclear risk (Table 3).
Table 3.
Risk of bias of included studies
| Study ID | Patient selection
|
Index test
|
Reference standard
|
Flow and timing
|
Summary risk of bias | Applicability | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |||
| Adams et al28 1998 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Akoglu et al29 2005 | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Anzai et al30 1994 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Ao et al31 1998 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Bondt et al32 2009 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Braams et al33 1996 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Braams et al34 1995 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Bruschini et al35 2003 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Curtin et al36 1997 | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Dammann et al37 2005 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Ding et al38 2005 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Dirix et al39 2010 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Eida et al40 2003 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Fan et al41 2006 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | N | A | H |
| Fukunari et al42 2010 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Gross et al43 2001 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Gu et al44 2000 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Guenzel et al45 2013 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Guo et al46 2006 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | N | A | H |
| Hannah et al47 2002 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Hao et al48 2000 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Hafidh et al49 2006 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Hlawitschka et al50 2002 | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | N | A | H |
| Hoffman et al51 2000 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Jeong et al52 2007 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Kau et al53 1999 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Kawai et al54 2005 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Ke et al55 2006 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Krabbe et al56 2008 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Laubenbacher et al57 1994 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Lee et al58 2013 | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Lu et al59 2007 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Lwin et al60 2012 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Mcguirt et al61 1995 | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Nakamoto et al62 2009 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Nishimura et al63 2006 | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Olmos et al64 1999 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | Y | Y | N | A | H |
| Ou et al65 2007 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Paulus et al66 1998 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Perrone et al67 2011 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Peters et al68 2013 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Pohar et al69 2006 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Ren et al70 2000 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Schwartz et al71 2004 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Semedo et al72 2006 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Seitz et al73 2009 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | C | H |
| Stokkel et al74 2000 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Stuckensen et al75 2000 | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Sumi et al76 2007 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Sumi et al77 2006 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Sumi et al78 2003 | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Sun et al79 2013 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Tai et al80 2002 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | N | A | H |
| Takashima et al81 1997 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Tuli et al82 2008 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Van den Brekel et al83 1991 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Vandecaveye et al84 2008 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Wang et al85 1999 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | C | H |
| WIDE et al86 1999 | U | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Wilson et al87 1994 | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Wu et al88 2010 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | U | Y | Y | B | H |
| Yoon et al89 2008 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
| Yuan et al90 2000 | U | Y | Y | U | Y | U | Y | Y | Y | B | H |
Abbreviations: Y, yes; U, unclear; N, no; A, high risk of bias; B, unclear risk of bias; C, low risk of bias; H, high applicability.
Comparison of CT and MRI in detecting cervical lymph node metastasis with node as unit of analysis
For CT, meta-regression analysis showed that the diagnostic efficacy was not affected by any of the tested variables. These variables thus did not account for heterogeneity between studies. After pooling 22 studies, we detected that CT had a mean (CI) SEN of 0.77 (95% CI 0.73–0.80), SPE of 0.85 (0.84–0.87), +LR of 3.84 (2.51–5.87), −LR of 0.34 (0.24–0.27), ACC of 0.8357, and DOR of 13.57 (6.99–26.33). The SROC was demonstrated in Figure 2 and the AUC was 0.8429 and Q* was 0.7745. For MRI, meta-regression analysis also showed that the diagnostic efficacy was not affected by any of the tested variables. After pooling 30 studies, we identified that MRI had a mean (CI) SEN of 0.72 (0.70–0.74), SPE of 0.84 (0.83–0.85), +LR of 5.06 (3.72–6.88), −LR of 0.27 (0.21–0.34), ACC of 0.8126, and DOR of 25.21 (15.97–39.80). The SROC is shown in Figure 2 and the AUC was 0.9054 and Q* was 0.8371.
Figure 2.
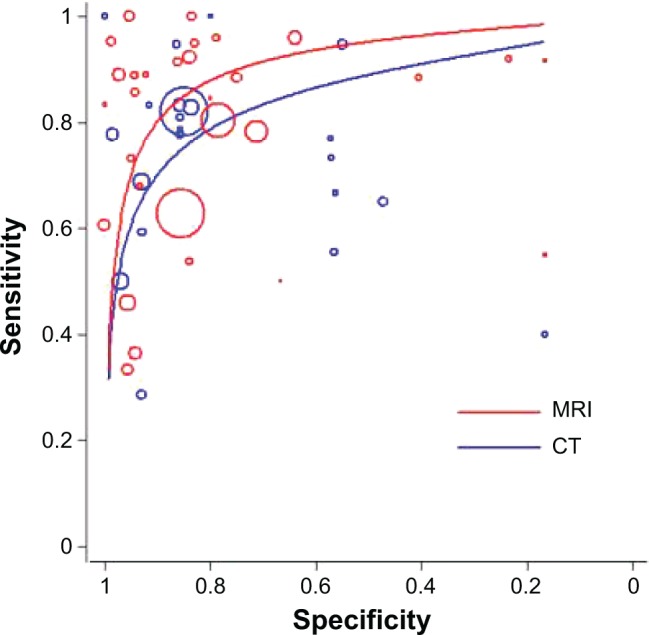
Summary receiver operator characteristic curves of CT and MRI (node as unit of analysis).
Abbreviations: CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
By comparing the diagnostic efficacy between CT and MRI when node was treated as the unit of analysis, the results indicated that CT had a higher SEN, although the SPE and summarized diagnostic efficacy were comparable. The details are listed in Table 4.
Table 4.
Comparison of meta-analysis results on diagnostic efficacy between CT and MRI
| Unit | Variable | Number detected | SEN (95% CI) | SPE (95% CI) | AUC (SE) | Q* (SE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Node | CT | 2,483 | 0.77 (0.73–0.87) | 0.85 (0.84–0.87) | 0.8429 (0.0341) | 0.7745 (0.0318) |
| MRI | 7,100 | 0.72 (0.70–0.74) | 0.84 (0.83–0.85) | 0.9054 (0.0198) | 0.8371 (0.0215) | |
| P | 0.0176 | 0.2739 | 0.1098 | 0.1262 | ||
| Neck level | CT | 1,665 | 0.84 (0.75–0.84) | 0.72 (0.69–0.74) | 0.8787 (0.0268) | 0.8091 (0.0270) |
| MRI | 4,022 | 0.80 (0.77–0.82) | 0.81 (0.80–0.82) | 0.8860 (0.0262) | 0.8165 (0.0269) | |
| P | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.8689 | 0.8702 | ||
| Patient | CT | 230 | 0.67 (0.52–0.80) | 0.74 (0.68–0.81) | 0.6860 (0.0815) | 0.6418 (0.0643) |
| MRI | 716 | 0.78 (0.70–0.81) | 0.76 (0.72–0.80) | 0.8631 (0.0437) | 0.7937 (0.0424) | |
| P | 0.1992 | 0.6161 | 0.0491 | 0.0683 |
Abbreviations: AUC, area under the curve; CI, confidence interval; SE, standard error; CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; SEN, sensitivity; SPE, specificity.
Comparison of CT and MRI in detecting cervical lymph node metastasis with neck level as unit of analysis
For MRI, meta-regression analysis detected that none of the tested variables accounted for heterogeneity between studies. After pooling 16 studies, it was detected that MRI had a mean (CI) SEN of 0.80 (0.77–0.82), SPE of 0.81 (0.80–0.82), +LR of 5.34 (3.24–8.82), −LR of 0.27 (0.20–0.37), ACC of 0.5257, DOR of 24.61 (12.21–49.61) and the AUC was 0.8860 and Q* was 0.8165 (Figure 3). For CT, similarly none of the tested variables accounted for heterogeneity. The pooling of available studies identified that CT had a mean (CI) SEN of 0.80 (0.75–0.84), SPE of 0.72 (0.69–0.74), +LR of 5.60 (2.13–14.73), −LR of 0.26 (0.19–0.36), ACC of 0.6888, DOR of 23.76 (7.87–71.79) and the AUC was 0.8787 and Q* was 0.8091 (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
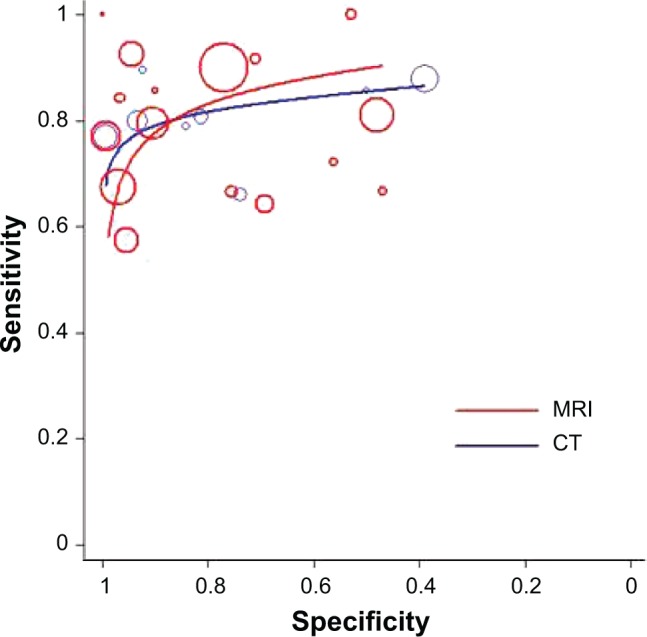
Summary receiver operator characteristic curves of CT and MRI (neck level as unit of analysis).
Abbreviations: CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging.
The comparison between CT and MRI showed that MRI had significantly higher SPE than CT while the other variables were comparable between these two techniques (Table 4).
Comparison of CT and MRI in detecting cervical lymph node metastasis with patient as unit of analysis
For the two studies, the pooled results showed that CT had a mean (CI): SEN, 0.81 (0.65–0.92); SPE, 0.35 (0.24–0.42); +LR, 1.14 (0.87–1.50); −LR, 0.70 (0.32–1.52); DOR, 1.66 (0.57–4.82) (Figure S1). For MRI, which included ten studies, meta-regression analysis showed that study type significantly affected the assessment of diagnostic efficacy (P=0.04) (Table 5). Based on the subgroup analysis according to study types, for the four retrospective studies, the pooled results indicated that MRI had a mean (CI) SEN, 0.77 (0.69–0.85); SPE, 0.48 (0.42–0.55); +CR, 2.42 (0.99–5.91); −CR, 0.54 (0.27–1.06); DOR, 5.24 (0.96–28.55) (Figure S2). For the five prospective studies, the pooled results showed that MRI had a mean (CI) SEN, 0.80 (0.72–0.86); SPE, 0.35 (0.67–0.86); +LR, 2.79 (1.44–5.40); −LR, 0.25 (0.08–0.76); DOR, 14.63 (3.64–58.70) (Figure S3). Pooling of the overall nine studies indicated the mean (CI) values for the following parameters to be: SEN, 0.79 (0.73–0.84); SPE, 0.56 (0.51–0.62); +LR, 2.64 (1.30–5.34); −LR, 0.37(0.20–0.71); DOR, 8.87 (2.42–32.55); AUC (0.8158); Q* (0.7498) (Figure S4).
Table 5.
Results of meta-regression (MRI patient)
| Variable | Coefficient | SE | P-value | RDOR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cte | −0.511 | 2.5493 | 0.8539 | – | – |
| S | −0.330 | 0.1896 | 0.1798 | – | – |
| Publication year | 0.881 | 1.5156 | 0.6020 | 2.41 | (0.02–300.01) |
| Race | 1.786 | 1.1884 | 0.2298 | 5.97 | (0.14–262.04) |
| Study type | 3.288 | 0.9742 | 0.0432 | 26.80 | (1.21–595.04) |
| Blinding of radiologists | −0.774 | 1.1952 | 0.5636 | 0.46 | (0.01–20.70) |
| Blinding of pathologists | −0.290 | 1.5278 | 0.8615 | 0.75 | (0.01–96.74) |
| Risk of bias | −0.227 | 0.9225 | 0.8217 | 0.80 | (0.04–15.02) |
Abbreviations: MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; CI, confidence interval; SE, standard error; RDOR, relative diagnostic odds ratio.
The comparison between CT and MRI showed that MRI had significantly higher AUC than CT while the other variables demonstrated no statistical significance between them. The details are listed in Table 4.
Lymph node size criteria
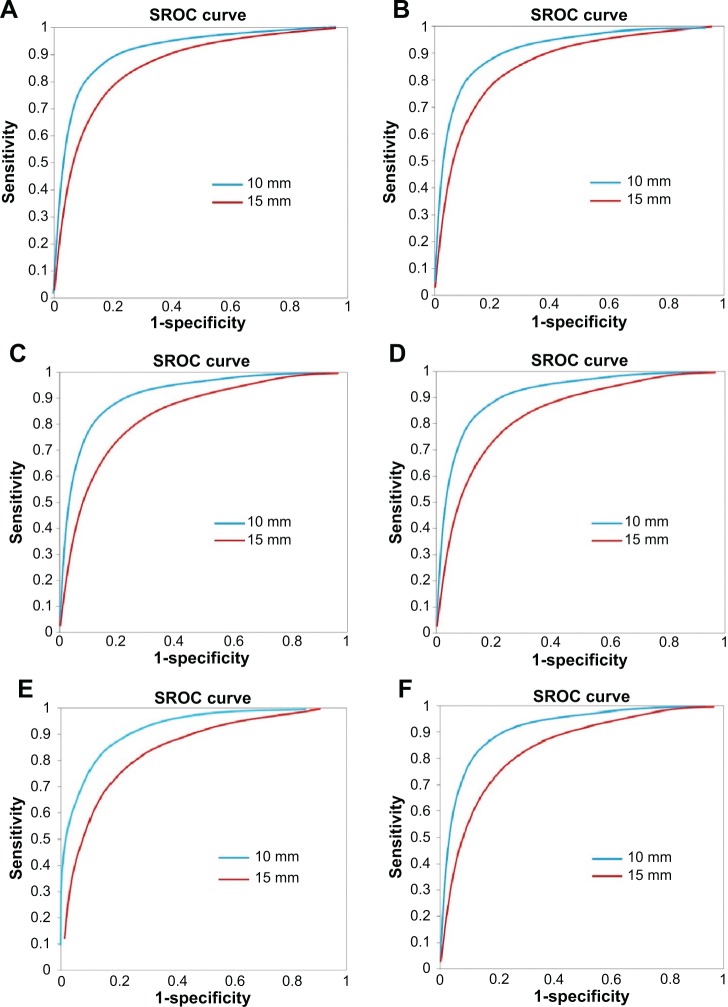
The size of metastatic lymph nodes used as diagnostic criteria of MRI and CT varied considerably among studies and among different neck levels (Table S1). To determine the best diagnostic criteria, a meta-analysis was conducted for different neck levels with lymph node unit data. For each neck level, the SROC curve was drawn to show the diagnostic efficacy of MRI for different node sizes (Figure 4). The results revealed that the minimal axial diameter of 10 mm in lymph node-bearing regions could be considered as the best size criterion for assessing cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with head and neck cancer (Table S2). For CT, the suggested criterion was 12 mm (Table S3). Considering the limited number of studies for CT, SROC curves were not drawn.
Figure 4.
Summary receiver operator characteristic curves of CT and MRI (lymph node size criteria).
Abbreviations: CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; SROC, summary receiver operating characteristic.
Discussion
Head and neck cancer is a common malignant neoplasm worldwide.1 One of the most important factors that influences treatment approaches and therapeutic outcomes for patients with head and neck cancer is the presence of metastatic cervical lymph node. The accurate detection of the cervical lymph node metastasis is thus very important.91,92 Clinical palpation used to be the method to detect cervical nodal metastasis before the development of imaging technologies. However, studies have shown that both the SEN and the SPE of this technique were unsatisfactory, with a high false positive rate of 25%–51%. The improvements in imaging technologies may make it possible for cervical lymph nodes metastasis in head and neck cancer patients can be effectively diagnosed, especially with CT and MRI.11,12,93–96 However, under current health care settings usually only one imaging technique will be performed. Thus a systematic evaluation regarding whether one of the two imaging techniques (CT and MRI) can have a better efficacy than the other will be critical to better guide the clinical practice.
In our systematic review and meta-analysis, we comprehensively evaluated all available evidence from 63 studies for evaluating this question whether one of the two imaging techniques (CT and MRI) can have a better efficacy. Besides pooling results from available studies, we assessed potential sources of heterogeneities via meta-regression and conducted sub-group analyses for significant heterogeneity sources detected. Our meta-analyses suggested that CT had a higher SEN than MRI when node was used as unit of analysis; MRI had a higher SPE when neck level was used as unit of analysis; and MRI had a higher AUC when patient was used as unit of analysis. Our findings showed that CT and MRI are effective tools for detecting the cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with head and neck cancer. Since the diagnostic criteria presented in relevant studies varied significantly, we also summarized available evidence to reveal the most appropriate ones for these two techniques, respectively. Usually, the diagnosis of metastatic cervical lymph nodes consisted of two parts, namely, structural and size changes. The structural changes included central necrosis or cystic degeneration, spherical (rather than flat or bean) shape, or abnormal grouping of nodes (a cluster of three or more lymph nodes of borderline size). In different studies, the description of the structural changes differed only mildly. However, the criteria for sizes differed considerably. Most authors recommended using the minimal axial diameter to assess metastasis. The criterion for minimal axial diameter varied between 5 to 15 mm. Our meta-analysis showed that the minimal axial diameter of 10 mm in lymph node-bearing regions could be considered as the best criterion for assessing cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with head and neck cancer for MRI, compared to 12 mm for CT. Several limitations should be acknowledged for the interpretation of our findings. Firstly, although we conducted meta-regression analyses and showed that the assessed variables largely did not account for heterogeneities between studies, additional undetected variables may account for heterogeneities which warrants further research. Secondly, in some of our analyses, only a very limited number of studies were available. For example, when focusing on the 12 mm size criterion, there was only one study available for evaluating CT with node unit, and future studies for evaluating relevant topics are warranted. In conclusion, through this comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis, we identified that CT and MRI had acceptable diagnostic efficacy in detecting cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with head and neck cancer. When node was used as unit of analysis, CT had a higher SEN. When neck level was used as unit of analysis, MRI had a higher SPE. Out findings suggest that MRI is superior to CT in the diagnosis of cervical lymph node metastasis, especially in diagnosis confirmation. While CT had a better efficacy in diagnosis exclusion. The diagnostic criteria for MRI and CT for size of metastatic lymph nodes were established. Further high-quality studies are warranted to confirm our findings.
Supplementary materials
Meta-analysis of CT for detecting cervical lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer patients (patient as unit of analysis).
Abbreviations: CT, computed tomography; CI, confidence interval; LR, likelihood ratio; df, degrees of freedom; SROC, summary receiver operating characteristic; AUC, area under the curve; SE, standard error.
Meta-analysis of MRI for detecting cervical lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer patients (patient as unit of analysis) (retrospective studies).
Abbreviations: MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; CI, confidence interval; df, degrees of freedom; LR, likelihood ratio; OR, odds ratio.
Meta-analysis of MRI for detecting cervical lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer patients (patient as unit of analysis) (prospective studies).
Abbreviations: MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; CI, confidence interval; df, degrees of freedom; LR, likelihood ratio; OR, odds ratio.
Meta-analysis of MRI for detecting cervical lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer patients (patient as unit of analysis).
Abbreviations: MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; CI, confidence interval; df, degrees of freedom; LR, likelihood ratio; OR, odds ratio; SROC, summary receiver operating characteristic; AUC, area under the curve; SE, standard error.
Table S1.
Study characteristics of lymph node size per neck level
| Study ID | Method | Unit | I | II | III | IV | Retro | Others | TP | FP | FN | TN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adams et al1 1998 | CT | node | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 96 | 175 | 21 | 992 |
| Adams et al1 1998 | MRI | node | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 94 | 250 | 23 | 917 |
| Akoglu et al2 2005 | CT | node | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 21 | 2 | 6 | 12 |
| Akoglu et al2 2005 | MRI | node | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 16 | 1 | 11 | 13 |
| Anzai et al4 1994 | MRI | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 38 | 7 | 2 | 34 |
| Braams et al7 1995 | CT | node | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 4 | 13 |
| Braams et al7 1995 | MRI | node | 10 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 6 | 10 | 134 |
| Braams et al7 1995 | MRI | node | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 14 | 167 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | CT | neck level | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 57 | 415 | 1 | 62 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | CT | neck level | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 56 | 396 | 2 | 81 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | CT | neck level | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 55 | 372 | 3 | 105 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | CT | neck level | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 53 | 329 | 5 | 148 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | CT | neck level | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 51 | 291 | 7 | 186 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | CT | neck level | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 46 | 210 | 12 | 267 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | CT | neck level | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 43 | 157 | 15 | 320 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | CT | neck level | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 32 | 76 | 26 | 401 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | MRI | neck level | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 53 | 382 | 5 | 95 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | MRI | neck level | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 52 | 367 | 6 | 110 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | MRI | neck level | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 50 | 329 | 8 | 148 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | MRI | neck level | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 48 | 281 | 10 | 196 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | MRI | neck level | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 47 | 248 | 11 | 229 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | MRI | neck level | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 41 | 167 | 17 | 310 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | MRI | neck level | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 38 | 134 | 20 | 343 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | MRI | neck level | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 30 | 67 | 28 | 410 |
| Dammann et al10 2005 | CT | neck level | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 32 | 17 | 8 | 236 |
| Dammann et al10 2005 | MRI | neck level | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 37 | 14 | 3 | 239 |
| Ding et al12 2005 | MRI | neck level | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 132 | 27 | 34 | 255 |
| Dirix et al12 2010 | MR-DW | neck level | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 30 | 3 | 2 | 93 |
| Dirix et al12 2010 | MR-DW | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 40 | 4 | 5 | 149 |
| Dirix et al12 2010 | MR-DW | patient | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 13 | 2 | 0 | 6 |
| Eida et al13 2003 | CT | node | 8 | 9 | 6 | 7 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 162 | ||
| Fan et al14 2006 | CT | patient | 10 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 23 | 11 | 4 | 4 |
| Fukunari et al15 2010 | MR | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 19 | 13 | 0 | 66 |
| Gross et al16 2001 | MR | node | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 143 | 22 | 6 | 39 |
| Gu et al17 2000 | MRI | node | 10 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 50 |
| Guenzel et al18 2013 | MR | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 23 | 26 | 2 | 8 |
| Guenzel et al18 2013 | MR | node | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 20 | 6 | 2 | 28 |
| Guo et al19 2006 | MRI | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 36 |
| Hafidh et al22 2006 | CT | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 2 |
| Hafidh et al22 2006 | MRI | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 2 |
| Hao et al21 2000 | MRI | node | 15 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 30 | 2 | 11 | 38 |
| Kau et al26 1999 | CT | neck level | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 6 | 17 | 1 | 17 |
| Kau et al26 1999 | MRI | neck level | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 2 | 17 | 1 | 15 |
| Kau et al26 1999 | CT | node | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 13 | 20 | 7 | 18 |
| Kau et al26 1999 | MRI | node | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 23 | 22 | 3 | 15 |
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level I | 5 | 8 | 28 | 0 | 22 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level I | 6 | 8 | 18 | 0 | 32 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level I | 7 | 8 | 10 | 1 | 39 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level I | 8 | 8 | 5 | 1 | 44 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level I | 9 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 48 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level I | 10 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 51 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level I | 5 | 8 | 24 | 0 | 26 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level I | 6 | 8 | 16 | 0 | 34 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level I | 7 | 8 | 7 | 0 | 43 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level I | 8 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 44 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level I | 9 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 48 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level I | 10 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 48 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level II | 5 | 25 | 21 | 0 | 12 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level II | 6 | 25 | 19 | 0 | 14 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level II | 7 | 25 | 16 | 1 | 16 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level II | 8 | 25 | 10 | 2 | 21 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level II | 9 | 25 | 1 | 6 | 26 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level II | 10 | 24 | 0 | 6 | 28 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level II | 5 | 25 | 22 | 0 | 11 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level II | 6 | 25 | 19 | 1 | 13 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level II | 7 | 25 | 19 | 1 | 13 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level II | 8 | 25 | 11 | 1 | 21 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level II | 9 | 25 | 6 | 2 | 25 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level II | 10 | 25 | 4 | 2 | 27 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level III | 5 | 5 | 15 | 7 | 0 | 36 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level III | 6 | 6 | 15 | 4 | 2 | 37 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level III | 7 | 7 | 15 | 2 | 2 | 39 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level III | 8 | 8 | 15 | 2 | 2 | 39 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level III | 9 | 9 | 13 | 0 | 3 | 42 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level III | 10 | 10 | 12 | 0 | 3 | 43 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level III | 5 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 0 | 33 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level III | 6 | 6 | 15 | 8 | 1 | 34 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level III | 7 | 7 | 15 | 3 | 4 | 36 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level III | 8 | 8 | 15 | 2 | 4 | 37 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level III | 9 | 9 | 11 | 0 | 4 | 43 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level III | 10 | 10 | 8 | 0 | 7 | 43 | ||||
| Ke et al28 2006 | CT | node | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Laubenbacher et al30 1994 | MRI | neck level | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 13 | 7 | 5 | 9 |
| Laubenbacher et al30 1994 | MRI | node | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 65 | 126 | 18 | 312 |
| Lee et al31 2013 | MR-DW | patient | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 11 |
| Lee et al31 2013 | MR-TSE | patient | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 8 |
| Lu et al32 2007 | CT | node | 15 | 10 | 10 | 19 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 1 | 3 | 6 |
| Lwin et al33 2012 | MR | patient | 10 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 63 | 82 | 15 | 24 |
| Mcguirt et al34 1995 | CT | node | 15 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 18 | 3 | 1 | 19 |
| Nakamoto et al35 2009 | MRI | patient | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 16 | 2 | 4 | 30 |
| Olmos et al37 1999 | MRI | neck level | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 22 | 11 | 2 | 27 |
| Paulus et al39 1998 | CT | node | 15 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| Peters et al41 2013 | CT | patient | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 10 | 56 | 0 | 1 |
| Peters et al41 2013 | CT | patient | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 48 | 2 | 9 |
| Peters et al41 2013 | CT | patient | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 29 | 4 | 28 |
| Peters et al41 2013 | CT | patient | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 18 | 5 | 39 |
| Peters et al41 2013 | CT | patient | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 51 |
| Peters et al41 2013 | CT | patient | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 52 |
| Peters et al41 2013 | CT | patient | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 7 | 56 |
| Peters et al41 2013 | CT | patient | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 3 | 1 | 7 | 56 |
| Ren et al43 2000 | CT | node | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 36 | 9 | 2 | 11 |
| Schwartz et al44 2004 | CT | node | 10 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 21 | 1 | 6 | 68 |
| Semedo et al45 2006 | MR | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 24 | 8 | 1 | 30 |
| Seitz et al46 2009 | MR | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 92 | 6 | 12 | 18 |
| Tai et al53 2002 | MRI | patient | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 3 | 1 | 10 | 2 |
| Van den Brekel et al56 1991 | MRI | neck level | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 87 | 13 | 42 | 415 |
| Van den Brekel et al56 1991 | MRI | patient | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 63 | 6 | 15 | 46 |
| Vandecaveye et al57 2008 | MR-TSE | neck level | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 27 | 10 | 20 | 208 |
| Vandecaveye et al57 2008 | MR-TSE | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 34 | 10 | 40 | 217 |
| Vandecaveye et al57 2008 | MR-TSE | patient | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 5 | 1 | 7 |
| Wang et al58 1999 | MRI | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 23 | 0 | 15 | 130 |
| WIDE et al59 1999 | MRI | neck level | 10 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 18 | 11 | 9 | 34 |
| Wilson et al60 1994 | MRI | neck level | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 17 | 16 | 0 | 18 |
| Wu et al61 2010 | CT | node | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 1 | 2 | 11 |
| Yoon et al62 2008 | CT | neck level | 15 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 57 | 2 | 17 | 326 |
| Yoon et al62 2008 | MRI | neck level | 15 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 57 | 2 | 17 | 326 | |
| Yuan et al63 2000 | MRI | neck level | 12 | 12 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 12 | 1 | 2 | 9 |
Abbreviations: MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; CT, computed tomography; MR-TSE,; MR-DW,; MRSTIR,; MRSPIR,; TP, true positive; FP, false positive; TN, true negative.
Table S2.
Meta-analysis results on diagnostic efficacy of MRI on size of metastatic lymph nodes
| Unit | Node size (mm) | SEN (95% CI) | SPE (95% CI) | AUC (SE) | Q* (SE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level I | 10 | 0.768 (0.725–0.808) | 0.901 (0.880–0.919) | 0.9159 (0.0348) | 0.8487 (0.0394) |
| 11 | 0.883 | 0.866 | |||
| 12 | 0.803 | 0.786 | |||
| 15 | 0.774 (0.709–0.830) | 0.721 (0.682–0.758) | 0.8653 (0.0295) | 0.7959 (0.0287) | |
| Level II | 10 | 0.812 (0.778–0.844) | 0.883 (0.861–0.902) | 0.9151 (0.0341) | 0.8477 (0.0385) |
| 11 | 0.542 | 0.953 | |||
| 12 | 0.803 | 0.786 | |||
| 15 | 0.774 (0.709–0.830) | 0.721 (0.682–0.758) | 0.8653 (0.0295) | 0.7959 (0.0287) | |
| Level III | 10 | 0.801 (0.767–0.833) | 0.894 (0.875–0.911) | 0.9121 (0.0314) | 0.8444 (0.0350) |
| 12 | 0.803 | 0.786 | |||
| 15 | 0.785 (0.712–0.846) | 0.704 (0.662–0.742) | 0.8385 (0.0274) | 0.7705 (0.0253) | |
| Level IV | 10 | 0.801 (0.767–0.833) | 0.894 (0.875–0.911) | 0.9121 (0.0314) | 0.8444 (0.0350) |
| 12 | 0.803 | 0.786 | |||
| 15 | 0.785 (0.712–0.846) | 0.704 (0.662–0.742) | 0.8385 (0.0274) | 0.7705 (0.0253) | |
| Retro | 5 | 0.885 | 0.750 | ||
| 10 | 0.780 (0.742–0.814) | 0.899 (0.880–0.915) | 0.9138 (0.0315) | 0.8464 (0.0354) | |
| 12 | 0.803 | 0.786 | |||
| 15 | 0.785 (0.712–0.846) | 0.704 (0.662–0.742) | 0.8385 (0.0274) | 0.7705 (0.0253) | |
| Others | 10 | 0.801 (0.767–0.833) | 0.894 (0.875–0.911) | 0.9121 (0.0314) | 0.8444 (0.0350) |
| 12 | 0.803 | 0.786 | |||
| 15 | 0.785 (0.712–0.846) | 0.704 (0.662–0.742) | 0.8385 (0.0274) | 0.7705 (0.0253) |
Abbreviations: MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; SEN, sensitivity; CI, confidence interval; SPE, specificity; AUC, area under the curve; SE, standard error.
Table S3.
Meta-analysis results on diagnostic efficacy of CT on size of metastatic lymph nodes
| Unit | Node size (mm) | SEN (95% CI) | SPE (95% CI) | AUC (SE) | Q* (SE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level I | 5 | 0.947 | 0.550 | ||
| 8 | 0.722 (0.465–0.903) | 0.966 (0.928–0.988) | |||
| 10 | 0.617 (0.464–0.755) | 0.864 (0.770–0.930) | |||
| 11 | 0.556 | 0.565 | |||
| 12 | 0.821 | 0.850 | |||
| 15 | 0.802 (0.711–0.875) | 0.677 (0.573–0.771) | 0.8519 (0.0818) | 0.7830 (0.0776) | |
| Level II | 5 | 0.947 | 0.550 | ||
| 8 | 0.769 | 0.917 | |||
| 9 | 0.500 | 0.970 | |||
| 10 | 0.607 (0.468–0.735) | 0.510 (0.363–0.656) | 0.7272 (0.1426) | 0.6747 (0.1157) | |
| 11 | 0.556 | 0.565 | |||
| 12 | 0.821 | 0.850 | |||
| 15 | 0.802 (0.711–0.875) | 0.818 (0.746–0.876) | 0.9083 (0.0599) | 0.8402 (0.0658) | |
| Level III | 5 | 0.947 | 0.550 | ||
| 6 | 0.500 | 0.970 | |||
| 8 | 0.500 | 0.970 | |||
| 10 | 0.746 (0.659–0.820) | 0.809 (0.739–0.867) | 0.8499 (0.0783) | 0.7811 (0.0740) | |
| 12 | 0.821 | 0.850 | |||
| 15 | 0.723 (0.574–0.844) | 0.577 (0.432–0.713) | |||
| Level IV | 5 | 0.947 | 0.550 | ||
| 7 | 0.500 | 0.970 | |||
| 8 | 0.500 | 0.970 | |||
| 10 | 0.746 (0.659–0.820) | 0.809 (0.739–0.867) | 0.8499 (0.0783) | 0.7811 (0.0740) | |
| 12 | 0.821 | 0.850 | |||
| 15 | 0.723 (0.574–0.844) | 0.577 (0.432–0.713) | |||
| Retro | 5 | 0.947 | 0.550 | ||
| 8 | 0.500 | 0.970 | |||
| 10 | 0.746 (0.659–0.820) | 0.809 (0.739–0.867) | 0.8499 (0.0783) | 0.7811 (0.0740) | |
| 12 | 0.821 | 0.850 | |||
| 15 | 0.723 (0.574–0.844) | 0.577 (0.432–0.713) | |||
| Others | 5 | 0.947 | 0.550 | ||
| 8 | 0.500 | 0.970 | |||
| 10 | 0.746 (0.659–0.820) | 0.809 (0.739–0.867) | 0.8499 (0.0783) | 0.7811 (0.0740) | |
| 12 | 0.821 | 0.850 | |||
| 15 | 0.723 (0.574–0.844) | 0.577 (0.432–0.713) |
Abbreviations: CT, computed tomography; SEN, sensitivity; CI, confidence interval; SPE, specificity; AUC, area under the curve; SE, standard error.
References
- 1.Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;60(5):277–300. doi: 10.3322/caac.20073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Foote RL, Olsen KD, Davis DL, et al. Base of tongue carcinoma: patterns of failure and predictors of recurrence after surgery alone. Head Neck. 1993;15(4):300–307. doi: 10.1002/hed.2880150406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ferlito A, Rinaldo A, Robbins KT, et al. Changing concepts in the surgical management of the cervical node metastasis. Oral Oncol. 2003;39(5):429–435. doi: 10.1016/s1368-8375(03)00010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tankéré F, Camproux A, Barry B, et al. Prognostic value of lymph node involvement in oral cancers: a study of 137 cases. Laryngoscope. 2000;110(12):2061–2065. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200012000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Shah J. Cervical lymph node metastases: diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications. Oncology. 1990;4(10):61–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Golder WA. Lymph node diagnosis in oncologic imaging: a dilemma still waiting to be solved. Onkologie. 2004;27(2):194–199. doi: 10.1159/000076912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.O’Brien CJ, McNeil EB, McMahon JD, et al. Significance of clinical stage, extent of surgery, and pathologic findings in metastatic cutaneous squamous carcinoma of the parotid gland. Head Neck. 2002;24(5):417–422. doi: 10.1002/hed.10063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kau RJ, Alexiou C, Stimmer H, Arnold W. Diagnostic procedures for detection of lymph node metastases in cancer of the larynx. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2000;62(4):199–203. doi: 10.1159/000027746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Castelijns JA, Van den Brekel MW. Imaging of lymphadenopathy in the neck. Eur Radiol. 2002;12(4):727–738. doi: 10.1007/s003300101102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Castelijns JA, Van den Brekel MW. Detection of lymph node metastases in the neck: radiologic criteria. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22(1):3–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hao SP, Ng SH. Magnetic resonance imaging versus clinical palpation in evaluating cervical metastasis from head and neck cancer. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000;123(3):324–327. doi: 10.1067/mhn.2000.105252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Stern WB, Silver CE, Zeifer BA, Persky MS, Heller KS. Computed tomography of the clinically negative neck. Head Neck. 1990;12(2):109–113. doi: 10.1002/hed.2880120203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kitagawa Y, Nishizawa S, Sano K, et al. Prospective comparison of 18F-FDG PET with conventional imaging modalities (MRI, CT, and 67Ga scintigraphy in assessment of combined intraarterial chemotherapy and radiotherapy for head and neck carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 2003;44(2):198–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Schöder H, Carlson DL, Kraus DH, et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT for detecting nodal metastases in patients with oral cancer staged N0 by clinical examination and CT/MRI. J Nucl Med. 2006;47(5):755–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Li H, Chen TW, Li ZL, et al. Tumour size of resectable oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma measured with multidetector computed tomography for predicting regional lymph node metastasis and N stage. Eur Radiol. 2012;22(11):2487–2493. doi: 10.1007/s00330-012-2512-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rumboldt Z, Gordon L, Gordon L, Bonsall R, Ackermann S. Imaging in head and neck cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2006;7(1):23–34. doi: 10.1007/s11864-006-0029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chandawarkar RY, Kakegawa T, Fujita H, Yamana H, Hayabuthi N. Comparative analysis of imaging modalities in the preoperative assessment of nodal metastasis in esophageal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 1996;61(3):214–217. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9098(199603)61:3<214::AID-JSO10>3.0.CO;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Escott EJ, Rao VM, Ko WD, Guitierrez JE. Comparison of dynamic contrast-enhanced gradient-echo and spin-echo sequences in MRI of head and neck neoplasms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997;18(8):1411–1419. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hamsberger HR. Handbook of Head and Neck Imaging. Chicago: Mosby Year-Book; 1995. pp. 283–298. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J, et al. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Version 5.1.0. England: The Cochrane Collaboration; 2011. Searching for studies; pp. 6.1–6.43. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, et al. QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155(8):529–536. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-155-8-201110180-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lau J, Ioannidis JP, Schmid CH. Quantitative synthesis in systematic reviews. Ann Intern Med. 1997;127(9):820–826. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-127-9-199711010-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(414):557–560. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Higgins J, Thompson S, Deeks J, Altman D. Statistical heterogeneity in systematic reviews of clinical trials: a critical appraisal of guidelines and practice. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2002;7(1):51–61. doi: 10.1258/1355819021927674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schmida CH, Starka PC, Berlinb JA, Landais P, Lau J. Meta-regression detected association between heterogeneous treatment effects and study-level, but not patient-level, factors. J Clin Epidemiol. 2004;57(7):683–697. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2003.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zamora J, Abraira V, Muriel A, Khan K, Coomarasamy A. Meta-DiSc: a software for meta-analysis of test accuracy data. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2006;6:31. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-6-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Deeks JJ, Higgins JP, Altman DG, et al. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Version 5.1.0. England: The Cochrane Collaboration; 2011. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses; pp. 9.1–9.43. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Adams S, Baum RP, Stuckensen T, Bitter K, Hör G. Prospective comparison of 18F-FDG PET with conventional imaging modalities (CT, MRI, US) in lymph node staging of head and neck cancer. Eur J Nucl Med. 1998;25(9):1255–1260. doi: 10.1007/s002590050293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Akoğlu E, Dutipek M, Bekiş R, et al. Assessment of cervical lymph node metastasis with different imaging methods in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Otolaryngol. 2005;34(6):384–394. doi: 10.2310/7070.2005.34605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Okumura K, Fujimoto Y, Hasegawa Y, et al. [Retropharyngeal node metastasis in cancer of the oropharynx and hypopharynx: analysis of retropharyngeal node dissection regarding preoperative radiographic diagnosis] Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho. 1998;101(5):573–577. doi: 10.3950/jibiinkoka.101.5_573. Japanese. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Anzai Y, Blackwell KE, Hirschowitz SL, et al. Initial clinical experience with dextran-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide for detection of lymph node metastases in patients with head and neck cancer. Radiology. 1994;192(3):709–715. doi: 10.1148/radiology.192.3.7520182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.De Bondt RB, Hoeberigs MC, Nelemans PJ, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and additional value of diffusion-weighted imaging for discrimination of malignant cervical lymph nodes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Neuroradiology. 2009;51(3):183–192. doi: 10.1007/s00234-008-0487-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Braams JW, Pruim J, Nikkels PG, et al. Nodal spread of squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity detected with PET-tyrosine, MRI and CT. J Nucl Med. 1996;37(6):897–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Braams JW, Pruim J, Freling NJ, et al. Detection of lymph node metastases of squamous-cell cancer of the head and neck with FDG-PET and MRI. J Nucl Med. 1995;36(2):211–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bruschini P, Giorgetti A, Bruschini L, et al. Positron emission tomography (PET) in the staging of head neck cancer: comparison between PET and CT. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2003;23(6):446–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Curtin HD, Ishwaran H, Mancuso AA, et al. Comparison of CT and MRI imaging in staging of neck metastases. Radiology. 1998;207(1):123–130. doi: 10.1148/radiology.207.1.9530307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dammann F, Horger M, Mueller-Berg M, et al. Rational diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck region: comparative evaluation of CT, MRI, and 18FDG PET. AJNR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;184(4):1326–1331. doi: 10.2214/ajr.184.4.01841326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ding ZX, Liang BL, Shen J, et al. [Magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis of cervical lymph node metastasis from lingual squamous cell carcinoma] Ai Zheng. 2005;24(2):199–203. Chinese. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dirix P, Vandecaveye V, De Keyzer F, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI for nodal staging of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: impact on radiotherapy planning. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;76(3):761–766. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.02.068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Eida S, Sumi M, Yonetsu K, Kimura Y, Nakamura T. Combination of helical CT and Doppler sonography in the follow-up of patients with clinical N0 stage neck disease and oral cancer. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24(3):312–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Fan WY, Sun JW. Evaluation of enhanced CT on the cervical lymph node metastasis of head and neck neoplasms. Chinese Journal of Clinical Healthcare. 2006;9:236–237. Chinese. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fukunari F, Okamura K, Zeze R, et al. Cervical lymph nodes with or without metastases from oral squamous carcinoma: a correlation of MRI findings and histopathologic architecture. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;109(6):890–899. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Gross ND, Weissman JL, Talbot JM, et al. MRI detection of cervical metastasis from differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 2001;111(11 Pt 1):1905–1909. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200111000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gu YF, Qiu WL, Luo JC. Comparison on MRI and CT for Diagnosing Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis. Journal of Shang Hai Tie Dao University. 2000;21:33–36. Chinese. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Guenzel T, Franzen A, Wiegand S, et al. The value of PET compared to MRI in malignant head and neck tumors. Anticancer Res. 2013;33(3):1141–1146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Guo B, Shu DL, Ran W. A [Clinical Study of Early-stage-diagnosis in Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Oral Carcinoma Using MRI] International Medicine and Health Guidance News. 2002;12:25–26. Chinese. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hannah A, Scott AM, Tochon-Danguy H, et al. Evaluation of 18 F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and computed tomography with histopathologic correlation in the initial staging of head and neck cancer. Ann Surg. 2002;236(2):208–217. doi: 10.1097/00000658-200208000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hao SP, Ng SH. Magnetic resonance imaging versus clinical palpation in evaluating cervical metastasis from head and neck cancer. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000;123(3):324–327. doi: 10.1067/mhn.2000.105252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hafidh MA, Lacy PD, Hughes JP, Duffy G, Timon CV. Evaluation of the impact of addition of PET to CT and MRI scanning in the staging of patients with head and neck carcinomas. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2006;263(9):853–859. doi: 10.1007/s00405-006-0067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hlawitschka M, Neise E, Bredow J, et al. FDG-PET in the pretherapeutic evaluation of primary squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity and the involvement of cervical lymph nodes. Mol Imaging Biol. 2002;4(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/s1095-0397(01)00059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hoffman HT, Quets J, Toshiaki T, et al. Functional magnetic resonance imaging using iron oxide particles in characterizing head and neck adenopathy. Laryngoscope. 2000;110(9):1425–1430. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200009000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Jeong HS, Baek CH, Son YI, et al. Use of integrated 18F-FDG PET/CT to improve the accuracy of initial cervical nodal evaluation in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2007;29(3):203–210. doi: 10.1002/hed.20504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kau RJ, Alexiou C, Laubenbacher C, et al. Lymph node detection of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas by positron emission tomography with Fluorodeoxyglucose F 18 in a routine clinical setting. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999;125(12):1322–1328. doi: 10.1001/archotol.125.12.1322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kawai Y, Sumi M, Nakamura T. Turbo short tau inversion recovery imaging for metastatic node screening in patients with head and neck cancer. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27(6):1283–1287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ke Z, Liu M, Liu Y, et al. Diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the detection of the cervical lymph nodes metastasis. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 2006;20(6):243–245. Chinese. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Krabbe CA, Dijkstra PU, Pruim J, et al. FDG PET in oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Value for confirmation of N0 neck and detection of occult metastases. Oral Oncol. 2008;44(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2006.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Laubenbacher C, Saumweber D, Wagner-Manslau C, et al. Comparison of fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose PET, MRI and endoscopy for staging head and neck squamous-cell carcinomas. J Nucl Med. 1995;36(10):1747–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Lee MC, Tsai HY, Chuang KS, Liu CK, Chen MK. Prediction of nodal metastasis in head and neck cancer using a 3T MRI ADC map. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34(4):864–869. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A3281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Lu HJ, Ribere-Brugel Lydia, Emmanuel IT, et al. The comparison of PET/CT with contrast enhanced CT in the assessment of cervical lymph nodes in head and neck cancer. Modern Oncology. 2007;15:1555–1557. Chinese. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lwin CT, Hanlon R, Lowe D, et al. Accuracy of MRI in prediction of tumour thickness and nodal stage in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2012;48(2):149–154. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2011.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.McGuirt W, Williams DW, 3rd, Keyes JW, Jr, et al. A comparative diagnostic study of head and neck nodal metastases using positron emission tomography. Laryngoscope. 1995;105(4 Pt 1):373–375. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199504000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Nakamoto Y, Tamai K, Saga T, et al. Clinical value of image fusion from MRI and PET in patients with head and neck cancer. Mol Imaging Biol. 2009;11(1):46–53. doi: 10.1007/s11307-008-0168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Nishimura H, Tanigawa N, Hiramatsu M, et al. Preoperative esophageal cancer staging: magnetic resonance imaging of lymph node with ferumoxtran-10, an ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide. J Am Coll Surg. 2006;202(4):604–611. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2005.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Valdés Olmos RA, Koops W, Loftus BM, et al. Correlative 201Tl SPECT, MRI and ex vivo 201Tl uptake in detecting and characterizing cervical lymphadenopathy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 1999;40(9):1414–1419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Ou YQ, Lin Y. Magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis of 24 cases of cervical lymph node metastasis from oral carcinoma. Fujian Med J. 29:3–6. Chinese. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Paulus P, Sambon A, Vivegnis D, et al. 18FDG-PET for the assessment of primary head and neck tumors: clinical, computed tomography, and histopathological correlation in 38 patients. Laryngoscope. 1998;108(10):1578–1583. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199810000-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Perrone A, Guerrisi P, Izzo L, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI in cervical lymph nodes: differentiation between benign and malignant lesions. Eur J Radiol. 2011;77(2):281–286. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.07.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Peters TT, Castelijns JA, Ljumanovic R, et al. Diagnostic value of CT and MRI in the detection of paratracheal lymph node metastasis. Oral Oncol. 2012;48(5):450–455. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2011.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Pohar S, Brown R, Newman N, et al. What does PET imaging add to conventional staging of head and neck cancer patients? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;68(2):383–387. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.12.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Ren K, Zhang JR, Ma SS, et al. CT-Pathologic Correlative Study on the Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Laryngeal Cancer. Chinese J Med Imaging. 2000;8:347–351. Chinese. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Schwartz DL, Ford E, Rajendran J, et al. FDG-PET/CT imaging for preradiotherapy staging of head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;61(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.03.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Curvo-Semedo L, Diniz M, Miguéis J, et al. USPIO-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for nodal staging in patients with head and neck cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2006;24(1):123–131. doi: 10.1002/jmri.20602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Seitz O, Chambron-Pinho N, Middendorp M, et al. 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose-PET/CT to evaluate tumor, nodal disease, and gross tumor volume of oropharyngeal and oral cavity cancer: comparison with MRI imaging and validation with surgical specimen. Neuroradiology. 2009;51(10):677–686. doi: 10.1007/s00234-009-0586-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Stokkel MP, ten Broek FW, Hordijk GJ, Koole R, van Rijk PP. Preoperative evaluation of patients with primary head and neck cancer using dual-head 18fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. Ann Surg. 2000;231(2):229–234. doi: 10.1097/00000658-200002000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Stuckensen T, Kovács AF, Adams S, Baum RP. Staging of the neck in patients with oral cavity squamous cell carcinomas: a prospective comparison of PET, ultrasound, CT and MRI. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2000;28(6):319–324. doi: 10.1054/jcms.2000.0172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Sumi M, Kimura Y, Sumi T, Nakamura T. Diagnostic performance of MRI relative to CT for metastatic nodes of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;26(6):1626–1633. doi: 10.1002/jmri.21187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Sumi M, Van Cauteren M, Nakamura T. MRI microimaging of benign and malignant nodes in the neck. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;186(3):749–757. doi: 10.2214/AJR.04.1832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Sumi M, Sakihama N, Sumi T, et al. Discrimination of metastatic cervical lymph nodes with diffusion-weighted MRI imaging in patients with head and neck cancer. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24(8):1627–1634. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Sun JT, Zhang ZX, Zhang WJ, et al. Diagnosis of molecular imaging on head and neck carcinoma and cercical lymph node metastasis. Chinese Journal of Coal Industry Medicine. 2013;16:1049–1052. Chinese. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Tai CJ, Shiau YC, Tsai MH, et al. Detection of cervical lymph node metastases in nasopharyngeal carcinomas: comparison between technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile single photon emission computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Neoplasma. 2002;49(4):251–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Takashima S, Sone S, Takayama F, et al. Papillary thyroid carcinoma: MRI diagnosis of lymph node metastasis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998;19(3):509–513. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Tuli HS, Singh B, Prasad V, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of 99mTc-MIBI-SPECT in the detection of lymph node metastases in patients with carcinoma of the tongue: comparison with computed tomography and MRI. Nucl Med Commun. 2008;29(9):803–808. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0b013e328302ccfa. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Van den Brekel MW, Castelijns JA, Croll GA, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging vs palpation of cervical lymph node metastasis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1991;117(6):663–673. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1991.01870180102020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Vandecaveye V, De Keyzer F, Vander Poorten V, et al. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: value of diffusion-weighted MRI imaging for nodal staging. Radiology. 2009;251(1):134–146. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2511080128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Wang Q, Takashima S, Fukuda H, et al. Detection of medullary thyroid carcinoma and regional lymph node metastases by magnetic resonance imaging. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999;125(8):842–848. doi: 10.1001/archotol.125.8.842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Wide JM, White DW, Woolgar JA, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of cervical nodal metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Radiol. 1999;54(2):90–94. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(99)91066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Wilson GR, McLean NR, Chippindale A, et al. The role of MRI scanning in the diagnosis of cervical lymphadenopathy. Br J Plast Surg. 1994;47(3):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0007-1226(94)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Wu YQ, Fan XC, Deng Y, et al. Value of Spiral CT Scan on Cervical Lymph node Metastasis of Laryngo and Hypolaryngo carcinoma. Hei Long Jiang Medical Journal. 34:761–763. Chinese. [Google Scholar]
- 89.Yoon DY, Hwang HS, Chang SK, et al. CT, MRI, US, 18F-FDG PET/CT, and their combined use for the assessment of cervical lymph node metastases in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Eur Radiol. 2009;19(3):634–642. doi: 10.1007/s00330-008-1192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Yuan YG, Han DM, Fan EZ, et al. The evaluation of cervical lymph node metastasis of laryngeal cancer using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 2000;14(10):449–451. Chinese. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Shum JW, Dierks EJ. Evaluation and Staging of the Neck in Patients with Malignant Disease. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2014;26(2):209–221. doi: 10.1016/j.coms.2014.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Sun F, Li YF, Liu JH, Xiong Y. Impact of postoperative adjuvant therapy on prognosis of low-risk cervical cancer: analysis of 208 cases. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2014;34:401–405. Chinese. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Lindberg R. Distribution of cervical lymph node metastases from squamous cell carcinoma of the upper respiratory and digestive tracts. Cancer. 1972;29(6):1446–1449. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197206)29:6<1446::aid-cncr2820290604>3.0.co;2-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Bocca E, Calearo C, de Vincentiis I, et al. Occult metastases in cancer of the larynx and their relationship to clinical and histological aspects of the primary tumor: a four year multicentric research. Laryngoscope. 1984;94(8):1086–1090. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198408000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Friedman M, Roberts N, Kirshenbaum G, Colombo J. Nodal size of metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the neck. Laryngoscope. 1993;103(8):854–856. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199308000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Johnson JT. A surgeon looks at cervical lymph nodes. Radiology. 1990;175(3):607–610. doi: 10.1148/radiology.175.3.2188292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Footnotes
Disclosure
The first and corresponding authors had full access to all of the data in the study and had final responsibility for the decision to submit for publication. The authors have no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Adams S, Baum RP, Stuckensen T, et al. Prospective comparison of 18F-FDG PET with conventional imaging modalities (CT, MRI, US) in lymph node staging of head and neck cancer. Eur J Nucl Med. 1998;25:1255–1260. doi: 10.1007/s002590050293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Akoğlu E, Dutipek M, Bekiş R, et al. Assessment of cervical lymph node metastasis with different imaging methods in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Otolaryngol. 2005;34:384–394. doi: 10.2310/7070.2005.34605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Okumura K, Fujimoto Y, Hasegawa Y, et al. Retropharyngeal node metastasis in cancer of the oropharynx and hypopharynx: analysis of retropharyngeal node dissection regarding preoperative radiographic diagnosis [Article in Japanese] Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho. 1998;101:573–577. doi: 10.3950/jibiinkoka.101.5_573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Anzai Y, Blackwell KE, Hirschowitz SL, et al. Initial clinical experience with dextran-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide for detection of lymph node metastases in patients with head and neck cancer. Radiology. 1994;192:709–715. doi: 10.1148/radiology.192.3.7520182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.De Bondt RB, Hoeberigs MC, Nelemans PJ, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and additional value of diffusion-weighted imaging for discrimination of malignant cervical lymph nodes in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Neuroradiology. 2009;51:183–192. doi: 10.1007/s00234-008-0487-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Braams JW, Pruim J, Nikkels PG, et al. Nodal spread of squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity detected with PET-tyrosine, MRI and CT. J Nucl Med. 1996;37:897–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Braams JW, Pruim J, Freling NJ, et al. Detection of lymph node metastases of squamous-cell cancer of the head and neck with FDG-PET and MRI. J Nucl Med. 1995;36:211–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bruschini P, Giorgetti A, Bruschini L, et al. Positron emission tomography (PET) in the staging of head neck cancer: comparison between PET and CT. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2003;23:446–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Curtin HD, Ishwaran H, Mancuso AA, et al. Comparison of CT and MRI imaging in staging of neck metastases. Radiology. 1998;207:123–130. doi: 10.1148/radiology.207.1.9530307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dammann F, Horger M, Mueller-Berg M, et al. Rational diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck region: comparative evaluation of CT, MRI, and 18FDG PET. AJNR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;184:1326–1331. doi: 10.2214/ajr.184.4.01841326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ding ZX, Liang BL, Shen J, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis of cervical lymph node metastasis from lingual squamous cell carcinoma [Article in Chinese] Ai Zheng. 2005;24:199–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dirix P, Vandecaveye V, De Keyzer F, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI for nodal staging of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: impact on radiotherapy planning. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;76:761–766. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.02.068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Eida S, Sumi M, Yonetsu K, et al. Combination of helical CT and Doppler sonography in the follow-up of patients with clinical N0 stage neck disease and oral cancer. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24:312–318. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fan WY, Sun JW. Evaluation of enhanced CT on hte cervical lymph node metastasis of head and neck neoplasms. Chinese Journal of Clinical Healthcare [Article in Chinese] 2006;9:236–237. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fukunari F, Okamura K, Zeze R, et al. Cervical lymph nodes with or without metastases from oral squamous carcinoma: a correlation of MRI findings and histopathologic architecture. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010;109:890–899. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gross ND, Weissman JL, Talbot JM, et al. MRI detection of cervical metastasis from differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 2001;111:1905–1909. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200111000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gu YF, Qiu WL, Luo JC. Comparison on MRI and CT for Diagnosing Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis [Article in Chinese] Journal of Shang Hai Tie Dao University. 2000;21:33–36. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Guenzel T, Franzen A, Wiegand S, et al. The value of PET compared to MRI in malignant head and neck tumors. Anticancer Res. 2013;33:1141–1146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Guo B, Shu DL, Ran W. A Clinical Study of Early-stage-diagnosis in Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Oral Carcinoma Using MRI [Article in Chinese] International Medicine and Health Guidance News. 2002;12:25–26. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hannah A, Scott AM, Tochon-Danguy H, et al. Evaluation of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and computed tomography with histopathologic correlation in the initial staging of head and neck cancer. Ann Surg. 2002;236:208–217. doi: 10.1097/00000658-200208000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hao SP, Ng SH. Magnetic resonance imaging versus clinical palpation in evaluating cervical metastasis from head and neck cancer. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2000;123:324–327. doi: 10.1067/mhn.2000.105252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hafidh MA, Lacy PD, Hughes JP, et al. Evaluation of the impact of addition of PET to CT and MRI scanning in the staging of patients with head and neck carcinomas. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2006;263:853–859. doi: 10.1007/s00405-006-0067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hlawitschka M, Neise E, Bredow J, et al. FDG-PET in the pretherapeutic evaluation of primary squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity and the involvement of cervical lymph nodes. Mol Imaging Biol. 2002;4:91–98. doi: 10.1016/s1095-0397(01)00059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hoffman HT, Quets J, Toshiaki T, et al. Functional magnetic resonance imaging using iron oxide particles in characterizing head and neck adenopathy. Laryngoscope. 2000;110:1425–1430. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200009000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jeong HS, Baek CH, Son YI, et al. Use of integrated 18F-FDG PET/CT to improve the accuracy of initial cervical nodal evaluation in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2007;29:203–210. doi: 10.1002/hed.20504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kau RJ, Alexiou C, Laubenbacher C, et al. Lymph node detection of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas by positron emission tomography with Fluorodeoxyglucose F 18 in a routine clinical setting. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999;125:1322–1328. doi: 10.1001/archotol.125.12.1322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kawai Y, Sumi M, Nakamura T. Turbo short tau inversion recovery imaging for metastatic node screening in patients with head and neck cancer. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27:1283–1287. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ke Z, Liu M, Liu Y, et al. Diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the detection of the cervical lymph nodes metastasis [Article in Chinese] Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 2006;20:243–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Krabbe CA, Dijkstra PU, Pruim J, et al. FDG PET in oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Value for confirmation of N0 neck and detection of occult metastases. Oral Oncol. 2008;44:31–36. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2006.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Laubenbacher C, Saumweber D, Wagner-Manslau C, et al. Comparison of fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose PET, MRI and endoscopy for staging head and neck squamous-cell carcinomas. J Nucl Med. 1995;36:1747–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lee MC, Tsai HY, Chuang KS, et al. Prediction of nodal metastasis in head and neck cancer using a 3T MRI ADC map. Ajnr Am J Neuroradiol. 2013;34:864–869. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A3281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.LU HJ, Lydia RIBERE – BRUGEL, Emmanue lITT et al. The comparison of PET/CT with contrast enhanced CT in the assessment of cervical lymph nodes in head and neck cancer [Article in Chinese] Modern Oncology. 2007;15:1555–1557. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lwin CT, Hanlon R, Lowe D, et al. Accuracy of MRI in prediction of tumour thickness and nodal stage in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2012;48:149–154. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2011.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.McGuirt W, Williams DW, III, Keyes JW, Jr, et al. A comparative diagnostic study of head and neck nodal metastases using positron emission tomography. Laryngoscope. 1995;105:373–375. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199504000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Nakamoto Y, Tamai K, Saga T, et al. Clinical value of image fusion from MRI and PET in patients with head and neck cancer. Mol Imaging Biol. 2009;11:46–53. doi: 10.1007/s11307-008-0168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Nishimura H, Tanigawa N, Hiramatsu M, et al. Preoperative esophageal cancer staging: magnetic resonance imaging of lymph node with ferumoxtran-10, an ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide. J Am Coll Surg. 2006;202:604–611. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2005.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Olmos RA, Koops W, Loftus BM, et al. Correlative 201Tl SPECT, MRI and ex vivo 201Tl uptake in detecting and characterizing cervical lymphadenopathy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 1999;40:1414–1419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ou YQM, Lin Y. Magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis of 24 cases of cervical lymph node metastasis from oral carcinoma [Article in Chinese] Fu jian Med J. 29:3–6. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Paulus P, Sambon A, Vivegnis D, et al. 18FDG-PET for the assessment of primary head and neck tumors: clinical, computed tomography, and histopathological correlation in 38 patients. Laryngoscope. 1998;108:1578–1583. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199810000-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Perrone A, Guerrisi P, Izzo L, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI in cervical lymph nodes: differentiation between benign and malignant lesions. Eur J Radiol. 2011;77:281–286. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.07.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Peters TT, Castelijns JA, Ljumanovic R, et al. Diagnostic value of CT and MRI in the detection of paratracheal lymph node metastasis. Oral Oncol. 2012;48:450–455. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2011.12.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Pohar S, Brown R, Newman N, et al. What does PET imaging add to conventional staging of head and neck cancer patients? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;68:383–387. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.12.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ren K, Zhang JR, Ma SS, et al. CT-Pathologic Correlative Study on the Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of Laryngeal Cancer [Article in Chinese] Chines e J Med Imaging. 2000;8:347–351. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Schwartz DL, Ford E, Rajendran J, et al. FDG-PET/CT imaging for preradiotherapy staging of head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;61:129–136. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.03.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Curvo-Semedo L, Diniz M, Miguéis J, et al. USPIO-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for nodal staging in patients with head and neck cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2006;24:123–131. doi: 10.1002/jmri.20602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Seitz O, Chambron-Pinho N, Middendorp M, et al. 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose-PET/CT to evaluate tumor, nodal disease, and gross tumor volume of oropharyngeal and oral cavity cancer: comparison with MRI imaging and validation with surgical specimen. Neuroradiology. 2009;51:677–686. doi: 10.1007/s00234-009-0586-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Stokkel MP, ten Broek FW, Hordijk GJ, et al. Preoperative evaluation of patients with primary head and neck cancer using dual-head 18fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. Ann Surg. 2000;231:229–234. doi: 10.1097/00000658-200002000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Stuckensen T, Kovács AF, Adams S, et al. Staging of the neck in patients with oral cavity squamous cell carcinomas: a prospective comparison of PET, ultrasound, CT and MRI. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2000;28:319–324. doi: 10.1054/jcms.2000.0172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sumi M, Kimura Y, Sumi T, et al. Diagnostic performance of MRI relative to CT for metastatic nodes of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;26:1626–1633. doi: 10.1002/jmri.21187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sumi M, Van Cauteren M, Nakamura T. MRI microimaging of benign and malignant nodes in the neck. AJNR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;186:749–757. doi: 10.2214/AJR.04.1832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sumi M, Sakihama N, Sumi T, et al. Discrimination of metastatic cervical lymph nodes with diffusion-weighted MRI imaging in patients with head and neck cancer. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24:1627–1634. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sun JT, Zhang ZX, Zhang WJ, et al. Diagnosis of molecular imaging on head and neck carcinoma and cercical lymph node metastasis [Article in Chinese] Chinese Journal of Coal Industry Medicine. 2013;16:1049–1052. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Tai CJ, Shiau YC, Tsai MH, et al. Detection of cervical lymph node metastases in nasopharyngeal carcinomas: comparison between technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile single photon emission computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Neoplasma. 2002;49:251–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Takashima S, Sone S, Takayama F, et al. Papillary thyroid carcinoma: MRI diagnosis of lymph node metastasis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998;19:509–513. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Tuli HS, Singh B, Prasad V, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of 99mTc-MIBI-SPECT in the detection of lymph node metastases in patients with carcinoma of the tongue: comparison with computed tomography and MRI. Nucl Med Commun. 2008;29:803–808. doi: 10.1097/MNM.0b013e328302ccfa. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Van den Brekel MW, Castelijns JA, Croll GA, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging vs palpation of cervical lymph node metastasis. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1991;117:663–673. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1991.01870180102020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Vandecaveye V, De Keyzer F, Vander Poorten V, et al. Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: value of diffusion-weighted MRI imaging for nodal staging. Radiology. 2009;251:134–146. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2511080128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Wang Q, Takashima S, Fukuda H, et al. Detection of medullary thyroid carcinoma and regional lymph node metastases by magnetic resonance imaging [Article in Chinese] Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999;125:842–848. doi: 10.1001/archotol.125.8.842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wide JM, White DW, Woolgar JA, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of cervical nodal metastasis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Radiol. 1999;54:90–94. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(99)91066-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Wilson GR, McLean NR, Chippindale A, et al. The role of MRI scanning in the diagnosis of cervical lymphadenopathy. Br J Plast Surg. 1994;47:175–179. doi: 10.1016/0007-1226(94)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Wu YQ, Fan XC, Deng Y, et al. Value of Spiral CT Scan on Cervical Lymph node Metastasis of Laryngo and Hypolaryngo carcinoma [Article in Chinese] Hei Long Jiang Medical Journal. 34:761–763. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yoon DY, Hwang HS, Chang SK, et al. CT, MRI, US, 18F-FDG PET/CT, and their combined use for the assessment of cervical lymph node metastases in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Eur Radiol. 2009;19:634–642. doi: 10.1007/s00330-008-1192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Yuan YG, Han DM, Fan EZ, et al. The evaluation of cervical lymph node metastasis of laryngeal cancer using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) [Article in Chinese] Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 2000;14:449–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Meta-analysis of CT for detecting cervical lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer patients (patient as unit of analysis).
Abbreviations: CT, computed tomography; CI, confidence interval; LR, likelihood ratio; df, degrees of freedom; SROC, summary receiver operating characteristic; AUC, area under the curve; SE, standard error.
Meta-analysis of MRI for detecting cervical lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer patients (patient as unit of analysis) (retrospective studies).
Abbreviations: MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; CI, confidence interval; df, degrees of freedom; LR, likelihood ratio; OR, odds ratio.
Meta-analysis of MRI for detecting cervical lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer patients (patient as unit of analysis) (prospective studies).
Abbreviations: MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; CI, confidence interval; df, degrees of freedom; LR, likelihood ratio; OR, odds ratio.
Meta-analysis of MRI for detecting cervical lymph node metastasis in head and neck cancer patients (patient as unit of analysis).
Abbreviations: MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; CI, confidence interval; df, degrees of freedom; LR, likelihood ratio; OR, odds ratio; SROC, summary receiver operating characteristic; AUC, area under the curve; SE, standard error.
Table S1.
Study characteristics of lymph node size per neck level
| Study ID | Method | Unit | I | II | III | IV | Retro | Others | TP | FP | FN | TN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adams et al1 1998 | CT | node | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 96 | 175 | 21 | 992 |
| Adams et al1 1998 | MRI | node | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 94 | 250 | 23 | 917 |
| Akoglu et al2 2005 | CT | node | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 21 | 2 | 6 | 12 |
| Akoglu et al2 2005 | MRI | node | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 16 | 1 | 11 | 13 |
| Anzai et al4 1994 | MRI | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 38 | 7 | 2 | 34 |
| Braams et al7 1995 | CT | node | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 4 | 13 |
| Braams et al7 1995 | MRI | node | 10 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 6 | 10 | 134 |
| Braams et al7 1995 | MRI | node | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 14 | 167 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | CT | neck level | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 57 | 415 | 1 | 62 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | CT | neck level | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 56 | 396 | 2 | 81 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | CT | neck level | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 55 | 372 | 3 | 105 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | CT | neck level | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 53 | 329 | 5 | 148 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | CT | neck level | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 51 | 291 | 7 | 186 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | CT | neck level | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 46 | 210 | 12 | 267 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | CT | neck level | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 43 | 157 | 15 | 320 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | CT | neck level | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 32 | 76 | 26 | 401 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | MRI | neck level | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 53 | 382 | 5 | 95 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | MRI | neck level | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 52 | 367 | 6 | 110 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | MRI | neck level | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 50 | 329 | 8 | 148 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | MRI | neck level | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 48 | 281 | 10 | 196 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | MRI | neck level | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 47 | 248 | 11 | 229 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | MRI | neck level | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 41 | 167 | 17 | 310 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | MRI | neck level | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 38 | 134 | 20 | 343 |
| Curtin et al9 1997 | MRI | neck level | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 30 | 67 | 28 | 410 |
| Dammann et al10 2005 | CT | neck level | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 32 | 17 | 8 | 236 |
| Dammann et al10 2005 | MRI | neck level | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 37 | 14 | 3 | 239 |
| Ding et al12 2005 | MRI | neck level | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 132 | 27 | 34 | 255 |
| Dirix et al12 2010 | MR-DW | neck level | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 30 | 3 | 2 | 93 |
| Dirix et al12 2010 | MR-DW | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 40 | 4 | 5 | 149 |
| Dirix et al12 2010 | MR-DW | patient | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 13 | 2 | 0 | 6 |
| Eida et al13 2003 | CT | node | 8 | 9 | 6 | 7 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 162 | ||
| Fan et al14 2006 | CT | patient | 10 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 23 | 11 | 4 | 4 |
| Fukunari et al15 2010 | MR | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 19 | 13 | 0 | 66 |
| Gross et al16 2001 | MR | node | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 143 | 22 | 6 | 39 |
| Gu et al17 2000 | MRI | node | 10 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 50 |
| Guenzel et al18 2013 | MR | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 23 | 26 | 2 | 8 |
| Guenzel et al18 2013 | MR | node | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 20 | 6 | 2 | 28 |
| Guo et al19 2006 | MRI | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 36 |
| Hafidh et al22 2006 | CT | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 2 |
| Hafidh et al22 2006 | MRI | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 2 |
| Hao et al21 2000 | MRI | node | 15 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 30 | 2 | 11 | 38 |
| Kau et al26 1999 | CT | neck level | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 6 | 17 | 1 | 17 |
| Kau et al26 1999 | MRI | neck level | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 2 | 17 | 1 | 15 |
| Kau et al26 1999 | CT | node | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 13 | 20 | 7 | 18 |
| Kau et al26 1999 | MRI | node | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 23 | 22 | 3 | 15 |
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level I | 5 | 8 | 28 | 0 | 22 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level I | 6 | 8 | 18 | 0 | 32 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level I | 7 | 8 | 10 | 1 | 39 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level I | 8 | 8 | 5 | 1 | 44 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level I | 9 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 48 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level I | 10 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 51 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level I | 5 | 8 | 24 | 0 | 26 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level I | 6 | 8 | 16 | 0 | 34 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level I | 7 | 8 | 7 | 0 | 43 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level I | 8 | 8 | 6 | 0 | 44 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level I | 9 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 48 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level I | 10 | 6 | 0 | 4 | 48 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level II | 5 | 25 | 21 | 0 | 12 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level II | 6 | 25 | 19 | 0 | 14 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level II | 7 | 25 | 16 | 1 | 16 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level II | 8 | 25 | 10 | 2 | 21 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level II | 9 | 25 | 1 | 6 | 26 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level II | 10 | 24 | 0 | 6 | 28 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level II | 5 | 25 | 22 | 0 | 11 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level II | 6 | 25 | 19 | 1 | 13 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level II | 7 | 25 | 19 | 1 | 13 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level II | 8 | 25 | 11 | 1 | 21 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level II | 9 | 25 | 6 | 2 | 25 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level II | 10 | 25 | 4 | 2 | 27 | |||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level III | 5 | 5 | 15 | 7 | 0 | 36 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level III | 6 | 6 | 15 | 4 | 2 | 37 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level III | 7 | 7 | 15 | 2 | 2 | 39 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level III | 8 | 8 | 15 | 2 | 2 | 39 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level III | 9 | 9 | 13 | 0 | 3 | 42 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSPIR | neck level III | 10 | 10 | 12 | 0 | 3 | 43 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level III | 5 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 0 | 33 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level III | 6 | 6 | 15 | 8 | 1 | 34 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level III | 7 | 7 | 15 | 3 | 4 | 36 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level III | 8 | 8 | 15 | 2 | 4 | 37 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level III | 9 | 9 | 11 | 0 | 4 | 43 | ||||
| Kawai et al27 2005 | MRSTIR | neck level III | 10 | 10 | 8 | 0 | 7 | 43 | ||||
| Ke et al28 2006 | CT | node | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 3 | 3 | 4 |
| Laubenbacher et al30 1994 | MRI | neck level | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 13 | 7 | 5 | 9 |
| Laubenbacher et al30 1994 | MRI | node | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 65 | 126 | 18 | 312 |
| Lee et al31 2013 | MR-DW | patient | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 11 |
| Lee et al31 2013 | MR-TSE | patient | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 8 |
| Lu et al32 2007 | CT | node | 15 | 10 | 10 | 19 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 1 | 3 | 6 |
| Lwin et al33 2012 | MR | patient | 10 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 63 | 82 | 15 | 24 |
| Mcguirt et al34 1995 | CT | node | 15 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 18 | 3 | 1 | 19 |
| Nakamoto et al35 2009 | MRI | patient | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 16 | 2 | 4 | 30 |
| Olmos et al37 1999 | MRI | neck level | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 22 | 11 | 2 | 27 |
| Paulus et al39 1998 | CT | node | 15 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| Peters et al41 2013 | CT | patient | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 10 | 56 | 0 | 1 |
| Peters et al41 2013 | CT | patient | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 48 | 2 | 9 |
| Peters et al41 2013 | CT | patient | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 29 | 4 | 28 |
| Peters et al41 2013 | CT | patient | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 18 | 5 | 39 |
| Peters et al41 2013 | CT | patient | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 51 |
| Peters et al41 2013 | CT | patient | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 52 |
| Peters et al41 2013 | CT | patient | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 3 | 1 | 7 | 56 |
| Peters et al41 2013 | CT | patient | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 3 | 1 | 7 | 56 |
| Ren et al43 2000 | CT | node | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 36 | 9 | 2 | 11 |
| Schwartz et al44 2004 | CT | node | 10 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 21 | 1 | 6 | 68 |
| Semedo et al45 2006 | MR | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 24 | 8 | 1 | 30 |
| Seitz et al46 2009 | MR | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 92 | 6 | 12 | 18 |
| Tai et al53 2002 | MRI | patient | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 3 | 1 | 10 | 2 |
| Van den Brekel et al56 1991 | MRI | neck level | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 87 | 13 | 42 | 415 |
| Van den Brekel et al56 1991 | MRI | patient | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 63 | 6 | 15 | 46 |
| Vandecaveye et al57 2008 | MR-TSE | neck level | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 27 | 10 | 20 | 208 |
| Vandecaveye et al57 2008 | MR-TSE | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 34 | 10 | 40 | 217 |
| Vandecaveye et al57 2008 | MR-TSE | patient | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 5 | 1 | 7 |
| Wang et al58 1999 | MRI | node | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 23 | 0 | 15 | 130 |
| WIDE et al59 1999 | MRI | neck level | 10 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 18 | 11 | 9 | 34 |
| Wilson et al60 1994 | MRI | neck level | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 17 | 16 | 0 | 18 |
| Wu et al61 2010 | CT | node | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 1 | 2 | 11 |
| Yoon et al62 2008 | CT | neck level | 15 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 57 | 2 | 17 | 326 |
| Yoon et al62 2008 | MRI | neck level | 15 | 15 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 57 | 2 | 17 | 326 | |
| Yuan et al63 2000 | MRI | neck level | 12 | 12 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 12 | 1 | 2 | 9 |
Abbreviations: MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; CT, computed tomography; MR-TSE,; MR-DW,; MRSTIR,; MRSPIR,; TP, true positive; FP, false positive; TN, true negative.
Table S2.
Meta-analysis results on diagnostic efficacy of MRI on size of metastatic lymph nodes
| Unit | Node size (mm) | SEN (95% CI) | SPE (95% CI) | AUC (SE) | Q* (SE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level I | 10 | 0.768 (0.725–0.808) | 0.901 (0.880–0.919) | 0.9159 (0.0348) | 0.8487 (0.0394) |
| 11 | 0.883 | 0.866 | |||
| 12 | 0.803 | 0.786 | |||
| 15 | 0.774 (0.709–0.830) | 0.721 (0.682–0.758) | 0.8653 (0.0295) | 0.7959 (0.0287) | |
| Level II | 10 | 0.812 (0.778–0.844) | 0.883 (0.861–0.902) | 0.9151 (0.0341) | 0.8477 (0.0385) |
| 11 | 0.542 | 0.953 | |||
| 12 | 0.803 | 0.786 | |||
| 15 | 0.774 (0.709–0.830) | 0.721 (0.682–0.758) | 0.8653 (0.0295) | 0.7959 (0.0287) | |
| Level III | 10 | 0.801 (0.767–0.833) | 0.894 (0.875–0.911) | 0.9121 (0.0314) | 0.8444 (0.0350) |
| 12 | 0.803 | 0.786 | |||
| 15 | 0.785 (0.712–0.846) | 0.704 (0.662–0.742) | 0.8385 (0.0274) | 0.7705 (0.0253) | |
| Level IV | 10 | 0.801 (0.767–0.833) | 0.894 (0.875–0.911) | 0.9121 (0.0314) | 0.8444 (0.0350) |
| 12 | 0.803 | 0.786 | |||
| 15 | 0.785 (0.712–0.846) | 0.704 (0.662–0.742) | 0.8385 (0.0274) | 0.7705 (0.0253) | |
| Retro | 5 | 0.885 | 0.750 | ||
| 10 | 0.780 (0.742–0.814) | 0.899 (0.880–0.915) | 0.9138 (0.0315) | 0.8464 (0.0354) | |
| 12 | 0.803 | 0.786 | |||
| 15 | 0.785 (0.712–0.846) | 0.704 (0.662–0.742) | 0.8385 (0.0274) | 0.7705 (0.0253) | |
| Others | 10 | 0.801 (0.767–0.833) | 0.894 (0.875–0.911) | 0.9121 (0.0314) | 0.8444 (0.0350) |
| 12 | 0.803 | 0.786 | |||
| 15 | 0.785 (0.712–0.846) | 0.704 (0.662–0.742) | 0.8385 (0.0274) | 0.7705 (0.0253) |
Abbreviations: MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; SEN, sensitivity; CI, confidence interval; SPE, specificity; AUC, area under the curve; SE, standard error.
Table S3.
Meta-analysis results on diagnostic efficacy of CT on size of metastatic lymph nodes
| Unit | Node size (mm) | SEN (95% CI) | SPE (95% CI) | AUC (SE) | Q* (SE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level I | 5 | 0.947 | 0.550 | ||
| 8 | 0.722 (0.465–0.903) | 0.966 (0.928–0.988) | |||
| 10 | 0.617 (0.464–0.755) | 0.864 (0.770–0.930) | |||
| 11 | 0.556 | 0.565 | |||
| 12 | 0.821 | 0.850 | |||
| 15 | 0.802 (0.711–0.875) | 0.677 (0.573–0.771) | 0.8519 (0.0818) | 0.7830 (0.0776) | |
| Level II | 5 | 0.947 | 0.550 | ||
| 8 | 0.769 | 0.917 | |||
| 9 | 0.500 | 0.970 | |||
| 10 | 0.607 (0.468–0.735) | 0.510 (0.363–0.656) | 0.7272 (0.1426) | 0.6747 (0.1157) | |
| 11 | 0.556 | 0.565 | |||
| 12 | 0.821 | 0.850 | |||
| 15 | 0.802 (0.711–0.875) | 0.818 (0.746–0.876) | 0.9083 (0.0599) | 0.8402 (0.0658) | |
| Level III | 5 | 0.947 | 0.550 | ||
| 6 | 0.500 | 0.970 | |||
| 8 | 0.500 | 0.970 | |||
| 10 | 0.746 (0.659–0.820) | 0.809 (0.739–0.867) | 0.8499 (0.0783) | 0.7811 (0.0740) | |
| 12 | 0.821 | 0.850 | |||
| 15 | 0.723 (0.574–0.844) | 0.577 (0.432–0.713) | |||
| Level IV | 5 | 0.947 | 0.550 | ||
| 7 | 0.500 | 0.970 | |||
| 8 | 0.500 | 0.970 | |||
| 10 | 0.746 (0.659–0.820) | 0.809 (0.739–0.867) | 0.8499 (0.0783) | 0.7811 (0.0740) | |
| 12 | 0.821 | 0.850 | |||
| 15 | 0.723 (0.574–0.844) | 0.577 (0.432–0.713) | |||
| Retro | 5 | 0.947 | 0.550 | ||
| 8 | 0.500 | 0.970 | |||
| 10 | 0.746 (0.659–0.820) | 0.809 (0.739–0.867) | 0.8499 (0.0783) | 0.7811 (0.0740) | |
| 12 | 0.821 | 0.850 | |||
| 15 | 0.723 (0.574–0.844) | 0.577 (0.432–0.713) | |||
| Others | 5 | 0.947 | 0.550 | ||
| 8 | 0.500 | 0.970 | |||
| 10 | 0.746 (0.659–0.820) | 0.809 (0.739–0.867) | 0.8499 (0.0783) | 0.7811 (0.0740) | |
| 12 | 0.821 | 0.850 | |||
| 15 | 0.723 (0.574–0.844) | 0.577 (0.432–0.713) |
Abbreviations: CT, computed tomography; SEN, sensitivity; CI, confidence interval; SPE, specificity; AUC, area under the curve; SE, standard error.