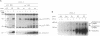Abstract
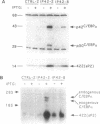
Previous studies showed that CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBP alpha) is required for differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes induced by exogenous hormonal agents. It was not possible to ascertain, however, whether C/EBP alpha alone is sufficient to induce differentiation because its antimitogenic activity precluded propagating 3T3-L1 cell lines that constitutively express C/EBP alpha at high levels. This problem was circumvented by using 3T3-L1 preadipocytes stably transfected with an isopropyl beta-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG)-inducible p42 C/EBP alpha expression vector system. IPTG-induced expression of the 42-kDa isoform of C/EBP alpha in preadipocytes caused expression of several endogenous adipocyte-specific genes (genes encoding the 422 adipose P2 protein, glucose transporter 4, and C/EBP alpha) and the accumulation of cytoplasmic triglyceride. Thus, C/EBP alpha is not only necessary but also is sufficient to trigger differentiation of growth-arrested 3T3-L1 preadipocytes without use of exogenous hormonal agents.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernlohr D. A., Angus C. W., Lane M. D., Bolanowski M. A., Kelly T. J., Jr Expression of specific mRNAs during adipose differentiation: identification of an mRNA encoding a homologue of myelin P2 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5468–5472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernlohr D. A., Bolanowski M. A., Kelly T. J., Jr, Lane M. D. Evidence for an increase in transcription of specific mRNAs during differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5563–5567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Gwynn B., Howard S., Jerry J., Gordon J. I., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1146–1156. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham M. Making muscle in mammals. Trends Genet. 1992 Apr;8(4):144–148. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90373-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheneval D., Christy R. J., Geiman D., Cornelius P., Lane M. D. Cell-free transcription directed by the 422 adipose P2 gene promoter: activation by the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8465–8469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Kaestner K. H., Geiman D. E., Lane M. D. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein gene promoter: binding of nuclear factors during differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2593–2597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Yang V. W., Ntambi J. M., Geiman D. E., Landschulz W. H., Friedman A. D., Nakabeppu Y., Kelly T. J., Lane M. D. Differentiation-induced gene expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein interacts with and activates the promoters of two adipocyte-specific genes. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1323–1335. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman R. A., Reed B. C., Mackall J. C., Student A. K., Lane M. D., Bell R. M. Selective changes in microsomal enzymes of triacylglycerol phosphatidylcholine, and phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthesis during differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7256–7261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook K. S., Hunt C. R., Spiegelman B. M. Developmentally regulated mRNAs in 3T3-adipocytes: analysis of transcriptional control. J Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;100(2):514–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.2.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelius P., MacDougald O. A., Lane M. D. Regulation of adipocyte development. Annu Rev Nutr. 1994;14:99–129. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.14.070194.000531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O., Geddes T. J. Reciprocal regulation of adipogenesis by Myc and C/EBP alpha. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):379–382. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Kehinde O. An established preadipose cell line and its differentiation in culture. II. Factors affecting the adipose conversion. Cell. 1975 May;5(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Kehinde O. Spontaneous heritable changes leading to increased adipose conversion in 3T3 cells. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R., Ro H. S., Robinson G. S., Xanthopoulos K. G., Spiegelman B. M. A direct role for C/EBP and the AP-I-binding site in gene expression linked to adipocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5331–5339. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Christy R. J., Lane M. D. Mouse insulin-responsive glucose transporter gene: characterization of the gene and trans-activation by the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):251–255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Christy R. J., McLenithan J. C., Braiterman L. T., Cornelius P., Pekala P. H., Lane M. D. Sequence, tissue distribution, and differential expression of mRNA for a putative insulin-responsive glucose transporter in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3150–3154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legraverend C., Antonson P., Flodby P., Xanthopoulos K. G. High level activity of the mouse CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP alpha) gene promoter involves autoregulation and several ubiquitous transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1735–1742. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. T., Lane M. D. Antisense CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein RNA suppresses coordinate gene expression and triglyceride accumulation during differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):533–544. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. T., MacDougald O. A., Diehl A. M., Lane M. D. A 30-kDa alternative translation product of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha message: transcriptional activator lacking antimitotic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9606–9610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackall J. C., Student A. K., Polakis S. E., Lane M. D. Induction of lipogenesis during differentiation in a "preadipocyte" cell line. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6462–6464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N. MyoD family: a paradigm for development? Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1454–1461. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossipow V., Descombes P., Schibler U. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein mRNA is translated into multiple proteins with different transcription activation potentials. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8219–8223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed B. C., Lane M. D. Insulin receptor synthesis and turnover in differentiating 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):285–289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Smith C. J., Hirsch A., Lai E., Rubin C. S. Recent studies of the 3T3-L1 adipocyte-like cell line. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1979;35:477–499. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571135-7.50015-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson L., Strömberg K., Vikman K., Bjursell G., Enerbäck S. The CCAAT/enhancer binding protein and its role in adipocyte differentiation: evidence for direct involvement in terminal adipocyte development. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3787–3793. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04948.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Student A. K., Hsu R. Y., Lane M. D. Induction of fatty acid synthetase synthesis in differentiating 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4745–4750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umek R. M., Friedman A. D., McKnight S. L. CCAAT-enhancer binding protein: a component of a differentiation switch. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):288–292. doi: 10.1126/science.1987644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasseur-Cognet M., Lane M. D. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBP alpha) undifferentiated protein: a developmentally regulated nuclear protein that binds to the C/EBP alpha gene promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7312–7316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E. Muscle basic helix-loop-helix proteins and the regulation of myogenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):243–248. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]