Abstract
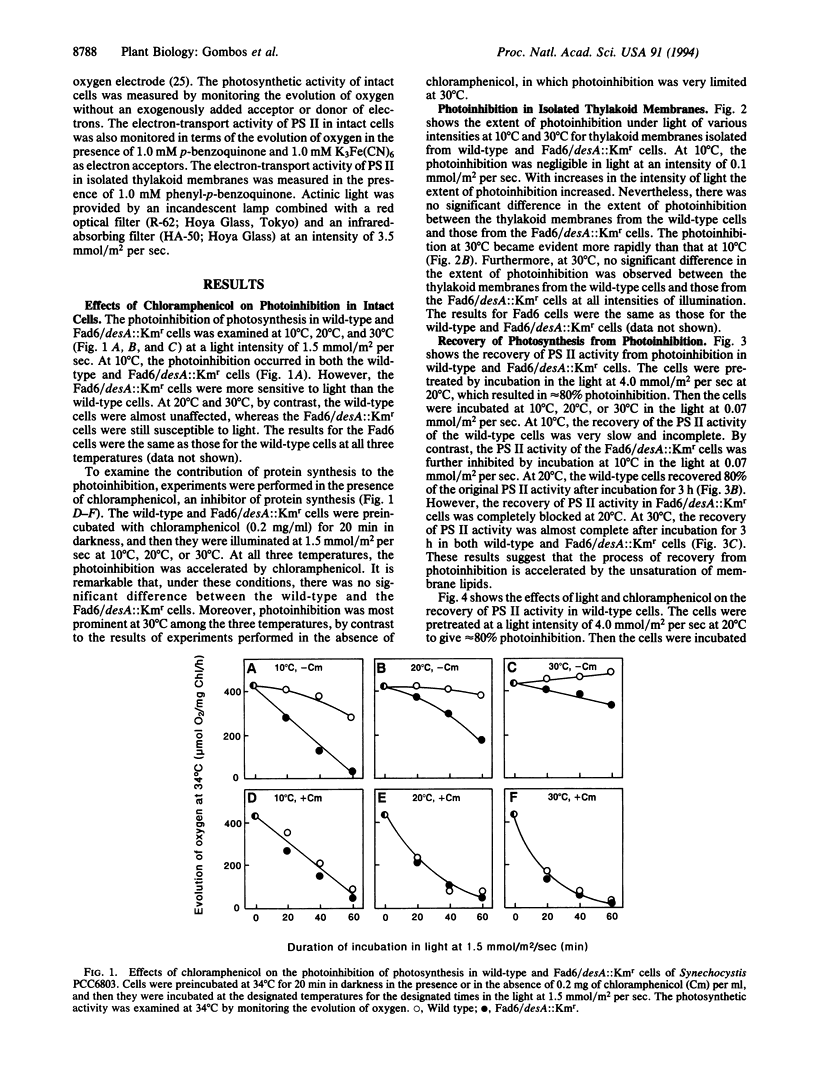
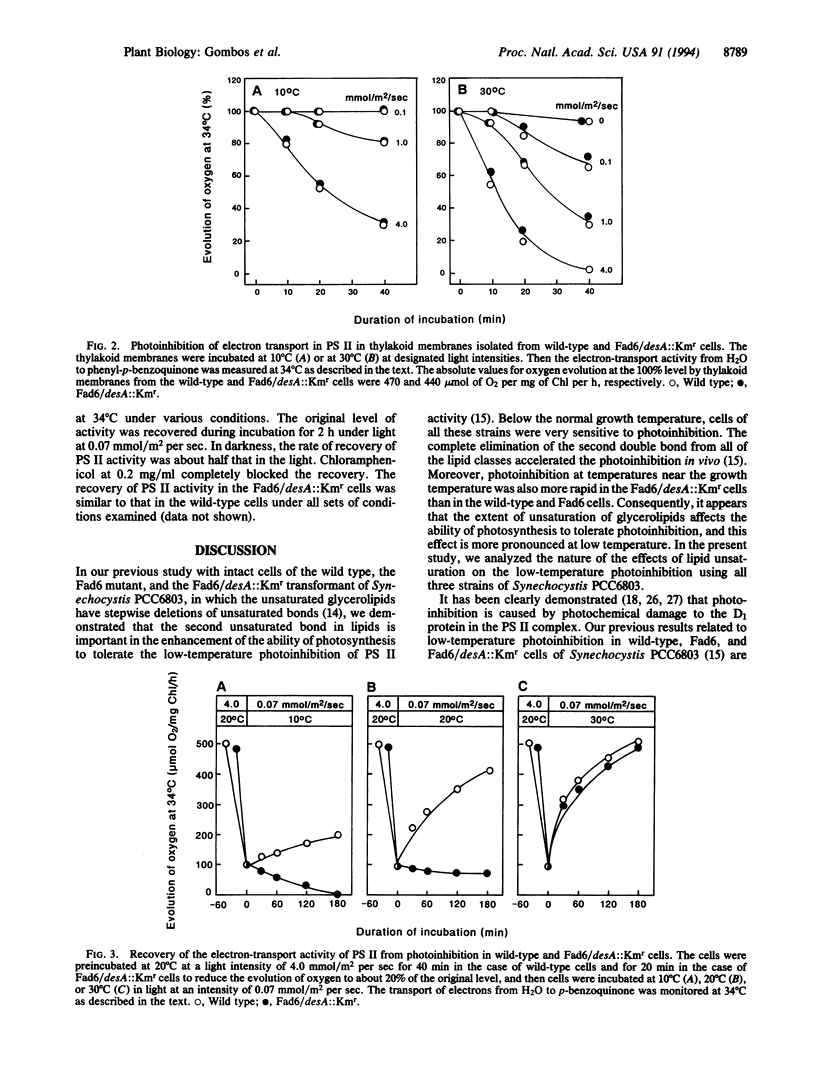
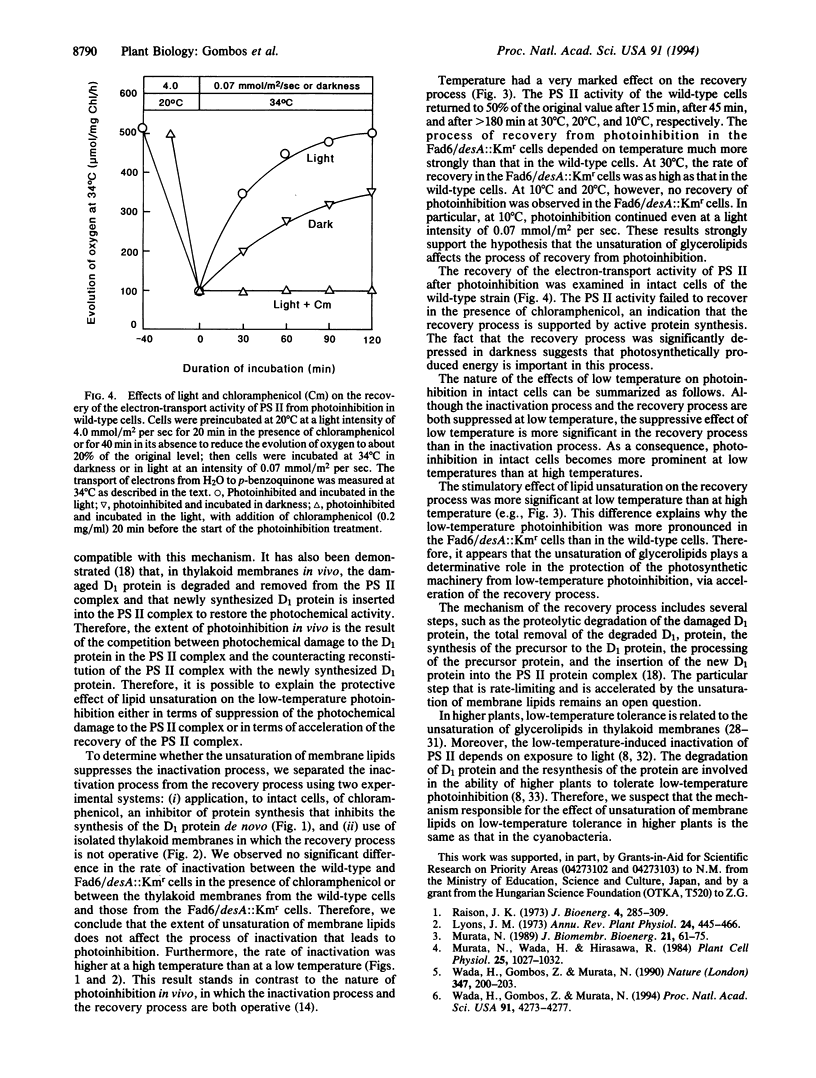
In a previous study of mutants in fatty-acid desaturation of Synechocystis PCC6803, it was demonstrated that the photoinhibition of photosynthesis at low temperature in vivo is tolerated by cells as a result of the unsaturation of glycerolipids of thylakoid membranes. Since the extent of photoinhibition of photosynthesis in vivo depends on a balance between the photoinduced inactivation and the recovery from the photoinhibited state, an examination was made of the effects of the unsaturation of membrane lipids on these processes. It appears that the unsaturation of the membrane lipids does not affect the inactivation process but accelerates the recovery process and, moreover, that the apparent increase in the photoinhibition in vivo of photosynthesis at low temperature is caused by a depressed rate of recovery at low temperature.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aro E. M., Virgin I., Andersson B. Photoinhibition of Photosystem II. Inactivation, protein damage and turnover. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jul 5;1143(2):113–134. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(93)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry-Opersteny D., Heusinkveld K. B. Prophylactic antiemetics for chemotherapy-associated nausea and vomiting. Cancer Nurs. 1983 Apr;6(2):117–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Las Rivas J., Andersson B., Barber J. Two sites of primary degradation of the D1-protein induced by acceptor or donor side photo-inhibition in photosystem II core complexes. FEBS Lett. 1992 Apr 27;301(3):246–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80250-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gombos Z., Wada H., Murata N. Unsaturation of fatty acids in membrane lipids enhances tolerance of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC6803 to low-temperature photoinhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9959–9963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugly S., Somerville C. A role for membrane lipid polyunsaturation in chloroplast biogenesis at low temperature. Plant Physiol. 1992 May;99(1):197–202. doi: 10.1104/pp.99.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyle D. J., Ohad I., Arntzen C. J. Membrane protein damage and repair: Selective loss of a quinone-protein function in chloroplast membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4070–4074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata N. Low-temperature effects on cyanobacterial membranes. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1989 Feb;21(1):61–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00762212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohad I., Kyle D. J., Arntzen C. J. Membrane protein damage and repair: removal and replacement of inactivated 32-kilodalton polypeptides in chloroplast membranes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;99(2):481–485. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.2.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono T. A., Murata N. Chilling Susceptibility of the Blue-green Alga Anacystis nidulans: I. EFFECT OF GROWTH TEMPERATURE. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jan;67(1):176–181. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raison J. K. The influence of temperature-induced phase changes on the kinetics of respiratory and other membrane-associated enzyme systems. J Bioenerg. 1973 Jan;4(1):285–309. doi: 10.1007/BF01516063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster G., Timberg R., Ohad I. Turnover of thylakoid photosystem II proteins during photoinhibition of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Nov 1;177(2):403–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14389.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Kunisawa R., Mandel M., Cohen-Bazire G. Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Jun;35(2):171–205. doi: 10.1128/br.35.2.171-205.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollemar J., Groth C. G., Korsgren O., Andersson A., Blombäck M., Olsson P. Injection of xenogeneic endocrine pancreatic tissue into the portal vein--effects on coagulation, liver function, and hepatic hemodynamics. A study in the pig-to-dog model. Transplantation. 1992 Jan;53(1):139–142. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199201000-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada H., Gombos Z., Murata N. Contribution of membrane lipids to the ability of the photosynthetic machinery to tolerate temperature stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4273–4277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada H., Gombos Z., Murata N. Enhancement of chilling tolerance of a cyanobacterium by genetic manipulation of fatty acid desaturation. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):200–203. doi: 10.1038/347200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolter F. P., Schmidt R., Heinz E. Chilling sensitivity of Arabidopsis thaliana with genetically engineered membrane lipids. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4685–4692. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



