Abstract
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) have potential applications in clinical disease therapy, such as autoimmune diseases and transplant rejection. However, their numbers are limited. Forkhead box protein 3 (FoxP3) is a key transcription factor that controls Treg development and function. Here, we generated a cell-permeable fusion protein, protein transduction domain (PTD)-conjugated mouse FoxP3 protein (PTD-mFoxP3), and evaluated whether PTD-mFoxp3 can alleviate rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in the collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mouse model. As expected, PTD-mFoxP3 was transduced into cells effectively, and inhibited T cell activation and attenuated the cell proliferation. It decreased interleukin (IL) 2 and interferon (IFN)-γ expression, and increased IL-10 expression in activated CD4+CD25− T cells. PTD-mFoxP3-transduced CD4+CD25− T cells attenuated proliferation of activated CD4+CD25− T cells. In addition, PTD-mFoxP3 blocked the Th17 differentiation programme in vitro and down-regulated IL-17 production from T cells by modulating induction and levels of retinoid-related orphan receptor gamma t (RORγt). Intra-articular delivery of PTD-mFoxP3 delayed disease incidence remarkably and alleviated autoimmune symptoms of CIA mice. Moreover, protective effects of PTD-mFoxP3 were associated with regulating the balance of T helper type 17 (Th17) and Tregs. These results suggest that PTD-mFoxP3 may be a candidate for RA therapy.
Keywords: collagen-induced arthritis, FoxP3, PTD, rheumatoid arthritis, Tregs
Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, invasive and systemic autoimmune disease, affecting approximately 1% of the world's population. It predominantly involves the peripheral synovium, causing synovitis, inflammatory cell infiltration, increased synovial fluid and pannus formation, as well as destruction of cartilage, bone and surrounding tissue. Collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) has been used extensively as a model for RA 1,2. However, the aetiology and pathogenesis mechanisms in RA are not yet clear. Recent studies have shown that the occurrence and development of RA is related closely to T helper type 17 (Th17) cells and their secreted cytokines. Nakae et al. found that CIA was suppressed markedly in interleukin (IL)-17–/– mice and interleukin-17 (IL-17) was responsible for priming collagen-specific T cells and collagen-specific immunoglobulin (Ig)G2a production 3. Lubberts et al. treated type II collagen (CII)-immunized dark brown Agouti (DBA)-1 mice with soluble murine interleukin (muIL)-17 receptor protein (muIL-17R:Fc) to block endogenous IL-17 and observed that this treatment suppressed the incidence severity of arthritis 4. In recent years, increasing evidence suggests that regulatory T cell (Treg) function is impaired in RA, and the immune inhibitory effects of Tregs in RA are important. The absence of Treg cells in K/B×N mice results in faster and more aggressive arthritis, and Treg cells are involved in constraining the immune phase of disease, as well as limiting articular damage 5. CD4+CD25+ T cell-depleted DBA/1J mice have significantly more severe RA compared to control mice following collagen immunization. Adoptively transferring CD4+CD25+ T cells into depleted mice was shown to reverse the heightened severity 6. Beavis and colleagues demonstrated that resistance to regulatory T cell-mediated suppression in RA can be bypassed by ectopic forkhead box protein 3 (FoxP3) expression in pathogenic synovial T cells 7. Reducing the number and functional defects of Tregs can cause the occurrence and aggravation of arthritis. Therefore, increasing Treg numbers, enhancing their function or regulating the balance between Tregs and Th17 cells may be therapeutic targets for arthritis.
FoxP3 belongs to the forkhead family, which is critically important for Treg development and function. It has been demonstrated that ectopic FoxP3 expression in naive T cells is sufficient to convert them into phenotypically and functionally natural Treg-like cells in mouse 8,9. Furthermore, FoxP3 transduction can induce a Treg phenotype in Jurkat T cells, as evidenced by increased expression of Treg-associated cell surface markers and inhibition of cytokine production following phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate/phytohaemagglutinin (PMA/PHA) stimulation, as well as by repression of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) activity 10. However, it is mandatory to prove that these vectors are safe for gene transfection in human subjects. Moreover, low Treg numbers, the difficulty of isolating Tregs and low transfection efficiency limit the clinical application of Tregs or FoxP3 gene transfer for autoimmune disease therapy.
Cell-penetrating peptide (CPP) or protein transduction domain (PTD), such as transacting activator of transcription (TAT), VP22, Antp, R7 and R9, has been shown to efficiently deliver iron nanobeads, fluorescent quantum dots and various proteins into cells for diagnoses or disease therapy in vitro and in vivo 11–16. In this study, we purified recombinant PTD-mFoxP3 fusion protein, and explored the feasibility of PTD-mediated transduction of FoxP3 into CD4+T cells. We demonstrated that PTD-mFoxP3 could convert CD4+CD25− T cells into Treg-like suppressor cells, inhibited polarization of Th17 cells and down-regulated the expression of IL-17 and retinoid-related orphan receptor gamma t (RORγt). Moreover, PTD-mFoxP3 could effectively inhibit the development of experimental arthritis in CIA mice. Therefore, our findings pave the way for the future utilization of PTD-mediated transduction of FoxP3 into T cells for the treatment of immune diseases.
Materials and methods
Mice and cell lines
DO11.10 mice, which are transgenic for a T cell receptor (TCR) specific for a major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-II-restricted ovalbumin (OVA) peptide, were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME, USA). Male DBA/1J mice (aged 8∼10 weeks) were obtained from the Shanghai Laboratory Animal Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). C57BL/6 (B6) (H-2b) and Balb/c mice were purchased from the Comparative Medicine Centre of Yang Zhou University (Yang Zhou, China). All mice were housed in microisolator units at 22 °C ∼24 °C under a 12 : 12-h light–dark cycle (lights off at 21:00 hours). All animal studies were approved by the Scientific Investigation Board of Jiangsu University in China for the Use and Care of Animals (licence number: SYXK 2013-0036).
The cell lines EL4 (B6-derived thymoma cells) and D2SC/1 [an early progenitor of the murine splenic dendritic cell (DC) cell line, derived from Balb/c mice] were kind gifts from Professor Weifeng Chen (Department of Immunology, Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing 100191, China).
Fusion protein construction, expression and purification
The pET-28a(+) plasmid (Novagen, Darmstadt, Germany) was used as the expression vector. All expression plasmids were constructed as indicated (Fig. 1a). The PTD-enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) sequence was amplified from the pEGFP-N1 plasmid [Clontech, Takara Biomedical Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd, Beijing, China] using primer pair 1 (Table1). The pET-28a(+)-PTD-eGFP plasmid was constructed by inserting polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products (PTD-eGFP sequence) into the pET-28a(+) plasmid digested with SacI and BamHI restriction endonucleases. pET-28a(+)-PTD was obtained from the pET-28a(+)-PTD-eGFP plasmid after digestion with the restriction endonuclease SacI (Promega, Beijing, China). The complete mouse FoxP3 (mFoxP3) sequence was PCR amplified from BALB/c splenocytes using specific primers (Table1), and inserted into pET-28a(+), pET-28a(+)-PTD and pET-28a(+)-PTD-eGFP plasmids to generate the mFoxP3, PTD-mFoxP3 and PTD-eGFP-mFoxP3 expression vectors, respectively. Fusion proteins were generated from Escherichia coli Rosetta (DE3) (Novagen, Darmstadt, Germany) induced for 5 h at 37oC with 1 mM IPTG. Fusion proteins were purified using Profinity IMAC Ni-Charged resin (Bio-Rad, Shanghai, China), according to the manufacturer's instructions. The eluted proteins were desalted using PD-10 Sephadex G-25 columns (GE Healthcare, Shanghai, China) with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and endotoxins were removed with ToxinEraser™ endotoxin removal resin (GenScript USA Inc., Piscataway, NJ, USA). Protein concentrations were evaluated by the Bradford method. Proteins were filtered through a 0.20 μm filters (Pall Corporation, Ann Arbor, MI, USA) and 0.25 ml aliquots were stored at −80 °C until use.
Figure 1.
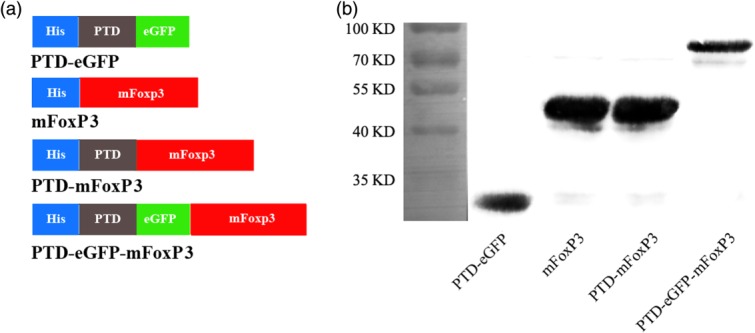
Preparation of the protein transduction domain (PTD) fusion proteins. (a) Schematic structures of the various recombinant proteins prepared and used in this study, including full-length mouse forkhead box protein 3 (mFoxP3), full-length mFoxP3 fused with the PTD sequence (PTD-mFoxP3) or with PTD plus enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) (PTD-eGFP-mFoxP3) and a control PTD-eGFP. All the proteins were tagged a 6 × His sequence, represented by blue boxes. The grey box represents PTD peptide (YGRKKRRQRRR) derived from HIV-1 PTD protein. The green box represents an eGFP. (b) Western blotting analysis of purified recombinant proteins probed with mouse anti-6 × His Tag monoclonal antibody (mAb). Expected sizes of recombinant proteins were PTD-mFoxP3, 51 kDa; PTD-eGFP-mFoxP3, 80 kDa; mFoxP3, 50 kDa and PTD-eGFP, 33 kDa.
Table 1.
Primer pairs used to detect expression of target genes by real-time reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT–PCR)
| Genes | Primer sequence (5′–3′) | Amplicon size(bp) | Annealing temp(°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TAT-eGFP | For: AAGGATCCTATGGCAGGAAGAAGCGGAGAC | 808 | 56 |
| Rev: AGCGACGAAGAGAGCTCATGGTGAGCAAGG | |||
| FoxP3 | For: ATAAAGCTTCCCCCAACCCTAGGC | 1290 | 56 |
| Rev: ATACTCGAGTTAAGGGCAGGGATTG | |||
| CTLA-4 | For: GTCAAGGGAACATTAGGG | 349 | 58 |
| Rev: ATTCAAACCACCAGCAAA | |||
| IL-2 | For: CTTGCTAATCACTCCTCACAG | 451 | 57 |
| Rev: GTGTTGTCAGCCCTT | |||
| IFN-γ | For: AAGCGTCATTGAATCACACC | 202 | 58 |
| Rev: CGAATCAGCAGCGACTCCTTAG | |||
| IL-10 | For: ATCGATTTCTCCCCTGTG | 318 | 58 |
| Rev: AATGGGAACTGAGGTATCAG | |||
| TGF-β | For: AAATCAACGGGATCAGC | 332 | 57 |
| Rev: TTGGTTGTAGAGGGCAAG | |||
| β-actin | For: TGGAATCCTGTGGCATCCATGAAAC | 349 | 58 |
| Rev: TAAAACGCAGCTCAGTAACAGTCCG |
Tat-eGFP = transactivating transcriptional factor-enhanced green fluorescent protein; FoxP3 = forkhead box protein 3; CTLA-4 = cytotoxic T lymphocyte 4; IL = interleukin; IFN = interferon; TGF = transforming growth factor; For = forward; Rev = reverse.
Flow cytometry and confocal microscopy analysis
Epilepsy 4 (EL-4) cells were seeded at a density of 4 × 106 cells/well in six-well plates and cultured for 4 h with 320, 640 or 1280 nM fusion proteins (PTD-mFoxP3). Cells were harvested, stained with anti-FoxP3-phycoerythrin (PE) and analysed by flow cytometry (BD FACSCalibur™ system; BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). The expression of intracellular cytokines and FoxP3 in PTD-mFoxP3-transduced CD4+CD25− T cells was detected by staining with anti-CD4-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), anti-FoxP3-PE [or anti-FoxP3-allophycocyanin (APC)] and anti-IL-17A-PE (or anti- IL-17A-APC), respectively. To confirm the transduction ability of PTD-eGFP-mFoxP3, EL-4 cells were treated for 2 h with 640 nM PTD-eGFP-mFoxP3, washed twice with cold PBS and fixed with 0.5 ml 4% paraformaldehyde. Cell nuclei were then stained for 30 min with 50 μg/ml propidium iodide (PI) (Sigma, Shanghai, China). Specimens were examined using confocal laser-scanning microscopy (Nikon C1Si; Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) to identify the permeability and cellular localization of the fusion proteins.
Western blot analysis
EL-4 cells were seeded into 25 cm2 culture flasks at a density of 5 × 105 cells/ml, treated for 2 or 12 h with 640 nM PTD-mFoxP3, mFoxP3 or PTD-eGFP and washed twice with cold PBS. Nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts were prepared as described previously 17, and protein concentrations were determined by Bradford protein assays. Proteins were separated by 12% sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and transferred to polyvinyidine difluoride (PVDF) membranes (Millipore, Shanghai, China). Membranes were blocked for 1 h with 5% skimmed milk powder, washed three times with Tris-buffered saline containing 0.1% Tween 20 and incubated with the following primary antibodies: rabbit anti-FoxP3 monoclonal antibody (mAb) (1 : 1000; Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, MA, USA) or anti-glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) antibody (1 : 5000; Cell Signaling Technology). After washing, the secondary horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (1 : 5000; Cell Signaling Technology) was added and blots were incubated for 1 h at 25 °C. Blots were developed using an Immobilon Western Chemiluminescent HRP substrate (Merck Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany), according to the manufacturer's protocol, and scanned using a ImageQuant LAS 4000 Mini (GE Healthcare, Pittsburgh, PA, USA).
Isolation of CD4+ T cells, CD4+CD25– T cells and CD4+CD25+ Tregs
Splenocytes were obtained from 6–8-week-old DO11.10 transgenic mice, C57BL/6 or BALB/c mice. CD4+ T cells were enriched by negative selection using a Dynal® Mouse CD4 Negative Isolation kit (Life Technologies Co., Shanghai, China). CD4+CD25– T cells and CD4+CD25+ Tregs were isolated from splenocytes according to the manufacturer's instructions using a Dynabeads® FlowComp™ Mouse CD4+CD25+ Treg cell kit (Life Technologies Co.). Unless stated otherwise, all cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (FCS), 2 mM glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 mg/ml streptomycin and 2 mM 2-mercaptoethanol (ME), and maintained at 37 °C in 5% CO2.
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) assays
Splenocytes were isolated from DO11.10 mice. Cells were washed with PBS, centrifuged at 200 g for 10 min at 4 °C and suspended in RPMI-1640 media supplemented with 10% FCS, 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin G and 100 mg/ml streptomycin (Life Technologies Co.). Splenocytes were plated at a density of 2 × 105 cells/well in 24-well plates and treated for 24 h with 320, 640 and 1280 nM PTD-mFoxP3 in a total volume of 2 ml. At 1280 nM, mFoxP3 and PTD-eGFP proteins served as controls. We assessed the cytotoxicity of PTD fusion proteins by evaluating lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in the culture media using the LDH kit (AusBio Laboratories Co., Ltd., Shandong, China), according to the manufacturer's instructions 18. Briefly, cell culture media were harvested and centrifuged at 900 g for 5 min to obtain a cell-free supernatant. LDH activity was measured on the Olympus AU2700™ Chemistry-Immuno Analyzer (Olympus Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). Triplicates were set up for each condition, and experiments were repeated independently three times.
Cell proliferation and suppression assay
The effect of PTD-mFoxP3 on CD4+ T cell proliferation was measured using a Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8; Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan), according to the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, CD4+ T cells (1 × 105/well) were isolated from DO11.10 mice and mixed with 25 μg/ml mitomycin C (MMC)-treated D2SC/1 cells (5 × 105/well) and OVA323–339 (2 μM), and co-cultured for 48 h in 96-well plates with or without 1280 nM PTD-eGFP, 1280 nM mFoxP3 and PTD-mFoxP3 (320 nM, 640 nM or 1280 nM). Triplicate wells were set up for each experimental condition. CCK-8 (20 μl/well) was added 4 h prior to the end of culture. The absorbance at 450 nm, with a reference wavelength of 650 nm, was measured using a microplate reader (Bio-Tek Instruments, Winooski, VT, USA).
PTD-mFoxP3 may convert CD4+CD25– T cells to Treg-like cells, which thus act as suppressor cells. To test our hypothesis, a total of 5 × 104 responder cells (CD4+CD25− T cells from DO11.10 mice) were stimulated for 2 h with MMC-treated D2SC/1 cells plus OVA323–339 (2 μM), and co-cultured for 48 h with 5 × 104 protein-pretreated CD4+CD25− T cells (from C57BL/6 mice, PTD-mFoxP3, mFoxP3 or PTD-eGFP pretreated for 2 h at the indicated concentration). Cell proliferation was analysed using CCK-8, as described above.
In-vitro induction and culture of Th17 cells
CD4+ T cells isolated from C57BL/6 mice were seeded in 48-well plates at a density of 3 × 105 cells/well, and stimulated for 3 days with plate-bound anti-CD3 (plates were coated at 5 μg/ml) and soluble anti-CD28 (1 μg/ml) in the presence of anti-interferon (IFN)-γ (10 μg/ml), anti-IL-4 (10 μg/ml), transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, (1 ng/ml), IL-1β (10 ng/ml), IL-23 (10 ng/ml) and IL-6 (20 ng/ml). Cells were harvested and incubated in new wells without stimulation, but in the presence of the neutralizing antibodies and recombinant cytokines described above. Next, 1280 nM PTD-eGFP and mFoxP3, and PTD-mFoxP3 (320, 640, 1280 nM) were added. On day 4, cells were divided into two portions. RNA was isolated from one portion and served as the template for real-time reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT–PCR) assays. The other portion of cells was re-stimulated for 4 h with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (50 ng/ml; Sigma), ionomycin (1 mg/ml; Sigma) and GolgiStop (BD Pharmingen, San Jose, CA, USA) and intracellular cytokine levels were analysed using flow cytometry. Alternatively, the entire content of each well was re-stimulated for 48 h with plate-bound anti-CD3 before analysing cytokines in the supernatant using a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Mouse CIA model
CIA was induced in male DBA/1J mice (aged 8–10 weeks) by intradermal immunization with chicken type II collagen (CC II, prepared from chicken cartilage, digested with proteases and purified by DE52 cellulose) in complete Freund's adjuvant (FCA). The severity of arthritis was assessed using an established scoring system of 0–4, as described previously 19–21. Briefly, 100 μg CC II emulsified in FCA was administered intradermally at the base of the tail of anaesthetized DBA/1J mice. After 21 days, a boost of collagen (100 μg) in FCA was injected intradermally. After the second collagen injection, mice were evaluated daily for the onset of CIA based on two clinical parameters: paw swelling and clinical score. Paw thickness was measured using 0–10-mm calipers. For the clinical score, a four-point scale (AI) was used, where 0 = no evidence of erythema and swelling, 1 = erythema and mild swelling confined to the tarsals or ankle joints, 2 = erythema and mild swelling extending from the ankle to the tarsals, 3 = erythema and moderate swelling extending from the ankle to metatarsal joints and 4 = erythema and severe swelling encompassing the ankle, foot and digits or ankylosis of the limb. Mice were considered to have arthritis if the arthritis score was greater than two points. For treatment, purified endotoxin-free PTD-mFoxP3 (0.25 mg/kg, 1.25 mg/kg) was injected into the local joint three times a week starting from the 22nd day after primary immunization to the 50th day. PBS and mFoxP3 protein (1.25 mg/kg) were negative controls, and MTX (2.5 mg/kg) was the positive treatment control. Mice were killed by over-anaesthetization on day 50. The percentages of Treg cells and Th17 cells in the inguinal lymph nodes were evaluated using flow cytometry.
Quantitative RT–PCR (qRT–PCR)
CD4+ T cells (5 × 105/well) were cultured in six-well plates for 4 or 8 h with MMC-treated D2SC/1 cells (2.5 × 106/well) plus OVA323–339 (2 μM) in the presence or absence of 1280 nM PTD-eGFP, 1280 nM mFoxP3 or PTD-mFoxP3 (320 nM, 640 nM, 1280 nM). Total RNA, isolated using Trizol™ reagent (Life Technologies), was reverse-transcribed to cDNA using the reverse transcriptase ReverTra Ace® (Toyobo, Osaka, Japan). qRT–PCR was performed using SYBR Premix EX Taq™ II (Takara, Shiga, Japan) and a Bio-Rad real-time thermal cycler CFX 96 for transcripts encoding IL-17A, RORγt, IL-2, IFN-γ, IL-10, TGF-β and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen (CTLA)-4. Primers sequences are listed in Table1. Relative mRNA expression was normalized to the housekeeping gene β-actin. Values are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (s.d.) of triplicate measurements.
ELISA assays
CD4+CD25− T cells (1 × 105/well), which were isolated from DO11.10 mice and pretreated for 1 h with PTD-mFoxP3, mFoxP3 or PTD-eGFP, were stimulated for 48 h with MMC-treated D2SC/1 cells (5 × 106/well) plus OVA323–339 (2 μM). Supernatants were harvested for analysis. IL-17A, IL-2, IL-10, IFN-γ and TGF-β were measured using ELISA kits (eBioscience, Inc., Shanghai, China), according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Histopathological analysis
For histopathological analysis, the hind legs were obtained by cutting under the knee (including the ankle joint and paw). The hind legs were then fixed in phosphate-buffered 10% formaldehyde, decalcified with 10% ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) and embedded in paraffin using a general method. Sections of hind paws were made by slicing the footpads horizontally. Sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Using microscopy, inflammation, pannus formation, cartilage destruction and bone damage were evaluated: 0, normal; 1, very small range; 2, mild; 3, moderate; 4, severe; and 5, very severe, based on a previously described scoring system 22,23.
Statistical analysis
For non-normative distributed values, median and ranges were used to summarize data. All other data are expressed as the mean ± s.d. Each sample was examined in replicate, each group contained seven to nine mice, barring loss of animals during the experiments, and each study was repeated at least twice. Unless noted otherwise, comparisons of averages between experimental groups were analysed using a two-sample independent t-test or analysis of variance (anova). Intergroup survivals were compared using the log-rank test of Kaplan–Meier survival curves. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Expression, purification and identification of PTD recombinant fusion proteins
All expression plasmids contained an N-terminal 6 × His Tag and were constructed as indicated in Fig. 1a. All proteins were expressed in E. coli Rosetta (DE3) and identified by immunoblotting with the anti-6 × His antibody (Fig. 1b).
Intracellular location of PTD proteins
To test the capacity of PTD fusion proteins to permeate the membrane and localize in the nucleus, EL-4 cells were co-incubated with different concentrations of PTD-mFoxP3 and analysed by flow cytometry. We found that PTD-mFoxP3 was transduced successfully and effectively into EL-4 cells (Fig. 2a). PTD-mFoxP3 had a transduction peak at 2 h (data not shown) and the optimal concentration was 640 nM (Fig. 2a). Furthermore, confocal microscopy and Western blot analysis were used to validate the permeability of PTD-eGFP-mFoxP3. The confocal microscopy results showed that PTD-eGFP-mFoxP3 could be transduced into the cytoplasm and localize in the nucleus of EL-4 cells (Fig. 2b). Western blot experiments indicated further that PTD-mFoxP3, but not mFoxP3, permeated into the cytoplasm and nucleus (Fig. 2c), and remained in the nucleus for at least 12 h (Fig. 2d).
Figure 2.
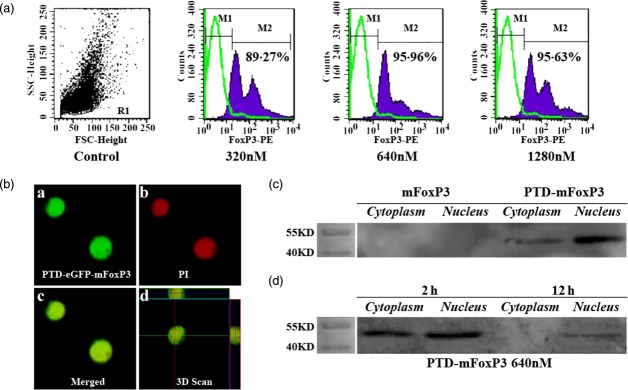
Epilepsy 4 (EL-4) cells transducted with protein transduction domain (PTD) recombinant proteins. (a) EL-4 cells were incubated with increasing doses of PTD-mouse forkhead box protein 3 (mFoxP3) (320 nM, 640 nM and 1280 nM) for 4 h. The expression of intracellular FoxP3 in PTD-mFoxP3-transduced EL-4 cells was detected by staining with anti-FoxP3-phycoerythrin (PE) using flow cytometry. (b) Cells were transduced with 640 nM PTD-enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP)- mouse forkhead box protein 3 (mFoxP3) for 2 h (a), the nuclei were stained with propidium iodide (PI) (b), and merged (c,d) examined by confocal microscopy. (c) EL-4 cells co-cultured with or without mFoxP3, PTD-mFoxP3 for 2 h at 640 nM, then cytoplasm and nucleus proteins were extracted and probed for the presence of recombinant proteins with anti-6 × His-Tag monoclonal antibody (mAb) (1 : 1000). (d) EL-4 cells were cultured with 640 nM PTD-mFoxP3 and harvested at 2 and 12 h, then cytoplasm and nucleus proteins were extracted and probed for the presence of recombinant proteins with anti-6 × His-Tag monoclonal antibody (mAb) (1 : 1000).
PTD-mFoxP3 is not cytotoxic for CD4+ CD25− T cells and suppresses antigen-specific CD4+CD25− T cell activation
We evaluated the viability of CD4+CD25− T cells treated with PTD-mFoxP3, mFoxpP3 or PTD-eGFP using LDH release assays. CD4+CD25− T cells did not exhibit increased LDH release after co-culture with fusion proteins for 24 h (Fig. 3a). Cell proliferation assays indicated that PTD-mFoxP3-treated cells were less proliferative than mFoxP3 or PTD-eGFP treated cells, and this effect was dose-dependent (Fig. 3b). Cell inhibition assays indicated that PTD-mFoxP3-treated CD4+CD25− T cells inhibited the proliferation of CD4+CD25− T cells stimulated with OVA323–339 (Fig. 3c). We evaluated cytokine and adhesion molecule expression and found that PTD-mFoxP3 suppressed IL-2 and IFN-γ expression and increased IL-10 expression. TGF-β expression levels were equivalent between the groups (Fig. 3d,e).
Figure 3.
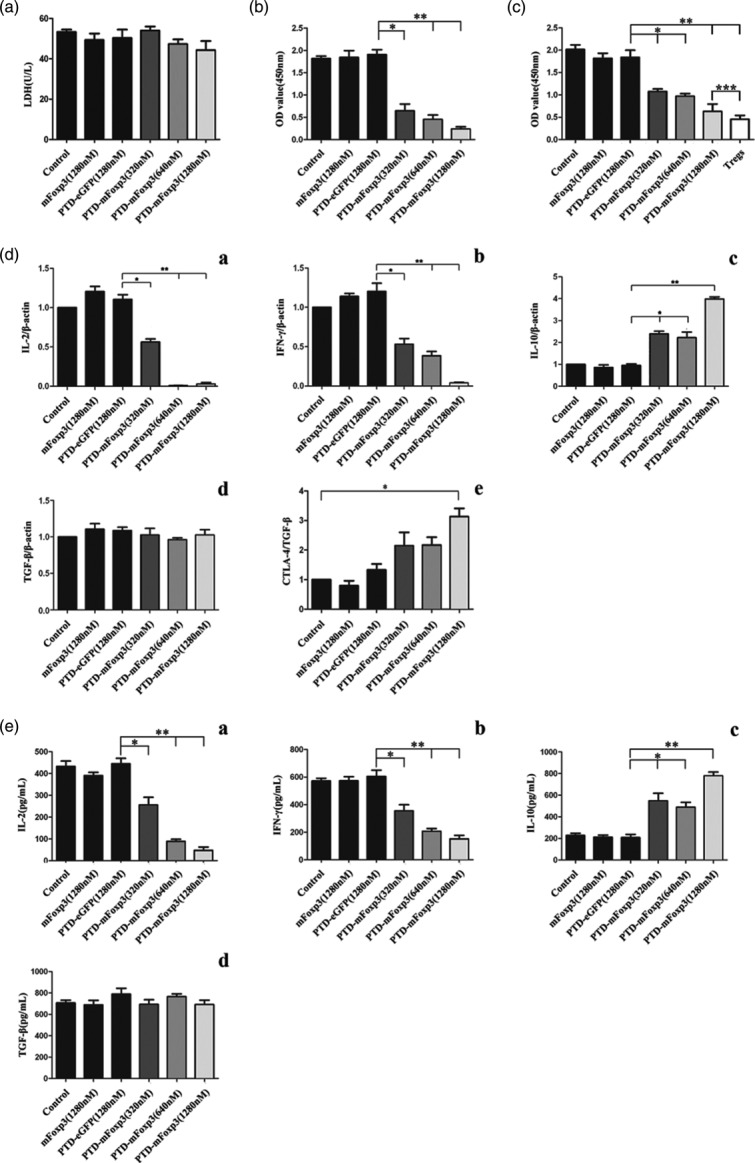
Effect of fusion proteins on cell viabilities and proliferation in T cells. (a) Purified CD4+ T cells co-cultured with mitomycin C (MMC)-treated D2SC/1 along with ovalbumin (OVA)323–339 (2 μM), treated with or without mouse forkhead box protein 3 (mFoxP3), protein transduction domain (PTD)-enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP), PTD-mFoxP3 (320 nM, 640 nM, 1280 nM) for 24 h. Cell viabilities were measured by a lactate dehydrogenase activity (LDH) assay. Data are represented as the mean ± standard deviation (s.d.) of three independent experiments. (b) PTD-mFoxp3-treated CD4+CD25− T cells are hypoproliferative. After CD4+CD25− T cells were treated with PTD-mFoxP3, mFoxP3 or PTD-green fluorescent protein (GFP) for 1 h, cells were stimulated with OVA323–339 (2 μM) and MMC-treated D2SC/1 for 48 h, and cell proliferation was analysed by CCK-8. (c) PTD-mFoxP3 converts CD4+CD25− T cells to suppressor cells. A total of 5 × 104 responder cells (CD4+CD25− T cells) were stimulated with OVA323–339 (2 μM) and MMC-treated D2SC/1 for 48 h with 5 × 104 suppressor cells (PTD-mFoxpP3-, mFoxP3- or PTD-GFP-treated CD4+CD25− T cells). All cell proliferation was analysed by cell counting kit 8 (CCK-8). (d) PTD–mFoxP3 regulates cytokine and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) expression at mRNA level from activated T cells. After CD4+CD25− T cells were treated with PTD-mFoxP3, mFoxP3 or PTD-GFP for 1 h, cells were stimulated with OVA323–339 (2 μM) and MMC-treated D2SC/1. Total RNA of 8 h-activated cells were extracted and examined for interleukin (IL)-2 and interferon (IFN)-γ, and 4-h-activated cells were for the examination of IL-10, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β and CTLA-4 expression. The ratio of the target gene versus β-actin at the control was set as 1. (e) PTD-mFoxP3 regulates cytokine secretion from activated T cells. After CD4+CD25− T cells were treated with PTD-mFoxP3, mFoxP3 or PTD-GFP for 1 h, cells were stimulated with OVA323–339 (2 μM) and MMC-treated D2SC/1 for 48 h. IL-2, IL-10, IFN-γ and TGF-β expression level in the same culture medium was analysed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Data from three independent experiments are presented as mean ± standard deviation (s.d.), *P < 0·05 versus control; **P < 0·01 versus control.
PTD-mFoxP3 inhibits Th17 induction and IL-17 production
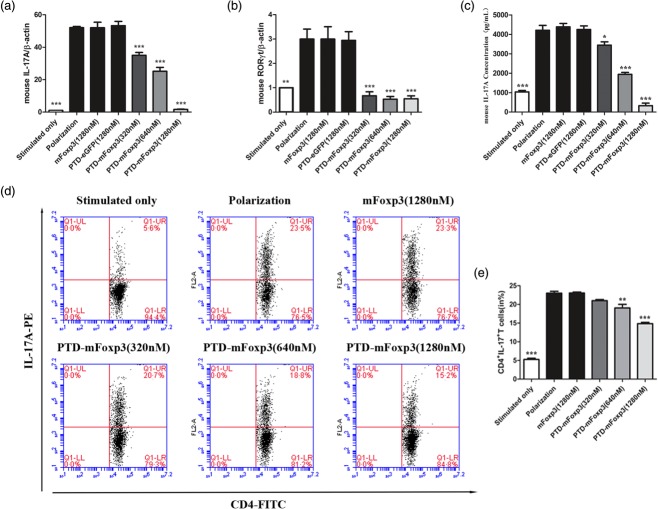
Th17 cells were induced under Th17-polarizing conditions and treated with PTD-mFoxP3, plate-bound anti-CD3 and soluble anti-CD28. We observed that CD4+ T cells produced significantly less IL-17A mRNA and protein (Fig. 4a,c,d). As expected, RORγt mRNA expression and Th17 cell numbers were reduced significantly (Fig. 4b,e).
Figure 4.
Protein transduction domain (PTD)-mouse forkhead box protein 3 (mFoxP3) inhibits T helper type 17 (Th17) inducing and interleukin (IL)-17 production. (a) Real-time reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction (RT–PCR) analysis of transcripts encoding IL-17A in polarized CD4+ T cells. Purified CD4+ T cells were stimulated for 3 days with plate-bound anti-CD3 and soluble anti-CD28 in the presence of anti-interferon (IFN)-γ (10 μg/ml), anti-IL-4 (10 μg/ml), transforming growth factor (TGF)-β (1 ng/ml), IL-1β (10 ng/ml), IL-23 (10 ng/ml) and IL-6 (20 ng/ml), and then treated for another 24 h with 1280 nM PTD-enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) and mFoxP3 and PTD-mFoxP3 (320, 640, 1280 nM) in the presence of neutralizing antibodies and recombinant cytokines but absence of stimulation of anti-CD3 or anti-CD28. RNA was extracted from treated cells, and IL-17A and RORγt mRNA expression was examined by real-time PCR. The data shown were normalized to expression of a reference gene β-actin, and the expression level in stimulated T cells was referred as 1. (b) Real-time RT–PCR analysis of transcripts encoding RORγt in polarized CD4+ T cells. Purified CD4+ T cells were treated as described in (a). (c) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) of IL-17A in the supernatants of polarized CD4+ T cells. CD4+ T cells were treated as described in (a), and restimulated with anti-CD3 or anti-CD28 for another 48 h. IL-17A production was assayed by ELISA. (d) Flow cytometry of intracellular cytokine production by total CD4+ T cells under Th17-polarizing condition. IL-17A expression was analysed after 4 h of restimulation with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA)/ionomycin by intracellular cytokine staining. (e) Frequency of CD4+ IL-17+ T cells after PTD fusion proteins treatment. Data are representative of three experiments and are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. *P < 0·05; **P < 0·01.
PTD-mFoxP3 therapy alleviates the severity of CIA by regulating the balance of Th17 and Treg cells
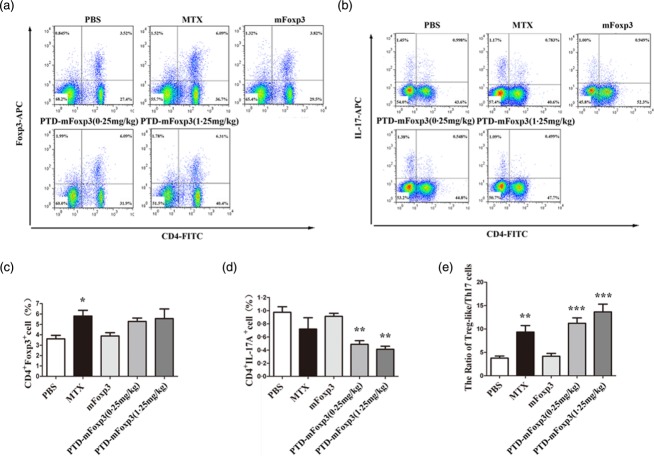
To evaluate the therapeutic effect of PTD-mFoxP3 on arthritis, we treated CIA mice with different concentrations of PTD-mFoxP3. As shown in Fig. 5a,b, after treatment with PTD-mFoxP3 (0.25 or 1.25 mg/kg), arthritic score and AI decreased more significantly than the mFoxP3-treated (1.25 mg/kg) group. The PTD-mFoxP3 (1.25 mg/kg) group was similar to the MIX group, and more effective than the PTD-mFoxP3 (0.25 mg/kg) group (Fig. 5a,b). Histopathological analysis indicated that PTD-mFoxP3- and MIX-treated CIA mice suffered mild inflammation, minimal cartilage damage with minimal pannus and less bone resorption. Mice receiving 1.25 mg/kg PTD-mFoxP3 had the least disease progression and exhibited significantly less inflammation and less permanent damage with regard to bone erosion, cartilage destruction and pannus formation compared to PBS- and mFoxP3-treated groups (Fig. 5c,d). It is well known that Th17 cells drive arthritic bone destruction in mice and humans 24. To understand the role of PTD-mFoxP3 in regulating the balance between Th17 cells and Tregs, we treated arthritic mice with PTD-mFoxP3. The results indicated that the onset of clinical signs of CIA was potently inhibited by PTD-mFoxP3 (Fig. 5). PTD-mFoxP3 also significantly increased the percentage of Tregs (CD4+FoxP3+ T cells) (Fig. 6a,c) and the ratio of Tregs/Th17 cells (Fig. 6e), and significantly decreased the percentage of Th17 cells (CD4+IL-17A+ T cells) (Fig. 6b,d) in draining inguinal lymph nodes in CIA mice.
Figure 5.
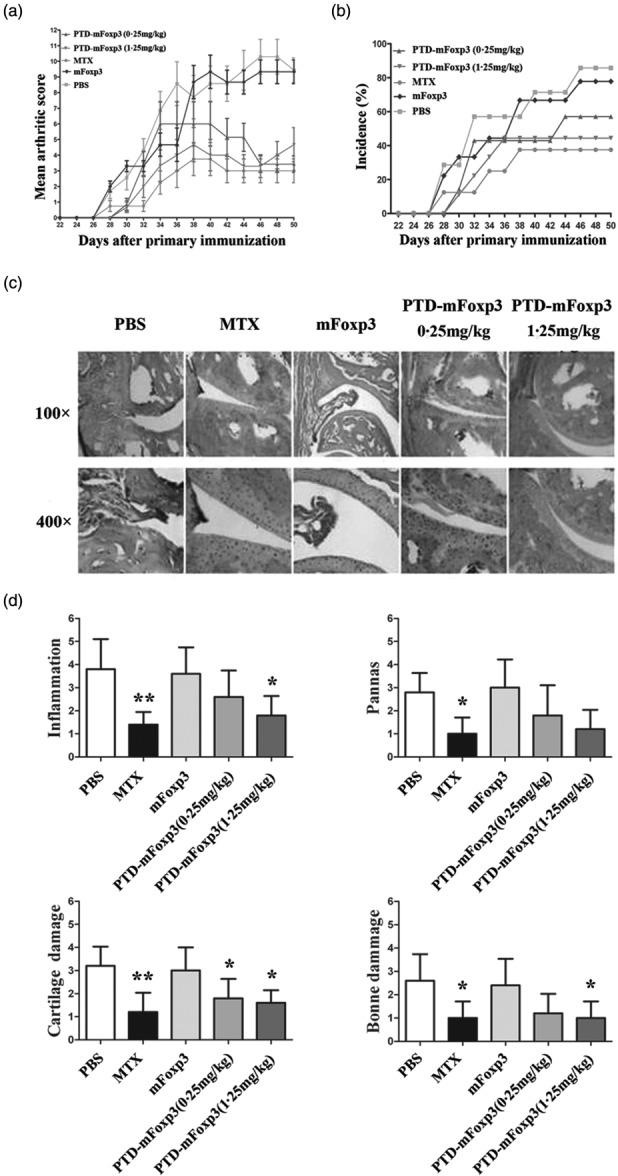
Effects of protein transduction domain (PTD)-mouse forkhead box protein 3 (mFoxP3) on the development of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in DBA/1 mice. Mice were treated with PTD-mFoxP3, mFoxP3 or methotrexate (MTX) on day 22 after chicken type II collagen (CII) immunization at the onset of disease. Attenuated clinical manifestation of arthritis was observed every day. The severity (a) and incidence (b) of arthritis were assessed as described in Materials and methods. Data are expressed as means of the total scores for four limbs or the incidence of arthritis after CII immunization (n = 7–9 per group). PTD-mFoxP3 (0·25 mg/kg) group: day 34 no significance, days 32 and 38 P < 0·05, others P < 0·0001; PTD-mFoxP3 (1·25 mg/kg) group: P < 0·0001; MTX group: P < 0·0001 in (a). (c) Representative joints pathological sections from each group were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E). (a) A normal mouse and (b) a type-II collagen (CII)-immunized mouse. (c) Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)-treated CIA mouse. (d) MTX treated an established CIA mouse. (e) mFoxP3 protein-treated group. (f,g) 0·25 mg/kg and 1·25 mg/kg PTD-mFoxP3-treated CII-immunized mouse. (d) Histopathological scores for the joints of each group. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation, n = 5, *P < 0·05; **P < 0·01 versus PBS-treated group.
Figure 6.
Protective effects of protein transduction domain (PTD)-mouse forkhead box protein 3 (mFoxP3) were associated with regulating the balance between T helper type 17 (Th170 and regulatory T cells (Tregs). Lymphocytes were obtained from DBA/1 mice treated with PTD-mFoxP3, mFoxP3 or MTX after CII immunization, and analysed by flow cytometry (FCM) for CD4+ FoxP3+ T cells or CD4+ interleukin (IL)-17A+ cells after in-vitro restimulation with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA)/ionomycin in the presence of GolgiStop for 4 h. (a) Representative dot-plots of Treg cells from draining lymph nodes of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mouse. For staining of Treg cells, anti-CD4-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) and anti-CD25-phycoerythrin (PE) surface-stained cells were fixed and permeabilized, and then stained with anti-FoxP3-allophycocyanin (APC). (b) Frequency of Treg cells subset in the CD4+ T lymphocytes of each group. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (s.d.), n = 5, *P < 0·05 versus phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)-treated group. (c) Representative dot-plots of Th17 cells from draining lymph nodes of CIA mouse isolated after treated for 4 weeks. For staining of Th17 cells, anti-CD4-FITC surface-stained cells were fixed and permeabilized, and then stained with anti-IL-17A-APC. (d) Frequency of Th17 cells subset in the CD4+ T lymphocytes of each group. Data are expressed as the mean ± s.d., n = 5, **P < 0·01 versus PBS-treated group. (e) The ratio of Treg-like/Th17 cells in the CD4+ T lymphocytes of each group. Data are expressed as the mean ± s.d., n = 5, **P < 0·01; ***P < 0·001 versus PBS-treated group.
Discussion
RA is one of the most common systemic autoimmune diseases and is characterized by chronic synovial inflammation and hyperplasia. The exact origin and pathogenesis of RA remains unknown, but increasing data regarding its pathogenic mechanism have shown that Th17 cells drive RA progression 24. Th17 cells may be a critical target in RA therapy. Adoptive transfusion of Tregs or ectopically expressed FoxP3 in T cells that convert T cells into Tregs may be a new RA therapeutic strategy 25–29. However, this strategy is limited by the numbers of Tregs 30,31, the safety of gene therapy, and whether induced Tregs (iTregs) reconvert to Th17 cells in the inflammatory microenvironment 29,32.
The HIV-1 PTD of TAT has potentially enhanced utility due to its small size (11 amino acids, YGRKKRRQRRR), which is rich in arginine and lysine residues. It is sufficient for intracellular transduction and subcellular localization 33. The current model for PTD-mediated protein transduction is a multi-step process that involves PTD binding to the cell surface, stimulation of macropinocytotic uptake of PTD and cargo into macropinosomes and endosomal escape into the cytoplasm 28. Many researchers have used PTD to generate fusion proteins 34,35. In our previous study, we expressed a PTD-conjugated human FoxP3 (PTD-hFoxP3) protein and demonstrated that the protein can be transduced into CD4+CD25– T cells and convert them to Treg-like cells in vitro 36. In order to explore that the potential of clinical application of the PTD-hFoxP3 for autoimmune diseases or transplantation therapy, in this study we generated a PTD-mouse FoxP3 (PTD-mFoxP3) fusion protein and examined its biofunctions both in vitro and in vivo. First, we confirmed that the protein is permeable and can penetrate into T cells. The murine thymoma EL-4 cell line was co-cultured with PTD-mFoxP3, and permeability was evaluated using flow cytometry, fluorescent confocal microscopy and Western blot. The data showed that PTD-mFoxP3 not only penetrated into cytoplasm but also translocated into nuclei (Fig. 2). Next, we evaluated the biofunctions of the PTD-mFoxP3. We found that PTD-mFoxP3 inhibits CD4+ T cells activation, Th17 cell generation and down-regulates expression of Th1- and Th17-associated cytokines or transcripts (IL-2, IFN-γ and RORγt), and up-regulates Treg-related cytokines or molecules (IL-10 and CTLA-4). However, it did not up-regulate TGF-β. CD4+ T cells transduced with PTD-mFoxP3 inhibited proliferation of CD4+ T cells stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies (Figs 3 and 4). Therefore, we hypothesize that PTD-mFoxP3 can convert CD4+ T cells into Treg-like cells. Moreover, the T cell therapy effect of PTD-mFoxP3 on RA was evaluated using a CIA mouse model. As expected, PTD-mFoxP3 decreased the clinical signs and symptoms of CIA (Fig. 5), as well as protected joints from the inflammation by increasing the numbers of Tregs, decreasing the numbers of Th17 cells and restoring the balance of Th17 cells/Tregs in the local microenvironment (Fig. 6).
Choi and colleagues have demonstrated that the cell-permeable FoxP3 protein (HHph-1-FoxP3) could convert CD4+CD25− T cells to Treg-like cells and prevent autoimmune diseases and allergic airway inflammation via increasing the expression of CD25 and CTLA-4 and decreasing the products of IL-2, IFN-γ, IL-13 and IL-4 16. Yomogida and colleagues also developed another cell-permeable FoxP3 protein (FoxP3-11R) and ameliorated arthritis of mice CIA model via increasing the numbers of suppressive function of T cells 37. In our previous research, we found that PTD-mFoxP3 up-regulated Treg-associated cytokines and molecules such as IL-10 and CLTA-4, but did not affect CD25 and TGF-β 16. CD25 is the α-chain of the IL-2 receptor (IL-2R). IL-2R receptor signalling is crucial for the functional maturation of natural Treg cells during thymic development 38. High CD25 expression is considered an important mechanism for maintaining FoxP3 expression in the periphery 39. IL-2R-deficient mice are not devoid of FoxP3+ T cells. Moreover, along with the decreased fraction of Tregs, FoxpP3 expression is also lower in the absence of IL-2R signalling 40. However, the ability of FoxP3 T cells to act as suppressors is not dependent upon CD25 expression. These data indicate that induction of FoxP3 expression is necessary and sufficient for regulatory cell function, but CD25 expression is not absolutely required. Our previous study also found that PTD-hFoxP3 could not increase CD25 expression in CD4+CD25– T cells. Therefore, the Treg-like cells induced by us do not perform like those of Choi's report 16, but are more similar to those of Yomogida's findings 37. Although previous studies have found that TGF-β plays a critical role in Treg induction and development 41, it is not required for Treg function 42.
Conclusions
In conclusion, we report that PTD-mFoxP3 can convert CD4+CD25– T cells into Treg-like cells and restore the balance of Th17 cells/Tregs in a CIA model. Administration of the PTD-FoxP3 protein can be used for experimental arthritis therapy to restore the impaired balance of Th17 cells/Tregs and improve Treg function.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the following grants: the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers: 30671984, 81273202, 31200676, 31400773 and 81172834), Clinical Medicine Science and Technology Project of Jiangsu Province of China (grant number: BL2013024), the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (grant number: 14KJB320001), Program of Innovative Research Team of Jiangsu Province, Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions and Project Funded by the Key Academic Program Development of Jiangsu University, and Senior Talents Scientific Research Foundation of Jiangsu University (grant number: 14JDG042). The study was also supported by the Postgraduate Students’ Innovation Program of General Higher Education of Jiangsu Province of China (grant numbers: CX10B_283Z, CXZZ11_0591 and CXLX12_0675).
Disclosure
The author(s) declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Authors’ contributions
X. L., B. J. and M. S. performed all experiments and data analysis and contributed to the drafting of the paper. L. H. and Y. Z. participated in fusion protein construction, expression and purification. W. W. participated in animal experiments, tissue processing and histology scoring. S. A., L. S., H. Q. and W. X. provided the necessary research reagents, animals and technical expertise. Q. S. and S. X. designed the experiments and evaluated all results. X. L., B. J., M. S. and Q. S. wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
References
- Brand DD, Latham KA, Rosloniec EF. Collagen-induced arthritis. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:1269–75. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfait AM, Williams RO, Malik AS, Maini RN, Feldmann M. Chronic relapsing homologous collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice as a model for testing disease-modifying and remission-inducing therapies. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2001;44:1215–24. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200105)44:5<1215::AID-ANR206>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae S, Nambu A, Sudo K, Iwakura Y. Suppression of immune induction of collagen-induced arthritis in IL-17-deficient mice. J Immunol. 2003;171:6173–7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.11.6173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubberts E, Joosten LA, Oppers B, et al. IL-1-independent role of IL-17 in synovial inflammation and joint destruction during collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 2001;167:1004–13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.2.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen LT, Jacobs J, Mathis D, Benoist C. Where FoxP3-dependent regulatory T cells impinge on the development of inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2007;56:509–20. doi: 10.1002/art.22272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan ME, Sutmuller RP, Witteveen HJ, et al. CD25+ cell depletion hastens the onset of severe disease in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2003;48:1452–60. doi: 10.1002/art.11063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavis PA, Gregory B, Green P, et al. Resistance to regulatory T cell-mediated suppression in rheumatoid arthritis can be bypassed by ectopic foxp3 expression in pathogenic synovial T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:16717–22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112722108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:330–6. doi: 10.1038/ni904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori S, Nomura T, Sakaguchi S. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science. 2003;299:1057–61. doi: 10.1126/science.1079490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim JY, Kim HJ, Hurt EM, Chen X, Howard OM, Farrar WL. Functional and genomic analyses of FOXP3-transduced Jurkat-T cells as regulatory T (Treg)-like cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;362:44–50. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.07.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephson L, Tung CH, Moore A, Weissleder R. High-efficiency intracellular magnetic labeling with novel superparamagnetic-Tat peptide conjugates. Bioconjug Chem. 1999;10:186–91. doi: 10.1021/bc980125h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittet MJ, Swirski FK, Reynolds F, Josephson L, Weissleder R. Labeling of immune cells for in vivo imaging using magnetofluorescent nanoparticles. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:73–9. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolgilevich S, Zaidi N, Song J, Abe E, Moonga BS, Sun L. Transduction of TAT fusion proteins into osteoclasts and osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;299:505–9. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(02)02664-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katterle Y, Brandt BH, Dowdy SF, Niggemann B, Zanker KS, Dittmar T. Antitumour effects of PLC-gamma1-(SH2)2-TAT fusion proteins on EGFR/c-erbB-2-positive breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:230–5. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengoku T, Bondada V, Hassane D, Dubal S, Geddes JW. Tat-calpastatin fusion proteins transduce primary rat cortical neurons but do not inhibit cellular calpain activity. Exp Neurol. 2004;188:161–70. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2004.03.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi JM, Shin JH, Sohn MH, et al. Cell-permeable Foxp3 protein alleviates autoimmune disease associated with inflammatory bowel disease and allergic airway inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:18575–80. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000400107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E, Matthias P, Muller MM, Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with ‘mini-extracts’, prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989;17:6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demers M, Ho-Tin-Noe B, Schatzberg D, Yang JJ, Wagner DD. Increased efficacy of breast cancer chemotherapy in thrombocytopenic mice. Cancer Res. 2011;71:1540–9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman DH, Taylor P, Bendele A, et al. CEL-2000: a therapeutic vaccine for rheumatoid arthritis arrests disease development and alters serum cytokine/chemokine patterns in the bovine collagen type II induced arthritis in the DBA mouse model. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010;10:412–21. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2009.12.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song X, Shen J, Wen H, et al. Impact of Schistosoma japonicum infection on collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice: a murine model of human rheumatoid arthritis. PLOS ONE. 2011;6:e23453. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu JG, Lee J, Kim EK. Treatment of IL-21R-Fc control autoimmune arthritis via suppression of STAT3 signal pathway mediated regulation of the Th17/Treg balance and plasma B cells. 2014;163:143–50. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2014.09.007. Immunol Lett. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao J, Kamanaka M, Hao J, et al. IL-10 signaling in CD4+ T cells is critical for the pathogenesis of collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13:R212. doi: 10.1186/ar3545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min SY, Yan M, Du Y, et al. Intra-articular nuclear factor-kappaB blockade ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by eliciting regulatory T cells and macrophages. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013;172:217–27. doi: 10.1111/cei.12054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollinger B, Junt T, Metzler B, et al. Th17 cells, not IL-17+ gammadelta T cells, drive arthritic bone destruction in mice and humans. J Immunol. 2011;186:2602–12. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Garra A. Vieira P. Regulatory T cells and mechanisms of immune system control. Nat Med. 2004;10:801–5. doi: 10.1038/nm0804-801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Borja F, Jury EC, Mauri C, Ehrenstein MR. Defects in CTLA-4 are associated with abnormal regulatory T cell function in rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:19396–401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0806855105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan ME, Flierman R, van Duivenvoorde LM, et al. Effective treatment of collagen-induced arthritis by adoptive transfer of CD25+ regulatory T cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:2212–21. doi: 10.1002/art.21195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard JP, Melikov K, Brooks H, Prevot P, Lebleu B, Chernomordik LV. Cellular uptake of unconjugated TAT peptide involves clathrin-dependent endocytosis and heparan sulfate receptors. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:15300–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401604200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong N, Lan Q, Chen M, et al. Antigen-specific transforming growth factor beta-induced Treg cells, but not natural Treg cells, ameliorate autoimmune arthritis in mice by shifting the Th17/Treg cell balance from Th17 predominance to Treg cell predominance. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:2548–58. doi: 10.1002/art.34513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esensten JH, Wofsy D, Bluestone JA. Regulatory T cells as therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009;5:560–5. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2009.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edinger M, Hoffmann P. Regulatory T cells in stem cell transplantation: strategies and first clinical experiences. Curr Opin Immunol. 2011;23:679–84. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2011.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang XO, Nurieva R, Martinez GJ, et al. Molecular antagonism and plasticity of regulatory and inflammatory T cell programs. Immunity. 2008;29:44–56. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.05.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J, Ryu J, Kim KA, et al. Mutational analysis of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein transduction domain which is required for delivery of an exogenous protein into mammalian cells. J Gen Virol. 2002;83:1173–81. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-83-5-1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou G, Shan P, Hu X, Zheng X, Zhou S. Neuroprotective effect of TAT PTD–Ngb fusion protein on primary cortical neurons against hypoxia-induced apoptosis. Neurol Sci. 2013;34:1771–8. doi: 10.1007/s10072-013-1333-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y, Thompson JD, Chan WK. A cell-penetrating peptide suppresses the hypoxia inducible factor-1 function by binding to the helix-loop-helix domain of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator. Chem Biol Interact. 2013;203:401–11. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2013.02.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X, Xu X, Lin X, et al. PTD-hFOXP3 protein acts as an immune regulator to convert human CD4(+)CD25(-) T cells to regulatory T-like cells. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113:3797–809. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yomogida K, Wu S, Baravati B, et al. Cell penetrating recombinant Foxp3 protein enhances Treg function and ameliorates arthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;434:263–7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.02.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng G, Yu A, Dee MJ, Malek TR. IL-2R signaling is essential for functional maturation of regulatory T cells during thymic development. J Immunol. 2013;190:1567–75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyara M, Sakaguchi S. Human FoxP3(+)CD4(+) regulatory T cells: their knowns and unknowns. Immunol Cell Biol. 2011;89:346–51. doi: 10.1038/icb.2010.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer AL, Yu A, Malek TR. Function of the IL-2R for thymic and peripheral CD4+CD25+ Foxp3+ T regulatory cells. J Immunol. 2007;178:4062–71. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.7.4062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S, Schramm C, Lehr HA, et al. Cutting edge: TGF-beta signaling is required for the in vivo expansion and immunosuppressive capacity of regulatory CD4+CD25+ T cells. J Immunol. 2004;173:6526–31. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.11.6526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kullberg MC, Hay V, Cheever AW, et al. TGF-beta1 production by CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells is not essential for suppression of intestinal inflammation. Eur J Immunol. 2005;35:2886–95. doi: 10.1002/eji.200526106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]