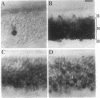
Abstract
Olfactory receptor neurons respond to odorant stimulation with a rapid increase in intracellular cAMP that opens cyclic nucleotide-gated (cng) cation channels. cng channels in rat olfactory neurons are activated by cAMP in the low micromolar range and are outwardly rectifying. The cloned rat olfactory cng channel (rOCNC1), however, is much less sensitive to cAMP and exhibits very weak rectification. Here we describe the cloning and characterization of a second rat cng channel subunit, denoted rOCNC2. rOCNC2 does not form functional channels when expressed alone. When rOCNC1 and rOCNC2 are coexpressed, however, an outwardly rectifying cation conductance with cAMP sensitivity near that of the native channel is observed. In situ hybridization with probes specific for the two subunits shows that they are coexpressed in olfactory receptor neurons. These data indicate that the native olfactory cng channel is likely to be a heterooligomer of the rOCNC1 and rOCNC2 subunits.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenhofen W., Ludwig J., Eismann E., Kraus W., Bönigk W., Kaupp U. B. Control of ligand specificity in cyclic nucleotide-gated channels from rod photoreceptors and olfactory epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9868–9872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakalyar H. A., Reed R. R. Identification of a specialized adenylyl cyclase that may mediate odorant detection. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1403–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.2255909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck L., Axel R. A novel multigene family may encode odorant receptors: a molecular basis for odor recognition. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):175–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90418-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. Y., Peng Y. W., Dhallan R. S., Ahamed B., Reed R. R., Yau K. W. A new subunit of the cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel in retinal rods. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):764–767. doi: 10.1038/362764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. Y., Yau K. W. Direct modulation by Ca(2+)-calmodulin of cyclic nucleotide-activated channel of rat olfactory receptor neurons. Nature. 1994 Apr 7;368(6471):545–548. doi: 10.1038/368545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhallan R. S., Yau K. W., Schrader K. A., Reed R. R. Primary structure and functional expression of a cyclic nucleotide-activated channel from olfactory neurons. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):184–187. doi: 10.1038/347184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eismann E., Müller F., Heinemann S. H., Kaupp U. B. A single negative charge within the pore region of a cGMP-gated channel controls rectification, Ca2+ blockage, and ionic selectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 1;91(3):1109–1113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.3.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein S., Darrow B., Shepherd G. M. Activation of the sensory current in salamander olfactory receptor neurons depends on a G protein-mediated cAMP second messenger system. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):825–835. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frings S., Lynch J. W., Lindemann B. Properties of cyclic nucleotide-gated channels mediating olfactory transduction. Activation, selectivity, and blockage. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Jul;100(1):45–67. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goulding E. H., Ngai J., Kramer R. H., Colicos S., Axel R., Siegelbaum S. A., Chess A. Molecular cloning and single-channel properties of the cyclic nucleotide-gated channel from catfish olfactory neurons. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):45–58. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90107-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heginbotham L., Abramson T., MacKinnon R. A functional connection between the pores of distantly related ion channels as revealed by mutant K+ channels. Science. 1992 Nov 13;258(5085):1152–1155. doi: 10.1126/science.1279807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Golf: an olfactory neuron specific-G protein involved in odorant signal transduction. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):790–795. doi: 10.1126/science.2499043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaupp U. B. The cyclic nucleotide-gated channels of vertebrate photoreceptors and olfactory epithelium. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Apr;14(4):150–157. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90087-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleene S. J. Origin of the chloride current in olfactory transduction. Neuron. 1993 Jul;11(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90276-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurahashi T. The response induced by intracellular cyclic AMP in isolated olfactory receptor cells of the newt. J Physiol. 1990 Nov;430:355–371. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurahashi T., Yau K. W. Co-existence of cationic and chloride components in odorant-induced current of vertebrate olfactory receptor cells. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):71–74. doi: 10.1038/363071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancet D., Ben-Arie N. Olfactory receptors. Curr Biol. 1993 Oct 1;3(10):668–674. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90064-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe G., Gold G. H. Nonlinear amplification by calcium-dependent chloride channels in olfactory receptor cells. Nature. 1993 Nov 18;366(6452):283–286. doi: 10.1038/366283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig J., Margalit T., Eismann E., Lancet D., Kaupp U. B. Primary structure of cAMP-gated channel from bovine olfactory epithelium. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 17;270(1-2):24–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81226-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R. Signaling pathways in odorant detection. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):205–209. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90287-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ressler K. J., Sullivan S. L., Buck L. B. A zonal organization of odorant receptor gene expression in the olfactory epithelium. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):597–609. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90145-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root M. J., MacKinnon R. Identification of an external divalent cation-binding site in the pore of a cGMP-activated channel. Neuron. 1993 Sep;11(3):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90150-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeren-Wiemers N., Gerfin-Moser A. A single protocol to detect transcripts of various types and expression levels in neural tissue and cultured cells: in situ hybridization using digoxigenin-labelled cRNA probes. Histochemistry. 1993 Dec;100(6):431–440. doi: 10.1007/BF00267823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shabb J. B., Corbin J. D. Cyclic nucleotide-binding domains in proteins having diverse functions. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5723–5726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassar R., Ngai J., Axel R. Spatial segregation of odorant receptor expression in the mammalian olfactory epithelium. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90422-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zufall F., Firestein S., Shepherd G. M. Analysis of single cyclic nucleotide-gated channels in olfactory receptor cells. J Neurosci. 1991 Nov;11(11):3573–3580. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-11-03573.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]