Abstract
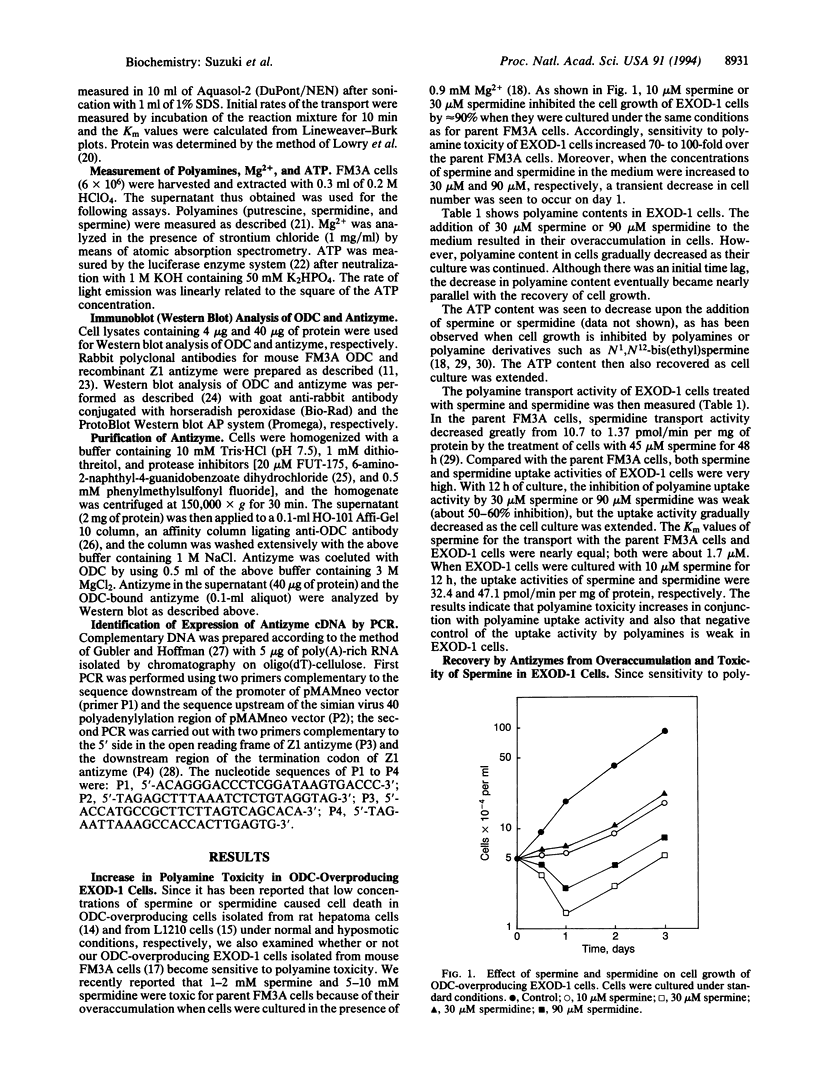
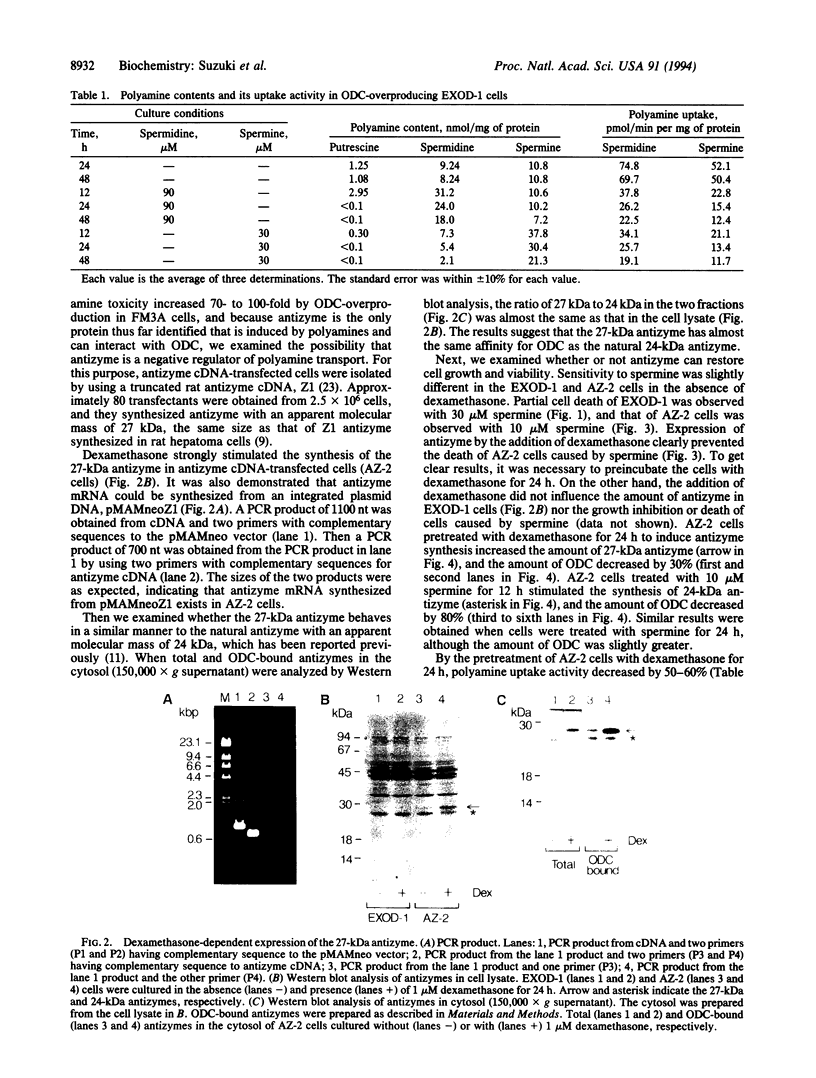
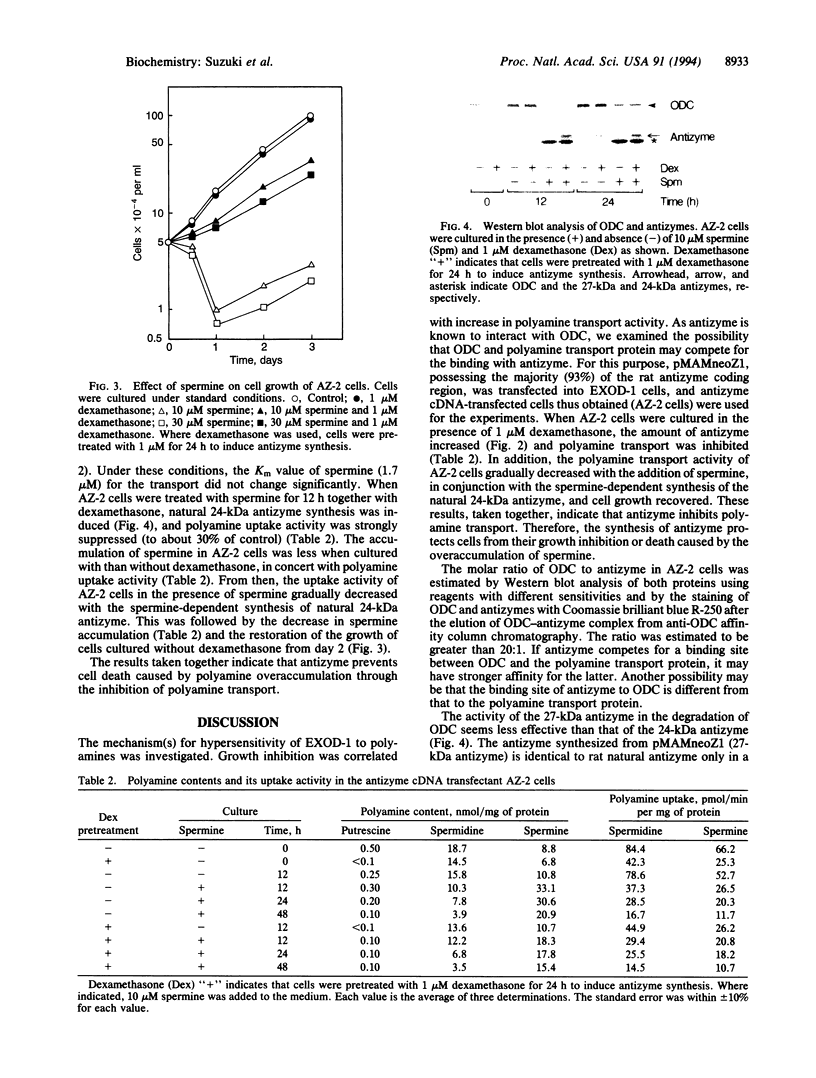
Exposure of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC; L-ornithine carboxy-lyase, EC 4.1.1.17)-overproducing mouse FM3A cells to micromolar levels of spermine or spermidine caused abnormal accumulation and toxicity of polyamines. This was apparently due to the inefficiency of negative feedback control of polyamine transport by polyamines in ODC-overproducing cells. Since antizyme is the only protein thus far recognized that can interact with ODC, depletion of free antizyme was regarded as the reason for the abnormal accumulation of polyamines. Accordingly, ODC-overproducing cells were transfected with pMAMneoZ1 possessing rat antizyme cDNA under the control of a glucocorticoid-inducible promoter. In the transfected cells, the addition of dexamethasone caused an increase in the amount of antizyme with an apparent molecular mass of 27 kDa, a decrease in the amount of ODC, a decrease in the polyamine transport activity, and the recovery of growth inhibition or cell death. The results indicate that antizyme can regulate not only the amount of ODC but also the activity of polyamine transport.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apel I., Yu C. L., Wang T., Dobry C., Van Antwerp M. E., Jove R., Prochownik E. V. Regulation of the junB gene by v-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3356–3364. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers T. L., Pegg A. E. Properties and physiological function of the polyamine transport system. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 1):C545–C553. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.257.3.C545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii S., Hitomi Y. New synthetic inhibitors of C1r, C1 esterase, thrombin, plasmin, kallikrein and trypsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 13;661(2):342–345. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuchi J., Kashiwagi K., Kusama-Eguchi K., Terao K., Shirahata A., Igarashi K. Mechanism of the inhibition of cell growth by N1,N12-bis(ethyl)spermine. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Oct 15;209(2):689–696. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesteland R. F., Weiss R. B., Atkins J. F. Recoding: reprogrammed genetic decoding. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1640–1641. doi: 10.1126/science.1529352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He Y., Kashiwagi K., Fukuchi J., Terao K., Shirahata A., Igarashi K. Correlation between the inhibition of cell growth by accumulated polyamines and the decrease of magnesium and ATP. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Oct 1;217(1):89–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He Y., Suzuki T., Kashiwagi K., Kusama-Eguchi K., Shirahata A., Igarashi K. Correlation between the inhibition of cell growth by bis(ethyl)polyamine analogues and the decrease in the function of mitochondria. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Apr 1;221(1):391–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller J. S., Fong W. F., Canellakis E. S. Induction of a protein inhibitor to ornithine decarboxylase by the end products of its reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Kashiwagi K., Hamasaki H., Miura A., Kakegawa T., Hirose S., Matsuzaki S. Formation of a compensatory polyamine by Escherichia coli polyamine-requiring mutants during growth in the absence of polyamines. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):128–134. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.128-134.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakinuma Y., Hoshino K., Igarashi K. Characterization of the inducible polyamine transporter in bovine lymphocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 15;176(2):409–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameji T., Hayashi S., Hoshino K., Kakinuma Y., Igarashi K. Multiple regulation of ornithine decarboxylase in enzyme-overproducing cells. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 15;289(Pt 2):581–586. doi: 10.1042/bj2890581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamoto R., Kameji T., Iwashita S., Igarashi K., Hayashi S. Spermidine-induced destabilization of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) is mediated by accumulation of antizyme in ODC-overproducing variant cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9393–9399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmich G. A., Randles J., Brand J. S. Assay of picomole amounts of ATP, ADP, and AMP using the luciferase enzyme system. Anal Biochem. 1975 Nov;69(1):187–206. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Coffino P. Degradation of ornithine decarboxylase: exposure of the C-terminal target by a polyamine-inducible inhibitory protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2377–2383. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsufuji S., Fujita K., Kameji T., Kanamoto R., Murakami Y., Hayashi S. A monoclonal antibody to rat liver ornithine decarboxylase. J Biochem. 1984 Nov;96(5):1525–1530. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsufuji S., Miyazaki Y., Kanamoto R., Kameji T., Murakami Y., Baby T. G., Fujita K., Ohno T., Hayashi S. Analyses of ornithine decarboxylase antizyme mRNA with a cDNA cloned from rat liver. J Biochem. 1990 Sep;108(3):365–371. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. L., Diveley R. R., Jr, Bareyal-Leyser A. Feedback repression of polyamine uptake into mammalian cells requires active protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 15;186(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80778-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. L., Diveley R. R., Jr, Bareyal-Leyser A., Mitchell J. L. Abnormal accumulation and toxicity of polyamines in a difluoromethylornithine-resistant HTC cell variant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Aug 12;1136(2):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90248-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki Y., Matsufuji S., Hayashi S. Cloning and characterization of a rat gene encoding ornithine decarboxylase antizyme. Gene. 1992 Apr 15;113(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Matsufuji S., Kameji T., Hayashi S., Igarashi K., Tamura T., Tanaka K., Ichihara A. Ornithine decarboxylase is degraded by the 26S proteasome without ubiquitination. Nature. 1992 Dec 10;360(6404):597–599. doi: 10.1038/360597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Matsufuji S., Miyazaki Y., Hayashi S. Destabilization of ornithine decarboxylase by transfected antizyme gene expression in hepatoma tissue culture cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13138–13141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Tanaka K., Matsufuji S., Miyazaki Y., Hayashi S. Antizyme, a protein induced by polyamines, accelerates the degradation of ornithine decarboxylase in Chinese-hamster ovary-cell extracts. Biochem J. 1992 May 1;283(Pt 3):661–664. doi: 10.1042/bj2830661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., Manchester K. L., Towbin H., Gordon J., Thomas G. The phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in rat tissues following cycloheximide injection, in diabetes, and after denervation of diaphragm. A simple immunological determination of the extent of S6 phosphorylation on protein blots. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12316–12321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegg A. E. Polyamine metabolism and its importance in neoplastic growth and a target for chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 1988 Feb 15;48(4):759–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulin R., Coward J. K., Lakanen J. R., Pegg A. E. Enhancement of the spermidine uptake system and lethal effects of spermidine overaccumulation in ornithine decarboxylase-overproducing L1210 cells under hyposmotic stress. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4690–4698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinehart C. A., Jr, Chen K. Y. Characterization of the polyamine transport system in mouse neuroblastoma cells. Effects of sodium and system A amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4750–4756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHORE P. A., COHN V. H., Jr Comparative effects of monoamine oxidase inhibitors on monoamine oxidase and diamine oxidase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1960 Oct;5:91–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(60)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor C. W., Tabor H. Polyamines. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:749–790. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





