Abstract
Nitric oxide (•NO, nitrogen monoxide) is one of the most unique biological signaling molecules associated with a multitude of physiologic and pathological conditions. In order to fully appreciate its numerous roles, it is essential to understand its basic biochemical properties. Most signaling effector molecules such as steroids or proteins have a significant life-span and function through classical receptor–ligand interactions. •NO, however, is a short-lived free-radical gas that only reacts with two types of molecules under biological conditions; metals and other free radicals. These simple interactions can lead to a myriad of complex intermediates which in turn have their own phenotypic effects. For these reasons, responses to •NO often appear to be random or contradictory when outcomes are compared across various experimental settings. This article will serve as a brief overview of the chemical, biological, and microenvironmental factors that dictate •NO signaling with an emphasis on •NO metabolism. The prominent role that oxygen (dioxygen, O2) plays in •NO metabolism and how it influences the biological effects of •NO will be highlighted. This information and these concepts are intended to help students and investigators think about the interpretation of data from experiments where biological effects of •NO are being elucidated.
Keywords: Nitric oxide, Diffusion, Oxygen, Metabolism, Half-life, Signaling
Graphical abstract
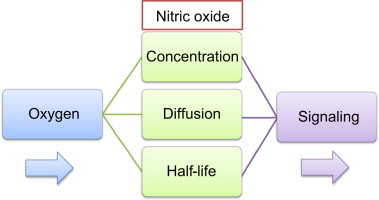
Highlights
-
●
Oxygen is a major determinant of the rates of nitric oxide synthesis and metabolism.
-
●
Under biological conditions nitric oxide only reacts with metals and other free radicals.
-
●
Oxygen determines the half-life, concentration, and diffusional distance of nitric oxide.
-
●
Proteins respond to nitric oxide in a concentration and time-dependent manner.
-
●
Oxygen and the redox environment will greatly influence signaling responses to nitric oxide.
Introduction to nitric oxide
Nitric oxide is a free radical, which is any molecule with an unpaired electron. Before •NO was found to be endogenously synthesized in humans in the 1980s, most free radicals were largely thought to have deleterious biological effects [1]. For example oxygen-, nitrogen-, and carbon-centered radicals are strong oxidants that can indiscriminately damage a host of macromolecules including DNA, lipids, and proteins. The most notable examples include the hydroxyl radical (•OH), superoxide (), nitrogen dioxide (•NO2), and carbonate anion radical () [2]. Nitric oxide, on the other hand, is considered a relatively stable free radical and under biological conditions it only reacts with two types of molecules: metals and other free radicals [3]. In this context, •NO is designated to be stable because it does not spontaneously decay or react with itself (dimerize) [4]. Although •NO rapidly reacts with other free radicals, the reaction of •NO with another •NO molecule to form N2O2 does not occur under biological conditions based largely on entropic grounds [1].
Unlike other biologically relevant free radicals, •NO does not directly undergo one-electron oxidation/reduction reactions to form the nitrosonium cation (NO+) or nitroxyl anion (NO−), or its conjugate acid (HNO), respectively [5,6]. Although these species can be formed via redox reactions between •NO and metals or O2, a significant thermodynamic barrier precludes their direct formation. For these reasons, •NO is not considered a particularly good oxidant or reductant. Nevertheless •NO does rapidly react with numerous cellular targets that contribute to its short biological life-time, which in most circumstances is less than 2 s [7]. When compared to other signaling molecules, this is extremely short. However, in relation to other free radicals, whose life-span is often on the order of milliseconds, this is a relatively long time. Being composed of only one atom of nitrogen and one atom of oxygen, •NO is one of the smallest known signaling molecules. Although it is a free radical with an unpaired electron, it does not possess an electrical charge. These are important properties because they allow •NO to readily cross biological membranes by passive diffusion. In addition, •NO is soluble in both hydrophobic and hydrophilic environments. In fact, it is more soluble in hydrophobic environments by a factor of about 10, which turns out to be an important determinant of its biological actions and reactivity [8].
Biological targets of •NO
Iron
As mentioned above, in a cellular setting, •NO will only react with transition metals and other free radicals. The majority of •NO/metal reactions involve ferrous iron (Fe2+) and to a lesser extent copper (Cu+) [3]. There are several forms of iron in cells and •NO is known to react with all of them, albeit to varying degrees. A large proportion of iron of exists in the form of heme (iron protoporphyrin), where it is used for enzyme catalysis or to transport O2. In erythrocytes and myocytes, the prominent heme-containing proteins are hemoglobin and myoglobin. The main function of these proteins is to transport dioxygen (O2), which binds directly to the ferrous heme. In these proteins, •NO can bind reversibly to the ferrous heme in the absence of O2, or it can react with an O2 bound to the heme [9]. The reaction and binding of •NO to reduced heme leads to the formation of iron-nitrosyls via a process called nitrosylation Eq. (1). In the absence of O2, this is a relatively stable bond. On the other hand, in the presence of O2, its reaction with the •NO-bound iron center converts it to nitrate () Eq. (2). Conversely, •NO can react with oxyHb, which also forms Eq. (3). Reactions (2) and (3) are extremely fast, diffusion limited reactions, and result in the rapid scavenging of •NO. This is one of the main consumptive mechanisms of •NO in the vasculature [4].
| Fe2++•NO→Fe2+−•NO | (1) |
| Fe2+−•NO+O2→Fe3++NO−3 | (2) |
| Fe2+−O2+•NO→Fe3++NO−3 | (3) |
In non-erythroid cells, the reactions of •NO with heme-proteins have important signaling consequences as opposed to merely scavenging bioavailable •NO. One of the most important examples is the reaction of •NO with soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC). This protein converts GTP to cGMP and binding of •NO to its heme center leads to a 100-fold increase in its catalytic activity [10].
Another key population of cellular iron is “chelatable iron” or the chelatable iron pool (CIP). This is iron in transition between cellular uptake and incorporation into iron storage protein (ferritin) or the catalytic site of enzymes. The CIP is methodologically defined as being the population of cellular iron that is accessible to chemical iron chelators [11]. It is mostly cytosolic but also has mitochondrial and nuclear components. The CIP is redox-active and represents a small but chemically significant population of total cellular iron (<3%). The rapid reaction of •NO with the CIP and cellular thiols results in the formation of dinitrosyliron complexes (DNIC, (RS−)2Fe+(NO+)2) Eq. (4) [12]. In fact, 100% of the CIP is quantitatively converted into DNIC upon cellular exposure to •NO [13]. Moreover, DNIC are the most abundant population of •NO-derived cellular adducts, much more than S-nitrosothiols, heme nitrosyls, or nitrotyrosine [14]. The consequences of DNIC formation can range from iron sequestration and signaling to participating in S-nitrosothiol (RSNO) formation [15–20].
| Fe2++3•NO+2RS−+H+→{(RS−)2Fe+(NO+)2}+½(N2O+H2O) | (4) |
Cellular iron is also used for the activity of non-heme iron oxygenases, which are important enzymes that catalyze a wide variety of degretory and biosynthetic reactions. The source of iron for these enzymes is the CIP [21–23]. Nitric oxide can bind reversibly to the catalytic iron and inhibit a variety of these enzymes to varying degrees. As O2 is the normal substrate for these enzymes, the reaction of •NO at the iron site is competitive and it will depend on the relative concentrations of the two gases. As a general rule, any protein that will bind O2 will also bind •NO (and CO) with either greater or lesser affinity. This will depend on the iron coordination and other bound ligands as well as the oxidation state. Lastly, there are iron–sulfur proteins which are used for redox and electron transfer reactions in a diverse set of proteins. The interaction of •NO with iron–sulfur proteins is usually destructive but they may also be involved in the formation of protein-bound DNIC [24,25].
Free radicals
Paired electrons are stable and nearly 100% of all electrons in our bodies are paired. Just as •NO reacts with iron and other transition metals because they have unpaired elections (in their d orbitals), •NO reacts with free radicals because they possess unpaired elections as well. In addition to •NO, there are several free radicals of biological interest. Superoxide () is probably the most notable. Superoxide is the one electron reduction product of O2 and it is formed as a natural byproduct of oxidative metabolism. It is also the substrate for several types of enzymes as well as the product; superoxide dismutase and xanthine oxidase, respectively. The reaction of •NO with is near diffusion limited and the product is peroxynitrite (ONOO−) [26]. Peroxynitrite can go on to react with numerous other molecules including •NO and [27]. In general, ONOO− performs strong oxidative chemistry. Depending on the relative flux rates of •NO and , however, the net effect of ONOO− formation is a decrease in the concentrations of both species. The most significant effect of ONOO− may simply be attributed to scavenging of •NO and , thereby diminishing their signaling capabilities [28]. There are other radical–radical reactions with •NO that have biological consequences (for detailed reviews on oxidative stress see and •NO reactivity see [3,6,9,29,30]).
Nitric oxide production
In mammalian systems the dominant mode of •NO production is via enzymatic synthesis from one of three isoforms of nitric oxide synthase (neuronal nNOS, inducible iNOS, and endothelial eNOS, or NOSI, NOSII, and NOSIII, respectively). The differences between each NOS are based on a variety of factors including their tissue distributions as well as their modes of expression and regulation. nNOS and eNOS are constitutively expressed and generally produce lower amounts of •NO (nM) for short periods of time. iNOS however is “inducible” and it becomes upregulated in response to various stimuli including cytokines and bacterial endotoxins. It is capable of producing greater amounts of •NO for prolonged periods of time. The NOS enzymes are flavoproteins that transfer electrons via NADH, FAD, FMN, and Fe2+. They also require the cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4). Substrates for NOS enzymes are dioxygen (O2) and the amino acid l-arginine (Arg), with the products being •NO and the amino acid l-citrulline Eq. (5) [31,32].
| (5) |
The amount of •NO being synthesized from NOS depends on a variety of factors including substrate and cofactor availability. Posttranslational modifications, such as phosphorylation, as well as tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) availability can both influence the rate of •NO synthesis. For example, BH4 deficiency can result in uncoupling of the enzyme and favor the generation of [33]. Arginine is usually not a limiting substrate except in disease states but other enzymes such as arginase can compete with NOS for its availability. Under conditions where there is an abundance of substrates and cofactors, the most significant determinant of the rate/amount of •NO synthesis is the local O2 concentration. The KM for O2 for each of the NOS isoforms varies widely (eNOS=23 µM, iNOS=135 µM, and nNOS=350 µM) [32]. At O2 concentrations below the KM for O2, the rate of •NO synthesized from each NOS will be proportional to the O2 concentration and it will increase linearly as the O2 concentration raises. For example, eNOS, with the lowest KM, will maximally produce •NO over a range of physiologic O2 concentrations. For nNOS, however, the production of •NO will increase over a wide range of O2 concentrations. Fig. 1A demonstrates how differences in O2 concentrations affect total •NO production from iNOS in cultured macrophages [34]. At 24 h, total •NO synthesis at 1% O2 is about half the amount that is produced at 21% O2. This is what would be predicted as 1% O2 is well below the KM for O2 for iNOS.
Fig. 1.
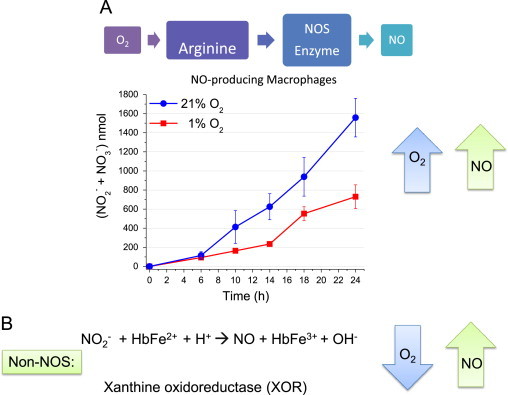
Oxygen determines the rate of •NO production. (A) Enzymatic synthesis of •NO is a function of O2 concentration. RAW 264.7 murine macrophages were cultured at 1% or 21% O2 and stimulated with LPS (t=0). Total •NO synthesis was assessed by measuring in the media at the indicated time points by chemiluminescence. (B) NOS independent mechanisms of •NO synthesis.
In addition to •NO synthesis from NOS enzymes, there are other biological mechanisms to generate •NO. These include nitrite reduction by heme proteins such as hemoglobin Eq. (6) as well as enzymatic reduction of nitrite by non-NOS enzymes such as xanthine oxidoreductase Eq. (7) (Fig. 1B) [35–37].
| NO−2+HbFe2++H+→•NO+HbFe3++OH− | (6) |
| XO+NO−2+e-→•NO | (7) |
Unlike NOS-mediated •NO synthesis which requires O2, the generation of •NO by the above reactions is enhanced at low O2. They are thought to serve as compensatory mechanisms for •NO synthesis under hypoxic conditions. Nitric oxide can also be generated by the acidification of nitrite in tissue compartments or cellular organelles where the pH is low Eq. (8) [38]. This reaction is known to occur in the low pH environment of the stomach from dietary nitrite.
| NO−2+H+→HNO2, 2HNO2→N2O3+H2O, N2O3→•NO+•NO2 | (8) |
As far as total body •NO synthesis, the above 3 mechanisms appear to be minor contributors. However, they do account for the physiologic and therapeutic effects of dietary and pharmacologic nitrite. Although nitrate and nitrite were once thought to be carcinogenic, it is now becoming increasingly clear that the physiologic benefits derived from their ability to generate •NO far outweigh their deleterious properties [39].
Nitric oxide consumption
Although it is well understood how •NO is produced under biological conditions, much less is known about its mode of catabolism. The half-life of •NO is short (0.1–2 s), which is a function of the mechanisms by which •NO is consumed by cells [7]. These consumptive mechanisms are determined by the rate at which •NO reacts with various cellular targets. Although •NO only reacts with transition metals and other free radicals including O2, there are a multitude of potential reactants that will differ based on the cell type and local redox environment. Regardless of what the cellular reactants are, cellular consumption of •NO most likely is not simply the result of stoichiometric reactions with cellular targets. Continuous exposure to •NO demonstrated that cells consume •NO at a constant rate which did not appear to be saturable [7]. This indicates that the reactants for •NO are either continuously produced or rapidly recycled. As mentioned above one well-known reaction of •NO is with oxyhemoglobin to form nitrate () (Eqs. (2) and (9)). This is an extremely rapid reaction and is the major consumptive mechanism of •NO in the vasculature.
| •NO+oxyHb→MetHb+NO−3 | (9) |
In non-erythroid cells, however, there are a multitude of other potential reactants for •NO including radicals like superoxide (), which forms nitrate (), or hypervalent metal oxo species (Fe4+=O), which form nitrite [9]. Nitric oxide will also react with many heme and non-heme iron proteins as well as chelatable iron, ultimately being oxidized to nitrate and nitrite. It is important to point out that the exact mechanism(s) by which •NO is metabolized by cells is not precisely known. This is because •NO has numerous cellular targets and therefore the means by which it is consumed is the sum of several dominant reactions. The contribution of each reaction toward the rate of •NO consumption is a function of the rate of each reaction and the concentration of each reactant. Fig. 2A demonstrates that when a bolus of 200 nM •NO is added to a suspension of cells, it disappears over time via its reactions with various cellular targets. It can be seen that the rate of •NO disappearance in the presence of cells is much more rapid than its disappearance in the absence of cells, which is known to occur via a direct reaction with O2 in solution [7,34].
Fig. 2.
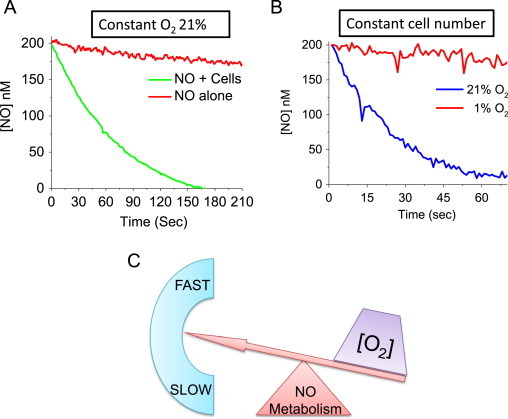
Oxygen determines the rate of •NO catabolism. RAW 264.7 cells were trypsinized and suspended into a sealed, water-jacketed, temperature-controlled (37 °C) reaction chamber with constant stirring. The reaction chamber was equipped with both •NO and O2 electrodes connected to an Apollo 4000 free radical analyzer (World Precision Instruments, Sarasota, FL, USA). Headspace in the vessel was negligible compared to the vessel volume to ensure that the rate of •NO volatilization was insignificant compared with its reaction in solution. Reactions were initiated by injection of a saturated •NO solution with a gas-tight syringe, and •NO metabolism was measured using an •NO-selective electrode (amiNO-700, Innovative Instruments, Tampa, FL, USA). (A) At time “0”, the cells were treated with a bolus of •NO (200 nM) and the disappearance of •NO was measured over time. Or •NO added to the reaction chamber in the absence of cell. (B) Disappearance of •NO was measured in cells treated with 200 nM •NO (at 21% O2) or the cells were allowed to consume O2 in the reaction chamber until a level of 1% O2 was achieved before the addition of •NO. (C) The direct relationship between the O2 concentration and the rate of •NO metabolism.
Although the types of specific cellular reactants for •NO may differ between cell types, research has shown that the predominant mechanisms of •NO metabolism require O2 [7]. This is illustrated in Fig. 2B, which demonstrates the rates of •NO disappearance in the presence of cells at two different O2 concentrations (21% and 1%). For the same number of cells, •NO is metabolized much more rapidly at 21% O2 than at 1% O2. Therefore, there is a direct relationship between the O2 concentration and the rate of cellular •NO metabolism (Fig. 2C). The discovery that •NO is metabolized by cells in an O2-dependent manner may not at first seem surprising as it is well-known that •NO directly reacts with O2 (autoxidation, Eq. (10)).
| 4•NO+O2+2H2O→4H++4NO−2 | (10) |
Rate law: −d[•NO]/dt =4kaq[•NO]2[O2]
There are two critical pieces of evidence that rule out autoxidation as a significant means of •NO metabolism. First, the autoxidation reaction is second-order in •NO concentration whereas the metabolism of •NO by cells follows first-order kinetics Eq. (11) [7,8].
| −d[•NO]/dt =kobs[O2][•NO][Cell] | (11) |
| kobs=5.38=±0.3×10−4 M−1 s−1(cell/mL)−1 |
Second, if •NO were reacting directly with O2, its rate of disappearance would be exceedingly slow at physiologic •NO concentrations. Because the rate of •NO autoxidation is second-order with respect to •NO, it means that at high •NO concentrations, the autoxidation reaction is much faster than at low concentrations. Fig. 3 illustrates how the half-life of •NO via autoxidation changes over a range of physiologic •NO and O2 concentrations. What should be emphasized is that if the dominant reaction of •NO within cells was directly with O2 (autoxidation), the half-life of •NO would be on the order of hours to days at physiologic •NO and O2 concentration. Even when the O2 concentration is high (21%), •NO could last for hours. This is not to say that •NO autoxidation does not occur under biological conditions. Experiments have shown that this reaction preferentially occurs in hydrophobic environments such as cell membranes and may be an important source of reactive nitrogen intermediates (N2O2, •NO2) [8,40]. We know, however, that the biological half-life of •NO is short (<2 s), therefore, autoxidation cannot quantitatively account for the loss of a significant proportion of total •NO.
Fig. 3.

Concentrations of •NO and O2 determine the rate autoxidation. Calculated theoretical half-lives of •NO via autoxidation at various O2 concentrations based on initial starting •NO concentrations of 50, 100, 200, 500, and 1000 nM. The half-life of a reaction is the amount of time it takes for the concentration of a reactant (•NO) to decrease to one-half of its initial value. These values represent the first half-life of •NO. Since the autoxidation reaction is a second-order reaction (with respect to the •NO concentrations), the half-life will change over time as the concentration of •NO changes.
Oxygen determines the steady-state concentration of •NO
Oxygen determines the rate of •NO synthesis by acting as a substrate for NOS and it also determines the rate of •NO metabolism. Therefore, the local O2 concentration will play a significant role in determining the steady-state concentration of •NO (Fig. 4A). If we think of the steady-state concentration of •NO as water in a bathtub, then the water level will be determined by the rate of water flow into the tub (•NO synthesis) relative to its rate of flow out of the drain (•NO metabolism). Since O2 differentially controls the rates of both •NO synthesis and metabolism, the steady-state concentration of •NO will be a function of the relative differences in their respective rates. At both the macroscopic and microscopic level, O2 gradients exist within the human body. Differences in O2 concentrations can vary widely based on the organ, tissue, cell type, and even the intercellular location. What determines the microenvironmental O2 concentration depends on the rate of O2 delivery from the vasculature as well as the rate of mitochondrial O2 consumption. Fig. 4B illustrates differences in the half-life of •NO calculated from average tissue O2 concentrations. This model, however, does not take into account the effects of O2 on •NO synthesis only the effect of O2 on the rate of •NO disappearance [7]. It does, however, emphasize how over a range of physiologic O2 concentrations the biological half-life of •NO can vary significantly.
Fig. 4.
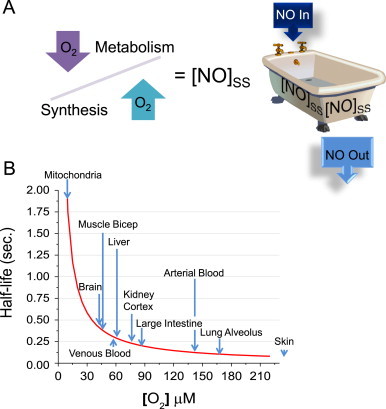
Oxygen determines the concentration of •NO and its half-life. (A) The steady-state concentration of •NO is a function of its rate of synthesis relative to its rate of degradation. (B) Different tissues have different average O2 concentrations. The half-life of •NO changes with respect to the O2 concentration.
Adapted from Ref. [7].
Why is the half-life of •NO important? The broad answer is that it ultimately determines the magnitude of •NO signaling. To properly understand this, it is important to appreciate how •NO moves within the cellular environment, i.e., by diffusion. Nitric oxide is small and uncharged and is soluble in both hydrophobic and hydrophilic environments. For these reasons, it is freely diffusible and cell membranes pose no barrier to its movement. With a relatively large diffusion coefficient (≈3800 µm2/s), •NO can travel considerable distances in a short period of time depending on the local environment (≈1 cell length/25 ms) [41]. Once •NO is synthesized, it moves away from its point of origin by random diffusion (Fig. 5A). Movement of •NO in any direction is equally likely at any point in time, however, net movement of molecules in one direction will occur if there is a spatial concentration gradient. The movement will always occur from a region of higher •NO concentration, such as in an •NO-producing cell, to a region of lower •NO concentration, an adjacent cell (Fig. 5B) [42].
Fig. 5.
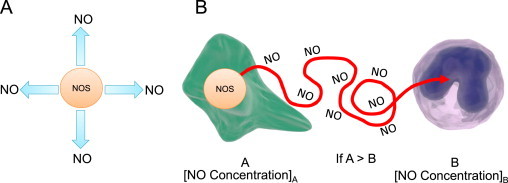
Nitric oxide moves by random diffusion. (A) Once •NO is synthesized by NOS, it diffuses away in all directions. (B) Net movement of •NO occurs from an area of high concentration (a cell “A” where •NO is being made) to a region of lower concentration (“B” surrounding cells). The movement of •NO is random but down a concentration gradient.
The distance •NO will diffuse is proportional to its concentration and half-life. This brings up the importance of O2. The O2 concentration is an important determinant of the •NO concentration, which is a factor in determining how far •NO diffuses. At high O2 concentrations, the half-life of •NO is short and so is the distance it can diffuse. The opposite is true for low O2 concentrations (Fig. 6A). Just as the half-life of •NO can be calculated as a function of O2 concentration, so can its diffusional distance (Fig. 6B). It can be seen that differences in physiologic O2 concentrations dramatically affect the diffusional distance of •NO [7]. This has important implications for predicting the magnitude of •NO signaling under various O2 concentrations. At a high pO2, for example, the half-life of •NO is short and so is the distance it will diffuse. At low pO2, •NO will travel significantly longer distances and potentially exert its influence many cell lengths away (Fig. 6B). What this means in terms of cell signaling is that the size of the diffusional sphere surrounding a •NO-producing cell will change in response to changes in the O2 concentration. This will ultimately determine the amount and types of cellular targets by changing the number of neighboring cells being affected in a spatially heterogeneous tissue environment.
Fig. 6.
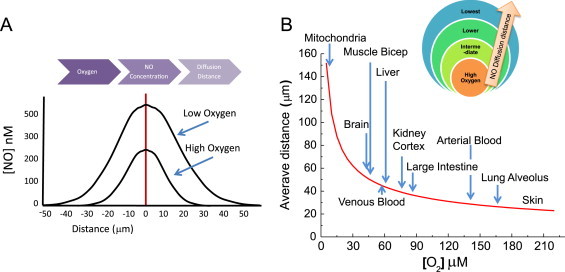
Oxygen determines the concentration of •NO and its diffusional distance. (A) At a constant rate of •NO synthesis, the lower the O2 concentration, the slower •NO is metabolized and the greater its steady-state concentration is. At high O2 concentrations, the steady-state •NO concentration is lower. The •NO concentration will determine its half-life as well as its diffusional distance. (B) The O2 concentration determines the half-life of •NO, which influences how far it will diffuse.
Although this discussion has focused on the impact of O2 on •NO bioavailability it would not be complete without mentioning how •NO can affect local O2 concentrations. One of the earlier discoveries about the biological functions of •NO was the observation that it could inhibit cellular respiration [43]. It was determined that •NO could regulate mitochondrial function and metabolism through its ability to interact at several sites in the respiratory chain. This is another example that emphasizes the importance of •NO/metal interactions. At Complex IV (cytochrome c oxidase) subnanomolar amounts of •NO competitively inhibit respiration. Here •NO binds to the ferrous heme-iron or oxidized copper, but not both simultaneously at the heme iron:copper binuclear center (a(3)/Cu(B)) [44]. At Complex 1 greater amounts of •NO were shown to be inhibitory but this was attributed to •NO-mediated oxidation or S-nitrosation of specific thiols [45]. The majority of total body O2 utilization is via its four-electron reduction to water at mitochondrial complex IV. Inhibition of mitochondrial respiration by •NO, therefore, prevents O2 consumption which extends the half-life of O2. This mechanism is thought to participate in O2 homeostasis by increasing local O2 delivery from the vascular and extending its delivery into tissues. Therefore, there is a reciprocal relationship between •NO and O2 whereby each molecule plays a role in regulating the concentration of the other [46].
Oxygen and •NO signaling
As we have seen, the O2 concentration is a key determinant of both the half-life of •NO as well as its diffusional distance. These parameters are important because they influence signaling responses to •NO. Most cellular targets for •NO respond in a concentration and time dependent manner [47–49]. Numerous examples have demonstrated that the activation of specific proteins or the induction of signal transduction cascades respond to distinct concentration thresholds of •NO. For example, soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) is one of the most important biological targets for •NO. It is activated by very low steady-state amounts of •NO ([0.5–5 nM]SS). ERK is another protein that becomes phosphorylated in the presence of •NO but it requires slightly higher amounts (>[100 nM]SS). Another class of proteins, non-heme iron oxygenases, are also targets for •NO. These include the HIF prolyl hydroxylases and the lysine histone demethylase (KDM) enzymes [28,50]. These are inhibited by intermediate concentrations of •NO ([100– 400 nM]SS). Proteins like p53 are regulated by •NO at the upper limits of physiologic concentrations. Phosphorylation of this protein occurs in the presence of high concentrations of •NO (>[500 nM]SS) (Fig. 7).
Fig. 7.
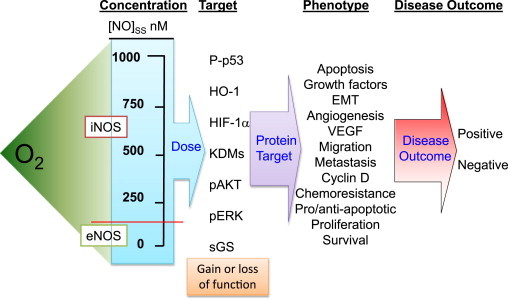
Oxygen is an upstream driving force of cell phenotype by regulating the •NO concentration. Many proteins differ in the threshold amounts of •NO necessary for regulation. Since O2 determines the concentration (dose) of •NO, it will indirectly influence proteins regulated by •NO in a concentration-dependent manner. •NO-mediated changes in the protein profile will result in altered cellular phenotypes. This will ultimately have a positive or negative effect on disease outcome.
A long-standing challenge for researchers in the •NO field has been to provide plausible mechanisms to explain opposite biological responses to •NO under seemingly similar circumstances. There are many physiologic and pathological examples where •NO has been shown to have a positive signaling effect and an equal number of situations where •NO has been shown to have a negative effect in the same system. For example, •NO has numerous purported roles in cancer etiology [49,51,52]. In some cases, •NO is beneficial in that it decreases tumor size, is cytotoxic, induces apoptosis, and is an antioxidant. There are other reports, however, where •NO is a negative prognostic indicator by virtue of its ability to increase angiogenesis, stimulate migration and invasion, and induce DNA damage. The question that is often raised, “is •NO good or bad?”. The answer is “both”. To appreciate how •NO can have such dissimilar and opposing responses, one has to understand the concentration and temporal-dependent effects of •NO signaling. Differences in tissue O2 concentrations will partially determine the steady-state concentration of •NO. The concentration of •NO will dictate what cellular targets it interacts with. The types and distributions of cellular targets will determine cell phenotype, ultimately leading to positive or negative effects on disease outcome (Fig. 7).
High O2 concentrations will maximize •NO production from NOS, however, it will also increase the rate of •NO metabolism. Conversely, low O2 concentrations will reduce enzymatic •NO synthesis while also decreasing the rate of •NO metabolism. Is there an optimal O2 concentration where a balance between •NO production and consumption is achieved to maximize steady-state •NO concentrations? One study showed that the amount of cGMP produced by the activation of sGC in •NO-producing cells was biphasic over a range of O2 concentrations [34]. The maximal amount of cGMP was measured at an O2 concentration of ≈8%. The interpretation was that this O2 concentration resulted in the highest steady-state •NO concentration and therefore maximal sGC activation.
Just as the concentration of •NO is a key determinant of cell phenotype, so is the duration of •NO exposure. Not only do the three NOS isoforms produce different amounts of •NO, they can also differ in the duration of synthesis. This becomes important because some proteins are activated (or inhibited) immediately by •NO whereas others require continuous and sometimes prolonged •NO exposure [47]. Also, the effect of •NO on certain proteins is reversible such that they become inactivated (or reactivated) when the •NO source is removed. Yet in other cases, prolonged activation is achieved long after •NO synthesis has ceased. This indicates that some proteins are real-time •NO sensors whose regulation parallels the duration of •NO synthesis. In cases where the effects of •NO result in prolonged protein regulation, even short bursts of •NO exposure could have long-lasting phenotypic effects.
Spatial constraints are also contributing factors that influence phenotypic responses to •NO. As described above, the concentration of •NO will diminish at further distances from its point of synthesis (Fig. 8). Since most proteins respond to •NO in a concentration-dependent manner, distance will ultimately dictate the population of targets being regulated by •NO. Proteins, with different concentration threshold requirements for activation by •NO, will be differentially regulated depending on their proximity to the •NO source. For example, a protein that requires small amounts of •NO like sGC may be fully activated at locations both near and far from the point of •NO synthesis (Fig. 8, green protein). Whereas a different protein requiring intermediate amounts of •NO (HIF-1α) will be fully activated when it is close to the point of •NO synthesis. At further distances where the steady-state •NO concentration has diminished, this protein may not be activated at all (Fig. 8, orange protein). Proteins with the highest •NO-concentration requirements such as p53 may not respond to •NO at all regardless of whether they are proximal or distal to the •NO source (Fig. 8, red protein). These examples demonstrate how spatial differences in the location of target proteins can dictate phenotypic outcomes based solely on the differences in their concentration thresholds for activation by •NO.
Fig. 8.
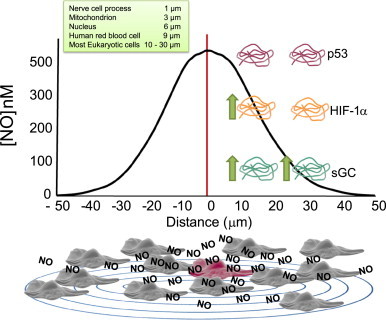
The location of target proteins relative to the •NO source will influence their degree of regulation. The concentration of •NO diminishes at further distances from an •NO-producing cell (red cell). Proteins requiring small amounts of •NO will be regulated even at distances far away from the •NO source (green protein). Proteins with higher concentration requirements for •NO must be closer to the •NO source (orange protein). Proteins requiring high steady-state amounts of •NO may not be regulated at any location within the radius of •NO diffusion if the threshold •NO concentration requirement is not achieved (red protein). Green arrows indicate the regulation, activation, or deactivation by •NO (relative sensitivity to •NO green>orange>red protein).
Fig. 9 illustrates the complexities surrounding the interpretation of phenotypic data from cultured cells treated with •NO when there are differences in both •NO concentration and exposure time. In this simple experiment, cancer cells in culture were exposed to different concentrations of •NO for 48 h and cell viability was measured at 3 separate time points (24, 30, and 48 h). If the experiment was terminated at 24 h, the interpretation would be that •NO stimulates tumor cell growth (•NO is bad). If end-point measurements were not made until 30 h, the interpretation might be that •NO has no effect on cell viability. However, if the cells were exposed to •NO for a full 48 h before measuring cell viability, the logical conclusion would be that •NO is cytotoxic to tumor cells (•NO is good). Furthermore, if we only looked at low concentrations of •NO (5 µM DETA/NO), the outcome would be that •NO has no effect on tumor cell viability from 0 to 48 h. However, if we only looked at higher concentrations of •NO, the interpretation would be completely different at every time point.
Fig. 9.
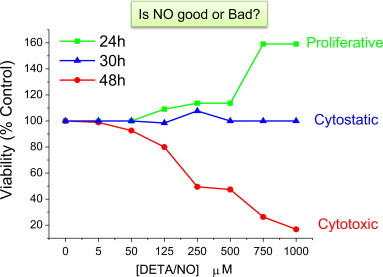
Both the concentration and the duration of •NO exposure determine the phenotypic outcome. MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells were exposed to a range of physiologic •NO concentrations using the •NO-donor DETA/NO. DETA/NO has a long half-life (t½=22 h), which enables prolonged and continuous •NO exposure. Real-time measurements of cell proliferation was conducted using the xCELLigence® DP system (ACEA Biosciences, Inc.) MDA-MB-231 cells were seeded in E-plates containing 10% serum and allowed to adhere for 12 h before the addition of •NO (5–1000 µM DETA/NO). Cell proliferation was measured continuously for 48 h following •NO treatment.
Conclusion
The concepts that have been presented herein are undoubtedly an oversimplification of numerous interrelated complex biochemical and signaling mechanisms of •NO. The aim of this short review, however, was to provide a framework for experimental design and data interpretation by taking into consideration these numerous confounding parameters. Although •NO may appear to have contradictory effects under seemingly similar biological situations, a careful look at the environmental conditions will often reveal logical explanations for these differences. By understanding the importance of O2, target location, •NO concentration, and exposure time on •NO signaling responses, it becomes much easier to comprehend the sheer magnitude of potential outcomes (Fig. 10). Phenotypic responses attributed to •NO suddenly do not appear to be random at all but rather predictable outcomes that are simply a reflection of the local redox environment. Nitric oxide, being a free radical, is unique among signaling molecules. It does not act indiscriminately and it follows the same rules of chemistry and physics as all molecules. With a better appreciation of its complex chemical biology, meaningful information will continue to be discovered about this fascinating and important molecule.
Fig. 10.
Oxygen is a dominant and vital regulator of •NO chemical biology.
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) under award number R01GM085232. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. The authors also acknowledge ongoing support from the UIC Cancer Center.
Footnotes
This article belongs to a special issue on Nitric Oxide and Cancer, edited by Jordi Muntané and Benjamin Bonavida.
References
- 1.Ignarro L. Nitric Oxide Biology and Pathobiology. Academic Press; Zürich, Switzerland: 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Pisoschi A.M., Pop A. The role of antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: a review. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 2015;97:55–74. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.04.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Thomas D.D., Ridnour L.A., Isenberg J.S., Flores-Santana W., Switzer C.H., Donzelli S., Hussain P. The chemical biology of nitric oxide: implications in cellular signaling. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2008;45(1):18–31. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.03.020. 18439435 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lancaster, J., Jr. Reactivity and diffusivity of nitrogen oxides in mammalian biology. In: Forman H., Fukuto J., Torres M., editors. Signal Transduction by Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species: Pathways and Chemical Principles. Springer; Netherlands: 2003. pp. 53–79. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jackson M.I., Han T.H., Serbulea L., Dutton A., Ford E., Miranda K.M., Houk K.N. Kinetic feasibility of nitroxyl reduction by physiological reductants and biological implications. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2009;47(8):1130–1139. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.06.034. 19577638 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Flores-Santana W., Switzer C., Ridnour L.A., Basudhar D., Mancardi D., Donzelli S., Thomas D.D. Comparing the chemical biology of NO and HNO. Archives of Pharmacal Research. 2009;32(8):1139–1153. doi: 10.1007/s12272-009-1805-x. 19727606 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Thomas D.D., Liu X., Kantrow S.P., Lancaster J.R., Jr. The biological lifetime of nitric oxide: implications for the perivascular dynamics of NO and O2. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2001;98(1):355–360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.011379598. 11134509 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Liu X., Miller M.J., Joshi M.S., Thomas D.D., Lancaster J.R., Jr. Accelerated reaction of nitric oxide with O2 within the hydrophobic interior of biological membranes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1998;95(5):2175–2179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.5.2175. 9482858 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Thomas D.D., Miranda K.M., Colton C.A., Citrin D., Espey M.G., Wink D.A. Heme proteins and nitric oxide (NO): the neglected, eloquent chemistry in NO redox signaling and regulation. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 2003;5(3):307–317. doi: 10.1089/152308603322110887. 12880485 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Derbyshire E.R., Marletta M.A. Structure and regulation of soluble guanylate cyclase. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 2012;81:533–559. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-050410-100030. 22404633 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Petrat F., de Groot H., Sustmann R., Rauen U. The chelatable iron pool in living cells: a methodically defined quantity. Biological Chemistry. 2002;383(3–4):489–502. doi: 10.1515/BC.2002.051. 12033438 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hickok J.R., Vasudevan D., Thatcher G.R., Thomas D.D. Is s-nitrosocysteine a true surrogate for nitric oxide? Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 2012;17(7):962–968. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4543. 22304688 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Toledo J.C., Jr., Bosworth C.A., Hennon S.W., Mahtani H.A., Bergonia H.A., Lancaster J.R., Jr. Nitric oxide-induced conversion of cellular chelatable iron into macromolecule-bound paramagnetic dinitrosyliron complexes. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2008;283(43):28926–28933. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707862200. 18480062 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hickok J.R., Sahni S., Shen H., Arvind A., Antoniou C., Fung L.W., Thomas D.D. Dinitrosyliron complexes are the most abundant nitric oxide-derived cellular adduct: biological parameters of assembly and disappearance. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2011;51(8):1558–1566. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.06.030. 21787861 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Vanin A.F., Stukan R.A., Manukhina E.B. Physical properties of dinitrosyl iron complexes with thiol-containing ligands in relation with their vasodilator activity. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1996;1295(1):5–12. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(95)00247-2. 8679673 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Vanin A.F., Papina A.A., Serezhenkov V.A., Koppenol W.H. The mechanisms of S-nitrosothiol decomposition catalyzed by iron. Nitric Oxide. 2004;10(2):60–73. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2004.02.005. 15135359 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Vanin A.F. Dinitrosyl iron complexes with thiolate ligands: physico-chemistry, biochemistry and physiology. Nitric Oxide. 2009;21(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2009.03.005. 19366636 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bosworth C.A., Toledo J.C., Jr., Zmijewski J.W., Li Q., Lancaster J.R., Jr. Dinitrosyliron complexes and the mechanism(s) of cellular protein nitrosothiol formation from nitric oxide. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009;106(12):4671–4676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710416106. 19261856 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hickok J.R., Sahni S., Mikhed Y., Bonini M.G., Thomas D.D. Nitric oxide suppresses tumor cell migration through N-Myc downstream-regulated gene-1 (NDRG1) expression: role of chelatable iron. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2011;286(48):41413–41424. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.287052. 21976667 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Boese M., Mordvintcev P.I., Vanin A.F., Busse R., Mülsch A. S-nitrosation of serum albumin by dinitrosyl–iron complex. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1995;270(49):29244–29249. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.49.29244. 7493954 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cyr A.R., Domann F.E. The redox basis of epigenetic modifications: from mechanisms to functional consequences. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 2011;15(2):551–589. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3492. 20919933 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jaakkola P., Mole D.R., Tian Y.M., Wilson M.I., Gielbert J., Gaskell S.J., von Kriegsheim A. Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel–Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science. 2001;292(5516):468–472. doi: 10.1126/science.1059796. 11292861 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Knowles H.J., Mole D.R., Ratcliffe P.J., Harris A.L. Normoxic stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by modulation of the labile iron pool in differentiating U937 macrophages: effect of natural resistance-associated macrophage protein 1. Cancer Research. 2006;66(5):2600–2607. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2351. 16510578 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Crack J.C., Green J., Thomson A.J., Le Brun N.E. Iron–sulfur clusters as biological sensors: the chemistry of reactions with molecular oxygen and nitric oxide. Accounts of Chemical Research. 2014;47(10):3196–3205. doi: 10.1021/ar5002507. 25262769 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Landry A.P., Duan X., Huang H., Ding H. Iron–sulfur proteins are the major source of protein-bound dinitrosyl iron complexes formed in Escherichia coli cells under nitric oxide stress. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2011;50(11):1582–1590. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.03.005. 21420489 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Carballal S., Bartesaghi S., Radi R. Kinetic and mechanistic considerations to assess the biological fate of peroxynitrite. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2014;1840(2):768–780. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.07.005. 23872352 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jourd’heuil D., Jourd’heuil F.L., Kutchukian P.S., Musah R.A., Wink D.A., Grisham M.B. Reaction of superoxide and nitric oxide with peroxynitrite. Implications for peroxynitrite-mediated oxidation reactions in vivo. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2001;276(31):28799–28805. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M102341200. 11373284 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Thomas D.D., Ridnour L.A., Espey M.G., Donzelli S., Ambs S., Hussain S.P., Harris C.C. Superoxide fluxes limit nitric oxide-induced signaling. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2006;281(36):25984–25993. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602242200. 16829532 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kalyanaraman B. Teaching the basics of redox biology to medical and graduate students: oxidants, antioxidants and disease mechanisms. Redox Biology. 2013;1:244–257. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2013.01.014. 24024158 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mancardi D., Ridnour L.A., Thomas D.D., Katori T., Tocchetti C.G., Espey M.G., Miranda K.M. The chemical dynamics of NO and reactive nitrogen oxides: a practical guide. Current Molecular Medicine. 2004;4(7):723–740. doi: 10.2174/1566524043359854. 15579020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wei C.C., Wang Z.Q., Durra D., Hemann C., Hille R., Garcin E.D., Getzoff E.D. The three nitric-oxide synthases differ in their kinetics of tetrahydrobiopterin radical formation, heme-dioxy reduction, and arginine hydroxylation. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2005;280(10):8929–8935. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409737200. 15632185 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Stuehr D.J., Santolini J., Wang Z.Q., Wei C.C., Adak S. Update on mechanism and catalytic regulation in the NO synthases. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2004;279(35):36167–36170. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R400017200. 15133020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tejero J., Stuehr D. Tetrahydrobiopterin in nitric oxide synthase. I. U.B.M.B. Life. 2013;65(4):358–365. doi: 10.1002/iub.1136. 23441062 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hickok J.R., Vasudevan D., Jablonski K., Thomas D.D. Oxygen dependence of nitric oxide-mediated signaling. Redox Biology. 2013;1:203–209. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2012.11.002. 24024154 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Shiva S. Nitrite: a physiological store of nitric oxide and modulator of mitochondrial function. Redox Biology. 2013;1(1):40–44. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2012.11.005. 23710434 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Van Faassen E.E., Bahrami S., Feelisch M., Hogg N., Kelm M., Kim-Shapiro D.B., Kozlov A.V. Nitrite as regulator of hypoxic signaling in mammalian physiology. Medicinal Research Reviews. 2009;29(5):683–741. doi: 10.1002/med.20151. 19219851 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Cantu-Medellin N., Kelley E.E. Xanthine oxidoreductase-catalyzed reduction of nitrite to nitric oxide: insights regarding where, when and how. Nitric Oxide. 2013;34:19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2013.02.081. 23454592 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kim-Shapiro D.B., Gladwin M.T. Mechanisms of nitrite bioactivation. Nitric Oxide. 2014;38:58–68. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2013.11.002. 24315961 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lundberg J.O., Weitzberg E., Gladwin M.T. The nitrate–nitrite–nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 2008;7(2):156–167. doi: 10.1038/nrd2466. 18167491 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Möller M., Botti H., Batthyany C., Rubbo H., Radi R., Denicola A. Direct measurement of nitric oxide and oxygen partitioning into liposomes and low density lipoprotein. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2005;280(10):8850–8854. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413699200. 15632138 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lancaster J.R., Jr. A tutorial on the diffusibility and reactivity of free nitric oxide. Nitric Oxide. 1997;1(1):18–30. doi: 10.1006/niox.1996.0112. 9701041 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lancaster J.R., Jr. Simulation of the diffusion and reaction of endogenously produced nitric oxide. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1994;91(17):8137–8141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8137. 8058769 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Brown G.C., Cooper C.E. Nanomolar concentrations of nitric oxide reversibly inhibit synaptosomal respiration by competing with oxygen at cytochrome oxidase. FEBS Letters. 1994;356(2–3):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01290-3. 7805858 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mason M.G., Nicholls P., Wilson M.T., Cooper C.E. Nitric oxide inhibition of respiration involves both competitive (heme) and noncompetitive (copper) binding to cytochrome c oxidase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2006;103(3):708–713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506562103. 16407136 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Clementi E., Brown G.C., Feelisch M., Moncada S. Persistent inhibition of cell respiration by nitric oxide: crucial role of S-nitrosylation of mitochondrial complex I and protective action of glutathione. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1998;95(13):7631–7636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.13.7631. 9636201 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Shiva S., Oh J.Y., Landar A.L., Ulasova E., Venkatraman A., Bailey S.M., Darley-Usmar V.M. Nitroxia: the pathological consequence of dysfunction in the nitric oxide–cytochrome c oxidase signaling pathway. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2005;38(3):297–306. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.10.037. 15629859 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Thomas D.D., Espey M.G., Ridnour L.A., Hofseth L.J., Mancardi D., Harris C.C., Wink D.A. Hypoxic inducible factor 1alpha, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, and p53 are regulated by distinct threshold concentrations of nitric oxide. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101(24):8894–8899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400453101. 15178764 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ridnour L.A., Thomas D.D., Switzer C., Flores-Santana W., Isenberg J.S., Ambs S., Roberts D.D. Molecular mechanisms for discrete nitric oxide levels in cancer. Nitric Oxide. 2008;19(2):73–76. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2008.04.006. 18472020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ridnour L.A., Thomas D.D., Donzelli S., Espey M.G., Roberts D.D., Wink D.A., Isenberg J.S. The biphasic nature of nitric oxide responses in tumor biology. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 2006;8(7–8):1329–1337. doi: 10.1089/ars.2006.8.1329. 16910780 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hickok J.R., Vasudevan D., Antholine W.E., Thomas D.D. Nitric oxide modifies global histone methylation by inhibiting Jumonji C domain-containing demethylases. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2013;288(22):16004–16015. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.432294. 23546878 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hickok J.R., Thomas D.D. Nitric oxide and cancer therapy: the emperor has NO clothes. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2010;16(4):381–391. doi: 10.2174/138161210790232149. 20236067 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Vasudevan D., Thomas D.D. Insights into the diverse effects of nitric oxide on tumor biology. Vitamins & Hormones. 2014;96:265–298. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800254-4.00011-8. 25189391 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


