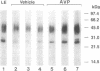
Abstract
AQP-CD is a vasopressin-regulated water channel expressed exclusively in the renal collecting duct. We have previously shown that AQP-CD is present in the apical plasma membrane and subapical vesicles of collecting duct cells, consistent with membrane-shuttling mechanisms that have been proposed to explain the short-term action of [Arg8] vasopressin (AVP) to regulate apical water permeability. We propose here that AVP may also have long-term actions on the collecting duct to regulate the expression of the AQP-CD water channel. We used immunoblotting, immunohistochemistry, and in vitro perfusion of renal tubules to investigate water channel regulation in collecting ducts of diabetes insipidus (Brattleboro) rats treated with a 5-day infusion of AVP or vehicle. Immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry demonstrated that collecting ducts of vehicle-infused Brattleboro rats had markedly reduced expression of AQP-CD relative to normal rats. In response to AVP infusion there was a nearly 3-fold increase in AQP-CD expression as detected by immunoblotting. Immunocytochemistry demonstrated that the increased expression was predominantly in the apical plasma membrane and subapical vesicles of collecting duct cells. Inner medullary collecting ducts of AVP-infused Brattleboro rats displayed a 3-fold increase in osmotic water permeability relative to vehicle-infused controls, in parallel with the change in AQP-CD expression. Based on these findings, we conclude that (i) long-term infusion of AVP, acting either directly or indirectly, regulates expression of the AQP-CD water channel and (ii) AQP-CD is the predominant AVP-regulated water channel.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Zahid G., Schafer J. A., Troutman S. L., Andreoli T. E. Effect of antidiuretic hormone on water and solute permeation, and the activation energies for these processes, in mammalian cortical collecting tubules: evidence for parallel ADH-sensitive pathways for water and solute diffusion in luminal plasma membranes. J Membr Biol. 1977 Feb 24;31(1-2):103–129. doi: 10.1007/BF01869401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M., Grantham J., Abramow M., Orloff J. Preparation and study of fragments of single rabbit nephrons. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1293–1298. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE WARDENER H. E., HERXHEIMER A. The effect of a high water intake on the kidney's ability to concentrate the urine in man. J Physiol. 1957 Nov 14;139(1):42–52. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. Q., Bennett V. Brain ankyrin. Purification of a 72,000 Mr spectrin-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1874–1881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deen P. M., Verdijk M. A., Knoers N. V., Wieringa B., Monnens L. A., van Os C. H., van Oost B. A. Requirement of human renal water channel aquaporin-2 for vasopressin-dependent concentration of urine. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8140421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denker B. M., Smith B. L., Kuhajda F. P., Agre P. Identification, purification, and partial characterization of a novel Mr 28,000 integral membrane protein from erythrocytes and renal tubules. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15634–15642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EPSTEIN F. H., KLEEMAN C. R., HENDRIKX A. The influence of bodily hydration on the renal concentrating process. J Clin Invest. 1957 May;36(5):629–634. doi: 10.1172/JCI103462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamion B., Spring K. R., Abramow M. Is there a paracellular water pathway in inner medullary collecting ducts (IMCD) from dehydrated rats? Regul Pept. 1993 Apr 29;45(1-2):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(93)90206-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamion B., Spring K. R. Water permeability of apical and basolateral cell membranes of rat inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 2):F986–F999. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.6.F986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fushimi K., Uchida S., Hara Y., Hirata Y., Marumo F., Sasaki S. Cloning and expression of apical membrane water channel of rat kidney collecting tubule. Nature. 1993 Feb 11;361(6412):549–552. doi: 10.1038/361549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellai M., Silverstein J. H., Hwang J. C., LaRochelle F. T., Jr, Valtin H. Influence of vasopressin on renal hemodynamics in conscious Brattleboro rats. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jun;246(6 Pt 2):F819–F827. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.6.F819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W., Vurek G. G. Picomole quantitation of ammonia by flow-through fluorometry. Anal Biochem. 1983 Apr 1;130(1):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90670-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington A. R., Valtin H. Impaired urinary concentration after vasopressin and its gradual correction in hypothalamic diabetes insipidus. J Clin Invest. 1968 Mar;47(3):502–510. doi: 10.1172/JCI105746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lankford S. P., Chou C. L., Terada Y., Wall S. M., Wade J. B., Knepper M. A. Regulation of collecting duct water permeability independent of cAMP-mediated AVP response. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 2):F554–F566. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.3.F554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma T., Hasegawa H., Skach W. R., Frigeri A., Verkman A. S. Expression, functional analysis, and in situ hybridization of a cloned rat kidney collecting duct water channel. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jan;266(1 Pt 1):C189–C197. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.266.1.C189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., DiGiovanni S. R., Christensen E. I., Knepper M. A., Harris H. W. Cellular and subcellular immunolocalization of vasopressin-regulated water channel in rat kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11663–11667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., Knepper M. A. Vasopressin activates collecting duct urea transporters and water channels by distinct physical processes. Am J Physiol. 1993 Aug;265(2 Pt 2):F204–F213. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.265.2.F204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S., Smith B. L., Christensen E. I., Knepper M. A., Agre P. CHIP28 water channels are localized in constitutively water-permeable segments of the nephron. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):371–383. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Carroll T. P., Guggino W. B., Agre P. Appearance of water channels in Xenopus oocytes expressing red cell CHIP28 protein. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):385–387. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J., Silverman M. Interaction of phlorizin and sodium with the renal brush-border membrane D-glucose transporter: stoichiometry and order of binding. J Membr Biol. 1981 Jan 30;58(1):43–55. doi: 10.1007/BF01871033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. B., Stetson D. L., Lewis S. A. ADH action: evidence for a membrane shuttle mechanism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;372:106–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb15464.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall S. M., Han J. S., Chou C. L., Knepper M. A. Kinetics of urea and water permeability activation by vasopressin in rat terminal IMCD. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 2):F989–F998. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.6.F989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]