Abstract
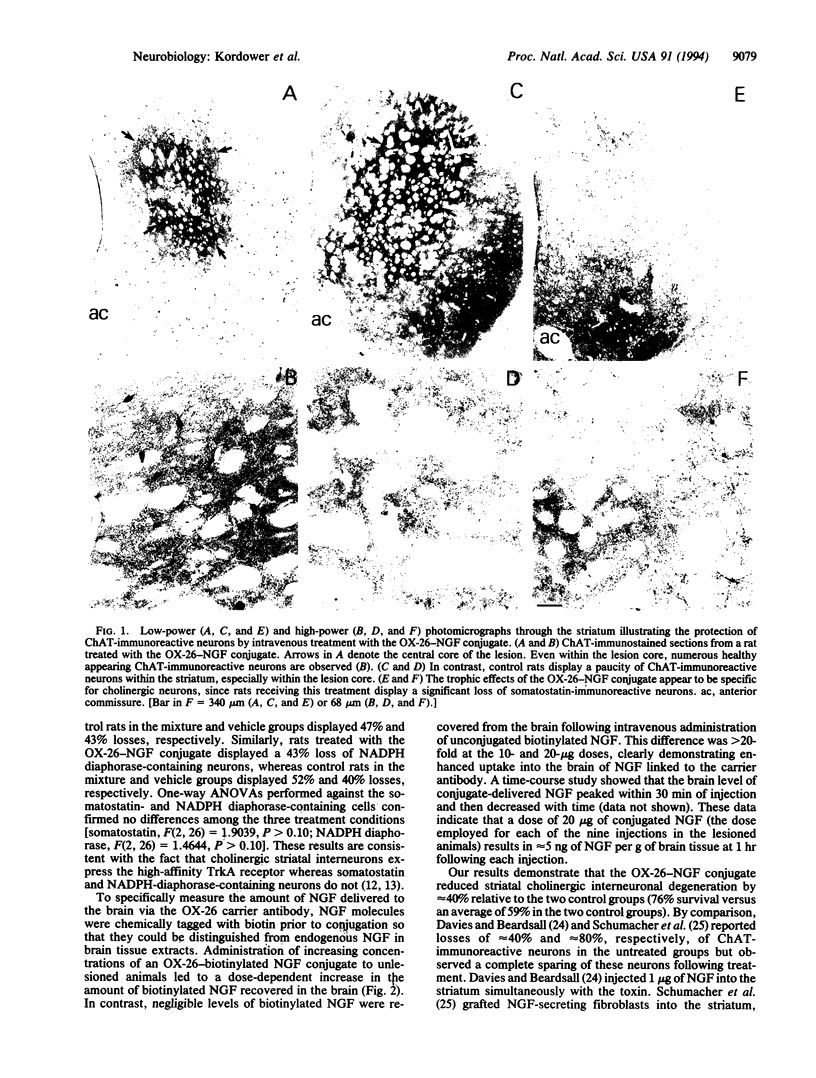
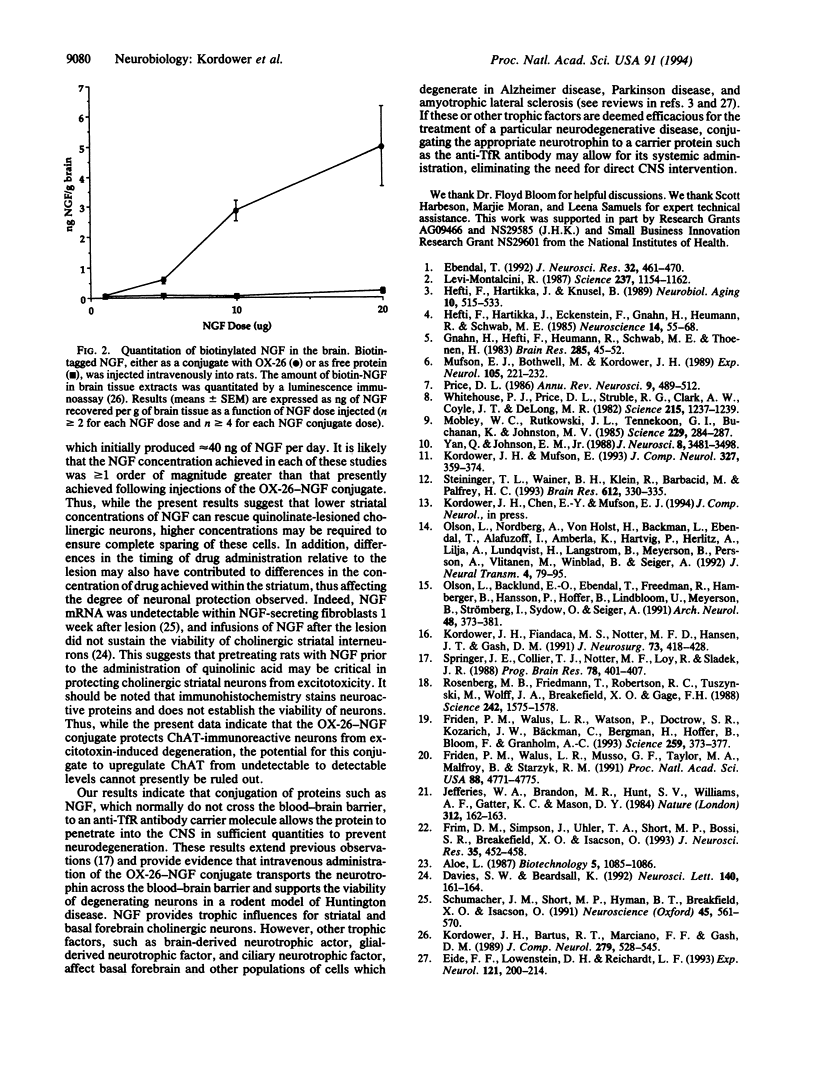
Intrastriatal injections of quinolinic acid induce a pattern of neuronal degeneration similar to that seen in Huntington disease. In the present study, nerve growth factor (NGF) crossed the blood-brain barrier in a dose-dependent fashion following intravenous infusion when conjugated to an antibody directed against the transferrin receptor (OX-26). Intravenous injections of the OX-26-NGF conjugate selectively prevented the loss of striatal choline acetyltransferase-immunoreactive neurons which normally occurs following quinolinic acid administration relative to control rats receiving vehicle or a nonconjugated mixture of OX-26 and NGF. These data demonstrate that a neurotrophic factor-antibody conjugate can prevent the degeneration of central NGF-responsive neurons following systemic administration.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davies S. W., Beardsall K. Nerve growth factor selectively prevents excitotoxin induced degeneration of striatal cholinergic neurones. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Jun 22;140(2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90092-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebendal T. Function and evolution in the NGF family and its receptors. J Neurosci Res. 1992 Aug;32(4):461–470. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490320402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide F. F., Lowenstein D. H., Reichardt L. F. Neurotrophins and their receptors--current concepts and implications for neurologic disease. Exp Neurol. 1993 Jun;121(2):200–214. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1993.1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friden P. M., Walus L. R., Musso G. F., Taylor M. A., Malfroy B., Starzyk R. M. Anti-transferrin receptor antibody and antibody-drug conjugates cross the blood-brain barrier. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4771–4775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friden P. M., Walus L. R., Watson P., Doctrow S. R., Kozarich J. W., Bäckman C., Bergman H., Hoffer B., Bloom F., Granholm A. C. Blood-brain barrier penetration and in vivo activity of an NGF conjugate. Science. 1993 Jan 15;259(5093):373–377. doi: 10.1126/science.8420006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frim D. M., Simpson J., Uhler T. A., Short M. P., Bossi S. R., Breakefield X. O., Isacson O. Striatal degeneration induced by mitochondrial blockade is prevented by biologically delivered NGF. J Neurosci Res. 1993 Jul 1;35(4):452–458. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490350413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnahn H., Hefti F., Heumann R., Schwab M. E., Thoenen H. NGF-mediated increase of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) in the neonatal rat forebrain: evidence for a physiological role of NGF in the brain? Brain Res. 1983 Jul;285(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(83)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefti F., Hartikka J., Eckenstein F., Gnahn H., Heumann R., Schwab M. Nerve growth factor increases choline acetyltransferase but not survival or fiber outgrowth of cultured fetal septal cholinergic neurons. Neuroscience. 1985 Jan;14(1):55–68. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hefti F., Hartikka J., Knusel B. Function of neurotrophic factors in the adult and aging brain and their possible use in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol Aging. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):515–533. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(89)90118-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferies W. A., Brandon M. R., Hunt S. V., Williams A. F., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. Transferrin receptor on endothelium of brain capillaries. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):162–163. doi: 10.1038/312162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordower J. H., Bartus R. T., Marciano F. F., Gash D. M. Telencephalic cholinergic system of the New World monkey (Cebus apella): morphological and cytoarchitectonic assessment and analysis of the projection to the amygdala. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Jan 22;279(4):528–545. doi: 10.1002/cne.902790403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordower J. H., Fiandaca M. S., Notter M. F., Hansen J. T., Gash D. M. NGF-like trophic support from peripheral nerve for grafted rhesus adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurosurg. 1990 Sep;73(3):418–428. doi: 10.3171/jns.1990.73.3.0418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordower J. H., Mufson E. J. NGF receptor (p75)-immunoreactivity in the developing primate basal ganglia. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Jan 15;327(3):359–375. doi: 10.1002/cne.903270305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor 35 years later. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1154–1162. doi: 10.1126/science.3306916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobley W. C., Rutkowski J. L., Tennekoon G. I., Buchanan K., Johnston M. V. Choline acetyltransferase activity in striatum of neonatal rats increased by nerve growth factor. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):284–287. doi: 10.1126/science.2861660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson E. J., Bothwell M., Kordower J. H. Loss of nerve growth factor receptor-containing neurons in Alzheimer's disease: a quantitative analysis across subregions of the basal forebrain. Exp Neurol. 1989 Sep;105(3):221–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(89)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson L., Backlund E. O., Ebendal T., Freedman R., Hamberger B., Hansson P., Hoffer B., Lindblom U., Meyerson B., Strömberg I. Intraputaminal infusion of nerve growth factor to support adrenal medullary autografts in Parkinson's disease. One-year follow-up of first clinical trial. Arch Neurol. 1991 Apr;48(4):373–381. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1991.00530160037011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson L., Nordberg A., von Holst H., Bäckman L., Ebendal T., Alafuzoff I., Amberla K., Hartvig P., Herlitz A., Lilja A. Nerve growth factor affects 11C-nicotine binding, blood flow, EEG, and verbal episodic memory in an Alzheimer patient (case report). J Neural Transm Park Dis Dement Sect. 1992;4(1):79–95. doi: 10.1007/BF02257624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. L. New perspectives on Alzheimer's disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:489–512. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. B., Friedmann T., Robertson R. C., Tuszynski M., Wolff J. A., Breakefield X. O., Gage F. H. Grafting genetically modified cells to the damaged brain: restorative effects of NGF expression. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1575–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.3201248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher J. M., Short M. P., Hyman B. T., Breakefield X. O., Isacson O. Intracerebral implantation of nerve growth factor-producing fibroblasts protects striatum against neurotoxic levels of excitatory amino acids. Neuroscience. 1991;45(3):561–570. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90271-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer J. E., Collier T. J., Notter M. F., Loy R., Sladek J. R., Jr Central nervous system grafts of nerve growth factor-rich tissue as an alternative source of trophic support for axotomized cholinergic neurons. Prog Brain Res. 1988;78:401–407. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60311-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steininger T. L., Wainer B. H., Klein R., Barbacid M., Palfrey H. C. High-affinity nerve growth factor receptor (Trk) immunoreactivity is localized in cholinergic neurons of the basal forebrain and striatum in the adult rat brain. Brain Res. 1993 May 28;612(1-2):330–335. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91681-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse P. J., Price D. L., Struble R. G., Clark A. W., Coyle J. T., Delon M. R. Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia: loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1237–1239. doi: 10.1126/science.7058341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan Q., Johnson E. M., Jr An immunohistochemical study of the nerve growth factor receptor in developing rats. J Neurosci. 1988 Sep;8(9):3481–3498. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-09-03481.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]