Abstract
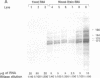
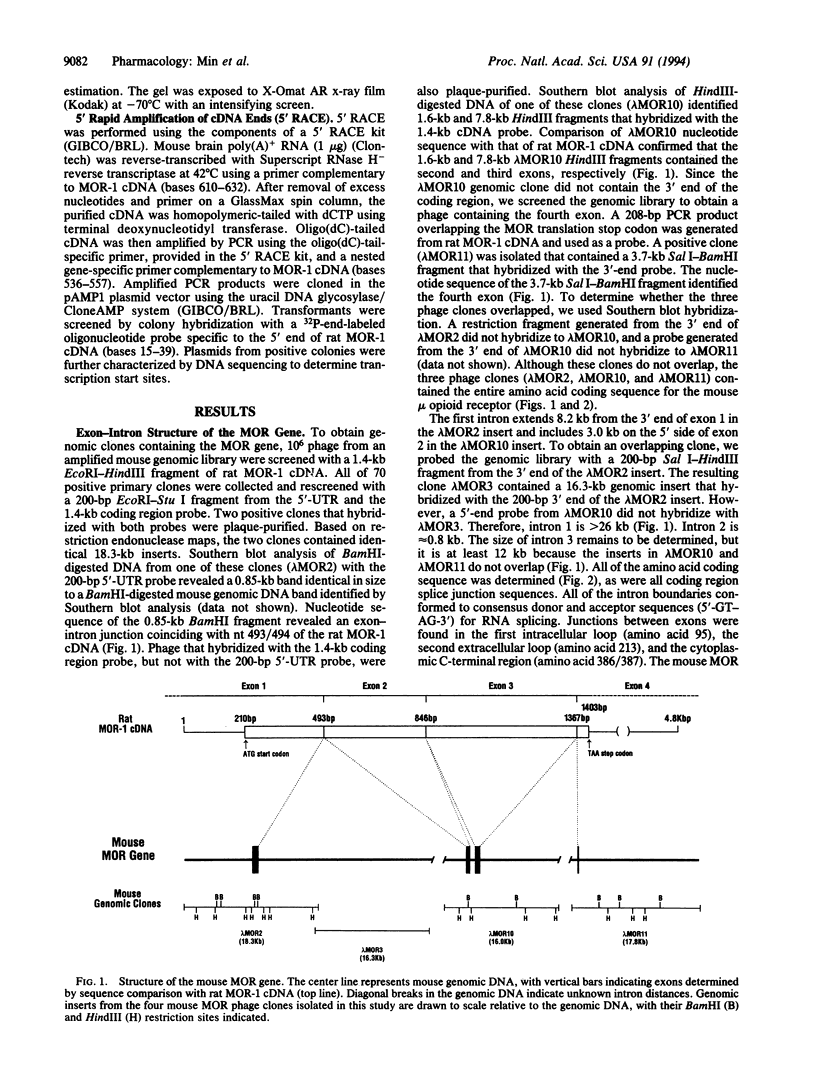
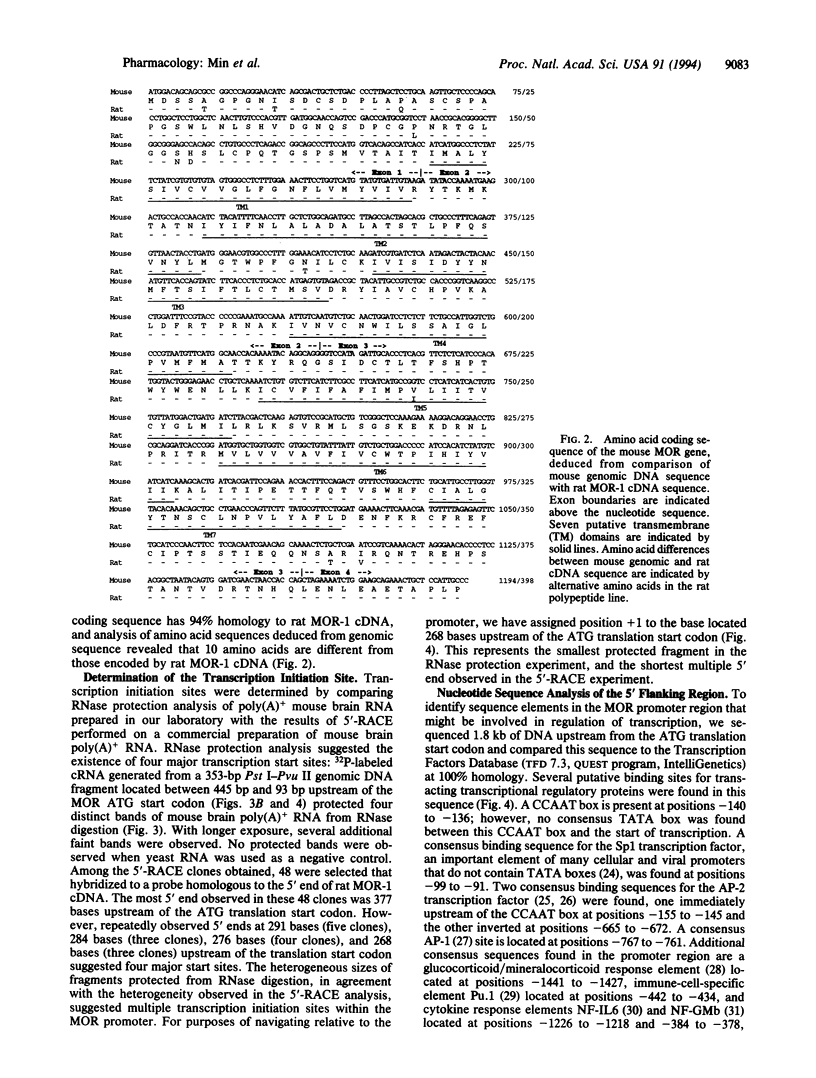
We have isolated mouse mu opioid receptor genomic clones (termed MOR) containing the entire amino acid coding sequence corresponding to rat MOR-1 cDNA, including additional 5' flanking sequence. The mouse MOR gene is > 53 kb long, and the coding sequence is divided by three introns, with exon junctions in codons 95 and 213 and between codons 386 and 387. The first intron is > 26 kb, the second is 0.8 kb, and the third is > 12 kb. Multiple transcription initiation sites were observed, with four major sites confirmed by 5' rapid amplification of cDNA ends and RNase protection located between 291 and 268 bp upstream of the translation start codon. Comparison of the 5' flanking sequence with a transcription factor database revealed putative cis-acting regulatory elements for transcription factors affected by cAMP, as well as those involved in the action of gluco- and mineralocorticoids, cytokines, and immune-cell-specific factors.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attali B., Saya D., Nah S. Y., Vogel Z. Kappa opiate agonists inhibit Ca2+ influx in rat spinal cord-dorsal root ganglion cocultures. Involvement of a GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):347–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beitner D. B., Duman R. S., Nestler E. J. A novel action of morphine in the rat locus coeruleus: persistent decrease in adenylate cyclase. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 May;35(5):559–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume A. J. Interaction of ligands with the opiate receptors of brain membranes: regulation by ions and nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1713–1717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Mestek A., Liu J., Hurley J. A., Yu L. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a mu-opioid receptor from rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;44(1):8–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Mestek A., Liu J., Yu L. Molecular cloning of a rat kappa opioid receptor reveals sequence similarities to the mu and delta opioid receptors. Biochem J. 1993 Nov 1;295(Pt 3):625–628. doi: 10.1042/bj2950625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chneiweiss H., Glowinski J., Premont J. Mu and delta opiate receptors coupled negatively to adenylate cyclase on embryonic neurons from the mouse striatum in primary cultures. J Neurosci. 1988 Sep;8(9):3376–3382. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-09-03376.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidne K. A., Taylor P. L., Zabavnik J., Saunders P. T., Inglis J. D. D2 receptor, a missing exon. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):865–865. doi: 10.1038/342865a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. J., Keith D. E., Jr, Morrison H., Magendzo K., Edwards R. H. Cloning of a delta opioid receptor by functional expression. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1952–1955. doi: 10.1126/science.1335167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedynyshyn J. P., Lee N. M. Mu-type opioid receptors in rat periaqueductal gray-enriched P2 membrane are coupled to guanine nucleotide binding proteins. Brain Res. 1989 Jan 2;476(1):102–109. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91541-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey E. A., Kebabian J. W. A mu-opiate receptor in 7315c tumor tissue mediates inhibition of immunoreactive prolactin release and adenylate cyclase activity. Endocrinology. 1984 Nov;115(5):1797–1804. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-5-1797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda K., Kato S., Mori K., Nishi M., Takeshima H. Primary structures and expression from cDNAs of rat opioid receptor delta- and mu-subtypes. FEBS Lett. 1993 Aug 2;327(3):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81011-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer B. L., Befort K., Gaveriaux-Ruff C., Hirth C. G. The delta-opioid receptor: isolation of a cDNA by expression cloning and pharmacological characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12048–12052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A. The macrophage and B cell-specific transcription factor PU.1 is related to the ets oncogene. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski G., Klee W. A. Opiates inhibit adenylate cyclase by stimulating GTP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4185–4189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law P. Y., Wu J., Koehler J. E., Loh H. H. Demonstration and characterization of opiate inhibition of the striatal adenylate cyclase. J Neurochem. 1981 May;36(5):1834–1846. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb00438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leza M. A., Hearing P. Cellular transcription factor binds to adenovirus early region promoters and to a cyclic AMP response element. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):3003–3013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.3003-3013.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Zhu J., Chen C., Chen Y. W., Deriel J. K., Ashby B., Liu-Chen L. Y. Molecular cloning and expression of a rat kappa opioid receptor. Biochem J. 1993 Nov 1;295(Pt 3):629–633. doi: 10.1042/bj2950629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh H. H., Smith A. P. Molecular characterization of opioid receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:123–147. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord J. A., Waterfield A. A., Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W. Endogenous opioid peptides: multiple agonists and receptors. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):495–499. doi: 10.1038/267495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng F., Xie G. X., Thompson R. C., Mansour A., Goldstein A., Watson S. J., Akil H. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a rat kappa opioid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):9954–9958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.9954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Erdos J. J., Terwilliger R., Duman R. S., Tallman J. F. Regulation of G proteins by chronic morphine in the rat locus coeruleus. Brain Res. 1989 Jan 9;476(2):230–239. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A., Williams J. T., Surprenant A., Christie M. J. Mu and delta receptors belong to a family of receptors that are coupled to potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5487–5491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratka A., Sutanto W., De Kloet E. R. Long-lasting glucocorticoid suppression of opioid-induced antinociception. Neuroendocrinology. 1988 Oct;48(4):439–444. doi: 10.1159/000125046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Ge B. L., Ramakrishnan S., Lee N. M., Loh H. H. [3H]morphine binding is enhanced by IL-1-stimulated thymocyte proliferation. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 5;287(1-2):93–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80023-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy S., Ramakrishnan S., Loh H. H., Lee N. M. Chronic morphine treatment selectively suppresses macrophage colony formation in bone marrow. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr 3;195(3):359–363. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90476-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon M. F., Gamble J. R., Vadas M. A. Nuclear proteins interacting with the promoter region of the human granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):674–678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibinga N. E., Goldstein A. Opioid peptides and opioid receptors in cells of the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:219–249. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathmann M., Hamilton B. A., Mayeda C. A., Simon M. I., Meyerowitz E. M., Palazzolo M. J. Transposon-facilitated DNA sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1247–1250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Gillespie D. Molecular hybridization with RNA probes in concentrated solutions of guanidine thiocyanate. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jun;163(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90225-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Mansour A., Akil H., Watson S. J. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a rat mu opioid receptor. Neuron. 1993 Nov;11(5):903–913. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90120-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. B., Imai Y., Eppler C. M., Gregor P., Spivak C. E., Uhl G. R. mu opiate receptor: cDNA cloning and expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10230–10234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. J., LoPresti D., James D. W. Activity of mu- and delta-selective opioid agonists in the guinea pig ileum preparation: differentiation into peptide and nonpeptide classes with beta-funaltrexamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Aug;238(2):625–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Tjian R. Analysis of the DNA-binding and activation properties of the human transcription factor AP-2. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):670–682. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda K., Raynor K., Kong H., Breder C. D., Takeda J., Reisine T., Bell G. I. Cloning and functional comparison of kappa and delta opioid receptors from mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6736–6740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Eiger S., Duan D. S., Lameh J., Sadée W. Regulation of cyclic AMP by the mu-opioid receptor in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. J Neurochem. 1990 Oct;55(4):1390–1396. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb03151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]