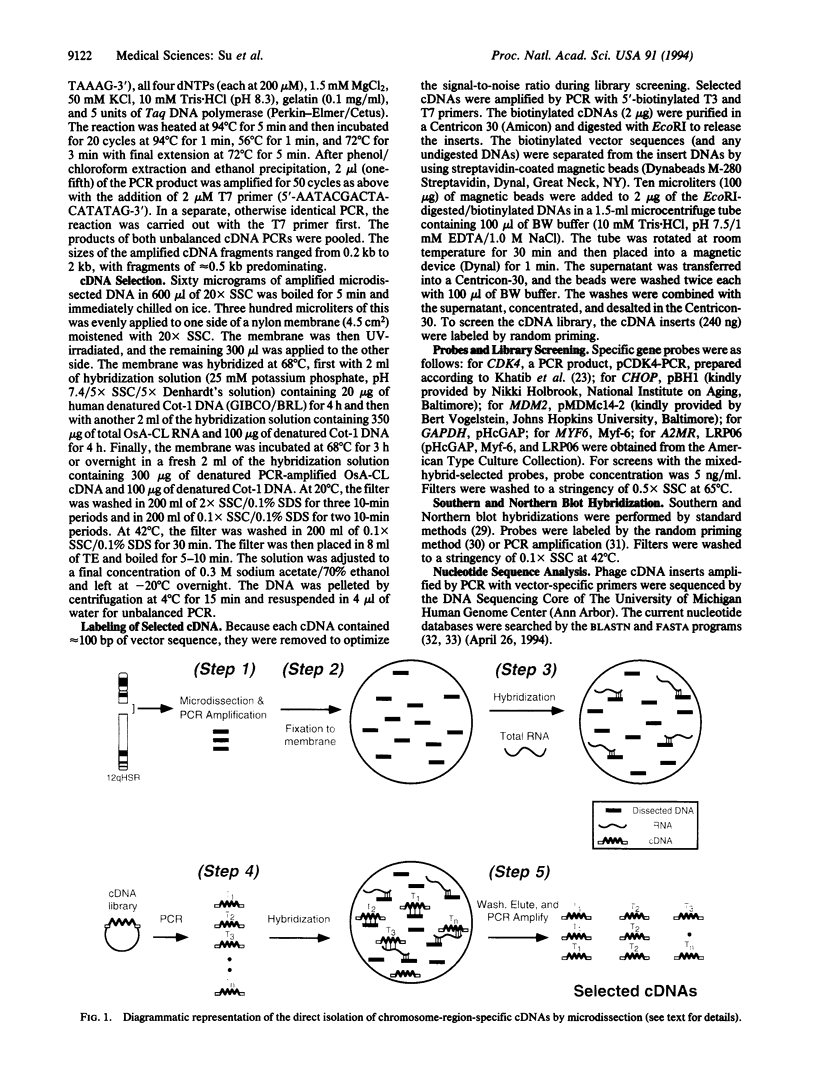
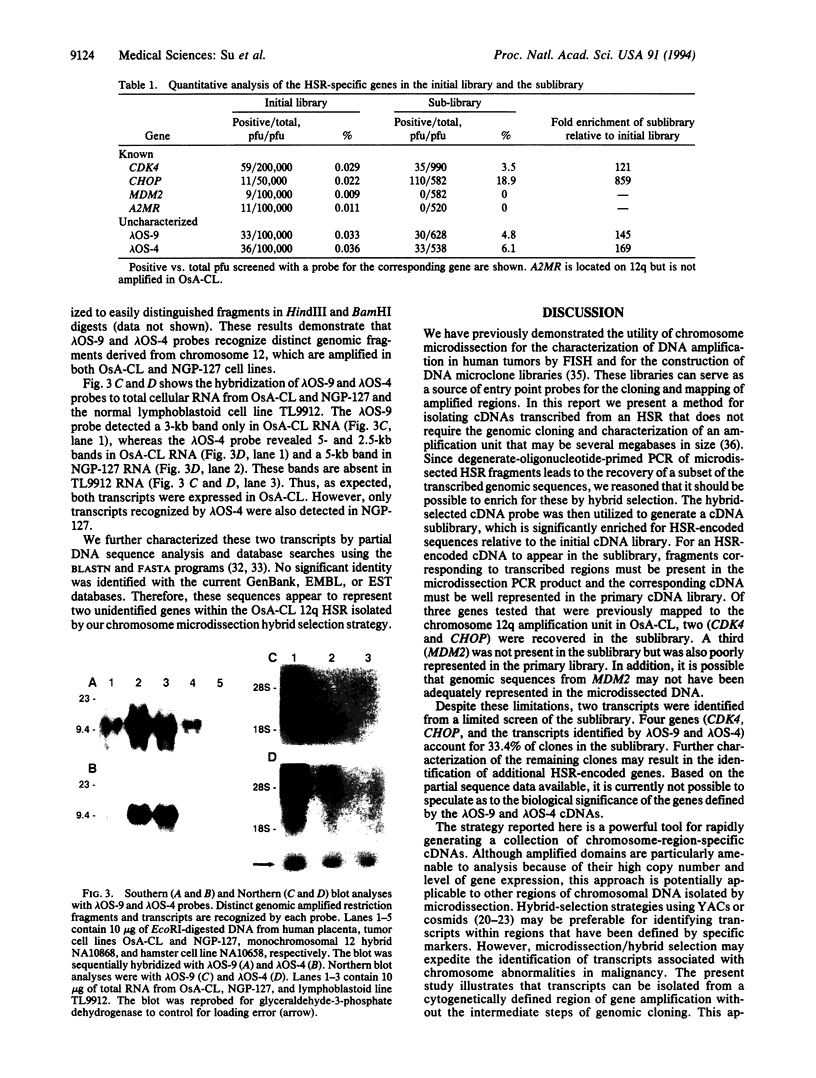
Abstract
Identification of genes involved in recurring chromosome rearrangements has provided significant insight into the molecular basis of malignancy. We describe here a strategy combining chromosome microdissection and hybrid selection for the direct isolation of chromosome region-specific genes. We modeled this strategy by using sequences recovered from the microdissection of a homogeneously staining region to allow isolation of genes that were overexpressed and present at high copy number within the homogeneously staining region, including the direct isolation of two genes encoded within a 12q homogeneously staining region found in the osteosarcoma cell line OsA-CL. Although first applied to amplified genes, this strategy should be applicable to the isolation of cDNAs from any chromosomal region.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Wei J. F., Wei F. S., Hsu Y. C., Uehara H., Artzt K., Bennett D. Searching for coding sequences in the mammalian genome: the H-2K region of the mouse MHC is replete with genes expressed in embryos. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3441–3449. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03218.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler A. J., Chang D. D., Graw S. L., Brook J. D., Haber D. A., Sharp P. A., Housman D. E. Exon amplification: a strategy to isolate mammalian genes based on RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):4005–4009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.4005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duyk G. M., Kim S. W., Myers R. M., Cox D. R. Exon trapping: a genetic screen to identify candidate transcribed sequences in cloned mammalian genomic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8995–8999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elvin P., Slynn G., Black D., Graham A., Butler R., Riley J., Anand R., Markham A. F. Isolation of cDNA clones using yeast artificial chromosome probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3913–3917. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forus A., Flørenes V. A., Maelandsmo G. M., Meltzer P. S., Fodstad O., Myklebost O. Mapping of amplification units in the q13-14 region of chromosome 12 in human sarcomas: some amplica do not include MDM2. Cell Growth Differ. 1993 Dec;4(12):1065–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan X. Y., Meltzer P. S., Cao J., Trent J. M. Rapid generation of region-specific genomic clones by chromosome microdissection: isolation of DNA from a region frequently deleted in malignant melanoma. Genomics. 1992 Nov;14(3):680–684. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(05)80168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochgeschwender U., Sutcliffe J. G., Brennan M. B. Construction and screening of a genomic library specific for mouse chromosome 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8482–8486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jankowski S. A., Mitchell D. S., Smith S. H., Trent J. M., Meltzer P. S. SAS, a gene amplified in human sarcomas, encodes a new member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily of proteins. Oncogene. 1994 Apr;9(4):1205–1211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khatib Z. A., Matsushime H., Valentine M., Shapiro D. N., Sherr C. J., Look A. T. Coamplification of the CDK4 gene with MDM2 and GLI in human sarcomas. Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 15;53(22):5535–5541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn B., Sedlacek Z., Manca A., Kioschis P., Konecki D., Lehrach H., Poustka A. A strategy for the selection of transcribed sequences in the Xq28 region. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):235–242. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.4.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen T., Moestrup S. K., Gliemann J., Bendtsen L., Sand O., Sottrup-Jensen L. Evidence that the newly cloned low-density-lipoprotein receptor related protein (LRP) is the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 10;276(1-2):151–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80530-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krizman D. B., Berget S. M. Efficient selection of 3'-terminal exons from vertebrate DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 11;21(22):5198–5202. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.22.5198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P., Legerski R., Siciliano M. J. Isolation of human transcribed sequences from human-rodent somatic cell hybrids. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):813–815. doi: 10.1126/science.2479099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovett M., Kere J., Hinton L. M. Direct selection: a method for the isolation of cDNAs encoded by large genomic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9628–9632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer P. S., Guan X. Y., Burgess A., Trent J. M. Rapid generation of region specific probes by chromosome microdissection and their application. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):24–28. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer P. S., Jankowski S. A., Dal Cin P., Sandberg A. A., Paz I. B., Coccia M. A. Identification and cloning of a novel amplified DNA sequence in human malignant fibrous histiocytoma derived from a region of chromosome 12 frequently rearranged in soft tissue tumors. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Oct;2(10):495–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaco A. P., Neve R. L., Colletti-Feener C., Bertelson C. J., Kurnit D. M., Kunkel L. M. Isolation of candidate cDNAs for portions of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):646–650. doi: 10.1038/323646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliner J. D., Kinzler K. W., Meltzer P. S., George D. L., Vogelstein B. Amplification of a gene encoding a p53-associated protein in human sarcomas. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):80–83. doi: 10.1038/358080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parimoo S., Patanjali S. R., Shukla H., Chaplin D. D., Weissman S. M. cDNA selection: efficient PCR approach for the selection of cDNAs encoded in large chromosomal DNA fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9623–9627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. M., Douglass E. C., Peiper S. C., Houghton P. J., Look A. T. Amplification of the gli gene in childhood sarcomas. Cancer Res. 1989 Oct 1;49(19):5407–5413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schowalter D. B., Sommer S. S. The generation of radiolabeled DNA and RNA probes with polymerase chain reaction. Anal Biochem. 1989 Feb 15;177(1):90–94. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Klempnauer K. H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Gilbert F., Brodeur G., Goldstein M., Trent J. Amplified DNA with limited homology to myc cellular oncogene is shared by human neuroblastoma cell lines and a neuroblastoma tumour. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):245–248. doi: 10.1038/305245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. H., Weiss S. W., Jankowski S. A., Coccia M. A., Meltzer P. S. SAS amplification in soft tissue sarcomas. Cancer Res. 1992 Jul 1;52(13):3746–3749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R. Regulation and mechanisms of mammalian gene amplification. Adv Cancer Res. 1993;61:87–113. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60956-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. M., Thompson F. H. Methods for chromosome banding of human and experimental tumors in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1987;151:267–279. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)51023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetrie D., Vorechovský I., Sideras P., Holland J., Davies A., Flinter F., Hammarström L., Kinnon C., Levinsky R., Bobrow M. The gene involved in X-linked agammaglobulinaemia is a member of the src family of protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1993 Jan 21;361(6409):226–233. doi: 10.1038/361226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace M. R., Marchuk D. A., Andersen L. B., Letcher R., Odeh H. M., Saulino A. M., Fountain J. W., Brereton A., Nicholson J., Mitchell A. L. Type 1 neurofibromatosis gene: identification of a large transcript disrupted in three NF1 patients. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):181–186. doi: 10.1126/science.2134734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoi T., Lovett M., Cheng Z. Y., Epstein C. J. Isolation of transcribed DNA sequences from chromosome 21 using mouse fetal cDNA. Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;74(2):137–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00282077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Trent J. M., Meltzer P. S. Rapid isolation and characterization of amplified DNA by chromosome microdissection: identification of IGF1R amplification in malignant melanoma. Oncogene. 1993 Oct;8(10):2827–2831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]