Abstract
SPG13, an autosomal dominant form of pure hereditary spastic paraplegia, was recently mapped to chromosome 2q24-34 in a French family. Here we present genetic data indicating that SPG13 is associated with a mutation, in the gene encoding the human mitochondrial chaperonin Hsp60, that results in the V72I substitution. A complementation assay showed that wild-type HSP60 (also known as “HSPD1”), but not HSP60 (V72I), together with the co-chaperonin HSP10 (also known as “HSPE1”), can support growth of Escherichia coli cells in which the homologous chromosomal groESgroEL chaperonin genes have been deleted. Taken together, our data strongly indicate that the V72I variation is the first disease-causing mutation that has been identified in HSP60.
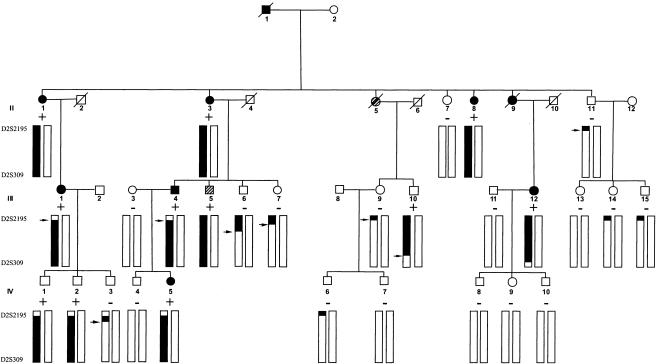
Hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) represents a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of neurodegenerative disorders that are characterized by progressive spasticity and weakness of the lower limbs. Seventeen different loci have been mapped, but only five of the corresponding genes have been cloned and identified so far (for reviews, see Tallaksen et al. 2001 and Casari and Rugarli 2001; for the recently identified fifth gene, see Zhao et al. 2001). Two of these five gene products—paraplegin (SPG7 [MIM *602783]) (Casari et al. 1998) and spastin (SPG4 [MIM 182601]) (Hazan et al. 1999)—feature AAA+ domains and are predicted to possess chaperone activity. Paraplegin is the human homologue of a yeast protease/chaperone that is involved in mitochondrial protein quality control (Casari et al. 1998; Langer 2000). We had previously localized the genes encoding the human mitochondrial chaperonin Hsp60 (heat-shock protein 60; also known as “Cpn60”) and its co-chaperonin Hsp10 (heat-shock protein 10; also known as “Cpn10”) to chromosome 2q33.1—that is, to the same region to which another locus for HSP (SPG13 [MIM *605280]) had been mapped in a French family (Fontaine et al. 2000)—which prompted us to propose that HSP60 and HSP10 are candidate genes for SPG13. After determination of the HSP60/HSP10 genomic structure (HSPD1 [GenBank accession number AJ250915]), sequencing of the 16 exons encoding the two genes and the intervening 656-bp bidirectional promoter region in two affected members of the family with SPG13 revealed that both individuals were heterozygous for a G→A variation at position 292 of the HSP60 cDNA, resulting in the substitution of a valine residue at position 72 in mature Hsp60 with isoleucine (V72I). Sequencing of HSP60 exon 3 in the other members of the SAL-612 family confirmed that the variant allele segregated with the disease (fig. 1), and a peak two-point LOD score of 3.43 at recombination fraction 0, similar to that calculated for D2S2392, was obtained for this variant allele (Fontaine et al. 2000). Since the penetrance of HSP is age dependent, a possible explanation for the observation that three individuals (II:10, IV:1, and IV:2) are not clinically affected even though they carry both the disease allele and the mutation is that they were younger than the mean age at onset of SPG13 at the time of clinical examination. Analysis of genomic DNA from unrelated control individuals of European descent showed that none of 800 control chromosomes carried the 292G→A variation.
Figure 1.
Pedigree of family SAL-612. SPG13 is flanked by D2S2195 and D2S309. The haplotype segregating with HSP is indicated, and recombinants are noted by an arrow. The plus sign identifies the individuals in whom the HSP60 292 G→A variant was found. A perfect segregation is observed between the disease haplotype and the HSP60 292 G→A variant.
To further investigate the frequency of HSP60 variations in a population of patients with HSP, we sequenced the coding region and the promoter of the HSP10 and HSP60 genes in four affected individuals belonging to two French families in which linkage to chromosome 2q24-34 was suggested (Fontaine et al. 2000) and in 20 index cases with autosomal dominant HSP from French families, which were not informative enough to be investigated by linkage analysis, and in which mutations in the gene encoding spastin (i.e., SPG4) had been excluded. In only one of these patients, we found a base pair change that resulted in an amino acid substitution—an A→G variation at position 551 of the HSP60 cDNA, replacing asparagine-158 with serine (N158S). However, the absence of this variation in another affected family member, as well as its presence in 1 of 800 alleles from control individuals of European descent, suggested that it represents a rare variation and not a disease-causing mutation.
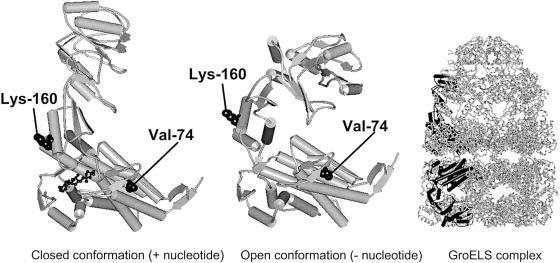
In an alignment of human Hsp60 with the Escherichia coli Hsp60 homologue GroEL, valine-72 and asparagine-158 correspond to valine-74 and lysine-160 in E. coli GroEL, respectively. Inspection of the crystal structure of E. coli GroEL (Xu et al. 1997) shows that valine-74 is located in helix C of the equatorial domain, buried inside a conserved substructure of the GroEL monomer, whereas lysine-160 is situated in the intermediate domain and its side chain protrudes from the outer surface of the barrel structure (fig. 2). This suggests that replacement of the conserved valine may have more-severe consequences than replacement at the other position. To experimentally determine the function of the HSP60 (V72I) and HSP60 (N158S) variants, we turned our attention to the E. coli genetic system. The groESgroEL operon encoding the E. coli chaperonins is essential for bacterial growth under a variety of growth conditions (Fayet et al. 1989). We have recently shown that the entire E. coli groESgroEL chromosomal operon can be deleted when the human HSP60 and HSP10 genes are supplied in trans (Richardson et al. 2001). However, the resulting E. coli–derivative strain grows slowly, at 37°C, or not at all, at 42°C. Thus, we reasoned that the ability of the HSP60 and HSP10 human chaperone genes to replace the endogenous groESgroEL operon may represent a very sensitive system to test our two HSP60 mutant alleles for their relative in vivo function.
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the structure of the Hsp60 chaperonin homologue GroEL from E. coli (Protein Data Bank entry 1AON). The architecture of a subunit in the closed and open conformations and an overview of the GroEL/GroES chaperonin complex with one subunit in the closed (upper ring) and open (lower ring) conformations highlighted in black are shown. The side chains of valine-74 and lysine-160, which correspond to valine-72 and asparagine-158, respectively, in human Hsp60, are shown in space-filling representation. The figure was produced with WebLab ViewerLite software (Molecular Simulations).
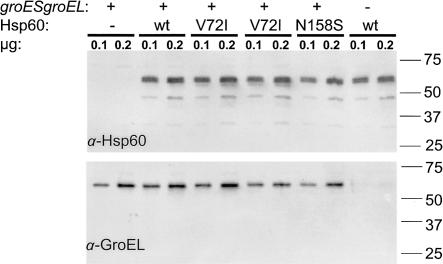
We found that when either the E. coli wild-type (wt) groESgroEL operon or the human HSP60 (wt)–HSP10 (wt) or Hsp60 (N158S)–HSP10 (wt) set of genes was expressed from a plasmid, they allowed the deletion of the chromosomally encoded groESgroEL operon—that is, ∼50% of the tetracycline-resistance (TetR) transductants simultaneously inherited the ω-chloramphenicol-resistance (CamR)–encoding cassette, replacing the groESgroEL operon (for details, see the note for table 1). In contrast, the presence of the HSP60 (V72I)–HSP10 (wt) set of genes on a plasmid did not allow the deletion of the groES+groEL+ chromosomally encoded operon—that is, none of the TetR transductants (0/206) inherited the CamR-encoding DNA cassette. The E. coli transductants maintained alive by either the HSP60 (wt)–HSP10 (wt) or HSP60 (N158S)–HSP10 (wt) operon could not be distinguished from each other by a variety of physiological and genetic tests. For example, the colony sizes of the two E. coli strains were indistinguishable from each other, and both strains failed to grow at ⩾40°C. In addition, both strains supported equally well the growth of bacteriophage T5, which requires both the GroES and GroEL proteins for its morphogenesis (Richardson et al. 2001). In contrast, neither strain supported the growth, at 37°C, of bacteriophage λ, T4, RB43, and RB49, in agreement with our previous results (Richardson et al. 2001). The following control experiments were performed to ensure the validity of our results and conclusions (fig. 3): first, western blot analysis indicated that all plasmid constructs expressed equal levels of Hsp60; second, western blot analysis with GroEL-specific antibody showed that CamR E. coli transductants did not express any GroEL, as expected; and, third, the three HSP60 plasmid constructs introduced into the E. coli B178 bacteria (table 1) were shown by DNA sequencing to possess the correct HSP60 allele (data not shown).
Table 1.
Replacement of the E. coli Chromosomally Encoded groESgroEL Operon by Plasmids That Express Various HSP60 Alleles and HSP10 (wt)[Note]
| Plasmid | TetRa | CamRa | Linkage(%) |
| None | 105 | 0 | 0 |
| pOFX groES+groEL+ | 114 | 59 | 49 |
| pOFX HSP60 (wt)–HSP10 (wt) | 218 | 100 | 46 |
| pOFX HSP60 (N158S)–HSP10 (wt) | 216 | 108 | 50 |
| pOFX HSP60 (V72I)–HSP10 (wt) | 206 | 0 | 0 |
Note.— A bacteriophage P1 lysate was first prepared on the donor strain AR189, a derivative of OF3465 (a kind gift from Drs. Marie-Pierre Castanié and Olivier Fayet, Centre National de Recherche Scientifiq, Toulouse), in which the groESgroEL operon has been deleted and replaced by a CamR DNA cassette (Richardson et al. 2001). The groESgroEL-deleted strain is maintained alive with plasmid pOFX groES+groEL+ (Castanie et al. 1997). In addition, AR189 carries a Tn10 insertion, zid1::Tn10, that encodes TetR and is ∼50% cotransferable with the groESgroEL operon by bacteriophage P1 transduction (Fayet et al. 1989). The resulting P1 lysate was used to infect the bacterial strain B178 transformed with derivatives of plasmid pOFX-tac1 (Castanie et al. 1997) carrying the cDNA for human HSP10 and wt or variant HSP60 (without mitochondrial transit peptide) as an operon under control of the tac promoter. Nontransformed cells or cells that were transformed with a plasmid that carried the E. coli groESgroEL operon were used as controls. After removal of unadsorbed P1 bacteriophage by centrifugation, cells were spread on plates that were supplemented with 10−3M isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG), 12.5 μg/ml of tetracycline and 5×10-3 M sodium citrate (to prevent bacteriophage P1 re-adsorption). After a 48-h incubation at 30°C, TetR colonies were replica plated onto LB-agar plates supplemented with 10 μg/ml chloramphenicol and IPTG, tetracycline, and sodium citrate, as described above, and were scored after a 48-h incubation at 30°C, for acquisition of the CamR marker. Inheritance of the CamR phenotype indicates that the endogenous, chromosomally encoded groESgroEL operon has been successfully deleted and replaced by the CamR-encoding DNA cassette.
The values represent the number of transductants and are the result of a single experiment, for recipient bacteria carrying no plasmid or pOFX groES+groEL+, and the sum of two independent experiments, for the rest of the constructs.
Figure 3.
Western blot analysis of Hsp60 and GroEL protein expression. E. coli B178 cells transformed with the plasmids carrying the cDNA for human HSP10 and wt or variant HSP60 (see table 1) or cells transformed with the vector plasmid were grown in dYT medium to midlog phase. Expression of plasmid-encoded chaperonins was induced for 3 h by addition of 1 mM IPTG. One of the groESgroEL deleted colonies that was maintained alive with plasmid pOFX HSP60 (wt)–HSP10 (wt) was grown overnight in dYT medium that was supplemented with 1 mM IPTG. Soluble extracts prepared as described elsewhere (Bross et al. 1995) were subjected to SDS-PAGE and western blot analysis through use of monoclonal antibodies that were directed against Hsp60 (H-3524; Sigma) and GroEL (SPA 870; StressGen), respectively. Blots were developed using ECL+ (Amersham Biosciences) and were scanned using a STORM molecular imager. The strain genotypes with respect to chromosomal groESgroEL and plasmid-expressed human Hsp60 variant and the amount of total protein loaded per lane are indicated at the top. The position and molecular mass (in kD) of co-electrophoresed marker proteins are indicated at the right margin.
The inevitable conclusion of all our genetic and protein-expression experiments is that, whereas the Hsp60 (N158S) mutant protein functions as well as its Hsp60 wt counterpart in the promotion of E. coli growth, the Hsp60 (V72I) mutant protein fails to do so. Dominant inheritance of the HSP60 (V72I) allele in spastic paraplegia may result from haploinsufficiency through the formation of mixed chaperonin rings consisting of active wt and functionally incapacitated Hsp60 (V72I) subunits. This would lead to a lowering of overall chaperonin activity, especially under stress conditions in which the up-regulation of the wt allele cannot fully compensate for the nonfunctional allele. Alternatively, Hsp60 (V72I) chaperonin subunits may perturb allosteric coupling between the subunits in the ring structure and thus exert a genuine dominant negative effect.
Taken together, our studies strongly suggest that the V72I amino acid change that is caused by the 292G→A mutation in HSP60 is responsible for SPG13. That three (SPG4, SPG7, and SPG13) of the six genes for HSP that have been identified so far encode proteins with putative chaperone activity supports the hypothesis that a significant fraction of the HSPs are “chaperonopathies.” The detection of the first disease-causing mutation in the biochemically well-characterized Hsp60 chaperonin enables the investigation of the mechanisms by which mutations in the various chaperone genes predominantly manifest in the distal regions of the very long axons of the corticospinal tract. A role of chaperones is increasingly recognized in neurodegenerative diseases (Slavotinek and Biesecker 2001), and our findings lend further weight to the notion that chaperones play an important role in neurodegenerative diseases in general.
Acknowledgments
We thank patients and their families, for their kind participation; the Association Strümpell-Lorrain and the physicians, for referring patients to us; and the DNA and cell bank from the Institut Fédératif de Recherche des Neurosciences, for sample preparations. Patients provided informed consent in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and European bioethics laws. This work was financially supported by the Karen Elise Jensen Foundation, Association Française contre les Myopathies, and INSERM, the Danish Centre for Human Genome Research, the Danish Research Council, and the Swiss National Foundation.
Electronic-Database Information
Accession numbers and URLs for data in this report are as follows:
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for human HSP60 (HSPD1) genome structure [accession number AJ250915])
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for SPG4 [MIM 182601], SPG7 [MIM *602783], and SPG13 [MIM *605280])
- Protein Data Bank (PDB), http://pdb.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/pdb/ (for GroESL structure coordinates [AOL])
References
- Bross P, Jespersen C, Jensen TG, Andresen BS, Kristensen MJ, Winter V, Nandy A, Kräutle F, Ghisla S, Bolund L, Kim JJP, Gregersen N (1995) Effects of two mutations detected in medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD)-deficient patients on folding, oligomer assembly, and stability of MCAD enzyme. J Biol Chem 270:10284–10290 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casari G, De Fusco M, Ciarmatori S, Zeviani M, Mora M, Fernandez P, De Michele G, Filla A, Cocozza S, Marconi R, Durr A, Fontaine B, Ballabio A (1998) Spastic paraplegia and OXPHOS impairment caused by mutations in paraplegin, a nuclear-encoded mitochondrial metalloprotease. Cell 93:973–983 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casari G, Rugarli E (2001) Molecular basis of inherited spastic paraplegias. Curr Opin Genet Dev 11:336–342 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castanie MP, Berges H, Oreglia J, Prere MF, Fayet O (1997) A set of pBR322-compatible plasmids allowing the testing of chaperone-assisted folding of proteins overexpressed in Escherichia coli. Anal Biochem 254:150–152 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayet O, Ziegelhoffer T, Georgopoulos C (1989) The groES and groEL heat shock gene products of Escherichia coli are essential for bacterial growth at all temperatures. J Bacteriol 171:1379–1385 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine B, Davoine CS, Durr A, Paternotte C, Feki I, Weissenbach J, Hazan J, Brice A (2000) A new locus for autosomal dominant pure spastic paraplegia, on chromosome 2q24-q34. Am J Hum Genet 66:702–707 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazan J, Fonknechten N, Mavel D, Paternotte C, Samson D, Artiguenave F, Davoine CS, Cruaud C, Durr A, Wincker P, Brottier P, Cattolico L, Barbe V, Burgunder JM, Prud'homme JF, Brice A, Fontaine B, Heilig B, Weissenbach J (1999) Spastin, a new AAA protein, is altered in the most frequent form of autosomal dominant spastic paraplegia. Nat Genet 23:296–303 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer T (2000) AAA proteases: cellular machines for degrading membrane proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 25:247–251 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson A, Schwager F, Landry SJ, Georgopoulos C (2001) The importance of a mobile loop in regulating chaperonin/co-chaperonin interaction: humans versus Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 276:4981–4987 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavotinek AM, Biesecker LG (2001) Unfolding the role of chaperones and chaperonins in human disease. Trends Genet 17:528–535 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallaksen CM, Durr A, Brice A (2001) Recent advances in hereditary spastic paraplegia. Curr Opin Neurol 14:457–463 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu ZH, Horwich AL, Sigler PB (1997) The crystal structure of the asymmetric GroEL-GroES-(ADP)7 chaperonin complex. Nature 388:741–750 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao X, Alvarado D, Rainier S, Lemons R, Hedera P, Weber CH, Tukel T, Apak M, Heiman-Patterson T, Ming L, Bui M, Fink JK (2001) Mutations in a newly identified GTPase gene cause autosomal dominant hereditary spastic paraplegia. Nat Genet 29:326–331 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]