Abstract
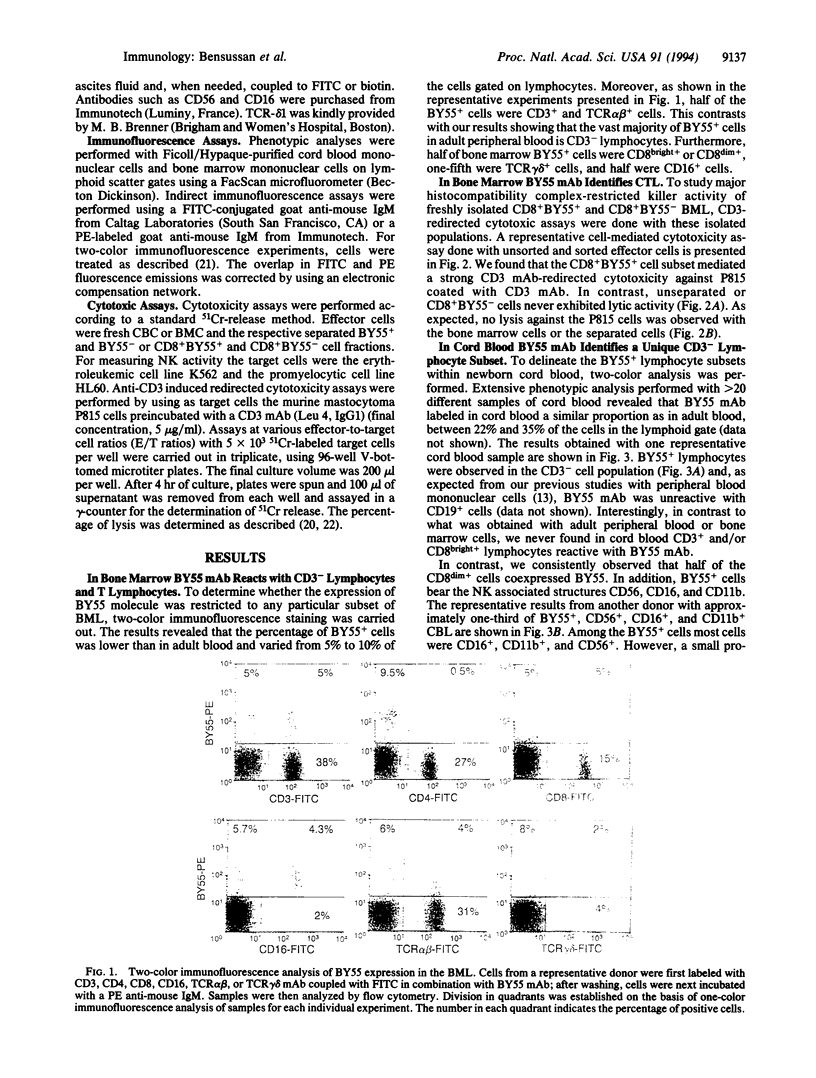
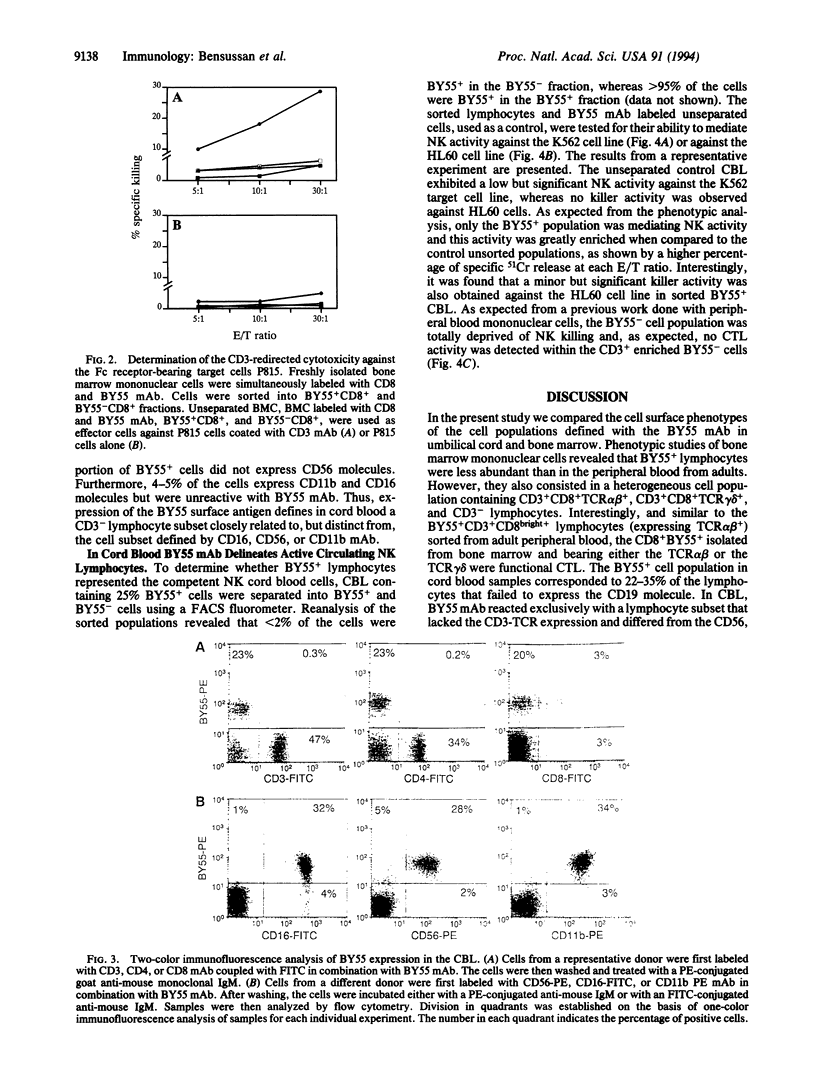
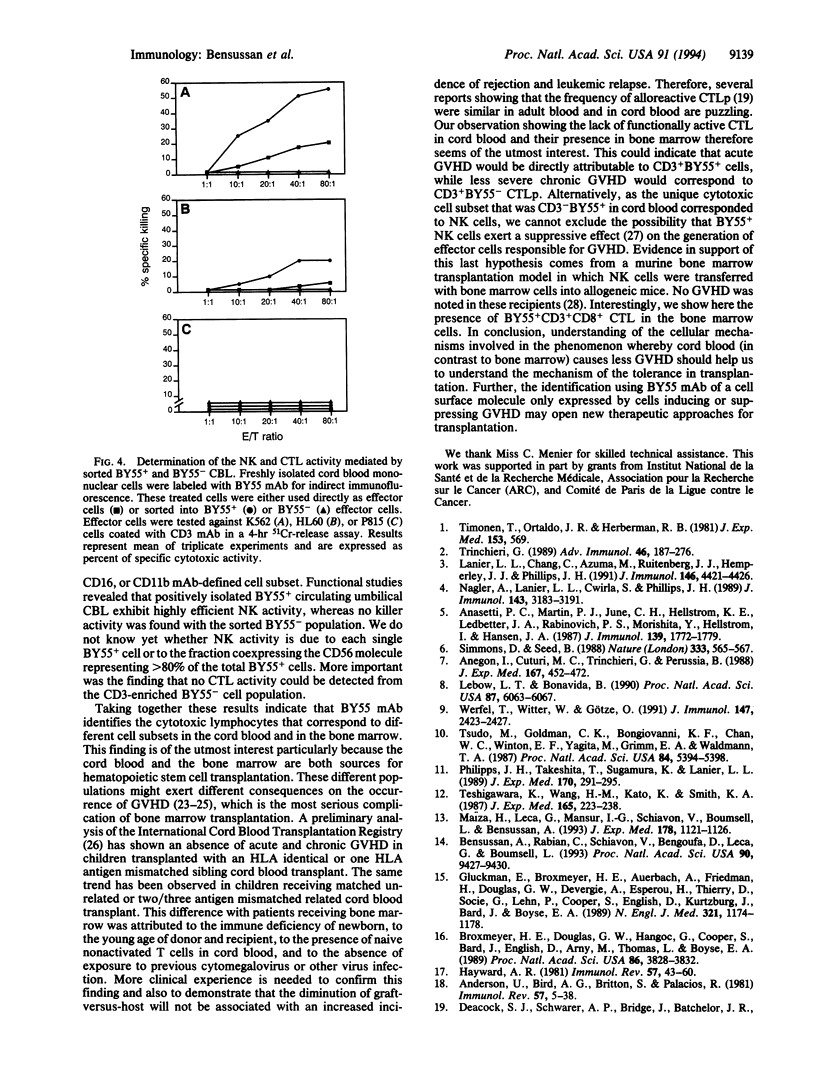
We had previously reported, using BY55 monoclonal antibody, a cell surface 80-kDa protein restricted to human functional peripheral blood cytotoxic lymphocytes with either natural killer CD3- or cytotoxic T lymphocyte CD3+CD8+ phenotype. In the present report, we studied the cytotoxic lymphocytes in adult bone marrow and newborn cord blood as these organs are commonly used as sources of hematological stem cells for allogeneic transplantation. Our results showed that BY55 mAb labeled only 5-10% of the bone marrow lymphocytes, which included a major proportion of CD3+ CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Interestingly, within cord blood cells, BY55+ lymphocytes represented 20-35% of the lymphocytes corresponding exclusively to a CD3- cell subset. Furthermore, we detected in cord blood no cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity but we demonstrated that the CD3-BY55+ cell subset contained the whole natural killer activity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abruzzo L. V., Mullen C. A., Rowley D. A. Immunoregulation by natural killer cells. Cell Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;98(2):266–278. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anasetti C., Martin P. J., June C. H., Hellstrom K. E., Ledbetter J. A., Rabinovitch P. S., Morishita Y., Hellstrom I., Hansen J. A. Induction of calcium flux and enhancement of cytolytic activity in natural killer cells by cross-linking of the sheep erythrocyte binding protein (CD2) and the Fc-receptor (CD16). J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1772–1779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson U., Bird A. G., Britton B. S., Palacios R. Humoral and cellular immunity in humans studied at the cell level from birth to two years of age. Immunol Rev. 1981;57:1–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anegón I., Cuturi M. C., Trinchieri G., Perussia B. Interaction of Fc receptor (CD16) ligands induces transcription of interleukin 2 receptor (CD25) and lymphokine genes and expression of their products in human natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):452–472. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensussan A., Klatzmann D., Gluckman J. C., Kalil J., Dausset J., Sasportes M. Probable role of suppressor cells and factors in kidney graft survival. Transplant Proc. 1982 Sep;14(3):584–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensussan A., Rabian C., Schiavon V., Bengoufa D., Leca G., Boumsell L. Significant enlargement of a specific subset of CD3+CD8+ peripheral blood leukocytes mediating cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activity during human immunodeficiency virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9427–9430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broxmeyer H. E., Douglas G. W., Hangoc G., Cooper S., Bard J., English D., Arny M., Thomas L., Boyse E. A. Human umbilical cord blood as a potential source of transplantable hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3828–3832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David V., Bourge J. F., Guglielmi P., Mathieu-Mahul D., Degos L., Bensussan A. Human T cell clones use a CD3-associated surface antigen recognition structure to exhibit both NK-like and allogeneic cytotoxic reactivity. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2831–2836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deacock S. J., Schwarer A. P., Bridge J., Batchelor J. R., Goldman J. M., Lechler R. I. Evidence that umbilical cord blood contains a higher frequency of HLA class II-specific alloreactive T cells than adult peripheral blood. A limiting dilution analysis. Transplantation. 1992 May;53(5):1128–1134. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199205000-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluckman E., Broxmeyer H. A., Auerbach A. D., Friedman H. S., Douglas G. W., Devergie A., Esperou H., Thierry D., Socie G., Lehn P. Hematopoietic reconstitution in a patient with Fanconi's anemia by means of umbilical-cord blood from an HLA-identical sibling. N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 26;321(17):1174–1178. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910263211707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouttefangeas C., Mansur I., Schmid M., Dastot H., Gélin C., Mahouy G., Boumsell L., Bensussan A. The CD39 molecule defines distinct cytotoxic subsets within alloactivated human CD8-positive cells. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Oct;22(10):2681–2685. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward A. R. Development of lymphocyte responses and interactions in the human fetus and newborn. Immunol Rev. 1981;57:39–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00441.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Chang C., Azuma M., Ruitenberg J. J., Hemperly J. J., Phillips J. H. Molecular and functional analysis of human natural killer cell-associated neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM/CD56). J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4421–4426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebow L. T., Bonavida B. Purification and characterization of cytolytic and noncytolytic human natural killer cell subsets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6063–6067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maïza H., Leca G., Mansur I. G., Schiavon V., Boumsell L., Bensussan A. A novel 80-kD cell surface structure identifies human circulating lymphocytes with natural killer activity. J Exp Med. 1993 Sep 1;178(3):1121–1126. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.3.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. J., Bennett M., Kumar V., Longo D. L. Donor-type activated natural killer cells promote marrow engraftment and B cell development during allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Immunol. 1992 May 1;148(9):2953–2960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagler A., Lanier L. L., Cwirla S., Phillips J. H. Comparative studies of human FcRIII-positive and negative natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3183–3191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Heterogeneity of natural killer cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:359–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Takeshita T., Sugamura K., Lanier L. L. Activation of natural killer cells via the p75 interleukin 2 receptor. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):291–296. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolstad B., Benestad H. B. The "natural resistance" to bone marrow allografts in normal and athymic nude rats. Rapid cytotoxic reactions both in vivo and in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Sep;14(9):793–799. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj P., Rosse W. F., Silber R., Springer T. A. The major Fc receptor in blood has a phosphatidylinositol anchor and is deficient in paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):565–567. doi: 10.1038/333565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teshigawara K., Wang H. M., Kato K., Smith K. A. Interleukin 2 high-affinity receptor expression requires two distinct binding proteins. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):223–238. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Characteristics of human large granular lymphocytes and relationship to natural killer and K cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):569–582. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. Biology of natural killer cells. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:187–376. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60664-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudo M., Goldman C. K., Bongiovanni K. F., Chan W. C., Winton E. F., Yagita M., Grimm E. A., Waldmann T. A. The p75 peptide is the receptor for interleukin 2 expressed on large granular lymphocytes and is responsible for the interleukin 2 activation of these cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5394–5398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werfel T., Witter W., Götze O. CD11b and CD11c antigens are rapidly increased on human natural killer cells upon activation. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2423–2427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





