Abstract
The posttranslational addition of a farnesyl moiety to the Ras oncoprotein is essential for its transforming activity. Cell-active inhibitors of the enzyme that catalyzes this reaction, protein farnesyltransferase, have been shown to selectively block ras-dependent transformation of cells in culture. Here we describe the protein farnesyltransferase inhibitor 2(S)-[2(S)-[2(R)-amino-3-mercapto]propylamino-3(S)-methyl] pentyloxy-3-phenylpropionylmethioninesulfone methyl ester (L-739,749), which suppressed the anchorage-independent growth of Rat1 cells transformed with viral H-ras and the human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line PSN-1, which harbors altered K-ras, myc, and p53 genes. This compound also suppressed the growth of tumors arising from ras-transformed Rat1 cells in nude mice by 66%. Under the same conditions, doxorubicin inhibited tumor growth by 33%. Control tumors formed by v-raf- or v-mos-transformed Rat1 cells were unaffected by L-739,749. Furthermore, mice treated with L-739,749 exhibited no evidence of systemic toxicity. This is a demonstration of antitumor activity in vivo using a synthetic small molecule inhibitor of protein farnesyltransferase.
Full text
PDF

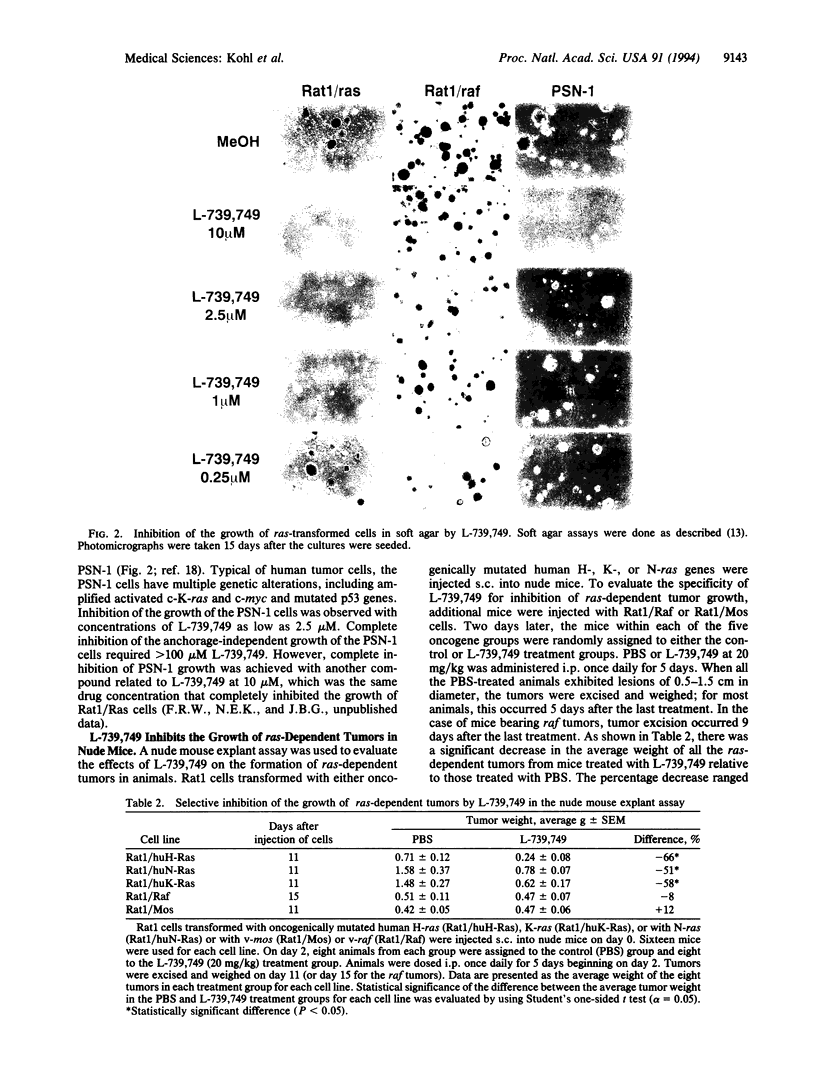


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 1989 Sep 1;49(17):4682–4689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplin B. E., Hettich L. A., Marshall M. S. Substrate characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein farnesyltransferase and type-I protein geranylgeranyltransferase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Mar 16;1205(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(94)90089-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Solski P. A., Der C. J., Buss J. E. p21ras is modified by a farnesyl isoprenoid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8323–8327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox A. D., Der C. J. The ras/cholesterol connection: implications for ras oncogenicity. Crit Rev Oncog. 1992;3(4):365–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox A. D., Hisaka M. M., Buss J. E., Der C. J. Specific isoprenoid modification is required for function of normal, but not oncogenic, Ras protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2606–2615. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Der C. J., Finkel T., Cooper G. M. Biological and biochemical properties of human rasH genes mutated at codon 61. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90495-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feig L. A., Cooper G. M. Inhibition of NIH 3T3 cell proliferation by a mutant ras protein with preferential affinity for GDP. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3235–3243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia A. M., Rowell C., Ackermann K., Kowalczyk J. J., Lewis M. D. Peptidomimetic inhibitors of Ras farnesylation and function in whole cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18415–18418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Oliff A., Kohl N. E. Farnesyltransferase inhibitors: Ras research yields a potential cancer therapeutic. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B. Ras C-terminal processing enzymes--new drug targets? Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90352-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haag J. D., Lindstrom M. J., Gould M. N. Limonene-induced regression of mammary carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1992 Jul 15;52(14):4021–4026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Magee A. I., Childs J. E., Marshall C. J. All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara M., Akasaka K., Akinaga S., Okabe M., Nakano H., Gomez R., Wood D., Uh M., Tamanoi F. Identification of Ras farnesyltransferase inhibitors by microbial screening. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2281–2285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. H., Cochrane C. G., Bourne J. R., Solski P. A., Buss J. E., Der C. J. Farnesol modification of Kirsten-ras exon 4B protein is essential for transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3042–3046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James G. L., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Rawson T. E., Somers T. C., McDowell R. S., Crowley C. W., Lucas B. K., Levinson A. D., Marsters J. C., Jr Benzodiazepine peptidomimetics: potent inhibitors of Ras farnesylation in animal cells. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1937–1942. doi: 10.1126/science.8316834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Cox A. D., Hisaka M. M., Graham S. M., Buss J. E., Der C. J. Isoprenoid addition to Ras protein is the critical modification for its membrane association and transforming activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6403–6407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitten G. T., Nigg E. A. The CaaX motif is required for isoprenylation, carboxyl methylation, and nuclear membrane association of lamin B2. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):13–23. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Mosser S. D., deSolms S. J., Giuliani E. A., Pompliano D. L., Graham S. L., Smith R. L., Scolnick E. M., Oliff A., Gibbs J. B. Selective inhibition of ras-dependent transformation by a farnesyltransferase inhibitor. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1934–1937. doi: 10.1126/science.8316833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moores S. L., Schaber M. D., Mosser S. D., Rands E., O'Hara M. B., Garsky V. M., Marshall M. S., Pompliano D. L., Gibbs J. B. Sequence dependence of protein isoprenylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14603–14610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam M., Seong C. M., Qian Y., Hamilton A. D., Sebti S. M. Potent inhibition of human tumor p21ras farnesyltransferase by A1A2-lacking p21ras CA1A2X peptidomimetics. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):20695–20698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omer C. A., Kral A. M., Diehl R. E., Prendergast G. C., Powers S., Allen C. M., Gibbs J. B., Kohl N. E. Characterization of recombinant human farnesyl-protein transferase: cloning, expression, farnesyl diphosphate binding, and functional homology with yeast prenyl-protein transferases. Biochemistry. 1993 May 18;32(19):5167–5176. doi: 10.1021/bi00070a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Davide J. P., deSolms S. J., Giuliani E. A., Graham S. L., Gibbs J. B., Oliff A., Kohl N. E. Farnesyltransferase inhibition causes morphological reversion of ras-transformed cells by a complex mechanism that involves regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):4193–4202. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.4193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss Y., Goldstein J. L., Seabra M. C., Casey P. J., Brown M. S. Inhibition of purified p21ras farnesyl:protein transferase by Cys-AAX tetrapeptides. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Der C. J., Verma I. M. ras-induced neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells: possible involvement of fos and jun. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3174–3183. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaber M. D., O'Hara M. B., Garsky V. M., Mosser S. C., Bergstrom J. D., Moores S. L., Marshall M. S., Friedman P. A., Dixon R. A., Gibbs J. B. Polyisoprenylation of Ras in vitro by a farnesyl-protein transferase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14701–14704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebti S. M., Tkalcevic G. T., Jani J. P. Lovastatin, a cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor, inhibits the growth of human H-ras oncogene transformed cells in nude mice. Cancer Commun. 1991 May;3(5):141–147. doi: 10.3727/095535491820873371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirasawa S., Furuse M., Yokoyama N., Sasazuki T. Altered growth of human colon cancer cell lines disrupted at activated Ki-ras. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):85–88. doi: 10.1126/science.8465203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., DeGudicibus S. J., Stacey D. W. Requirement for c-ras proteins during viral oncogene transformation. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):540–543. doi: 10.1038/320540a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Roudebush M., Day R., Mosser S. D., Gibbs J. B., Feig L. A. Dominant inhibitory Ras mutants demonstrate the requirement for Ras activity in the action of tyrosine kinase oncogenes. Oncogene. 1991 Dec;6(12):2297–2304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trueblood C. E., Ohya Y., Rine J. Genetic evidence for in vivo cross-specificity of the CaaX-box protein prenyltransferases farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase-I in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4260–4275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Norris K., Papageorge A. G., Hubbert N. L., Lowy D. R. Harvey murine sarcoma virus p21 ras protein: biological and biochemical significance of the cysteine nearest the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2581–2585. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Yoshida T., Sakamoto H., Terada M., Sugimura T. Establishment of a human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell line (PSN-1) with amplifications of both c-myc and activated c-Ki-ras by a point mutation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 15;140(1):167–173. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F. L., Diehl R. E., Kohl N. E., Gibbs J. B., Giros B., Casey P. J., Omer C. A. cDNA cloning and expression of rat and human protein geranylgeranyltransferase type-I. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3175–3180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




