Abstract
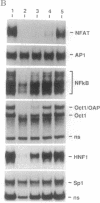
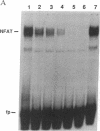
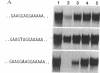
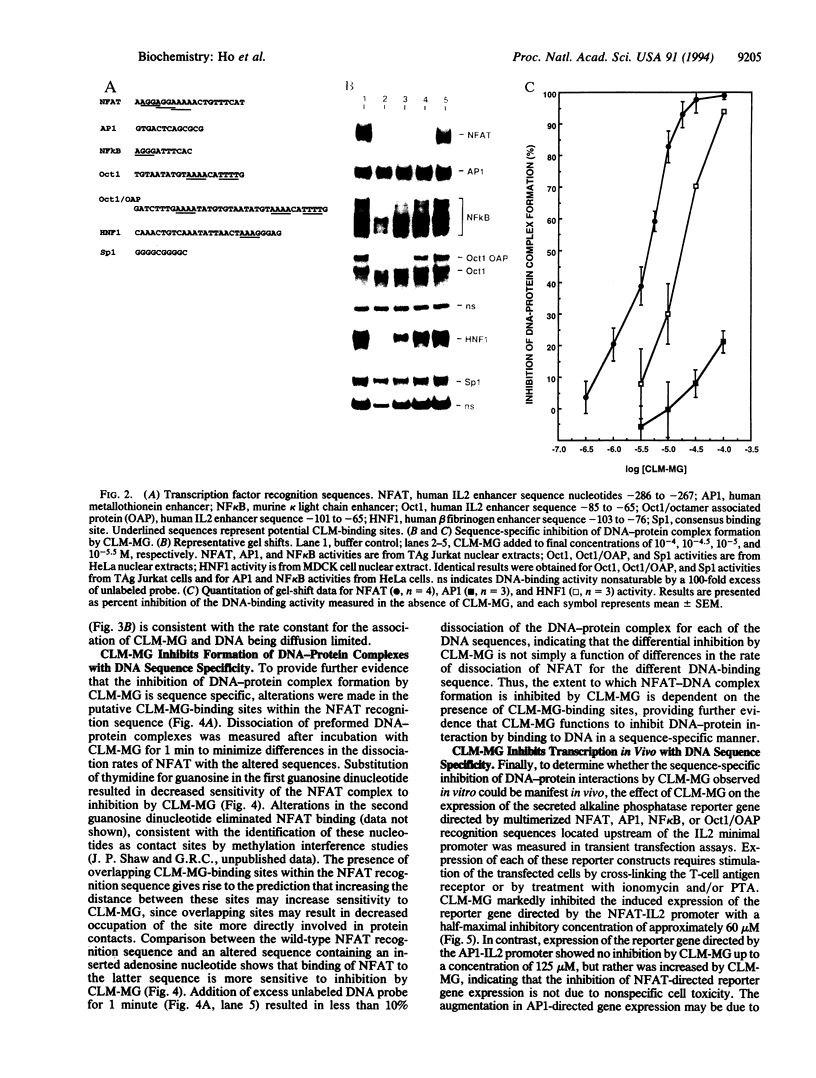
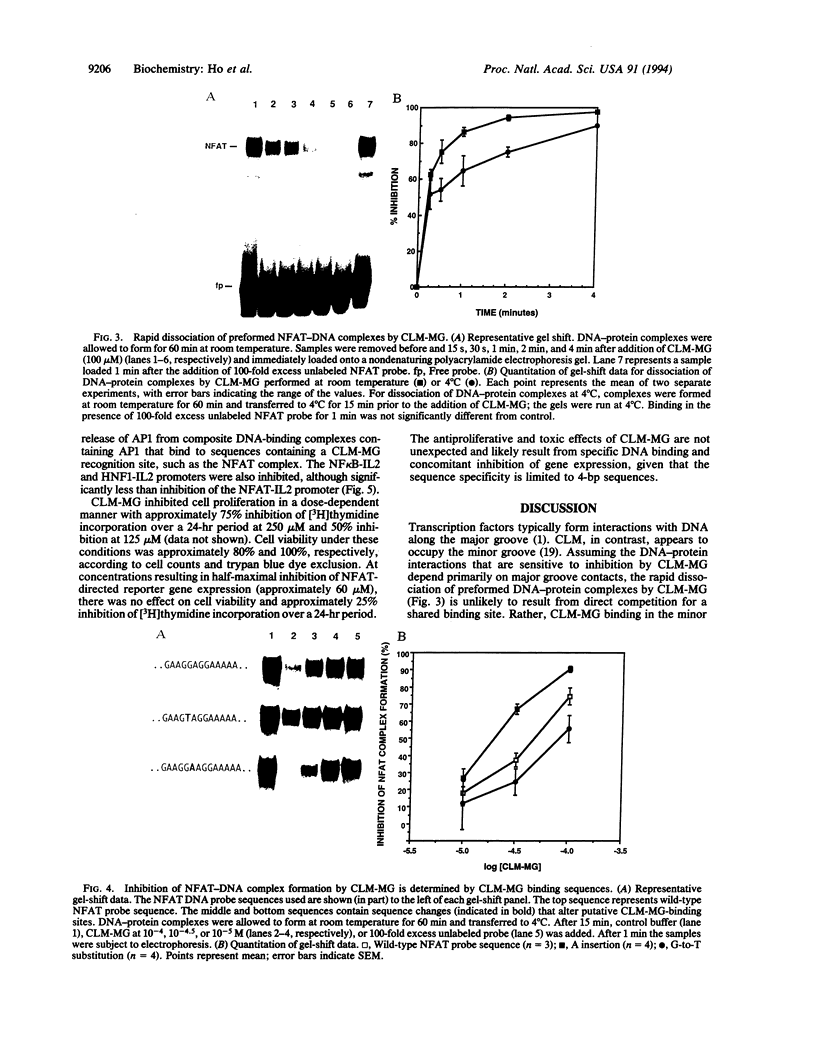
Sequence-specific DNA ligands that antagonize DNA-protein interactions represent a potentially powerful means of modulating gene expression. Calicheamicin gamma 1I, a member of the DNA-cleaving enediyne class of anticancer antibiotics, binds to specific DNA sequences through an aryltetrasaccharide domain. To take advantage of this unique sequence-specific recognition capability, the methyl glycoside of the aryltetrasaccharide of calicheamicin gamma 1I (CLM-MG) was used to investigate the ability of glycoconjugate DNA ligands to inhibit DNA-protein interactions. CLM-MG inhibits the formation of DNA-protein complexes at micromolar concentrations in a sequence-specific manner and rapidly dissociates preformed complexes. CLM-MG also inhibits transcription in vivo with similar sequence specificity. These results suggest a strategy for the development of a class of novel biological probes and therapeutic agents.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 10;1072(2-3):129–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beal P. A., Dervan P. B. Second structural motif for recognition of DNA by oligonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2003222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Hauber J., Hauber R., Geiger R., Cullen B. R. Secreted placental alkaline phosphatase: a powerful new quantitative indicator of gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Gene. 1988 Jun 15;66(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broggini M., Ponti M., Ottolenghi S., D'Incalci M., Mongelli N., Mantovani R. Distamycins inhibit the binding of OTF-1 and NFE-1 transfactors to their conserved DNA elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1051–1059. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll M., Frederick C. A., Wang A. H., Rich A. A bifurcated hydrogen-bonded conformation in the d(A.T) base pairs of the DNA dodecamer d(CGCAAATTTGCG) and its complex with distamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8385–8389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danishefsky S. J., McClure K. F., Randolph J. T., Ruggeri R. B. A strategy for the solid-phase synthesis of oligosaccharides. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1307–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.8493573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Affolter M., Müller M., Gehring W. J., Leupin W. Distamycin-induced inhibition of homeodomain-DNA complexes. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):279–286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drak J., Iwasawa N., Danishefsky S., Crothers D. M. The carbohydrate domain of calicheamicin gamma I1 determines its sequence specificity for DNA cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7464–7468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand D. B., Bush M. R., Morgan J. G., Weiss A., Crabtree G. R. A 275 basepair fragment at the 5' end of the interleukin 2 gene enhances expression from a heterologous promoter in response to signals from the T cell antigen receptor. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):395–407. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiering S., Northrop J. P., Nolan G. P., Mattila P. S., Crabtree G. R., Herzenberg L. A. Single cell assay of a transcription factor reveals a threshold in transcription activated by signals emanating from the T-cell antigen receptor. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1823–1834. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanvey J. C., Peffer N. J., Bisi J. E., Thomson S. A., Cadilla R., Josey J. A., Ricca D. J., Hassman C. F., Bonham M. A., Au K. G. Antisense and antigene properties of peptide nucleic acids. Science. 1992 Nov 27;258(5087):1481–1485. doi: 10.1126/science.1279811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley R. C., Kiessling L. L., Schreiber S. L. Model of the interactions of calichemicin gamma 1 with a DNA fragment from pBR322. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1105–1109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hélène C. The anti-gene strategy: control of gene expression by triplex-forming-oligonucleotides. Anticancer Drug Des. 1991 Dec;6(6):569–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klevit R. E., Wemmer D. E., Reid B. R. 1H NMR studies on the interaction between distamycin A and a symmetrical DNA dodecamer. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3296–3303. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käs E., Izaurralde E., Laemmli U. K. Specific inhibition of DNA binding to nuclear scaffolds and histone H1 by distamycin. The role of oligo(dA).oligo(dT) tracts. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 5;210(3):587–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel D. B., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1, a member of a novel class of dimerizing homeodomain proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):677–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaou K. C., Dai W. M., Tsay S. C., Estevez V. A., Wrasidlo W. Designed enediynes: a new class of DNA-cleaving molecules with potent and selective anticancer activity. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1172–1178. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaou K. C., Smith A. L., Yue E. W. Chemistry and biology of natural and designed enediynes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5881–5888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrop J. P., Ullman K. S., Crabtree G. R. Characterization of the nuclear and cytoplasmic components of the lymphoid-specific nuclear factor of activated T cells (NF-AT) complex. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2917–2923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley M. G., Mrksich M., Dervan P. B. Evidence that a minor groove-binding peptide and a major groove-binding protein can simultaneously occupy a common site on DNA. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 17;31(45):10969–10975. doi: 10.1021/bi00160a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1053–1095. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park Y. W., Breslauer K. J. Drug binding to higher ordered DNA structures: netropsin complexation with a nucleic acid triple helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6653–6657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Heguy A., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human lymphoid-specific octamer-binding protein (OTF-2) that activates transcription of an immunoglobulin promoter in vitro. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):783–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer D. M., Wandless T. J., Schreiber S. L., Crabtree G. R. Controlling signal transduction with synthetic ligands. Science. 1993 Nov 12;262(5136):1019–1024. doi: 10.1126/science.7694365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A. Why bend DNA? Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90729-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman K. S., Flanagan W. M., Edwards C. A., Crabtree G. R. Activation of early gene expression in T lymphocytes by Oct-1 and an inducible protein, OAP40. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):558–562. doi: 10.1126/science.1683003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S., Landovitz R., Ding W. D., Ellestad G. A., Kahne D. Cleavage behavior of calicheamicin gamma 1 and calicheamicin T. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4608–4612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zein N., Poncin M., Nilakantan R., Ellestad G. A. Calicheamicin gamma 1I and DNA: molecular recognition process responsible for site-specificity. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):697–699. doi: 10.1126/science.2717946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zein N., Sinha A. M., McGahren W. J., Ellestad G. A. Calicheamicin gamma 1I: an antitumor antibiotic that cleaves double-stranded DNA site specifically. Science. 1988 May 27;240(4856):1198–1201. doi: 10.1126/science.3240341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer C., Wähnert U. Nonintercalating DNA-binding ligands: specificity of the interaction and their use as tools in biophysical, biochemical and biological investigations of the genetic material. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1986;47(1):31–112. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(86)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]