Abstract
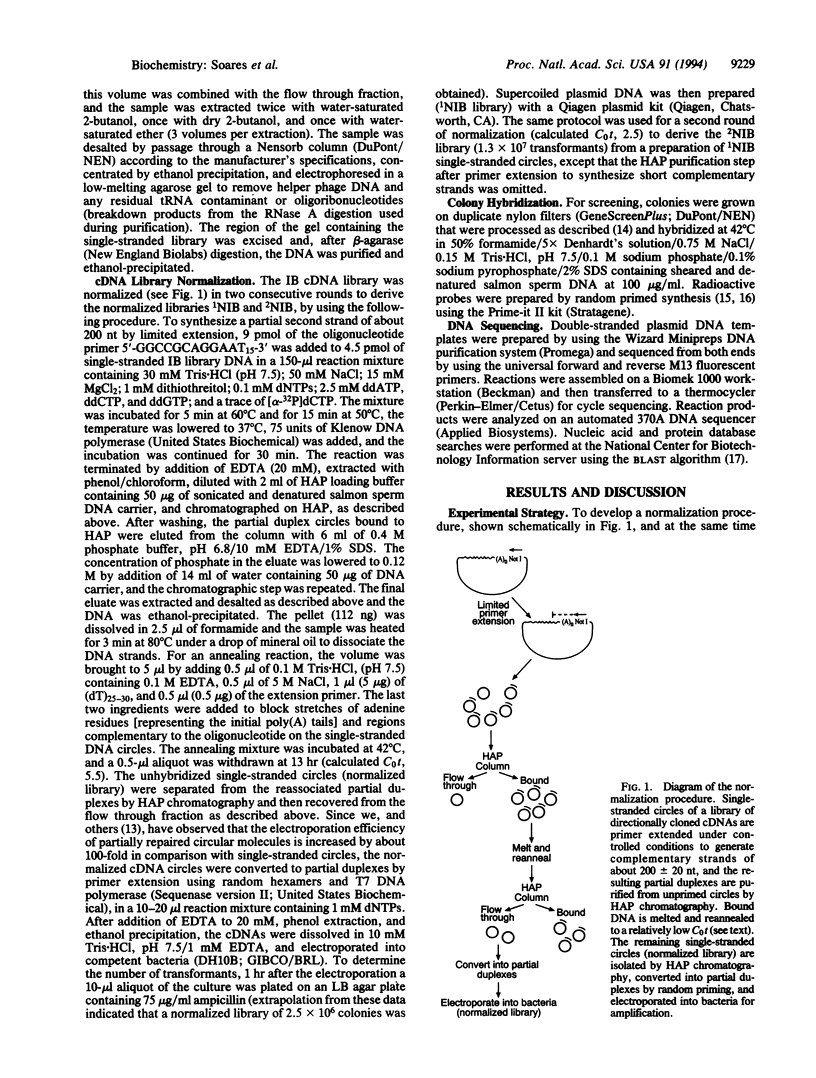
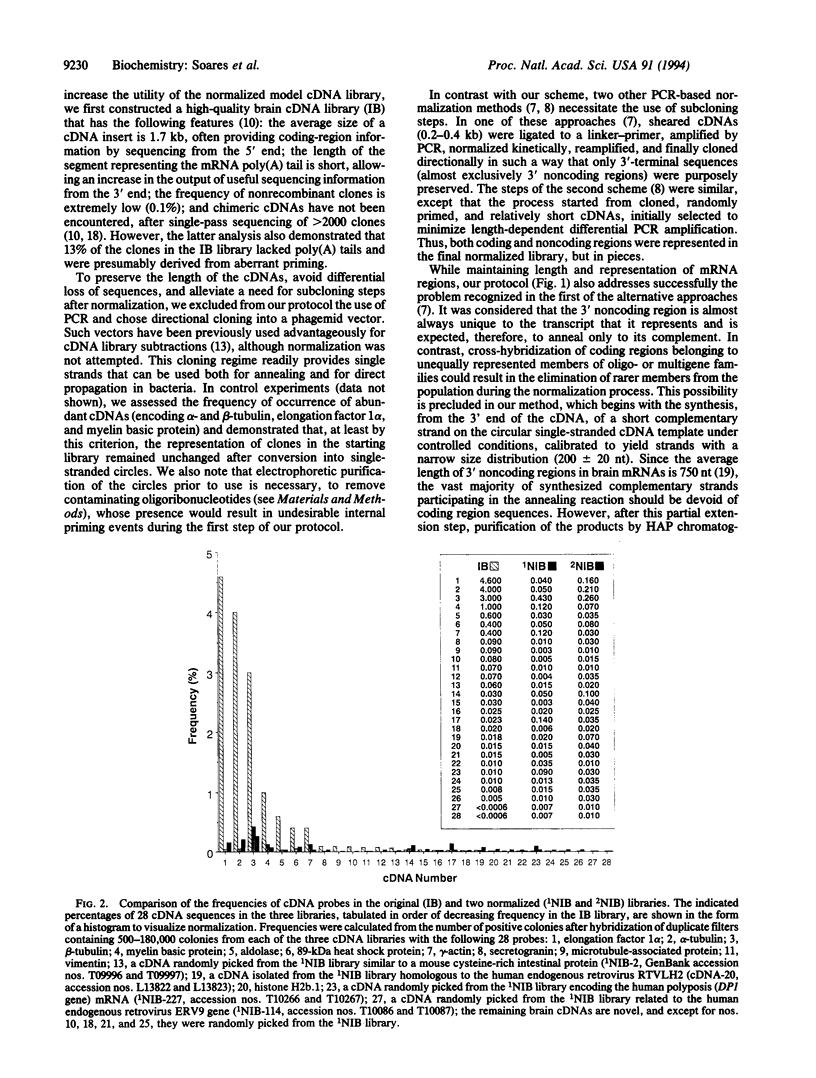
We have developed a simple procedure based on reassociation kinetics that can reduce effectively the high variation in abundance among the clones of a cDNA library that represent individual mRNA species. For this normalization, we used as a model system a library of human infant brain cDNAs that were cloned directionally into a phagemid vector and, thus, could be easily converted into single-stranded circles. After controlled primer extension to synthesize a short complementary strand on each circular template, melting and reannealing of the partial duplexes at relatively low C0t, and hydroxyapatite column chromatography, unreassociated circles were recovered from the flow through fraction and electroporated into bacteria, to propagate a normalized library without a requirement for subcloning steps. An evaluation of the extent of normalization has indicated that, from an extreme range of abundance of 4 orders of magnitude in the original library, the frequency of occurrence of any clone examined in the normalized library was brought within the narrow range of only 1 order of magnitude.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. D., Soares M. B., Kerlavage A. R., Fields C., Venter J. C. Rapid cDNA sequencing (expressed sequence tags) from a directionally cloned human infant brain cDNA library. Nat Genet. 1993 Aug;4(4):373–380. doi: 10.1038/ng0893-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bantle J. A., Hahn W. E. Complexity and characterization of polyadenylated RNA in the mouse brain. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):139–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90195-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga S. J., Linnenbach A. J., Malcolm S., Ghosh P., Malcolm A. D., Takeshita K., Forget B. G., Benz E. J., Jr Polyadenylation of a human mitochondrial ribosomal RNA transcript detected by molecular cloning. Gene. 1985;35(3):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Morton J. G., Rosbash M., Richardson M. Three abundance classes in HeLa cell messenger RNA. Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):199–204. doi: 10.1038/250199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhari N., Hahn W. E. Genetic expression in the developing brain. Science. 1983 May 27;220(4600):924–928. doi: 10.1126/science.6189184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christianson T. W., Clayton D. A. A tridecamer DNA sequence supports human mitochondrial RNA 3'-end formation in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4502–4509. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Regulation of gene expression: possible role of repetitive sequences. Science. 1979 Jun 8;204(4397):1052–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.451548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galau G. A., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Studies on nucleic acid reassociation kinetics: rate of hybridization of excess RNA with DNA, compared to the rate of DNA renaturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1020–1023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grouse L. D., Schrier B. K., Bennett E. L., Rosenzweig M. R., Nelson P. G. Sequence diversity studies of rat brain RNA: effects of environmental complexity on rat brain RNA diversity. J Neurochem. 1978 Jan;30(1):191–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb07052.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn W. E., Van Ness J., Maxwell I. H. Complex population of mRNA sequences in large polyadenylylated nuclear RNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5544–5547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins J. D. A survey on intron and exon lengths. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):9893–9908. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.9893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. S., Wilcox A. S., Polymeropoulos M. H., Hopkins J. A., Stevens T. J., Robinson M., Orpana A. K., Sikela J. M. Single pass sequencing and physical and genetic mapping of human brain cDNAs. Nat Genet. 1992 Nov;2(3):180–185. doi: 10.1038/ng1192-180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko M. S. An 'equalized cDNA library' by the reassociation of short double-stranded cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5705–5711. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazo A. M., Minchenko A. G., Avdonina T. A., Gause G. G., Jr, Pusyriov A. T. Discrete poly(A)- RNA species from rat liver mitochondria are fragments of 16S mitochondrial rRNA carrying its 5'-termini. Mol Biol Rep. 1983 Aug;9(3):155–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00775361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner R. J., Sutcliffe J. G. Gene expression in rat brain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5497–5520. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patanjali S. R., Parimoo S., Weissman S. M. Construction of a uniform-abundance (normalized) cDNA library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1943–1947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. A program for least squares analysis of reassociation and hybridization data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jun;4(6):1727–1737. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.6.1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein J. L., Brice A. E., Ciaranello R. D., Denney D., Porteus M. H., Usdin T. B. Subtractive hybridization system using single-stranded phagemids with directional inserts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4833–4842. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki Y. F., Ayusawa D., Oishi M. Construction of a normalized cDNA library by introduction of a semi-solid mRNA-cDNA hybridization system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Mar 25;22(6):987–992. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.6.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider B. J., Morrison-Bogorad M. Brain non-adenylated mRNAs. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1992 Sep-Dec;17(3):263–282. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(92)90019-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ness J., Hahn W. E. Physical parameters affecting the rate and completion of RNA driven hybridization of DNA: new measurements relevant to quantitation based on kinetics. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8061–8077. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman S. M. Molecular genetic techniques for mapping the human genome. Mol Biol Med. 1987 Jun;4(3):133–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., Liu J. P., Efstratiadis A. Cloning of PCR-amplified total cDNA: construction of a mouse oocyte cDNA library. Genet Anal Tech Appl. 1990 Feb;7(1):5–17. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(90)90038-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winick M. Changes in nucleic acid and protein content of the human brain during growth. Pediatr Res. 1968 Sep;2(5):352–355. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196809000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]