Fig. 1.
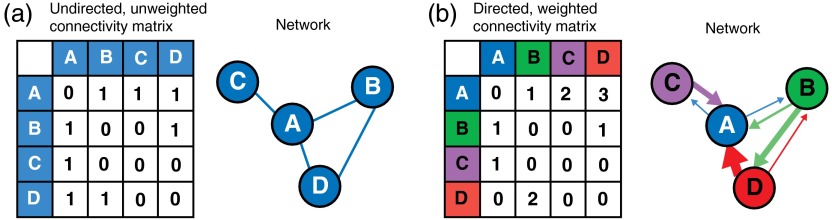
Construction of network diagrams from connectivity matrices: (a) example of a simple unweighted (binary), undirected connectivity matrix and network. Note that the connectivity matrix is symmetrical across the diagonal because all edges are reciprocal ( and are equivalent); (b) example of a weighted, directed connectivity matrix and network. The thickness of the edges corresponds to the weight of the edge. Note that the edges in the network diagram display a direction (arrowheads), and connections between nodes are not always reciprocal (for example, while there is a strong efferent connection from D to A, there is no afferent connection from A to D).
