Abstract
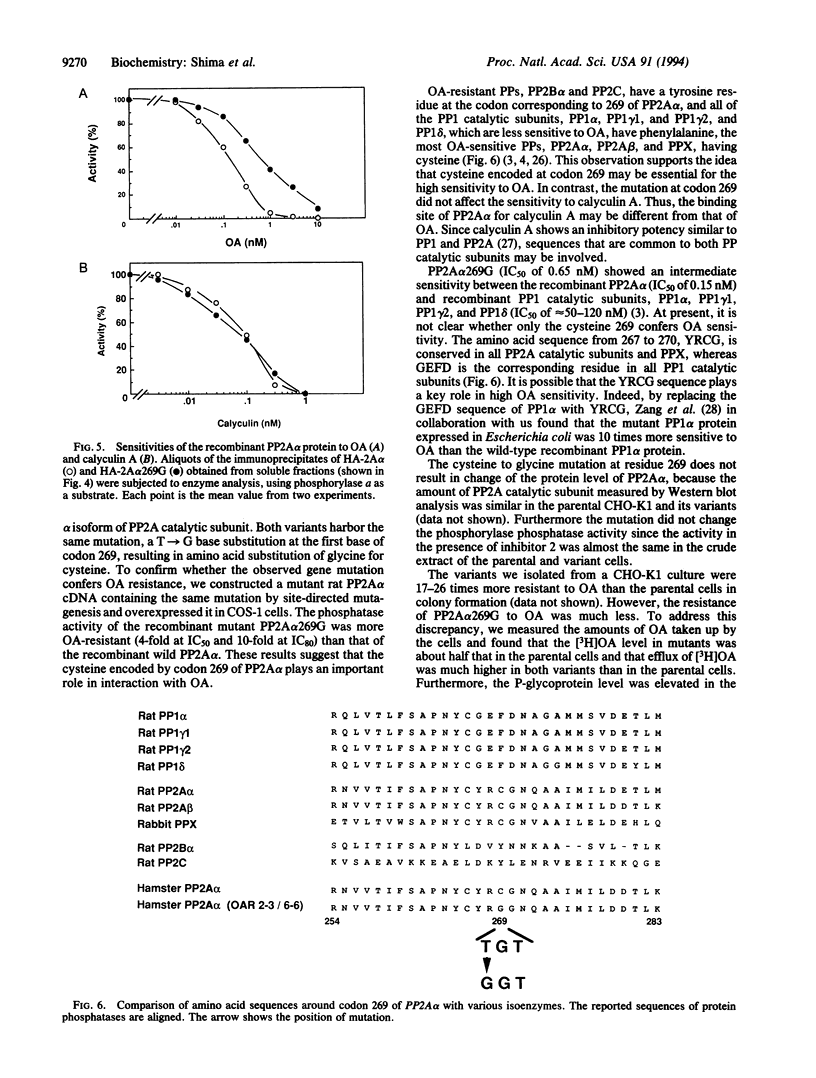
Okadaic acid (OA)-resistant variants of Chinese hamster ovary cells, clones CHO/OAR6-6 and CHO/OAR2-3, were isolated from a CHO-K1 culture. These variant cells were 17- to 26-fold more resistant to OA than the parental cells. The phosphorylase phosphatase activity of the variant cell extracts was 2- to 4-fold more resistant to OA than that of the parental cells in the presence of inhibitor 2, a specific inhibitor of type 1 protein serine/threonine phosphatase (PP1). Nucleotide sequencing of PP2A alpha (an isotype of PP2A catalytic subunit) cDNA demonstrated that both variants have a T-->G transversion at the first base of codon 269 (805 nt), which results in substitution of glycine for cysteine. We expressed in COS-1 cells a mutant PP2A alpha tagged with the influenza hemagglutinin epitope. The recombinant mutant PP2A alpha protein immunoprecipitated with an anti-influenza hemagglutinin antibody was more resistant than the wild type to OA, their IC50 values being 0.65 nM and 0.15 nM, and their IC80 values being 4.0 nM and 0.45 nM, respectively. The cysteine at residue 269 present only in highly OA-sensitive protein serine/threonine phosphatase catalytic subunit isozymes, PP2A alpha, PP2A beta, and PPX, is suggested to be involved in the binding of OA. CHO/OAR6-6 and CHO/OAR2-3 cells also overexpressed the P-glycoprotein, and the efflux of OA was more rapid. It is suggested that the PP2A alpha mutation in cooperation with a high level of P-glycoprotein makes the CHO-K1 variants highly resistant to OA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Afshari C. A., Kodama S., Bivins H. M., Willard T. B., Fujiki H., Barrett J. C. Induction of neoplastic progression in Syrian hamster embryo cells treated with protein phosphatase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 1993 Apr 15;53(8):1777–1782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aonuma S., Ushijima T., Nakayasu M., Shima H., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Mutation induction by okadaic acid, a protein phosphatase inhibitor, in CHL cells, but not in S. typhimurium. Mutat Res. 1991 Sep-Oct;250(1-2):375–381. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(91)90194-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewis N. D., Street A. J., Prescott A. R., Cohen P. T. PPX, a novel protein serine/threonine phosphatase localized to centrosomes. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):987–996. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05739.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Alemany S., Hemmings B. A., Resink T. J., Strålfors P., Tung H. Y. Protein phosphatase-1 and protein phosphatase-2A from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:390–408. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Holmes C. F., Tsukitani Y. Okadaic acid: a new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90192-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean N. M., Mordan L. J., Tse K., Mooberry S. L., Boynton A. L. Okadaic acid inhibits PDGF-induced proliferation and decreases PDGF receptor number in C3H/10T1/2 mouse fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Apr;12(4):665–670. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.4.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki H. Is the inhibition of protein phosphatase 1 and 2A activities a general mechanism of tumor promotion in human cancer development? Mol Carcinog. 1992;5(2):91–94. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940050202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hijikata M., Mizushima H., Akagi T., Mori S., Kakiuchi N., Kato N., Tanaka T., Kimura K., Shimotohno K. Two distinct proteinase activities required for the processing of a putative nonstructural precursor protein of hepatitis C virus. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4665–4675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4665-4675.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka Y., Shima H., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Detection of phosphorylated retTPC oncogene product in cytoplasm. Oncogene. 1992 Jul;7(7):1441–1444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim T. A., Velasquez B. R., Wenner C. E. Okadaic acid regulation of the retinoblastoma gene product is correlated with the inhibition of growth factor-induced cell proliferation in mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5460–5463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa Y., Tahira T., Ikeda I., Kikuchi K., Tsuiki S., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Molecular cloning of cDNA for the catalytic subunit of rat liver type 2A protein phosphatase, and detection of high levels of expression of the gene in normal and cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Nov 10;951(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
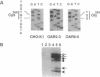
- Orita M., Suzuki Y., Sekiya T., Hayashi K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):874–879. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park I. K., Roach P., Bondor J., Fox S. P., DePaoli-Roach A. A. Molecular mechanism of the synergistic phosphorylation of phosphatase inhibitor-2. Cloning, expression, and site-directed mutagenesis of inhibitor-2. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):944–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai R., Ikeda I., Kitani H., Fujiki H., Takaku F., Rapp U., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Flat reversion by okadaic acid of raf and ret-II transformants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9946–9950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Shima H., Kitagawa Y., Irino S., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Identification of members of the protein phosphatase 1 gene family in the rat and enhanced expression of protein phosphatase 1 alpha gene in rat hepatocellular carcinomas. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1990 Dec;81(12):1272–1280. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1990.tb02690.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A., Feramisco J. R. Inhibition of histone H1 kinase expression, retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation, and cell proliferation by the phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):433–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shima H., Haneji T., Hatano Y., Kasugai I., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Protein phosphatase 1 gamma 2 is associated with nuclei of meiotic cells in rat testis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Jul 30;194(2):930–937. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suganuma M., Fujiki H., Okabe S., Nishiwaki S., Brautigan D., Ingebritsen T. S., Rosner M. R. Structurally different members of the okadaic acid class selectively inhibit protein serine/threonine but not tyrosine phosphatase activity. Toxicon. 1992 Aug;30(8):873–878. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(92)90385-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suganuma M., Fujiki H., Suguri H., Yoshizawa S., Hirota M., Nakayasu M., Ojika M., Wakamatsu K., Yamada K., Sugimura T. Okadaic acid: an additional non-phorbol-12-tetradecanoate-13-acetate-type tumor promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1768–1771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohda H., Nagao M., Sugimura T., Oikawa A. Okadaic acid, a protein phosphatase inhibitor, induces sister-chromatid exchanges depending on the presence of bromodeoxyuridine. Mutat Res. 1993 Oct;289(2):275–280. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(93)90078-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadzinski B. E., Eisfelder B. J., Peruski L. F., Jr, Mumby M. C., Johnson G. L. NH2-terminal modification of the phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit allows functional expression in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 25;267(24):16883–16888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z., Bai G., Shima M., Zhao S., Nagao M., Lee E. Y. Expression and characterization of rat protein phosphatases-1 alpha, -1 gamma 1, -1 gamma 2, and -1 delta. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Jun;303(2):402–406. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
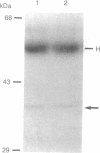
- Zhang Z., Zhao S., Long F., Zhang L., Bai G., Shima H., Nagao M., Lee E. Y. A mutant of protein phosphatase-1 that exhibits altered toxin sensitivity. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 24;269(25):16997–17000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]