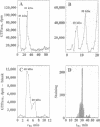
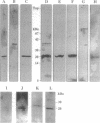
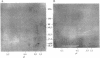
Abstract
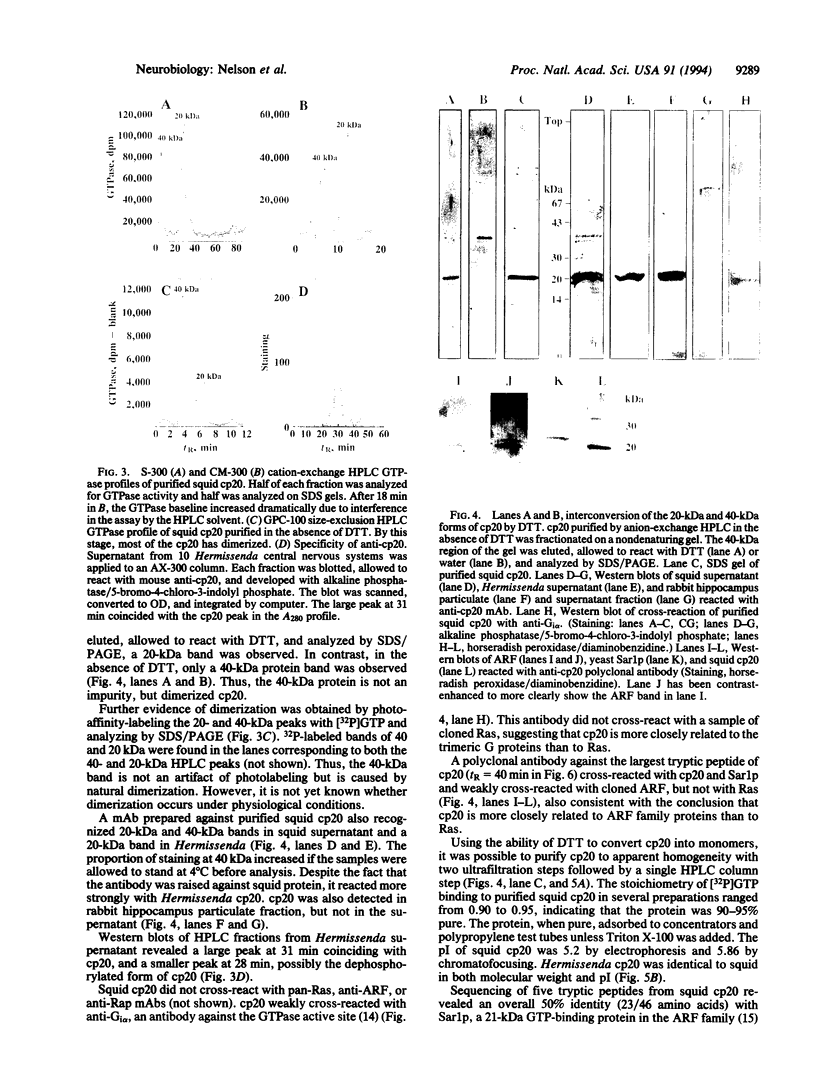
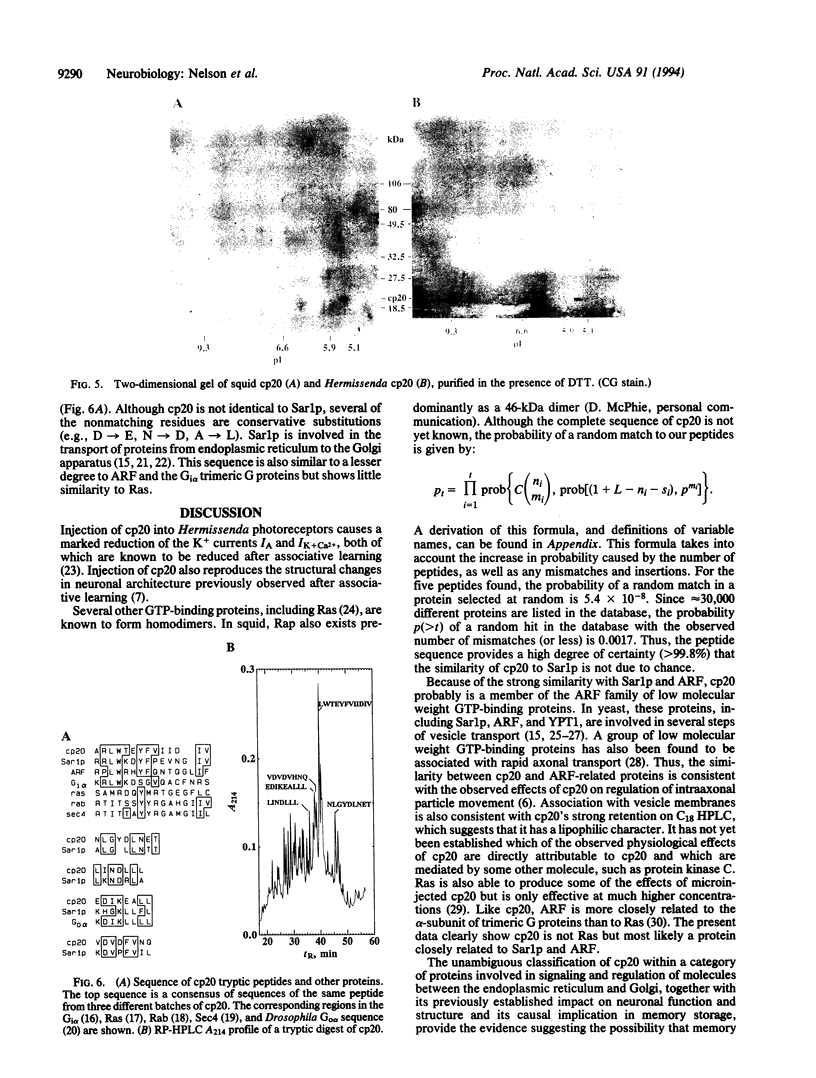
The phosphorylation state of cp20, a low molecular weight GTP-binding protein that is a high-affinity substrate for protein kinase C, was previously shown to change after associative conditioning of molluscs and mammals and to induce many of the biophysical and structural modifications that accompany memory retention. Here, cp20 was purified from squid optic lobes and biochemically characterized. A monoclonal antibody prepared against squid cp20 reacted with Hermissenda cp20 and a 20-kDa protein in rabbit hippocampus, while a polyclonal antibody also cross-reacted with Sar1p and ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF). A partial peptide sequence of squid cp20 was 50% identical (23/46 amino acids) with Sar1p, a yeast GTP-binding protein involved in vesicle transport, indicating that cp20 is probably a new member of the ARF family. This classification is consistent with our recent demonstration that cp20 affects retrograde movement of intraaxonal organelles or particles and suggests a possible role for particle traffic between intraneuronal organelles in memory acquisition.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alkon D. L., Ikeno H., Dworkin J., McPhie D. L., Olds J. L., Lederhendler I., Matzel L., Schreurs B. G., Kuzirian A., Collin C. Contraction of neuronal branching volume: an anatomic correlate of Pavlovian conditioning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1611–1614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L., Naito S., Kubota M., Chen C., Bank B., Smallwood J., Gallant P., Rasmussen H. Regulation of Hermissenda K+ channels by cytoplasmic and membrane-associated C-kinase. J Neurochem. 1988 Sep;51(3):903–917. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bank B., DeWeer A., Kuzirian A. M., Rasmussen H., Alkon D. L. Classical conditioning induces long-term translocation of protein kinase C in rabbit hippocampal CA1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1988–1992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlowe C., d'Enfert C., Schekman R. Purification and characterization of SAR1p, a small GTP-binding protein required for transport vesicle formation from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):873–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielinski D. F., Morin P. J., Dickey B. F., Fine R. E. Low molecular weight GTP-binding proteins are associated with neuronal organelles involved in rapid axonal transport and exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18363–18367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collin C., Papageorge A. G., Lowy D. R., Alkon D. L. Early enhancement of calcium currents by H-ras oncoproteins injected into Hermissenda neurons. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1743–1745. doi: 10.1126/science.2176747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudai Y. Some properties of adenylate cyclase which might be important for memory formation. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J., Richards W. G., Ling L. J., Liman E., Alkon D. L. Membrane changes in a single photoreceptor cause associative learning in Hermissenda. Science. 1983 Sep 16;221(4616):1201–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.6612335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P., Rossiter K., Carter A., Simonds W., Unson C. G., Vinitsky R., Spiegel A. M. Identification of the GTP-binding protein encoded by Gi3 complementary DNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6476–6479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter J. B., Hunter S. M. Quantification of proteins in the low nanogram range by staining with the colloidal gold stain AuroDye. Anal Biochem. 1987 Aug 1;164(2):430–433. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90515-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel T., Winslow J. W., Smith J. A., Seidman J. G., Neer E. J. Molecular cloning and characterization of cDNA encoding the GTP-binding protein alpha i and identification of a related protein, alpha h. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7663–7667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moshiach S., Nelson T. J., Sanchez-Andres J. V., Sakakibara M., Alkon D. L. G-protein effects on retrograde axonal transport. Brain Res. 1993 Mar 12;605(2):298–304. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91754-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakańo A., Muramatsu M. A novel GTP-binding protein, Sar1p, is involved in transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2677–2691. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neary J. T., Crow T., Alkon D. L. Change in a specific phosphoprotein band following associative learning in Hermissenda. Nature. 1981 Oct 22;293(5834):658–660. doi: 10.1038/293658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson T. J., Alkon D. L. GTP-binding proteins and potassium channels involved in synaptic plasticity and learning. Mol Neurobiol. 1991;5(2-4):315–328. doi: 10.1007/BF02935554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson T. J., Collin C., Alkon D. L. Isolation of a G protein that is modified by learning and reduces potassium currents in Hermissenda. Science. 1990 Mar 23;247(4949 Pt 1):1479–1483. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4949.1479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson T. J., Sanchez-Andres J. V., Schreurs B. G., Alkon D. L. Classical conditioning-induced changes in low-molecular-weight GTP-binding proteins in rabbit hippocampus. J Neurochem. 1991 Dec;57(6):2065–2069. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb06423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Nishikawa S., Nakano A. Reconstitution of GTP-binding Sar1 protein function in ER to Golgi transport. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):671–679. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A., Novick P. J. A ras-like protein is required for a post-Golgi event in yeast secretion. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90455-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos E., Nebreda A. R., Bryan T., Kempner E. S. Oligomeric structure of p21 ras proteins as determined by radiation inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9853–9858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos E., Nebreda A. R. Structural and functional properties of ras proteins. FASEB J. 1989 Aug;3(10):2151–2163. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.10.2666231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C. J., Garen-Fazio S., Chow Y. K., Neer E. J. Neuronal expression of a newly identified Drosophila melanogaster G protein alpha 0 subunit. Cell Regul. 1989 Nov;1(1):125–134. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. H., Greenberg S. M. Molecular mechanisms for memory: second-messenger induced modifications of protein kinases in nerve cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1987;10:459–476. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.10.030187.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segev N., Mulholland J., Botstein D. The yeast GTP-binding YPT1 protein and a mammalian counterpart are associated with the secretion machinery. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90433-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sewell J. L., Kahn R. A. Sequences of the bovine and yeast ADP-ribosylation factor and comparison to other GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4620–4624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shashoua V. E., Hesse G. W., Milinazzo B. Evidence for the in vivo polymerization of ependymin: a brain extracellular glycoprotein. Brain Res. 1990 Jul 9;522(2):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91460-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shashoua V. E. The role of brain extracellular proteins in neuroplasticity and learning. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1985 Jun;5(1-2):183–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00711092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. W., Bobak D. A., Tsai S. C., Moss J., Vaughan M. GTP but not GDP analogues promote association of ADP-ribosylation factors, 20-kDa protein activators of cholera toxin, with phospholipids and PC-12 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3230–3235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahraoui A., Touchot N., Chardin P., Tavitian A. The human Rab genes encode a family of GTP-binding proteins related to yeast YPT1 and SEC4 products involved in secretion. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12394–12401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]