Abstract
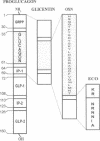
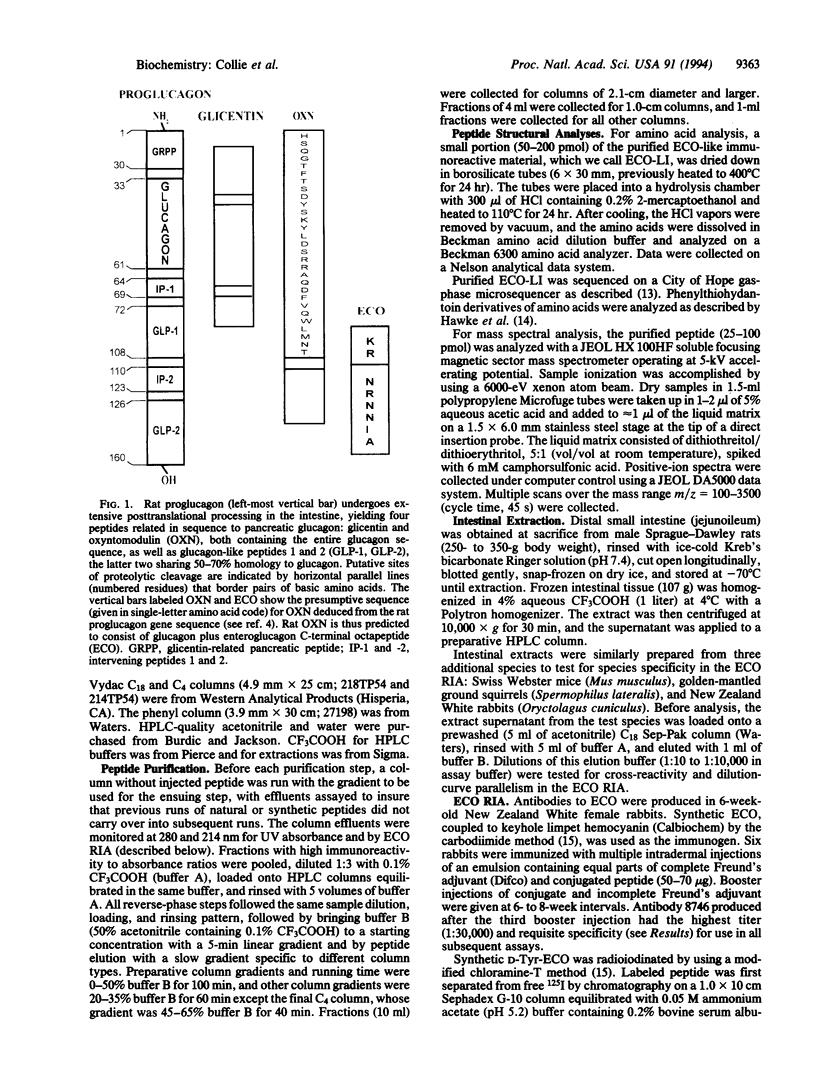
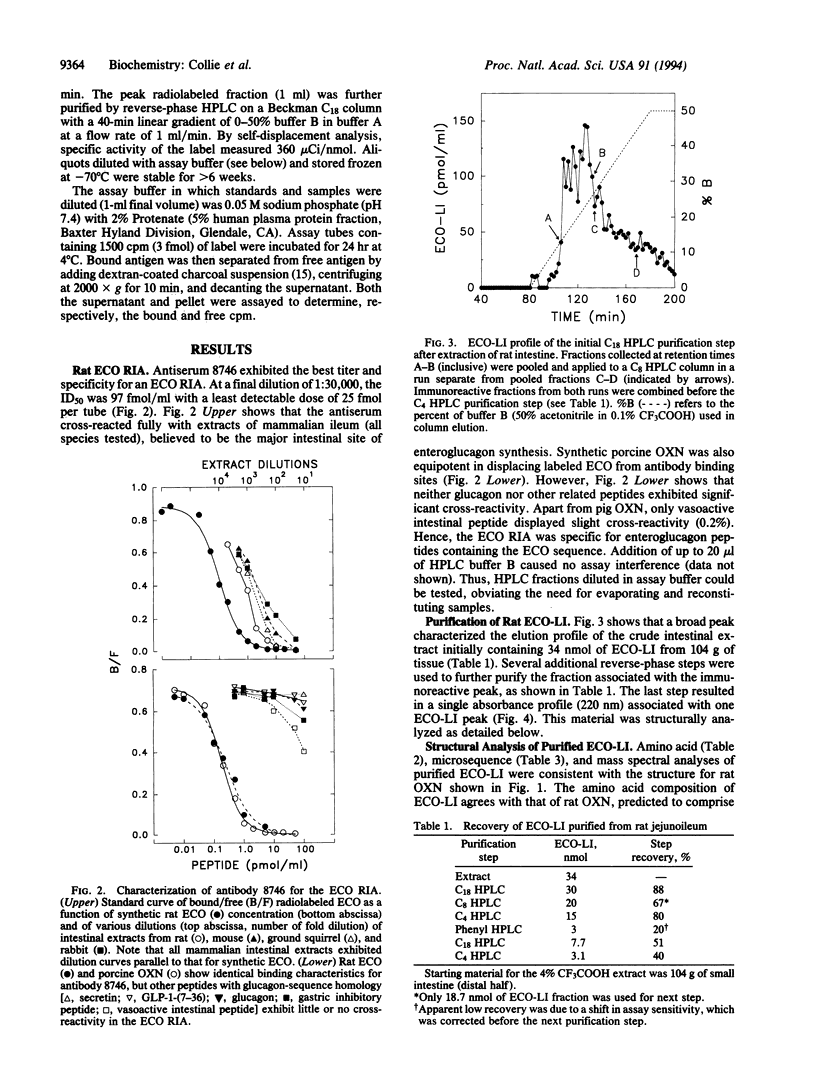
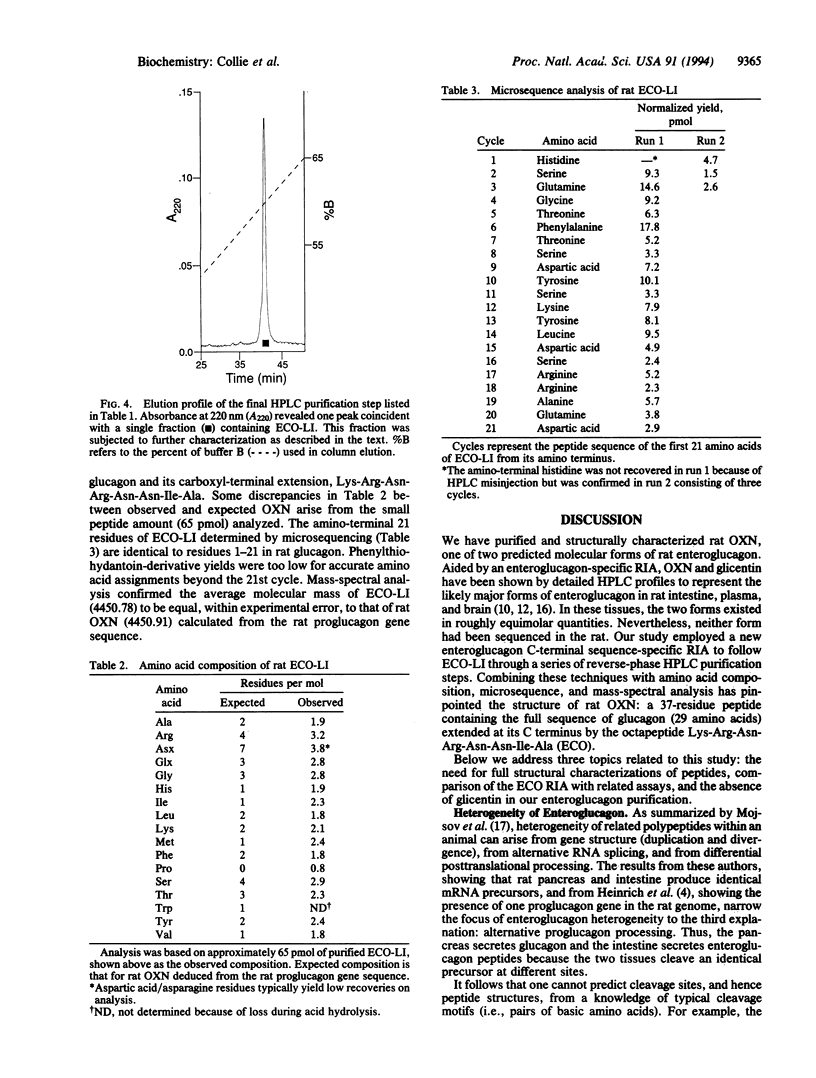
Structural information about rat enteroglucagon, intestinal peptides containing the pancreatic glucagon sequence, has been based previously on cDNA, immunologic, and chromatographic data. Our interests in testing the physiological actions of synthetic enteroglucagon peptides in rats required that we identify precisely the forms present in vivo. From knowledge of the proglucagon gene sequence, we synthesized an enteroglucagon C-terminal octapeptide common to both proposed enteroglucagon forms, glicentin and oxyntomodulin, but sharing no sequence overlap with glucagon. We then developed a radioimmunoassay using antibodies raised against the octapeptide that was specific for enteroglucagon peptides without cross-reacting with glucagon. Rat intestine was extracted, and one presumptive enteroglucagon form was purified by following the enteroglucagon C-terminal octapeptide-like immunoreactivity through several HPLC purification steps. Structural characterization of the material by amino acid composition, microsequence, and mass spectral analyses identified the peptide as rat oxyntomodulin. The 37-residue peptide consists of pancreatic glucagon plus the C-terminal extension, Lys-Arg-Asn-Arg-Asn-Asn-Ile-Ala. This now permits synthesis of an unambiguous duplicate of endogenous rat oxyntomodulin for physiological studies.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blache P., Kervran A., Bataille D. Oxyntomodulin and glicentin: brain-gut peptides in the rat. Endocrinology. 1988 Dec;123(6):2782–2787. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-6-2782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blache P., Kervran A., Martinez J., Bataille D. Development of an oxyntomodulin/glicentin C-terminal radioimmunoassay using a "thiol-maleoyl" coupling method for preparing the immunogen. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;173(1):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90172-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. The hormonal pattern of intestinal adaptation. A major role for enteroglucagon. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1982;74:93–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon J. M. Proglucagon-derived peptides: nomenclature, biosynthetic relationships and physiological roles. Diabetologia. 1988 Aug;31(8):563–566. doi: 10.1007/BF00264761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eysselein V. E., Eberlein G. A., Schaeffer M., Grandt D., Goebell H., Niebel W., Rosenquist G. L., Meyer H. E., Reeve J. R., Jr Characterization of the major form of cholecystokinin in human intestine: CCK-58. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 1):G253–G260. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.258.2.G253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller P. J., Beveridge D. J., Taylor R. G. Ileal proglucagon gene expression in the rat: characterization in intestinal adaptation using in situ hybridization. Gastroenterology. 1993 Feb;104(2):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90414-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawke D., Yuan P. M., Shively J. E. Microsequence analysis of peptides and proteins. II. Separation of amino acid phenylthiohydantoin derivatives by high-performance liquid chromatography on octadecylsilane supports. Anal Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;120(2):302–311. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich G., Gros P., Lund P. K., Bentley R. C., Habener J. F. Pre-proglucagon messenger ribonucleic acid: nucleotide and encoded amino acid sequences of the rat pancreatic complementary deoxyribonucleic acid. Endocrinology. 1984 Dec;115(6):2176–2181. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-6-2176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kervran A., Blache P., Bataille D. Distribution of oxyntomodulin and glucagon in the gastrointestinal tract and the plasma of the rat. Endocrinology. 1987 Aug;121(2):704–713. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-2-704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreymann B., Yiangou Y., Kanse S., Williams G., Ghatei M. A., Bloom S. R. Isolation and characterisation of GLP-1 7-36 amide from rat intestine. Elevated levels in diabetic rats. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 19;242(1):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez L. C., Frazier M. L., Su C. J., Kumar A., Saunders G. F. Mammalian pancreatic preproglucagon contains three glucagon-related peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5485–5489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. K., Ulshen M. H., Rountree D. B., Selub S. E., Buchan A. M. Molecular biology of gastrointestinal peptides and growth factors: relevance to intestinal adaptation. Digestion. 1990;46 (Suppl 2):66–73. doi: 10.1159/000200369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mojsov S., Heinrich G., Wilson I. B., Ravazzola M., Orci L., Habener J. F. Preproglucagon gene expression in pancreas and intestine diversifies at the level of post-translational processing. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11880–11889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov C., Holst J. J., Poulsen S. S., Kirkegaard P. Pancreatic and intestinal processing of proglucagon in man. Diabetologia. 1987 Nov;30(11):874–881. doi: 10.1007/BF00274797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock H. G., Kimmel J. R., Ebner K. E., Hamilton J. W., Rouse J. B., Lance V., Rawitch A. B. Isolation of alligator gar (Lepisosteus spatula) glucagon, oxyntomodulin, and glucagon-like peptide: amino acid sequences of oxyntomodulin and glucagon-like peptide. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1988 Jan;69(1):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(88)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rountree D. B., Ulshen M. H., Selub S., Fuller C. R., Bloom S. R., Ghatei M. A., Lund P. K. Nutrient-independent increases in proglucagon and ornithine decarboxylase messenger RNAs after jejunoileal resection. Gastroenterology. 1992 Aug;103(2):462–468. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90835-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomura Y., Eng J., Yalow R. S. Immunoreactive glucagons purified from dog pancreas, stomach and ileum. Regul Pept. 1988 Dec;23(3):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(88)90230-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. E., Miller P., Ronk M. Microsequence analysis of peptides and proteins. VI. A continuous flow reactor for sample concentration and sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jun;163(2):517–529. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90257-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thim L., Moody A. J. The primary structure of porcine glicentin (proglucagon). Regul Pept. 1981 May;2(2):139–150. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(81)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]