Background: GltPh couples uptake of one aspartate to the cotransport of three Na+.
Results: Slow binding of Na+ takes place before aspartate binding and has high activation energy.
Conclusion: Binding of Na+ is accompanied by a large conformational change enabling subsequent high affinity binding of aspartate.
Significance: Insight into the binding kinetics of coupling ions is essential to deduce a mechanism of transport.
Keywords: fluorescence, membrane protein, membrane transport, pre-steady-state kinetics, transporter, glutamate transport, Sodium-coupled transport, tryptophan fluorescence, binding kinetics, secondary transport
Abstract
GltPh from Pyrococcus horikoshii is a homotrimeric Na+-coupled aspartate transporter. It belongs to the widespread family of glutamate transporters, which also includes the mammalian excitatory amino acid transporters that take up the neurotransmitter glutamate. Each protomer in GltPh consists of a trimerization domain involved in subunit interactions and a transport domain containing the substrate binding site. Here, we have studied the dynamics of Na+ and aspartate binding to GltPh. Tryptophan fluorescence measurements on the fully active single tryptophan mutant F273W revealed that Na+ binds with low affinity to the apoprotein (Kd 120 mm), with a particularly low kon value (5.1 m−1s−1). At least two sodium ions bind before aspartate. The binding of Na+ requires a very high activation energy (Ea 106.8 kJ mol−1) and consequently has a large Q10 value of 4.5, indicative of substantial conformational changes before or after the initial binding event. The apparent affinity for aspartate binding depended on the Na+ concentration present. Binding of aspartate was not observed in the absence of Na+, whereas in the presence of high Na+ concentrations (above the Kd for Na+) the dissociation constants for aspartate were in the nanomolar range, and the aspartate binding was fast (kon of 1.4 × 105 m−1s−1), with low Ea and Q10 values (42.6 kJ mol−1 and 1.8, respectively). We conclude that Na+ binding is most likely the rate-limiting step for substrate binding.
Introduction
Glutamate is the main excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Glutamate transporters take up extracellular glutamate into glial cells and neurons surrounding the synaptic cleft and thus help to prevent prolonged elevated, neurotoxic extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitter and maintain efficient synaptic communication between the neurons (1, 2). Five mammalian subtypes of glutamate transporters (excitatory amino acid transporters (EAAT 1–5)4) each couple glutamate transport to the co- and countertransport of cations (3). Three Na+ and one proton are cotransported with a glutamate molecule, whereas the transport cycle is completed by the countertransport of one K+ (4).
The only glutamate transporter homologs for which high resolution crystal structures have been solved are the archaeal Na+-coupled aspartate transporters GltPh from Pyrococcus horikoshii (5) and GltTk from Thermococcus kodakarensis (6). Crystal structures in different conformations revealed that the protomers in the homotrimeric proteins consist of a trimerization domain involved in the subunit interactions and a transport domain, which contains the binding sites for aspartate and sodium ions. A transport mechanism has been proposed in which the transport domains move across the membrane like an elevator to expose the binding site alternately to the intracellular or extracellular space (7–10). Two helical hairpin regions (HP1 and HP2) form the inner and outer lids on the binding site, respectively, that may open when the transporting domain is located in the inward- or outward-facing conformation. Although three sodium ions are cotransported with one aspartate (11), the crystal structures revealed only two sodium ion binding sites (Na1 and Na2) within each protomer (9). The binding site for the third Na+ is still debated (12–18). Experiments and simulations on GltPh and EAAT3 have suggested that the third sodium ion (Na3) may be coordinated by Thr314 and Asn401 in GltPh (18). This location is in line with previous experimental data (19, 20). Simulations also indicated that binding to Na1 and Na3 takes place before glutamate/aspartate binding (17, 18), whereas the third sodium ion binds to the Na2 site only after the amino acid substrate has bound (9). These results again are in agreement with former experimental and computational studies on several glutamate transporters (12, 20–25). In previous characterizations of GltPh using tryptophan fluorescence measurements with a single tryptophan introduced at position Leu130 (Fig. 1), the affinity for aspartate binding was shown to strictly depend on the Na+ concentration and vice versa (9). The L130W mutant has several disadvantages for functional studies because its transport activity is severely reduced compared with the wild-type protein, and it only reports fluorescence changes upon binding of both aspartate and sodium ions.
FIGURE 1.
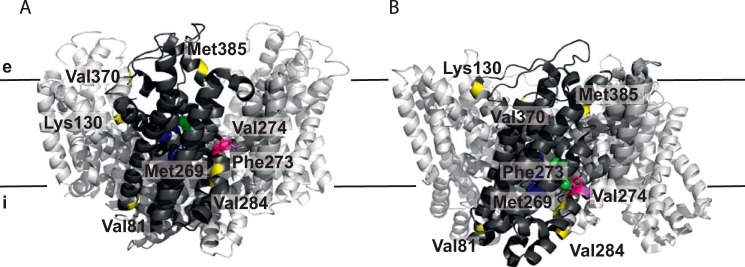
Schematic representation of the residues selected for tryptophan fluorescence measurements. A and B show a side view of the trimeric protein in the outward-facing (PDB code 2NWL) (9) (A) and inward-facing (PDB code 3KBC) (8) (B) crystal structures, respectively, with one protomer highlighted in dark gray. GltPh with tryptophan substitutions of residues Val81, Lys130, Met269, Val284, Val370, and Met385 marked in yellow showed no fluorescence change (Val81, Val284) or changes only when both Na+ and aspartate were added. GltPh with tryptophan substitutions of residues Phe273 (pink) and Val274 (magenta) reported both aspartate-independent Na+ binding and Na+-dependent aspartate binding. Bound aspartate is shown in green, and three putative Na+ binding sites are labeled in blue (18). Black lines represent the membrane with the extracellular (e) and intracellular side (i) indicated.
Here we constructed novel single tryptophan mutants with the aim to dissect Na+ and aspartate binding events in GltPh. Using steady-state and stopped-flow fluorescence measurements, we show that sodium binding to the apoprotein is of low affinity and is accompanied by large conformational changes. Sodium binding precedes aspartate binding, which is fast and of high affinity as long as sodium is present.
Experimental Procedures
Mutagenesis, Expression, and Purification of GltPh
Mutations for single tryptophan variants were introduced in recombinant GltPh possessing a C-terminal eight-histidine tag using site-directed mutagenesis. DNA sequencing confirmed the presence of only the desired mutations. GltPh was produced in Escherichia coli MC1061 and purified as previously described (11) with slight modifications. Buffer A containing 50 mm Tris-HCl, pH 8.0, 300 mm KCl, and 0.04% (w/v) n-dodecyl-β-d-maltoside (Anatrace) was used throughout the whole purification after solubilization including size exclusion chromatography on a Superdex200 column (GE Healthcare). Protein concentrations were determined using the calculated extinction coefficients of the variants.
Fluorescence Measurements
Steady-state fluorescence of purified, detergent-solubilized protein was monitored at 25 °C on a Spex Fluorolog 322 fluorescence spectrophotometer (Jobin Yvon). Fluorescence spectra were recorded with an excitation wavelength of 295 nm. For titration experiments with increasing Na+ or aspartate concentrations, emission was measured at 343 nm with excitation at 295 nm. Aspartate and sodium were titrated to 1 μm protein in 1 ml of buffer A as described in Erkens and Slotboom (26). The resulting curves were fitted in Origin 7.0 (OriginLab) to an equation describing equilibrium binding (26) or to the Hill equation. Stopped-flow measurements were performed on an Applied Photophysics SX20 spectrometer. An excitation wavelength of 295 nm and a cutoff filter of either 310 or 305 nm was used. All experiments were carried out in buffer A with 1.5–2 μm protein at temperatures as indicated. The protein was mixed with substrate-containing buffer A in a 1:1 ratio. 3–15 traces per concentration were recorded and averaged per condition. All indicated concentrations are final after mixing. Pseudo-first-order reactions were assumed when the substrates (Na+, l-aspartate, d-aspartate, or cysteine sulfinic acid) were at least in 5-fold excess compared with the protein. The data were fitted to a single exponential model using Origin 7.0 (OriginLab). In the cases of very long measurements slightly poorer fits were obtained using the single exponential model and double exponential models were used (indicated in the figure legends). The presence of the additional component, which had a small amplitude, depended on the measuring time and became more apparent in the slower reactions that required longer time range measurements (>5 s). We assume that bleaching accounts for this component. When double exponential models were used for one trace in a series, we chose to use it for all traces in the series (concentration-dependent l-aspartate, d-aspartate, and cysteine sulfinic acid binding data).
Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC)
ITC experiments were performed using an ITC200 calorimeter (MicroCal). 100 μm aspartate (in buffer A with indicated sodium concentrations) was titrated into the thermally equilibrated ITC cell filled with 200 μl of mutant GltPh (13–20 μm) in the presence of 10 or 200 mm NaCl. Temperature was kept constant at 25 °C. Data were analyzed using the Origin-based software provided by MicroCal.
Protein Reconstitution and Transport of [14C]Aspartate into Proteoliposomes
Reconstitution and transport of [14C]aspartate were performed as previously described (11) with the following modifications. Tryptophan variants were reconstituted 1:250 (w/w) into a mixture of synthetic lipids (Avanti Polar Lipids, Inc.) of a 3:1:1 weight ratio of 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DOPE):1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DOPC):1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1′-rac-glycerol) (DOPG). The transport of aspartate was initialized by diluting 2 μl of proteoliposomes (125 μg/μl lipid concentration) loaded with 50 mm KPi buffer, pH 7, into 200 μl of 50 mm sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7, containing 0.69 μm [14C]aspartate and 0.5 μm valinomycin.
Results
Construction of Single Tryptophan Variants of GltPh
To detect the binding of aspartate and sodium ions to GltPh, we constructed single tryptophan variants of the protein. We chose positions where the environment was expected to change upon binding of Na+ and aspartate based on the available crystal structures. Residues Val81 (at the cytoplasmic end of helix 3), Met269, Phe273, Val274, Val284 (all HP1), Val370 (HP2), and Met385 (periplasmic end of helix 8) were mutated (Fig. 1).
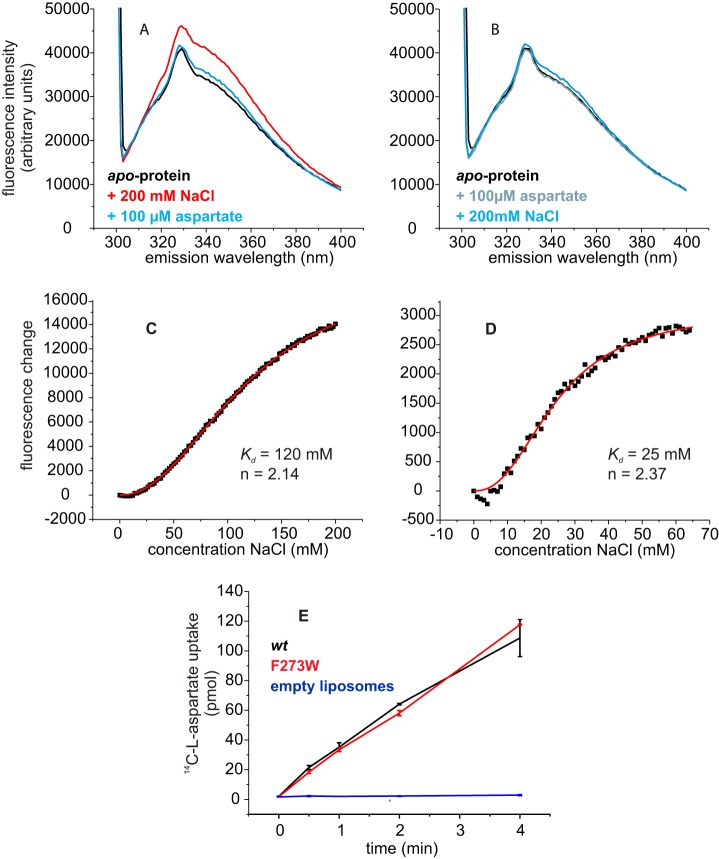
We purified the single tryptophan variants in the apo state (sodium- and aspartate-free), recorded fluorescence spectra in detergent solution, and tested whether the tryptophan fluorescence was sensitive to the addition of sodium ions and aspartate. The fluorescence properties of the variants fell into three groups as follows. V81W and V284W did not show any fluorescence changes upon substrate and coupling ion binding and were not analyzed further (data not shown). The tryptophan fluorescence of M269W, V370W, and M385W did not change upon the addition of either sodium ions or aspartate alone, but it was affected when both Na+ and aspartate were present (data not shown). This behavior is very similar to L130W (periplasmic end of helix 4), which was shown previously to report binding of aspartate and sodium ions (9). We chose L130W as representative for this group of mutants because it showed the most pronounced changes in fluorescence levels upon aspartate and sodium ion binding (Fig. 2, A and B). The fluorescence of F273W and V274W was affected by the binding of sodium ions alone to the apoprotein, as well as by subsequent binding of aspartate to the Na+-bound protein (Fig. 3A). We chose F273W as representative for this group, because (i) it showed the most pronounced changes in fluorescence levels upon Na+ and aspartate binding, and (ii) it was fully active in transport (Fig. 3E), in contrast to V274W.
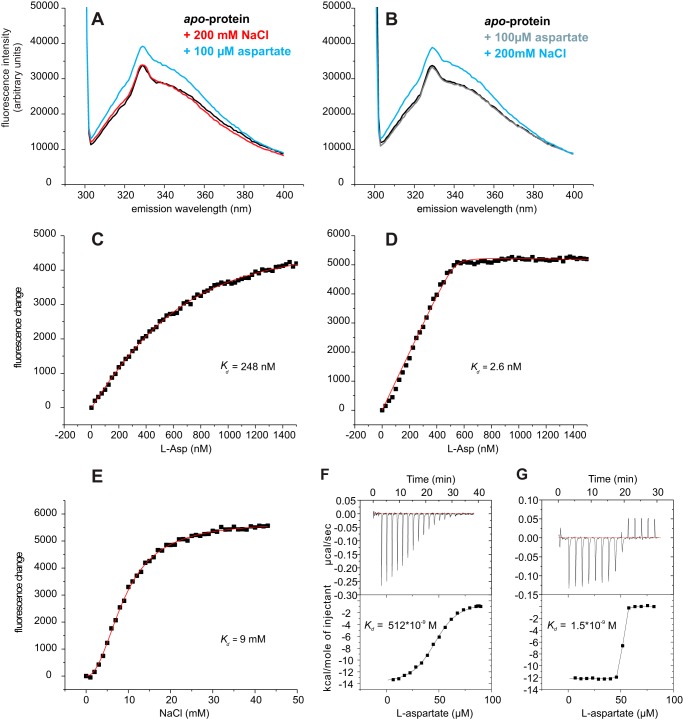
FIGURE 2.
Tryptophan fluorescence of GltPh variant L130W. A, fluorescence emission spectra of the apoprotein (black) and after the addition of 200 mm NaCl (red) followed by 100 μm aspartate (blue). B, reversed order of additions: apoprotein (black) with added 100 μm Asp (gray) followed by the addition of 200 mm NaCl. A fluorescence increase was observed only when both substrates were present. In panels C and D titrations of aspartate in the presence of 10 mm and 200 mm NaCl, respectively, are shown, whereas in E the fluorescence changes by the addition of NaCl in presence of 100 μm aspartate are plotted. The dots represent the average fluorescence levels corrected for dilution measured at the indicated aspartate and NaCl concentrations. The red line is the best fit to a one-site binding equation (26) or to the Hill equation. Panels F and G, ITC measurements of aspartate in presence of 10 mm (F) and 200 mm (G) NaCl are shown. The determined kd values were 512 nm and 2 nm, respectively.
FIGURE 3.
Tryptophan fluorescence and transport activity of GltPh variant F273W. A, fluorescence emission spectra of the apoprotein (black) after the addition of 200 mm NaCl (red) and after subsequent addition of 100 μm aspartate (blue). In panel B the order of additions was reversed: fluorescence emission spectra of the apoprotein (black) after the addition of 100 μm Asp (gray) and after the subsequent addition of 200 mm NaCl (blue). In panels C and D the fluorescence changes as a function of Na+ concentration are shown in the absence of aspartate and in the presence of 100 μm aspartate, respectively. The dots represent the average fluorescence levels corrected for dilution measured at the indicated NaCl concentrations. The red lines are best fits to the Hill equation. E, l-[14C]aspartate uptake of GltPh variant F273W (red) and wild-type GltPh (black) in proteoliposomes and in control liposomes without protein (blue).
Steady-state Binding of Na+ to GltPh
For all binding experiments detergent-solubilized proteins were used, and consequently, binding could take place to the outward- or inward-facing states. Because the binding affinities of the two states for the substrates are identical (27), the lack of sidedness is not expected to affect the steady-state Kd determinations. The tryptophan in F273W is located in HP1, close to the binding sites for aspartate and two sodium ions. The addition of Na+ to the purified, detergent-solubilized apo form of this variant resulted in an increase of the steady-state tryptophan fluorescence intensity, which allowed us to determine the affinity of GltPh for sodium ions in the absence of aspartate (Fig. 3A). Na+ binding was cooperative and of low affinity (Kd of 120 mm, Hill coefficient of 2.1 (Fig. 3C)). The Hill coefficient suggests that at least two sodium ions bind to the protein in a cooperative way in the absence of aspartate.
The apparent affinity for sodium was higher when aspartate was present. In the presence of 100 μm aspartate F273W bound Na+ with a Kd of 25 mm and a Hill coefficient of 2.4 (Fig. 3D). In the presence of aspartate the affinity for Na+ could also be determined in mutant L130W. The fluorescence of L130W increased when both Na+ and aspartate bound to the protein (Fig. 2, A and B). We found a Kd value of 9 mm for Na+ binding to L130W in presence of 100 μm aspartate and a Hill coefficient of 2.2 (Fig. 2E). These numbers compare well with previous data on the binding of sodium to variant L130W (9, 28).
Steady-state Binding of Aspartate to GltPh
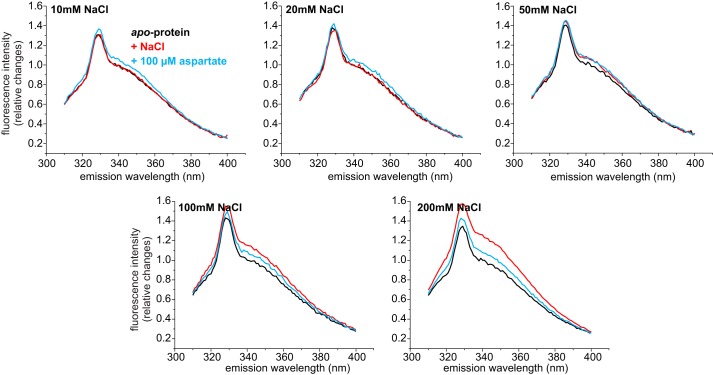
Whereas the binding of Na+ to GltPh F273W resulted in a concentration-dependent increase in the fluorescence intensity, the subsequent binding of aspartate caused a decrease in intensity. The level of fluorescence with both substrates bound was slightly higher than that of the apoprotein (Fig. 3A). The change in fluorescence upon the addition of aspartate to GltPh preincubated with sodium depended strongly on the concentration of sodium used. In the presence of 200 mm Na+, the addition of aspartate to F273W caused a relatively large decrease in fluorescence intensity. However, in the presence of lower concentrations of sodium (50 and 100 mm NaCl, which is below the Kd for sodium) the decrease was less pronounced. At these Na+ concentrations the protein is not fully occupied with Na+, and therefore, the reference level of fluorescence before the addition of aspartate is lower than in the presence of saturating sodium concentrations. Because the final level of fluorescence after the addition of aspartate was the same regardless of the sodium concentration, the decrease in fluorescence by aspartate binding was less pronounced at lower sodium concentrations (Fig. 4). At very low sodium concentrations (10 and 20 mm NaCl, respectively) the initial occupancy by sodium ions was so low that there was an increase rather than a decrease of fluorescence intensity upon the addition of aspartate. Nonetheless, in all cases the same end level of fluorescence was reached, indicating that aspartate pulls the carrier to the fully occupied state, and sodium and aspartate binding is mutually cooperative.
FIGURE 4.
Tryptophan fluorescence spectra of GltPh variant F273W in the presence of different NaCl concentrations. Fluorescence emission spectra of the apoprotein (black) after the addition of NaCl (red, concentration as indicated) and after subsequent addition of 100 μm aspartate (blue). For better comparison the spectra were normalized taking the fluorescence of the apoprotein at 343 nm as 1.
When we added the substrates in the reverse order, the addition of aspartate did not cause a change in fluorescence, suggesting that aspartate does not bind to GltPh in the absence of Na+, whereas subsequent addition of Na+ caused a slight increase (Fig. 3B). Regardless of the order of additions, the same end level of fluorescence intensity was reached (cf. Fig. 3, A and B).
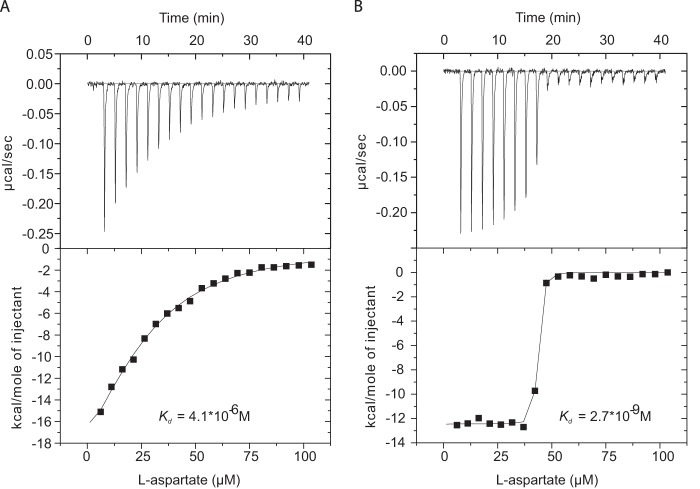
Because the changes in fluorescence intensity upon aspartate binding to F273W depended strongly on the sodium concentration and were very small in the presence of low sodium concentrations, we could not use the changes in fluorescence intensity to determine binding affinities for aspartate. Instead we used ITC measurements. The apparent affinity for aspartate depended on the NaCl concentration; with 10 mm NaCl present the Kd was 4 μm (Fig. 5A), whereas the affinity increased 3 orders of magnitude with 200 mm NaCl added (Kd of 2.6 nm; Fig. 5B). Taking into account that Kd values in the low nanomolar range obtained from ITC or fluorescence measurements are difficult to determine accurately, these numbers compare well with previous data on L130W (8). Using ITC measurements for L130W, we found a Kd of 513 nm for aspartate with 10 mm NaCl present (Fig. 2F) and a Kd of 1.5 nm with 200 mm NaCl present (Fig. 2G). Similar Kd values of 250 and 2.6 nm in the presence of 10 mm and 200 mm NaCl, respectively, were obtained from steady-state fluorescence measurements on L130W (Fig. 2, C and D).
FIGURE 5.
ITC measurement of variant F273W. Aspartate titration in presence of 10 mm (A) and 200 mm (B) NaCl. The determined Kd values were 4 μm and 3 nm, respectively.
Rates of Na+ and Aspartate Binding to GltPh F273W
We performed tryptophan fluorescence-based stopped-flow measurements on GltPh F273W in detergent solution to record the substrate-induced fluorescence changes over time. Although in detergent solution there is no sidedness and binding could in principle take place to both the outward- or inward-facing states, the data fitted well to a single exponential model. Therefore, it is likely that we observed a single type of event.
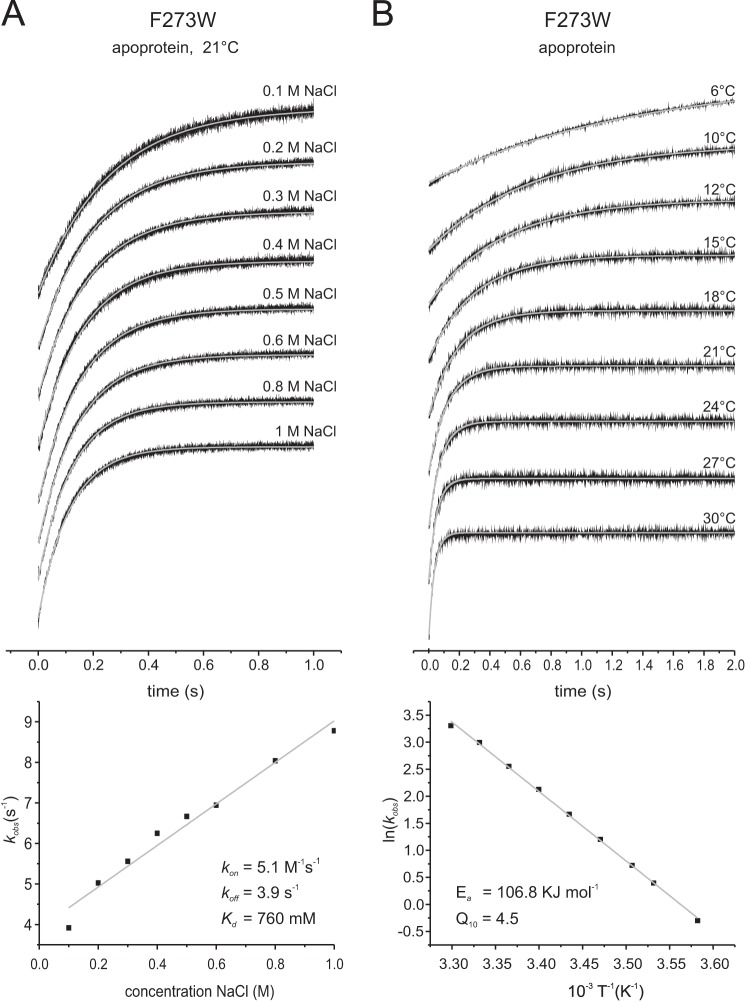
Fast mixing experiments on the binding of Na+ to the F273W variant revealed a very low kon value for Na+ of 5.1 m−1s−1 (Fig. 6A, Table 1). The kinetics data are consistent with the low affinity of GltPh for Na+ in the absence of aspartate measured in the steady-state experiments (cf. Figs. 3A and 6A). In the experiments the ionic strength was kept constant at 1 m by the addition of the appropriate concentrations of KCl to compensate for the different NaCl concentrations used. It must be noted though that the rate constants were identical in the absence of compensating KCl additions showing that differences in ionic strength had no detectable effect (data not shown). Rate constants were also determined at different temperatures between 6 °C and 30 °C. From these data values for the activation energy, Ea and Q10 of 106.8 kJ mol−1 and 4.5, respectively, were derived (Fig. 6B). These values suggest a relatively big conformational change either before or after binding of Na+. Nonetheless, the stopped-flow measurements with increasing Na+ concentrations (Fig. 6A) did not result in a saturation of the kobs values. A possible explanation for the lack of saturation is that the concentrations of Na+ required to reach saturation are too high to be compatible with the experimental setup.
FIGURE 6.
Rates of Na+ binding to GltPh F273W. The top panels show the stopped-flow fluorescence measurements. Each trace (black) represents an average of 6–15 individual traces, fitted with a single exponential equation (gray). A, 1.5 μm F273W apoprotein was mixed with solutions of the indicated concentrations of NaCl; KCl was present so that the sum of the NaCl and KCl concentrations was 1 m. All measurements were performed at room temperature. The bottom panel shows the kobs values plotted against the corresponding NaCl concentrations. The slope of the linear fit gives the kon, and the intercept with the kobs axis gives the koff value. B, 1.5 μm F273W was mixed with 1 m NaCl at different temperatures as indicated, and the bottom panel shows the Arrhenius plot of the derived kobs. The gray line is a linear fit of the data according to the Arrhenius equation ln(k) = B + (ln(Ea)/RT), with Ea representing the activation energy, B representing the frequency factor, T representing the absolute temperature, and R representing the gas constant. The linear fit results in an Ea = 106.8 kJ mol−1.
TABLE 1.
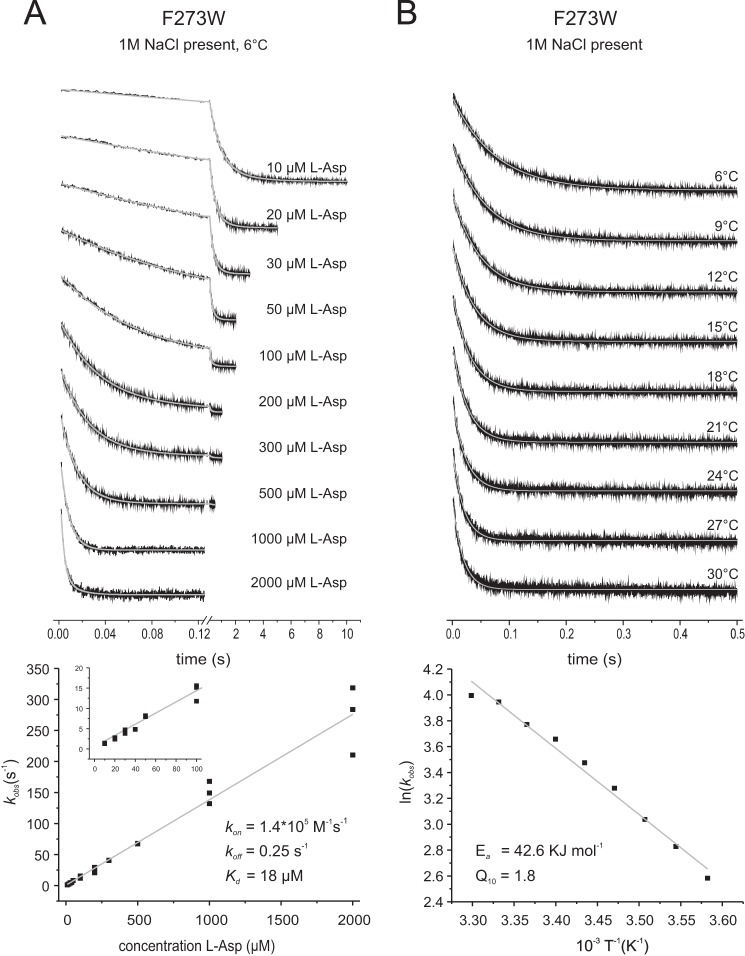
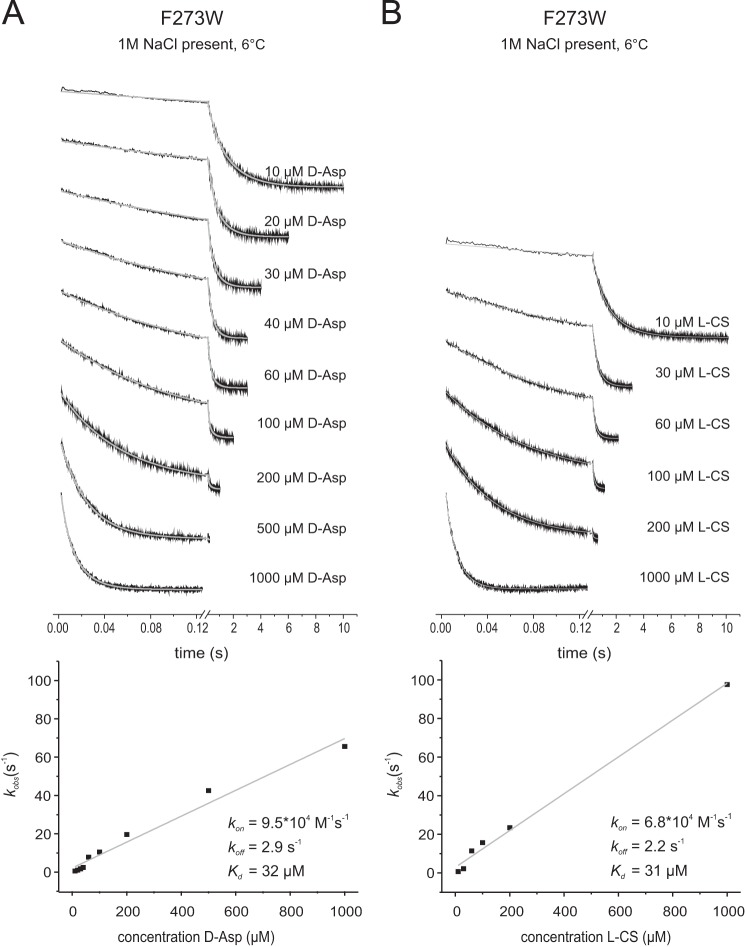
Rates of substrate and Na+ binding to variant F273W as derived from stopped-flow fluorescence measurements
l-CS, l-cysteine sulfinic acid.
| Substrate | kon | koff | Kda |
|---|---|---|---|
| m−1s−1 | s−1 | m | |
| Na+b | 5.1 (±0.237) | 3.9 (±0.134) | 0.76 |
| l-Aspartatec | 1.4 × 105 (±4.7 × 103) | 0.25 (±3.3) | 1.8 × 10−5 |
| d-Aspartatec | 6.8 × 104 (±4.1 × 103) | 2.2 (±1.6) | 3.2 × 10−5 |
| l-CSc | 9.5 × 104 (±3.9 × 103) | 2.9 (±1.6) | 3.1 × 10−5 |
a Derived from koff/kon.
b Measurements were performed at room temperature.
c Measurements were performed at 6 °C.
Rates of Na+ Binding to GltPh F273W in the Presence of Aspartate
Na+ binding was also monitored in the presence of three different aspartate concentrations of 1 μm, 10 μm, and 100 μm. At some aspartate-to-Na+ ratios (combinations of high Na+ and low aspartate concentrations) two phases became apparent (Fig. 7): a fast increase in tryptophan fluorescence followed by a slower decrease. The two observed rate constants kobs were in good agreement with the corresponding rates of Na+ binding to apoGltPh and aspartate binding to the Na+-loaded protein, indicating that the observed phases describe the binding of Na+ (fast at high Na+ concentration) before the binding of aspartate (slow at low aspartate concentration). At low sodium ion concentrations a single phase only was observed, corresponding to slow and rate-determining sodium binding. The subsequent aspartate binding was much faster in this condition.
FIGURE 7.
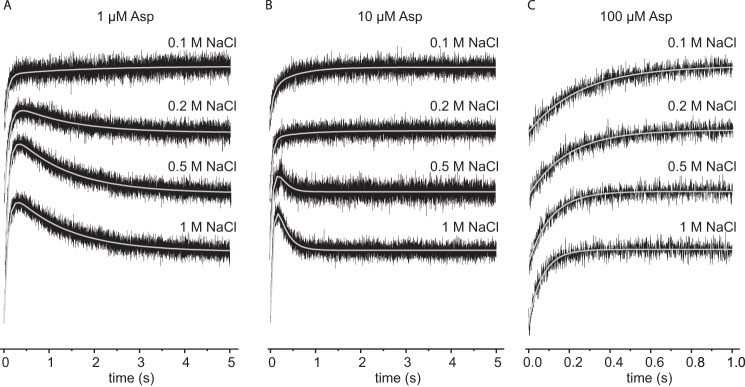
Sodium binding to GltPh variant F273W in the presence of different aspartate concentrations. Stopped-flow traces of the tryptophan fluorescence started by mixing 2 μm protein with different NaCl concentrations in presence of 1 μm (A), 10 μm (B), and 100 μm (C) aspartate, respectively. Each trace (black) represents an average of 10–15 individual traces, fitted with a double exponential equation (gray).
Rates of Aspartate Binding to Na+-loaded GltPh F273W
The binding of l-aspartate to F273W at room temperature was too fast for accurate determination of the rate constants at high aspartate concentrations. Therefore, binding rates for l-aspartate using GltPh preincubated with 1 m Na+ were determined at 6 °C and yielded kon and koff values of 1.4 × 105 m−1 s−1 and 0.25 s−1, respectively (Fig. 8A). The activation energy for binding of l-aspartate to GltPh F273W was 42.6 kJ mol−1 with a correlating Q10 value of 1.8 (Fig. 8B). The substantial activation energy and the small kon value, which is well below rate constant for diffusion limited binding, indicate that F273W reports a conformational change rather than the initial aspartate binding event. This observation is consistent with aspartate binding data for L130W, indicating an induced-fit mechanism (28). However, there are also differences between L130W and F273W. For F273W we did not observe saturation of kobs at high l-aspartate concentrations in contrast to previous data for L130W (28). Similarly, we did not observe saturation of kobs at high concentrations of the alternative substrates d-aspartate and l-cysteic acid, again in contrast with the reported work on L130W (Figs. 8A and 9, A and B, respectively). It is not clear why saturation was not observed for F273W, but it is possible that higher l-aspartate concentrations were required to reach saturation. However, at higher concentrations the rates were too high to measure accurately using our experimental setup. In addition, variant L130W showed greatly reduced transport activity, in contrast to F273W (cf. Ref. 9 and Fig. 3E), and therefore, L130W may have a more limited conformational flexibility than F273W, which becomes rate-limiting at lower substrate concentrations.
FIGURE 8.
Rates of l-aspartate binding to GltPh F273W in the presence of 1 m NaCl. The top panels show the stopped-flow fluorescence measurements. Each trace (black) represents an average of 6–10 individual traces. A, 1.5 μm F273W was mixed with varying l-Asp concentrations as indicated, and individual traces were fitted with a double exponential equation (gray). In the bottom panel the kobs values resulting from the fits with assumed pseudo-first-order reaction are plotted against the corresponding aspartate concentrations. The slope of the linear fit gives the kon, and the intercept with the kobs axis gives the koff value. The inset shows the data at low aspartate concentrations. B, 1.5 μm F273W was mixed with 100 μm l-asp at different temperatures as indicated, and individual traces were fitted with a single exponential equation. The bottom panel shows the Arrhenius plot of the derived kobs. The gray line demonstrates the linear fit of the data according to the Arrhenius equation ln(k) = B + (ln(Ea)/RT), with Ea representing the activation energy, B representing the frequency factor, T representing the absolute temperature, and R representing the gas constant. The linear fit results in an Ea = 42.6 kJ mol−1.
FIGURE 9.
Rates of d-aspartate and l-cysteine sulfinic acid binding to GltPh F273W in the presence of 1 m NaCl. The top panels show the stopped-flow fluorescence measurements. Each trace (black) represents an average of 3–8 individual traces, fitted with a double exponential equation (gray). In the bottom panels the kobs values resulting from the fits with assumed pseudo-first-order reaction are plotted against the corresponding substrate concentrations. All measurements were performed at 6 °C. The slopes of the linear fits give the kon, and the intercepts with the kobs axis give the koff values. A, 1.5 μm F273W was mixed with varying d-Asp concentrations as indicated. B, 1.5 μm F273W was mixed with varying l-cysteine sulfinic acid (l-CS) concentrations as indicated.
Discussion
The change in tryptophan fluorescence upon Na+ binding to F273W and the kinetics of binding as well as the temperature dependence indicate that a substantial conformational change is associated with the binding of sodium ions to the apoprotein. The change in fluorescence may arise either from local conformational changes before or upon the initial binding to the exposed binding site or by the subsequent redistribution of conformational states of the whole transport domain. Distinct local conformational changes forming the binding pocket for aspartate were proposed by molecular dynamic simulations (17, 18) and binding studies on GltPh (27, 28). Comparison of the recent crystal structures of apoGltPh (29) and the closely related protein apoGltTk (6) with the Na+- and aspartate-bound proteins (8, 9) are also consistent with a large local conformational change associated with sodium binding. Because the tryptophan residue in F273W is located in close proximity to the Na+ binding sites, this possibility is plausible. But also a Na+-induced overall movement of the transport domain as shown by EPR and single-molecule FRET studies (30–33) would be consistent with the present fluorescence data.
Similarly, the fluorescence decrease upon binding of aspartate to the Na+-loaded carrier is likely related to a conformational change. A previous EPR study showed that binding of aspartate to the Na+-saturated carrier caused a minor change in the occupancy of the conformational states of the transporting domain compared with the Na+-induced changes (30), whereas the molecular dynamic simulation again suggested a local rearrangement enabling the binding of the third sodium ion (18). The fluorescence measurements revealed that binding of Na+ takes place before aspartate binding. This is consistent with previous data (12–18, 27, 29, 34). However, our measurements allow no speculations about the binding of the third sodium ion.
ApoGltPh has a very low affinity for sodium ions (Kd = 120 mm). This value compares well with experiments in which a voltage-sensitive dye was used to measure Na+ binding to wild-type GltPh (Kd = 99 mm) (27) but differs to a larger extent from the Kd for Na+ determined by tyrosine fluorescence changes upon sodium binding to wild-type GltPh (25 mm) (28). The basis for these differences is not known. Nonetheless, in any case the Kd is in the physiologically relevant range, considering that the natural environment of P. horikoshii is seawater containing about 0.5 m NaCl. The kon value for sodium binding was only ∼5 m−1s−1, but at physiological Na+ concentrations relatively fast binding of the coupling ions is ensured (kobs values ∼7 s−1). In addition, this rate is in good agreement with rates previously determined for the human EAAT5 (35), in which case sodium binding preceded fast glutamate binding. The data are also consistent with several studies on glutamate transporters showing that slow binding of two Na+ is followed by fast binding of substrate and subsequently the third coupling ion (24, 36).
The change in fluorescence upon binding of aspartate to the Na+-loaded carrier L130W has been shown to report an induced fit event. The low rate constants of fluorescence changes upon aspartate binding to variant F273W (kon of 1.4 × 105 m−1s−1) are consistent with an induced fit mechanism. We hypothesize that the fluorescence of F273W reports a conformational change induced by substrate binding rather than the initial binding event. The conformational change reported by F273W is significantly slower than the initial substrate binding (kon), which is manifested by the difference between the Kd values calculated from the rate constants by stopped-flow fluorescence measurements and thermodynamics using ITC measurements (18 μm versus 2.7 nm, respectively). The conformation change could for example be associated with an opening of the inward-facing lid HP1 (37, 38) or a reorientation of the whole transport domain after binding of both Na+ and aspartate (32). However, for the F273W mutant the kobs values of aspartate binding did not saturate at high aspartate concentration, in contrast to L130W (28). Because L130W is much less active in transport than the wild-type or F273W (9), it is possible that the kinetics of the reported conformational changes are different and may become rate-limiting only in L130W at high aspartate concentrations.
In summary, this study provides new insights into the molecular mechanism of substrate binding in the archaeal aspartate transporter GltPh. Na+ binding is slow and involves conformational rearrangements that are essential for subsequent high affinity aspartate binding, which ensures the coupled uptake of cations and substrate as necessary for the transporter. Na+ binding is likely the rate-limiting step for substrate binding.
Acknowledgments
We thank A. Mulkidjanian and K. Glinka for help with stopped-flow measurements and R. H. Duurkens for performing uptake experiments.
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (HA 6322/1-1; to I. H.), the NWO (Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research; a NWO vici grant; to D. J. S.), and by the European Union (European Drug Initiative on Channels and Transporters program and a European Research Council starting grant (to D. J. S.).
- EAAT
- excitatory amino acid transporter
- ITC
- isothermal titration calorimetry.
References
- 1. Danbolt N. C. (2001) Glutamate uptake. Prog. Neurobiol. 65, 1–105 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Tzingounis A. V., Wadiche J. I. (2007) Glutamate transporters: confining runaway excitation by shaping synaptic transmission. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8, 935–947 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Kanner B. I., Bendahan A. (1982) Binding order of substrates to the sodium and potassium ion coupled l-glutamic acid transporter from rat brain. Biochemistry 21, 6327–6330 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Zerangue N., Kavanaugh M. P. (1996) Flux coupling in a neuronal glutamate transporter. Nature 383, 634–637 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Ryan R. M., Compton E. L., Mindell J. A. (2009) Functional characterization of a Na+-dependent aspartate transporter from Pyrococcus horikoshii. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 17540–17548 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Jensen S., Guskov A., Rempel S., Hänelt I., Slotboom D. J. (2013) Crystal structure of a substrate-free aspartate transporter. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 20, 1224–1226 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Verdon G., Boudker O. (2012) Crystal structure of an asymmetric trimer of a bacterial glutamate transporter homolog. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 19, 355–357 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Reyes N., Ginter C., Boudker O. (2009) Transport mechanism of a bacterial homologue of glutamate transporters. Nature 462, 880–885 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Boudker O., Ryan R. M., Yernool D., Shimamoto K., Gouaux E. (2007) Coupling substrate and ion binding to extracellular gate of a sodium-dependent aspartate transporter. Nature 445, 387–393 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Yernool D., Boudker O., Jin Y., Gouaux E. (2004) Structure of a glutamate transporter homologue from Pyrococcus horikoshii. Nature 431, 811–818 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Groeneveld M., Slotboom D. J. (2010) Na+:aspartate coupling stoichiometry in the glutamate transporter homologue Glt(Ph). Biochemistry 49, 3511–3513 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Huang Z., Tajkhorshid E. (2010) Identification of the third Na+ site and the sequence of extracellular binding events in the glutamate transporter. Biophys. J. 99, 1416–1425 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Teichman S., Qu S., Kanner B. I. (2012) Conserved asparagine residue located in binding pocket controls cation selectivity and substrate interactions in neuronal glutamate transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 17198–17205 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Tao Z., Rosental N., Kanner B. I., Gameiro A., Mwaura J., Grewer C. (2010) Mechanism of cation binding to the glutamate transporter EAAC1 probed with mutation of the conserved amino acid residue Thr-101. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 17725–17733 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Rosental N., Bendahan A., Kanner B. I. (2006) Multiple consequences of mutating two conserved β-bridge forming residues in the translocation cycle of a neuronal glutamate transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 27905–27915 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Holley D. C., Kavanaugh M. P. (2009) Interactions of alkali cations with glutamate transporters. Philos Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 364, 155–161 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Bastug T., Heinzelmann G., Kuyucak S., Salim M., Vandenberg R. J., Ryan R. M. (2012) Position of the third Na+ site in the aspartate transporter GltPh and the human glutamate transporter, EAAT1. PLoS ONE 7, e33058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Larsson H. P., Wang X., Lev B., Baconguis I., Caplan D. A., Vyleta N. P., Koch H. P., Diez-Sampedro A., Noskov S. Y. (2010) Evidence for a third sodium-binding site in glutamate transporters suggests an ion/substrate coupling model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 13912–13917 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Borre L., Kanner B. I. (2001) Coupled, but not uncoupled, fluxes in a neuronal glutamate transporter can be activated by lithium ions. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 40396–40401 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Tao Z., Zhang Z., Grewer C. (2006) Neutralization of the aspartic acid residue Asp-367, but not Asp-454, inhibits binding of Na+ to the glutamate-free form and cycling of the glutamate transporter EAAC1. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 10263–10272 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Wadiche J. I., Amara S. G., Kavanaugh M. P. (1995) Ion fluxes associated with excitatory amino acid transport. Neuron 15, 721–728 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Kanai Y., Nussberger S., Romero M. F., Boron W. F., Hebert S. C., Hediger M. A. (1995) Electrogenic properties of the epithelial and neuronal high affinity glutamate transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 16561–16568 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Watzke N., Bamberg E., Grewer C. (2001) Early intermediates in the transport cycle of the neuronal excitatory amino acid carrier EAAC1. J. Gen. Physiol. 117, 547–562 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Larsson H. P., Tzingounis A. V., Koch H. P., Kavanaugh M. P. (2004) Fluorometric measurements of conformational changes in glutamate transporters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101, 3951–3956 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Huang Z., Tajkhorshid E. (2008) Dynamics of the extracellular gate and ion-substrate coupling in the glutamate transporter. Biophys. J. 95, 2292–2300 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Erkens G. B., Slotboom D. J. (2010) Biochemical characterization of ThiT from Lactococcus lactis: a thiamin transporter with picomolar substrate binding affinity. Biochemistry 49, 3203–3212 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Reyes N., Oh S., Boudker O. (2013) Binding thermodynamics of a glutamate transporter homolog. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 20, 634–640 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Ewers D., Becher T., Machtens J. P., Weyand I., Fahlke C. (2013) Induced fit substrate binding to an archeal glutamate transporter homologue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 12486–12491 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Verdon G., Oh S., Serio R. N., Boudker O. (2014) Coupled ion binding and structural transitions along the transport cycle of glutamate transporters. Elife 3, e02283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Hänelt I., Wunnicke D., Bordignon E., Steinhoff H. J., Slotboom D. J. (2013) Conformational heterogeneity of the aspartate transporter Glt(Ph). Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 20, 210–214 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Georgieva E. R., Borbat P. P., Ginter C., Freed J. H., Boudker O. (2013) Conformational ensemble of the sodium-coupled aspartate transporter. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 20, 215–221 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Erkens G. B., Hänelt I., Goudsmits J. M., Slotboom D. J., van Oijen A. M. (2013) Unsynchronised subunit motion in single trimeric sodium-coupled aspartate transporters. Nature 502, 119–123 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Akyuz N., Altman R. B., Blanchard S. C., Boudker O. (2013) Transport dynamics in a glutamate transporter homologue. Nature 502, 114–118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Focke P. J., Annen A. W., Valiyaveetil F. I. (2015) Engineering the glutamate transporter homologue GltPh using protein semisynthesis. Biochemistry 54, 1694–1702 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Gameiro A., Braams S., Rauen T., Grewer C. (2011) The discovery of slowness: low-capacity transport and slow anion channel gating by the glutamate transporter EAAT5. Biophys. J. 100, 2623–2632 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Bergles D. E., Tzingounis A. V., Jahr C. E. (2002) Comparison of coupled and uncoupled currents during glutamate uptake by GLT-1 transporters. J. Neurosci. 22, 10153–10162 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. DeChancie J., Shrivastava I. H., Bahar I. (2011) The mechanism of substrate release by the aspartate transporter GltPh: insights from simulations. Mol. Biosyst. 7, 832–842 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Grazioso G., Limongelli V., Branduardi D., Novellino E., De Micheli C., Cavalli A., Parrinello M. (2012) Investigating the mechanism of substrate uptake and release in the glutamate transporter homologue Glt(Ph) through metadynamics simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 453–463 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]