Abstract
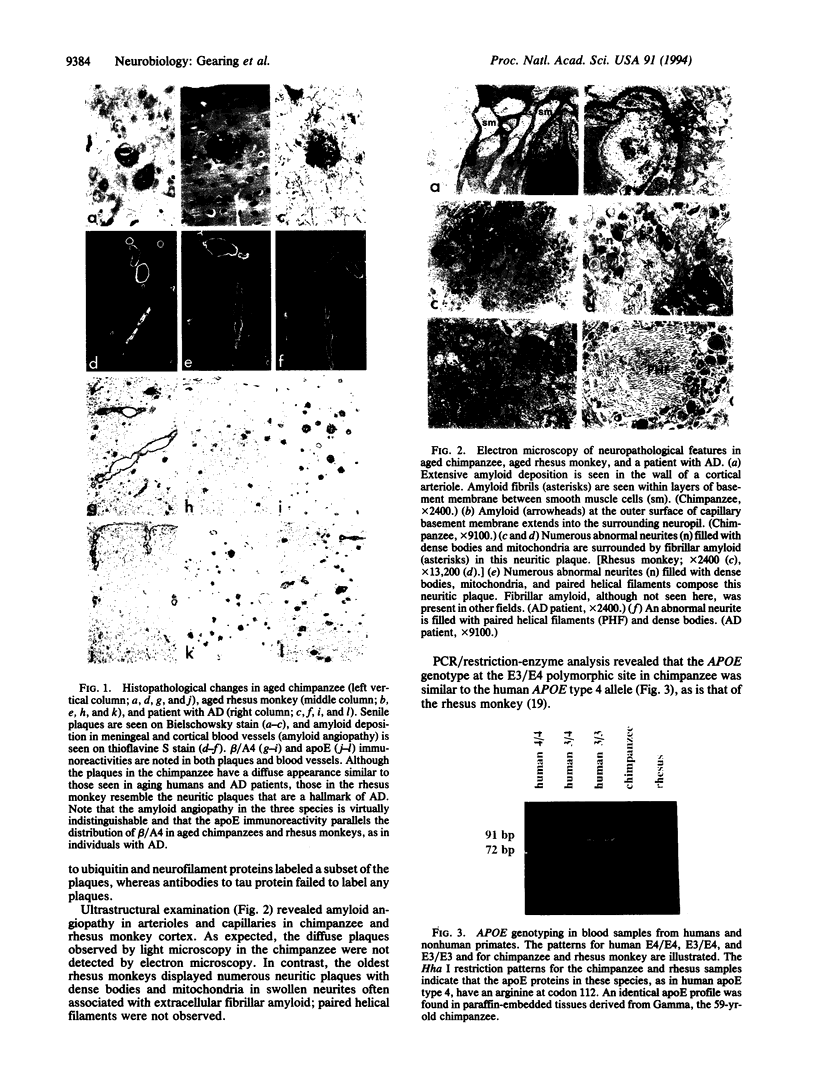
Neuropathological findings in three aged chimpanzees were compared with those in rhesus monkeys and individuals with Alzheimer disease. Senile plaques and blood vessels were immunoreactive for amyloid beta-protein and apolipoprotein E (apoE) in the nonhuman primates, recapitulating findings in human aging and Alzheimer disease. Neurofibrillary tangles, another hallmark of Alzheimer disease, were absent. PCR/restriction-enzyme analysis in chimpanzees revealed an APOE profile similar to the human APOE type 4 allele associated with an increased risk of Alzheimer disease. These findings militate against the hypothesis that the absence of APOE type 3 allele predisposes to neurofibrillary tangle formation and support the value of aged primates for exploring mechanisms of amyloid processing and the role of apoE.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham C. R., Selkoe D. J., Potter H., Price D. L., Cork L. C. Alpha 1-antichymotrypsin is present together with the beta-protein in monkey brain amyloid deposits. Neuroscience. 1989;32(3):715–720. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Lee V. M., Otvos L., Jr, Greenberg B. D., Lowery D. E., Sharma S. K., Schmidt M. L., Trojanowski J. Q. Defined neurofilament, tau, and beta-amyloid precursor protein epitopes distinguish Alzheimer from non-Alzheimer senile plaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2249–2253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisiegel U., Schneider W. J., Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Monoclonal antibodies to the low density lipoprotein receptor as probes for study of receptor-mediated endocytosis and the genetics of familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11923–11931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronson R. T., Schoene W. C. Spontaneous pallido-nigral accumulation of iron pigment and spheroid-like structures in macaque monkeys. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1980 Mar;39(2):181–196. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198003000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzozowska A., Fries R., Womack J. E., Grimholt U., Myklebost O., Rogne S. Isolation, sequencing, and expression analysis of a bovine apolipoprotein E (APOE) cDNA and chromosomal localization of the APOE locus. Mamm Genome. 1993;4(1):53–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00364665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G., Neal J. W. The brain in aged elephants. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1990 Mar;49(2):190–192. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199003000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Small G. W., Roses A. D., Haines J. L., Pericak-Vance M. A. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993 Aug 13;261(5123):921–923. doi: 10.1126/science.8346443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cork L. C., Masters C., Beyreuther K., Price D. L. Development of senile plaques. Relationships of neuronal abnormalities and amyloid deposits. Am J Pathol. 1990 Dec;137(6):1383–1392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cork L. C., Powers R. E., Selkoe D. J., Davies P., Geyer J. J., Price D. L. Neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaques in aged bears. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1988 Nov;47(6):629–641. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198811000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayan A. D. Comparative neuropathology of ageing. Studies on the brains of 47 species of vertebrates. Brain. 1971;94(1):31–42. doi: 10.1093/brain/94.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing M., Wilson R. W., Unger E. R., Shelton E. R., Chan H. W., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K., Mirra S. S. Amyloid precursor protein (APP) in the striatum in Alzheimer's disease: an immunohistochemical study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1993 Jan;52(1):22–30. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199301000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M., Koop B. F., Czelusniak J., Fitch D. H., Tagle D. A., Slightom J. L. Molecular phylogeny of the family of apes and humans. Genome. 1989;31(1):316–335. doi: 10.1139/g89-050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg S. G., Davies P., Schein J. D., Binder L. I. Hydrofluoric acid-treated tau PHF proteins display the same biochemical properties as normal tau. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):564–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Tung Y. C., Quinlan M., Wisniewski H. M., Binder L. I. Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4913–4917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hao Q. L., Yamin T. T., Pan T. C., Chen S. L., Chen B. S., Kroon P. A., Chao Y. S. Isolation and characterization of a full-length rabbit apolipoprotein E cDNA. Atherosclerosis. 1987 Jul;66(1-2):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(87)90187-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa M. Phylogeny and molecular evolution in primates. Jpn J Genet. 1990 Aug;65(4):243–266. doi: 10.1007/978-4-431-54011-3_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilbroner P. L., Kemper T. L. The cytoarchitectonic distribution of senile plaques in three aged monkeys. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;81(1):60–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00662638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson J. E., Cox L. A., Borenstein S. The baboon apolipoprotein E gene: structure, expression, and linkage with the gene for apolipoprotein C-1. Genomics. 1988 May;2(4):315–323. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson J. E., Vernier D. T. Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI. J Lipid Res. 1990 Mar;31(3):545–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. T., Tanzi R. E., Marzloff K., Barbour R., Schenk D. Kunitz protease inhibitor-containing amyloid beta protein precursor immunoreactivity in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1992 Jan;51(1):76–83. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199201000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. T., Van Hoesen G. W., Wolozin B. L., Davies P., Kromer L. J., Damasio A. R. Alz-50 antibody recognizes Alzheimer-related neuronal changes. Ann Neurol. 1988 Apr;23(4):371–379. doi: 10.1002/ana.410230410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joachim C., Games D., Morris J., Ward P., Frenkel D., Selkoe D. Antibodies to non-beta regions of the beta-amyloid precursor protein detect a subset of senile plaques. Am J Pathol. 1991 Feb;138(2):373–384. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985 Nov;42(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King F. A., Yarbrough C. J., Anderson D. C., Gordon T. P., Gould K. G. Primates. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1475–1482. doi: 10.1126/science.3287624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Joachim C. L., Selkoe D. J. Microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) is a major antigenic component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4044–4048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal R. C., Herz J., Goldstein J. L., Esser V., Brown M. S. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediates uptake of cholesteryl esters derived from apoprotein E-enriched lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5810–5814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Balin B. J., Otvos L., Jr, Trojanowski J. Q. A68: a major subunit of paired helical filaments and derivatized forms of normal Tau. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):675–678. doi: 10.1126/science.1899488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotti K. R., Whitted B. E., Castle C. K., Polites H. G., Melchior G. W. Nucleotide sequence of the cynomolgus monkey apolipoprotein E cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1778–1778. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin L. J., Sisodia S. S., Koo E. H., Cork L. C., Dellovade T. L., Weidemann A., Beyreuther K., Masters C., Price D. L. Amyloid precursor protein in aged nonhuman primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1461–1465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux R., Stern Y., Ottman R., Tatemichi T. K., Tang M. X., Maestre G., Ngai C., Tycko B., Ginsberg H. The apolipoprotein epsilon 4 allele in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1993 Nov;34(5):752–754. doi: 10.1002/ana.410340527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J. W., Elshourbagy N. A., Chang D. J., Mahley R. W., Taylor J. M. Human apolipoprotein E mRNA. cDNA cloning and nucleotide sequencing of a new variant. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6498–6504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J. W., Fukazawa C., Taylor J. M. Rat apolipoprotein E mRNA. Cloning and sequencing of double-stranded cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8993–9000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirra S. S., Heyman A., McKeel D., Sumi S. M., Crain B. J., Brownlee L. M., Vogel F. S., Hughes J. P., van Belle G., Berg L. The Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease (CERAD). Part II. Standardization of the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1991 Apr;41(4):479–486. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.4.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M. M., Koop B. F., Slightom J. L., Goodman M., Tennant M. R. Molecular systematics of higher primates: genealogical relations and classification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7627–7631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba Y., Tomonaga M., Kawasaki H., Otomo E., Ikeda K. Apolipoprotein E immunoreactivity in cerebral amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease and kuru plaque amyloid in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain Res. 1991 Feb 8;541(1):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91092-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. T., Marton L., Saper C. B. Alz-50 immunohistochemistry in the normal sheep striatum: a light and electron microscope study. Brain Res. 1993 Jan 15;600(2):285–297. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91385-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neve R. L., Kammesheidt A., Hohmann C. F. Brain transplants of cells expressing the carboxyl-terminal fragment of the Alzheimer amyloid protein precursor cause specific neuropathology in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3448–3452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pericak-Vance M. A., Bebout J. L., Gaskell P. C., Jr, Yamaoka L. H., Hung W. Y., Alberts M. J., Walker A. P., Bartlett R. J., Haynes C. A., Welsh K. A. Linkage studies in familial Alzheimer disease: evidence for chromosome 19 linkage. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jun;48(6):1034–1050. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podlisny M. B., Tolan D. R., Selkoe D. J. Homology of the amyloid beta protein precursor in monkey and human supports a primate model for beta amyloidosis in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jun;138(6):1423–1435. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poduri A., Gearing M., Rebeck G. W., Mirra S. S., Tigges J., Hyman B. T. Apolipoprotein E4 and beta amyloid in senile plaques and cerebral blood vessels of aged rhesus monkeys. Am J Pathol. 1994 Jun;144(6):1183–1187. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier J., Davignon J., Bouthillier D., Kogan S., Bertrand P., Gauthier S. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):697–699. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91705-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quon D., Wang Y., Catalano R., Scardina J. M., Murakami K., Cordell B. Formation of beta-amyloid protein deposits in brains of transgenic mice. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):239–241. doi: 10.1038/352239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajavashisth T. B., Kaptein J. S., Reue K. L., Lusis A. J. Evolution of apolipoprotein E: mouse sequence and evidence for an 11-nucleotide ancestral unit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8085–8089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebeck G. W., Reiter J. S., Strickland D. K., Hyman B. T. Apolipoprotein E in sporadic Alzheimer's disease: allelic variation and receptor interactions. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):575–580. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards S. J., Waters J. J., Beyreuther K., Masters C. L., Wischik C. M., Sparkman D. R., White C. L., 3rd, Abraham C. R., Dunnett S. B. Transplants of mouse trisomy 16 hippocampus provide a model of Alzheimer's disease neuropathology. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):297–303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rye D. B., Leverenz J., Greenberg S. G., Davies P., Saper C. B. The distribution of Alz-50 immunoreactivity in the normal human brain. Neuroscience. 1993 Sep;56(1):109–127. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90567-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders A. M., Schmader K., Breitner J. C., Benson M. D., Brown W. T., Goldfarb L., Goldgaber D., Manwaring M. G., Szymanski M. H., McCown N. Apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele distributions in late-onset Alzheimer's disease and in other amyloid-forming diseases. Lancet. 1993 Sep 18;342(8873):710–711. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91709-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D., George-Hyslop P. H., Pericak-Vance M. A., Joo S. H., Rosi B. L., Gusella J. F., Crapper-MacLachlan D. R., Alberts M. J. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1993 Aug;43(8):1467–1472. doi: 10.1212/wnl.43.8.1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D. E., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Crain B. J., Hulette C. M., Joo S. H., Pericak-Vance M. A., Goldgaber D., Roses A. D. Increased amyloid beta-peptide deposition in cerebral cortex as a consequence of apolipoprotein E genotype in late-onset Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9649–9653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Bell D. S., Podlisny M. B., Price D. L., Cork L. C. Conservation of brain amyloid proteins in aged mammals and humans with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):873–877. doi: 10.1126/science.3544219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Saunders A. M., Schmechel D., Pericak-Vance M., Enghild J., Salvesen G. S., Roses A. D. Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1977–1981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Weisgraber K. H., Goedert M., Saunders A. M., Huang D., Corder E. H., Dong L. M., Jakes R., Alberts M. J., Gilbert J. R. Hypothesis: microtubule instability and paired helical filament formation in the Alzheimer disease brain are related to apolipoprotein E genotype. Exp Neurol. 1994 Feb;125(2):163–174. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1994.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter W. J., Weisgraber K. H., Huang D. Y., Dong L. M., Salvesen G. S., Pericak-Vance M., Schmechel D., Saunders A. M., Goldgaber D., Roses A. D. Binding of human apolipoprotein E to synthetic amyloid beta peptide: isoform-specific effects and implications for late-onset Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8098–8102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struble R. G., Price D. L., Jr, Cork L. C., Price D. L. Senile plaques in cortex of aged normal monkeys. Brain Res. 1985 Dec 30;361(1-2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91298-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L. C., Kitt C. A., Schwam E., Buckwald B., Garcia F., Sepinwall J., Price D. L. Senile plaques in aged squirrel monkeys. Neurobiol Aging. 1987 Jul-Aug;8(4):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(87)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker L. C., Masters C., Beyreuther K., Price D. L. Amyloid in the brains of aged squirrel monkeys. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;80(4):381–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00307691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wischik C. M., Novak M., Thøgersen H. C., Edwards P. C., Runswick M. J., Jakes R., Walker J. E., Milstein C., Roth M., Klug A. Isolation of a fragment of tau derived from the core of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4506–4510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Sturman J. A., Shek J. W. Aluminum chloride induced neurofibrillary changes in the developing rabbit a chronic animal model. Ann Neurol. 1980 Nov;8(5):479–490. doi: 10.1002/ana.410080505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Frangione B. Apolipoprotein E: a pathological chaperone protein in patients with cerebral and systemic amyloid. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Feb 3;135(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90444-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski T., Golabek A., Matsubara E., Ghiso J., Frangione B. Apolipoprotein E: binding to soluble Alzheimer's beta-amyloid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Apr 30;192(2):359–365. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H. M., Ghetti B., Terry R. D. Neuritic (senile) plaques and filamentous changes in aged rhesus monkeys. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1973 Oct;32(4):566–584. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197310000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H., Johnson A. B., Raine C. S., Kay W. J., Terry R. D. Senile plaques and cerebral amyloidosis in aged dogs. A histochemical and ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1970 Sep;23(3):287–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolozin B. L., Pruchnicki A., Dickson D. W., Davies P. A neuronal antigen in the brains of Alzheimer patients. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):648–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3083509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Mirra S. S., Pollock N. J., Binder L. I. Neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer disease share antigenic determinants with the axonal microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4040–4043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Nicolosi R. J., Jensen E., Breslow J. L., Hayes K. C. Plasma and hepatic apoE isoproteins of nonhuman primates. Differences in apoE among humans, apes, and New and Old World monkeys. J Lipid Res. 1985 Dec;26(12):1421–1430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]