Abstract
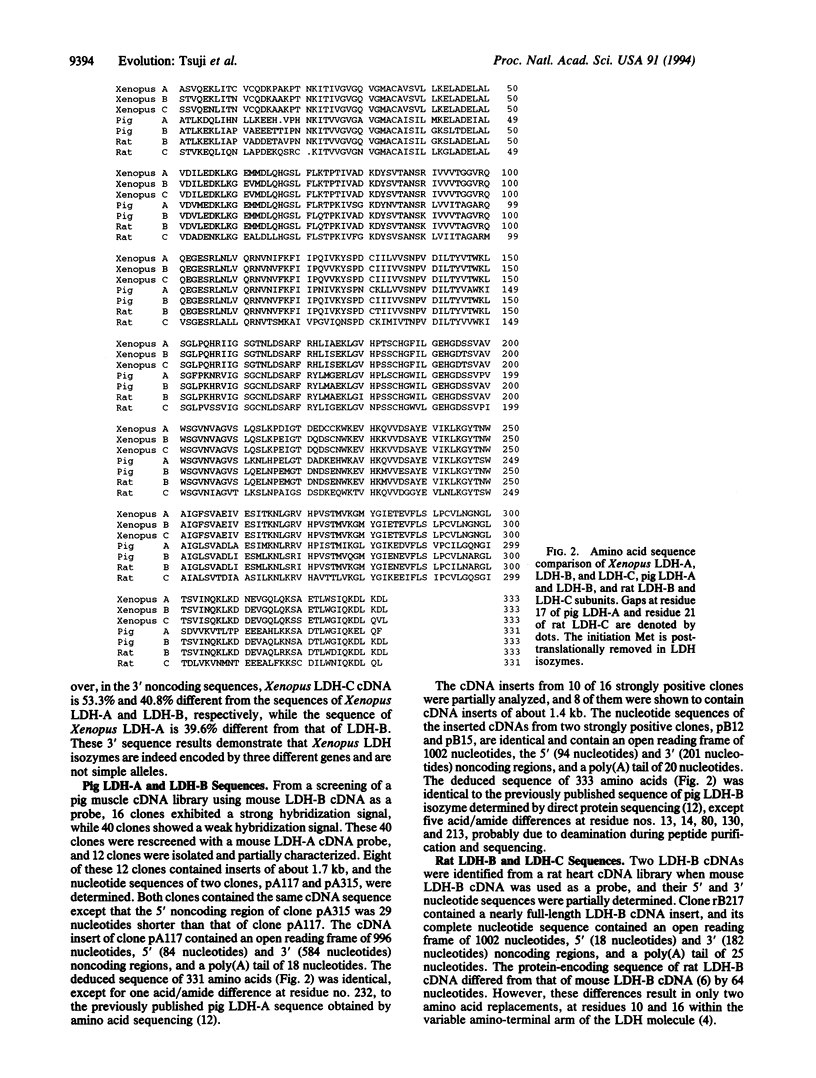
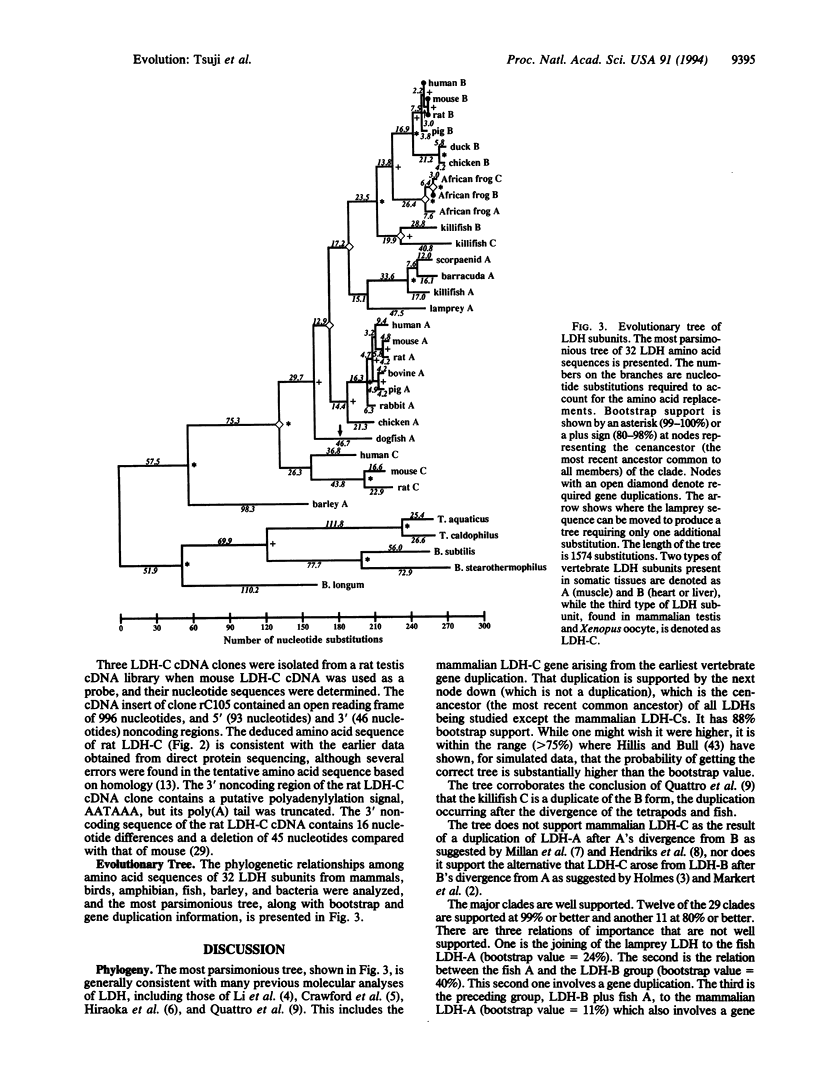
The nucleotide sequences of the cDNAs encoding LDH (EC 1.1.1.27) subunits LDH-A (muscle), LDH-B (liver), and LDH-C (oocyte) from Xenopus laevis, LDH-A (muscle) and LDH-B (heart) from pig, and LDH-B (heart) and LDH-C (testis) from rat were determined. These seven newly deduced amino acid sequences and 22 other published LDH sequences, and three unpublished fish LDH-A sequences kindly provided by G. N. Somero and D. A. Powers, were used to construct the most parsimonious phylogenetic tree of these 32 LDH subunits from mammals, birds, an amphibian, fish, barley, and bacteria. There have been at least six LDH gene duplications among the vertebrates. The Xenopus LDH-A, LDH-B, and LDH-C subunits are most closely related to each other and then are more closely related to vertebrate LDH-B than LDH-A. Three fish LDH-As, as well as a single LDH of lamprey, also seem to be more related to vertebrate LDH-B than to land vertebrate LDH-A. The mammalian LDH-C (testis) subunit appears to have diverged very early, prior to the divergence of vertebrate LDH-A and LDH-B subunits, as reported previously.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barstow D. A., Clarke A. R., Chia W. N., Wigley D., Sharman A. F., Holbrook J. J., Atkinson T., Minton N. P. Cloning, expression and complete nucleotide sequence of the Bacillus stearothermophilus L-lactate dehydrogenase gene. Gene. 1986;46(1):47–55. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglin T. R., Mattaj I. W., Newmeyer D. D., Zeller R., De Robertis E. M. Cloning of nucleoplasmin from Xenopus laevis oocytes and analysis of its developmental expression. Genes Dev. 1987 Mar;1(1):97–107. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.1.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. M., Lee C. Y., Li S. S. Structural relatedness of mouse lactate dehydrogenase isozymes, A4 (muscle), B4 (heart), and C4 (testis). Biochem Genet. 1979 Aug;17(7-8):715–729. doi: 10.1007/BF00502130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. L., Constantino H. R., Powers D. A. Lactate dehydrogenase-B cDNA from the teleost Fundulus heteroclitus: evolutionary implications. Mol Biol Evol. 1989 Jul;6(4):369–383. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M., Farris J. S. Evolutionary trees with minimum nucleotide replacements from amino acid sequences. J Mol Evol. 1974;3(4):263–278. doi: 10.1007/BF01796042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa K. M., Li S. S. Complete nucleotide sequence of the mouse lactate dehydrogenase-A functional gene: comparison of the exon-intron organization of dehydrogenase genes. Genetics. 1987 May;116(1):99–105. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf J. D. Genetic mapping in Xenopus laevis: eight linkage groups established. Genetics. 1989 Oct;123(2):389–398. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Frank G., Zuber H. Structure and function of L-lactate dehydrogenases from thermophilic and mesophilic bacteria, IV. The primary structure of the mesophilic lactate dehydrogenase from Bacillus subtilis. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1986 Sep;367(9):891–903. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1986.367.2.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks W., Mulders J. W., Bibby M. A., Slingsby C., Bloemendal H., de Jong W. W. Duck lens epsilon-crystallin and lactate dehydrogenase B4 are identical: a single-copy gene product with two distinct functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7114–7118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka B. Y., Sharief F. S., Yang Y. W., Li W. H., Li S. S. The cDNA and protein sequences of mouse lactate dehydrogenase B. Molecular evolution of vertebrate lactate dehydrogenase genes A (muscle), B (heart) and C (testis). Eur J Biochem. 1990 Apr 30;189(2):215–220. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15479.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota Y., Katsumata A., Takeya T. Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of chicken lactate dehydrogenase-A. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6432–6432. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. S. Evolution of lactate dehydrogenase genes. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):51–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80675-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hondred D., Hanson A. D. Hypoxically inducible barley lactate dehydrogenase: cDNA cloning and molecular analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7300–7304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro N., Osame S., Kagiya R., Ichijo S., Shinagawa M. Primary structure of bovine lactate dehydrogenase-A isozyme and its synthesis in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1990 Jul 16;91(2):281–285. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90101-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiltz H. H., Keil W., Griesbach M., Petry K., Meyer H. The primary structure of porcine lactate dehydrogenase: isoenzymes M4 and H4. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1977 Jan;358(1):123–127. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1977.358.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunai K., Machida M., Matsuzawa H., Ohta T. Nucleotide sequence and characteristics of the gene for L-lactate dehydrogenase of Thermus caldophilus GK24 and the deduced amino-acid sequence of the enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 15;160(2):433–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. S., Fitch W. M., Pan Y. C., Sharief F. S. Evolutionary relationships of vertebrate lactate dehydrogenase isozymes A4 (muscle), B4 (heart), and C4 (testis). J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7029–7032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. S., Tiano H. F., Fukasawa K. M., Yagi K., Shimizu M., Sharief F. S., Nakashima Y., Pan Y. E. Protein structure and gene organization of mouse lactate dehydrogenase-A isozyme. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 3;149(2):215–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert C. L., Shaklee J. B., Whitt G. S. Evolution of a gene. Multiple genes for LDH isozymes provide a model of the evolution of gene structure, function and regulation. Science. 1975 Jul 11;189(4197):102–114. doi: 10.1126/science.1138367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M., Rautmann G., Magun B. E., Breathnach R. Epidermal growth factor or serum stimulation of rat fibroblasts induces an elevation in mRNA levels for lactate dehydrogenase and other glycolytic enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):711–726. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millan J. L., Driscoll C. E., LeVan K. M., Goldberg E. Epitopes of human testis-specific lactate dehydrogenase deduced from a cDNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5311–5315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowa T., Iwata S., Sakai H., Masaki H., Ohta T. Sequence and characteristics of the Bifidobacterium longum gene encoding L-lactate dehydrogenase and the primary structure of the enzyme: a new feature of the allosteric site. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90476-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Matsuzawa H., Ohta T. Nucleotide sequence and characteristics of the gene for L-lactate dehydrogenase of Thermus aquaticus YT-1 and the deduced amino acid sequence of the enzyme. J Biochem. 1990 Jan;107(1):21–26. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Y. C., Sharief F. S., Okabe M., Huang S., Li S. S. Amino acid sequence studies on lactate dehydrogenase C4 isozymes from mouse and rat testes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7005–7016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quattro J. M., Woods H. A., Powers D. A. Sequence analysis of teleost retina-specific lactate dehydrogenase C: evolutionary implications for the vertebrate lactate dehydrogenase gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):242–246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai I., Sharief F. S., Li S. S. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of the cDNA for sperm-specific lactate dehydrogenase-C from mouse. Biochem J. 1987 Mar 1;242(2):619–622. doi: 10.1042/bj2420619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai I., Sharief F. S., Pan Y. C., Li S. S. The cDNA and protein sequences of human lactate dehydrogenase B. Biochem J. 1987 Dec 15;248(3):933–936. doi: 10.1042/bj2480933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sass C., Briand M., Benslimane S., Renaud M., Briand Y. Characterization of rabbit lactate dehydrogenase-M and lactate dehydrogenase-H cDNAs. Control of lactate dehydrogenase expression in rabbit muscle. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4076–4081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock D. W., Whitt G. S. Evolutionary implications of the cDNA sequence of the single lactate dehydrogenase of a lamprey. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1799–1803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T., Li S. S. Human testicular lactate dehydrogenase-C gene is interrupted by six introns at positions homologous to those of LDH-A (muscle) and LDH-B (heart) genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):579–583. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeno T., Li S. S. Structure of the human lactate dehydrogenase B gene. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 1;257(3):921–924. doi: 10.1042/bj2570921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S. Amino acid sequence of dogfish muscle lactate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1799–1806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujibo H., Tiano H. F., Li S. S. Nucleotide sequences of the cDNA and an intronless pseudogene for human lactate dehydrogenase-A isozyme. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;147(1):9–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirz B., Suter F., Zuber H. Structure and function of L-lactate dehydrogenases from thermophilic and mesophilic bacteria. III) The primary structure of thermophilic lactate dehydrogenase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Hydroxylamine-, o-iodosobenzoic acid- and tryptic-fragments. The complete amino-acid sequence. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 Jul;364(7):893–909. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1983.364.2.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Kobel H. R. Lactate dehydrogenase of Xenopus laevis laevis and Xenopus borealis depends on a multiple gene system. J Exp Zool. 1982 Nov 1;223(3):203–210. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402230302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu K. C., Chan K., Lee C. Y., Lau Y. F. Molecular isolation and sequence determination of the cDNA for the mouse sperm-specific lactate dehydrogenase-X gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 14;146(3):964–970. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90741-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




